Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Java Data Structures Cheat Sheet
Java Data Structures Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
study studioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Java Data Structures Cheat Sheet
Java Data Structures Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
study studioCopyright:
Available Formats
Java Data Structures Cheat Sheet
by Ieternalleo via cheatography.com/45716/cs/13401/
Array Linked List Hash Map
Defi‐ - Stores data elements based on an Defi‐ - Stores data with nodes that point to Defi‐ - Stores data with key value pairs. -
nitio‐ sequential, most commonly 0 based, nitio‐ other nodes. - Nodes, at its most basic nitio‐ Hash functions accept a key and
n index. - Based on [tuples] n it has one datum and one reference n return an output unique only to that
(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tuple) from (another node). - A linked list _chains_ specific key. - This is known as
set theory. - They are one of the nodes together by pointing one node's hashing, which is the concept that an
oldest, most commonly used data reference towards another node. input and an output have a one-to-one
structures. correspondence to map information. -
Detai - Designed to optimize insertion and
Detai - Optimal for indexing; bad at deletion, slow at indexing and Hash functions return a unique
ls
ls searching, inserting, and deleting searching. - Doubly linked list has address in memory for that data.
(except at the end). - Linear arrays, or nodes that reference the previous Detai - Designed to optimize searching,
one dimensional arrays, are the most node. - Circularly linked list is simple ls insertion, and deletion. - Hash
basic. - Are static in size, meaning that linked list whose tail, the last node, collisions are when a hash function
they are declared with a fixed size. - references the head, the first node. - returns the same output for two distinct
Dynamic arrays are like one inputs. - All hash functions have this
Stack, commonly implemented with
dimensional arrays, but have reserved problem. - This is often
linked lists but can be made from
space for additional elements. - If a accommodated for by having the hash
arrays too. - Stacks are last in, first
dynamic array is full, it copies it's tables be very large. - Hashes are
out (LIFO) data structures. - Made with
contents to a larger array. - Two important for associative arrays and
a linked list by having the head be the
dimensional arrays have x and y database indexing.
only place for insertion and removal. -
indices like a grid or nested arrays. Queues, too can be implemented with Big- - Indexing: Hash Tables: O(1) -
Big- - Indexing: Linear array: O(1), Dynamic a linked list or an array. - Queues are a O Search: Hash Tables: O(1) - Insertion:
O array: O(1) - Search: Linear array: O(n), first in, first out (FIFO) data structure. effici Hash Tables: O(1)
effici Dynamic array: O(n) - Optimized - Made with a doubly linked list that ency
ency Search: Linear array: O(log n), only removes from head and adds to
Dynamic array: O(log n) - Insertion: tail. Binary Tree
Linear array: n/a Dynamic array: O(n)
Big- - Indexing: Linked Lists: O(n) - Search:
Defi - Is a tree like data structure where
O Linked Lists: O(n) - Optimized Search:
niti every node has at most two children. -
effici Linked Lists: O(n) - Insertion: Linked
on There is one left and right child node.
ency Lists: O(1)
By Ieternalleo Published 6th November, 2017. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
cheatography.com/ieternalleo/ Last updated 6th November, 2017. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish Yours!
Page 1 of 3. https://apollopad.com
Java Data Structures Cheat Sheet
by Ieternalleo via cheatography.com/45716/cs/13401/
Binary Tree (cont) Search Basics Depth First Search (cont)
Detai - Designed to optimize searching and Detai - Optimal for searching a tree that is
ls sorting. - A degenerate tree is an ls deeper than it is wide. - Uses a stack
unbalanced tree, which if entirely one- Breadth First Search to push nodes onto. - Because a stack
sided is a essentially a linked list. - is LIFO it does not need to keep track
Defi‐ - An algorithm that searches a tree (or
They are comparably simple to of the nodes pointers and is therefore
nitio‐ graph) by searching levels of the tree
implement than other data structures. - less memory intensive than breadth
n first, starting at the root. - It finds every
Used to make binary search trees. - A first search. - Once it cannot go further
node on the same level, most often
binary tree that uses comparable keys left it begins evaluating the stack.
moving left to right. - While doing this it
to assign which direction a child is. - tracks the children nodes of the nodes Big- - Search: Depth First Search: O(|E| +
Left child has a key smaller than it's on the current level. - When finished O |V|) - E is number of edges - V is
parent node. - Right child has a key examining a level it moves to the left effici number of vertices
greater than it's parent node. - There most node on the next level. - The ency
can be no duplicate node. - Because of bottom-right most node is evaluated
the above it is more likely to be used as last (the node that is deepest and is
Breadth First Search Vs. Depth First Search
a data structure than a binary tree. An farthest right of it's level).
AVL Tree is a balanced binary search - The simple answer to this question is that it
Detai - Optimal for searching a tree that is
tree. -The process for inserting or depends on the size and shape of the tree.
ls wider than it is deep. - Uses a queue to
deleting is the same as in a - For wide, shallow trees use Breadth First
store information about the tree while it
regular(unbalanced) BST, except you Search
traverses a tree. - Because it uses a
have to rebalance after each operation. - For deep, narrow trees use Depth First
queue it is more memory intensive than
A node in an AVL tree is balanced if its Search
depth first search. - The queue uses
balance factor is either -1,0, or 1
more memory because it needs to
Big- - Indexing: Binary Search Tree: O(log Nuances:
stores pointers
O n) - Search: Binary Search Tree: O(log - Because BFS uses queues to store
Big- - Search: Breadth First Search: O(|E| +
effici n) - Insertion: Binary Search Tree: information about the nodes and its children, it
O |V|) - E is number of edges - V is
ency O(log n) could use more memory than is available on
effici number of vertices
ency your computer. (But you probably won't have
The balance factor of a node is the height of
to worry about this.)
its right subtree minus the height of its left
- If using a DFS on a tree that is very deep you
subtree Depth First Search
might go unnecessarily deep in the search. See
Defi - An algorithm that searches a tree (or [xkcd](http://xkcd.com/761/) for more
niti graph) by searching depth of the tree information.
on first, starting at the root. - It traverses left - Breadth First Search tends to be a looping
down a tree until it cannot go further. - algorithm.
Once it reaches the end of a branch it - Depth First Search tends to be a recursive
traverses back up trying the right child algorithm.
of nodes on that branch, and if possible
left from the right children. - When Efficient Sorting Basics
finished examining a branch it moves to
the node right of the root then tries to go
left on all it's children until it reaches the
bottom. - The right most node is
evaluated last (the node that is right of
all it's ancestors).
By Ieternalleo Published 6th November, 2017. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
cheatography.com/ieternalleo/ Last updated 6th November, 2017. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish Yours!
Page 2 of 3. https://apollopad.com
Java Data Structures Cheat Sheet
by Ieternalleo via cheatography.com/45716/cs/13401/
Merge Sort Quicksort (cont) Merge Sort vs. QuickSort
Defi‐ - A comparison based sorting algorithm Detai - While it has the same Big O as (or - Quicksort is likely faster in practice.
nitio‐ - Divides entire dataset into groups of ls worse in some cases) many other - Merge Sort divides the set into the smallest
n at most two. - Compares each number sorting algorithms it is often faster in possible groups immediately then reconstructs
one at a time, moving the smallest practice than many other sorting the incrementally as it sorts the groupings.
number to left of the pair. - Once all algorithms, such as merge sort. - Know - Quicksort continually divides the set by the
pairs sorted it then compares left most that it halves the data set by the average, until the set is recursively sorted.
elements of the two leftmost pairs average continuously until all the
creating a sorted group of four with the information is sorted. Heap Sort
smallest numbers on the left and the Big- - Best Case Sort: Merge Sort: O(n) -
largest ones on the right. - This process Definitio Sorts using a complete binary Tree.
O Average Case Sort: Merge Sort: O(n
is repeated until there is only one set. n:
effici log n) - Worst Case Sort: Merge Sort:
Detai - This is one of the most basic sorting O(n^2) Details: ArrayList can be used to store a
ency
ls algorithms. - Know that it divides all the Heap
data into as small possible sets then For a node of i:
Bubble Sort
compares them. -Left child: 2i+1
Defi‐ - A comparison based sorting algorithm -Right child: 2i+2
Big- - Best Case Sort: Merge Sort: O(n) -
Average Case Sort: Merge Sort: O(n nitio‐ - It iterates left to right comparing every -Parent: (i - 1)/2
O
log n) - Worst Case Sort: Merge Sort: n couplet, moving the smaller element to
effici Big-O: O(nlogn)
O(n log n) the left. - It repeats this process until it
ency
no longer moves and element to the
left.
Quicksort
Detai - While it is very simple to implement, it
Defi - A comparison based sorting algorithm - ls is the least efficient of these three
niti Divides entire dataset in half by selecting sorting methods. - Know that it moves
on the average element and putting all one space to the right comparing two
smaller elements to the left of the elements at a time and moving the
average. - It repeats this process on the smaller on to left.
left side until it is comparing only two
Big- - Best Case Sort: Merge Sort: O(n) -
elements at which point the left side is
O Average Case Sort: Merge Sort: O(n2)
sorted. - When the left side is finished - Worst Case Sort: Merge Sort: O(n2)
effici
sorting it performs the same operation
ency
on the right side. - Computer
architecture favors the quicksort
process.
By Ieternalleo Published 6th November, 2017. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
cheatography.com/ieternalleo/ Last updated 6th November, 2017. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish Yours!
Page 3 of 3. https://apollopad.com
You might also like
- COP3530 Cheat Sheet Data StructuresDocument2 pagesCOP3530 Cheat Sheet Data StructuresAndy OrtizNo ratings yet
- Meliodas - Algorithms and Datastructures Java - BWDocument3 pagesMeliodas - Algorithms and Datastructures Java - BWAnjali BissaNo ratings yet
- Data StructuresDocument3 pagesData Structures169DiptanshuNo ratings yet
- Computer Science - Data StructuresDocument1 pageComputer Science - Data StructuresMichael MohamedNo ratings yet
- DSA Tutorial3 Linked ListsDocument5 pagesDSA Tutorial3 Linked ListsKipyegon CheruiyotNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 ESO207 InventingBinarySearchTreesDocument23 pagesLecture 10 ESO207 InventingBinarySearchTreesIitianNo ratings yet
- Data Structure FAQDocument3 pagesData Structure FAQAffable kalyaniNo ratings yet
- Nuestro, L. Homework n0.1 Cpen 65Document5 pagesNuestro, L. Homework n0.1 Cpen 65Lyka NuestroNo ratings yet
- DataStructure and AlgorithmsDocument8 pagesDataStructure and AlgorithmsKaung Khant LinNo ratings yet
- CS 301 - Short NotesDocument13 pagesCS 301 - Short NotesMubshera SaddiqaNo ratings yet
- Next, For Those of You Who Haven'tDocument2 pagesNext, For Those of You Who Haven'tmostafa_lw'tnNo ratings yet
- Collection Framework PDFDocument8 pagesCollection Framework PDFSuryateja KokaNo ratings yet
- Abstract Data TypeDocument5 pagesAbstract Data TypeNamal No OorNo ratings yet
- Defined Manner.: Collections Are Nothing But Group of Objects Stored in WellDocument5 pagesDefined Manner.: Collections Are Nothing But Group of Objects Stored in WellGaneshNo ratings yet
- A Fast Method For Accessing Nodes in The Binary Search TreesDocument8 pagesA Fast Method For Accessing Nodes in The Binary Search TreesirinarmNo ratings yet
- Linked List Lecture NoteDocument4 pagesLinked List Lecture NoteMelatNo ratings yet
- Nandini Walia Learing ReportDocument3 pagesNandini Walia Learing ReportAbhinav MauryaNo ratings yet
- Ds Viva QDocument13 pagesDs Viva Qhackers earthNo ratings yet
- DS Question Bank SET-ADocument8 pagesDS Question Bank SET-AMADHULIKA SHARMANo ratings yet
- DSA610S Theory 2Document27 pagesDSA610S Theory 2Vaino UusikuNo ratings yet
- DS-Lecture-2 Summary of The First Lecture:: Differences Between Array VS ListDocument15 pagesDS-Lecture-2 Summary of The First Lecture:: Differences Between Array VS ListAřJűn DashNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Divide and Conquer: RecursivelyDocument10 pagesUnit - I Divide and Conquer: Recursivelyramesh_508No ratings yet
- Notes 4Document22 pagesNotes 4februarydtzNo ratings yet
- Ec8393 - Fundamentals of Data Structures in C: Linear DatastructuresDocument11 pagesEc8393 - Fundamentals of Data Structures in C: Linear DatastructuresRathiNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document81 pagesUnit - 1Dr.K. BhuvaneswariNo ratings yet
- DS Viva QuestionsDocument6 pagesDS Viva QuestionsDaniel MariadassNo ratings yet
- r19 Ds - Unit - I (Ref-2)Document26 pagesr19 Ds - Unit - I (Ref-2)balasubramanyam200517No ratings yet
- Dsa Lec3Document18 pagesDsa Lec3satyajeetsince2001No ratings yet
- Tree (Data Structure) : Preliminary Definition Mathematical DefinitionDocument23 pagesTree (Data Structure) : Preliminary Definition Mathematical Definitionhmltdt9221No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Viva VoceDocument168 pagesComprehensive Viva VoceDHANASEENUVASAN DNo ratings yet
- Data StructuresDocument2 pagesData StructuresUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Data Structure VIVA QuestionsDocument11 pagesData Structure VIVA Questionshackers earthNo ratings yet
- Data Structures-1Document26 pagesData Structures-1Raja KushwahNo ratings yet
- Algorithms and Data Structures (CSC112)Document4 pagesAlgorithms and Data Structures (CSC112)nishongopothikNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - DSADocument40 pagesModule 1 - DSAbarotshreedhar66No ratings yet
- Data StructuresDocument17 pagesData Structuresnaveen rajNo ratings yet
- DS LectureDocument27 pagesDS LectureAshutosh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Linear Data Structures: Primitive vs. Non PrimitiveDocument20 pagesLinear Data Structures: Primitive vs. Non PrimitiveJohane Grei WallNo ratings yet
- Theory of AlgorithmsDocument17 pagesTheory of AlgorithmsEleni AbebleNo ratings yet
- C DS BasicsDocument5 pagesC DS Basicsrojamani gantaNo ratings yet
- C&DS Unit-VII and VIII (Data Structures)Document21 pagesC&DS Unit-VII and VIII (Data Structures)N. Janaki Ram100% (1)
- Last in First Out: Linked List, Tree, Etc. A Programmer Selects An Appropriate Data Structure and Uses ItDocument2 pagesLast in First Out: Linked List, Tree, Etc. A Programmer Selects An Appropriate Data Structure and Uses ItanilperfectNo ratings yet
- Dbms PyqDocument6 pagesDbms PyqSaloni VaniNo ratings yet
- DSADocument3 pagesDSAKUMAR HARSHNo ratings yet
- CollectionsDocument28 pagesCollectionsrai471085No ratings yet
- DSA & DAA Fast StudyDocument6 pagesDSA & DAA Fast StudyrkpythonNo ratings yet
- 1-ListDataStructures - 1504Document15 pages1-ListDataStructures - 1504tunvde180193No ratings yet
- Lecture 1-DSADocument26 pagesLecture 1-DSATalha rajpootNo ratings yet
- Assignment SolutionDocument6 pagesAssignment SolutionseyiNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and AlgorithmsDocument12 pagesData Structures and AlgorithmsShubham SinghalNo ratings yet
- C 343 Final StudyDocument6 pagesC 343 Final StudyGabriela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Basic DSDocument15 pagesBasic DSvikrant kumarNo ratings yet
- Basic DSDocument15 pagesBasic DSN EDUNo ratings yet
- DSA ORAL Question BankDocument17 pagesDSA ORAL Question BankAadarsh ChandanvandanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document92 pagesUnit 4fasdfNo ratings yet
- Threaded Binary TreeDocument25 pagesThreaded Binary Treepramodsoni0007No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document39 pagesUnit 2Eklavya SudanNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Theoretical ApproachDocument6 pagesData Structure Theoretical ApproachEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Sample Linked Lists Chapter (Data Structure and Algorithmic Thinking With Python)Document48 pagesSample Linked Lists Chapter (Data Structure and Algorithmic Thinking With Python)nguyen.duongNo ratings yet
- 04-Tree of Thoughts White PapersDocument11 pages04-Tree of Thoughts White PaperssgearqantonioNo ratings yet
- Articulation PointsDocument4 pagesArticulation PointsaekdhoNo ratings yet
- Ds 3Document8 pagesDs 3GR RNo ratings yet
- Video Lecture Series - Engineering CoursesDocument15 pagesVideo Lecture Series - Engineering CoursesIrus RajanNo ratings yet
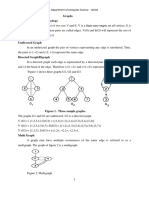
- Graph-1 BfsDocument40 pagesGraph-1 BfsNuzhat AfrinNo ratings yet
- Data Lab File 1 (AutoRecovered)Document44 pagesData Lab File 1 (AutoRecovered)sidNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Lab Manual: ACADEMIC YEAR: 2019-2020 Second SemesterDocument35 pagesArtificial Intelligence Lab Manual: ACADEMIC YEAR: 2019-2020 Second Semesterإيهاب توفيق القادريNo ratings yet
- Graphs NotesDocument59 pagesGraphs NotesRuby ChanNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science & Engineering Session 2020-2021Document125 pagesDepartment of Computer Science & Engineering Session 2020-2021rosh benNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument51 pagesArtificial IntelligenceHariNo ratings yet
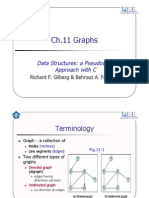
- Ch.11 Graphs: Data Structures: A Pseudocode Approach With CDocument65 pagesCh.11 Graphs: Data Structures: A Pseudocode Approach With CAjayaHSNo ratings yet
- GeorgiaTech CS-6515: Graduate Algorithms: Exam 2 Flashcards by Unknown Unknown - BrainscapeDocument8 pagesGeorgiaTech CS-6515: Graduate Algorithms: Exam 2 Flashcards by Unknown Unknown - BrainscapeJan_SuNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and Neural Networks (NEW)Document25 pagesArtificial Intelligence and Neural Networks (NEW)Shubham RawatNo ratings yet
- AIML MergedDocument275 pagesAIML MergedAman ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ai Problem Solving Search and Control StrategiesDocument74 pagesAi Problem Solving Search and Control Strategiessuperespol100% (2)
- Design & Analysis of Algorithm Code: IT501 Contact: 3L + 1T Credits: 4Document2 pagesDesign & Analysis of Algorithm Code: IT501 Contact: 3L + 1T Credits: 4Prasenjit DasNo ratings yet
- 2023 S1 AIF Assignment SpecificationDocument2 pages2023 S1 AIF Assignment SpecificationNextOx ProNo ratings yet
- Leetcode Questions - PublicDocument26 pagesLeetcode Questions - PublicSachin BehlNo ratings yet
- Algorithms Notes For Professionals PDFDocument256 pagesAlgorithms Notes For Professionals PDFgud2seeu5554No ratings yet
- Unit 8: Layout Compaction: Course ContentsDocument17 pagesUnit 8: Layout Compaction: Course Contentsprasanna241186No ratings yet
- (Systems Innovation Series) Badiru, Adedeji Bodunde - Project Management - Systems, Principles, and Applications-CRC Press LLC (2019) PDFDocument545 pages(Systems Innovation Series) Badiru, Adedeji Bodunde - Project Management - Systems, Principles, and Applications-CRC Press LLC (2019) PDFالبتلة اللطيف100% (1)
- Ada Lab Manual - Shitanshu JainDocument28 pagesAda Lab Manual - Shitanshu Jainshubh agrawalNo ratings yet
- Mca (Management) 2020 PatternDocument74 pagesMca (Management) 2020 PatternPruthviraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Graph TraversalsDocument11 pagesGraph TraversalsAnandhaSilambarasan DNo ratings yet
- Code: PCC-CS401: Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West BengalDocument20 pagesCode: PCC-CS401: Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West BengalPronoy Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- Cse Aiml 2020 SyllabusDocument72 pagesCse Aiml 2020 SyllabusSrijeeta SenNo ratings yet
- AIMA ExcersicesDocument61 pagesAIMA ExcersicesAnas HamdanNo ratings yet
- AI F20 Lecture-5-6Document23 pagesAI F20 Lecture-5-6Ishtiaq bhatti Ishtiaq bhattiNo ratings yet
- Control and Implementation of State Space SearchDocument25 pagesControl and Implementation of State Space SearchskyonNo ratings yet