Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanical Properties Material Properties Optical Properties
Mechanical Properties Material Properties Optical Properties
Uploaded by
Hardy SPCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pumps Problems 20 ItemsDocument11 pagesPumps Problems 20 ItemsMahmoud Mahmoud100% (1)
- MOB - 655 Mako Waterjet Versjon-SteyrDocument24 pagesMOB - 655 Mako Waterjet Versjon-SteyrDavid Mattos100% (1)
- Speck Perangkat Smart 3Document6 pagesSpeck Perangkat Smart 3indahdchyn100% (1)
- Thermador PRG484ECGDocument1 pageThermador PRG484ECGPurcellMurrayNo ratings yet
- ECISGROUP - Cooling Tower Water Treatment - Rev1Document31 pagesECISGROUP - Cooling Tower Water Treatment - Rev1Ecisgroup100% (2)
- Soot BlowerDocument9 pagesSoot BlowerParmeshwar Nath Tripathi100% (1)
- Mindmap 01Document2 pagesMindmap 01Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- Thermal ResistanceDocument1 pageThermal ResistanceLOPEZ BARAJAS GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Ashby Method - SM - 2.1Document25 pagesAshby Method - SM - 2.1Anand BhiseNo ratings yet
- Materials SelectionDocument29 pagesMaterials Selectionfikri wahyu pratamaNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Material SelectionDocument41 pages8.1 Material Selectiondina gunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Preumont Chapter 4Document36 pagesMechatronics Preumont Chapter 4ibrahim el hajjNo ratings yet
- L01 RN-Ch1Document8 pagesL01 RN-Ch1Chamille LescottNo ratings yet
- Physics 2023 CRDocument1 pagePhysics 2023 CRRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Junior Level Physics ScheduleDocument2 pagesJunior Level Physics ScheduleeltytanNo ratings yet
- 2022 Study Plan 11th Jan'22 - 27th Feb'22Document11 pages2022 Study Plan 11th Jan'22 - 27th Feb'22Abhigyan Mohan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Equivalent of HeatDocument5 pagesMechanical Equivalent of HeatJose GalvanNo ratings yet
- Electrodinamika-PETA KONSEPDocument1 pageElectrodinamika-PETA KONSEPMelfi NenchiNo ratings yet
- Meet00 1Document42 pagesMeet00 1Cj TilamNo ratings yet
- Magnetism - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesMagnetism - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedianirb2010No ratings yet
- UAITS Tests PlannerDocument2 pagesUAITS Tests Plannershashwat holkarNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties of SolidsDocument1 pageMagnetic Properties of SolidsRitu B.ANo ratings yet
- M5 - Magnetostriction and Magnetizaton Process PDFDocument14 pagesM5 - Magnetostriction and Magnetizaton Process PDFGuille AngonaNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 09-09-2021: Hardhik Pinjala - MM19B043 - September 15, 2021Document2 pagesMind Map 09-09-2021: Hardhik Pinjala - MM19B043 - September 15, 2021Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 2Document2 pagesActivity No. 2klaudevincent.cullaNo ratings yet
- Welding An OverviewDocument14 pagesWelding An OverviewAgus WidyiantoNo ratings yet
- Material Science Lec ExamDocument141 pagesMaterial Science Lec ExamCayle MalitNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument7 pagesPhysicsMurtaza AbbasNo ratings yet
- 12th Grade Chemistry by Byju'sDocument54 pages12th Grade Chemistry by Byju'srohan rajNo ratings yet
- Physics Galaxy Advanced Illustrations - CompressDocument2 pagesPhysics Galaxy Advanced Illustrations - Compressshreyas shahNo ratings yet
- Syllabus-CLASS 13TH-minDocument1 pageSyllabus-CLASS 13TH-minKartikey SengarNo ratings yet
- Paramagnetism and Conduction ElectronsDocument3 pagesParamagnetism and Conduction Electronsjose miranda100% (1)
- DMA PowerPoint Presentation Prepared by Yared FikreDocument24 pagesDMA PowerPoint Presentation Prepared by Yared FikreYAREDNo ratings yet
- Thermal Cracking in BeamsDocument5 pagesThermal Cracking in BeamsdikshithNo ratings yet
- Hysteresis (M-H) Curve: Domains in Ferromagnetic & Ferrimagnetic MaterialsDocument7 pagesHysteresis (M-H) Curve: Domains in Ferromagnetic & Ferrimagnetic MaterialsMukesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Welding Metallurgy, Part 1: Understanding Mechanical PropertiesDocument4 pagesWelding Metallurgy, Part 1: Understanding Mechanical PropertiesMau Atenas PerezNo ratings yet
- Zenith Revision Schedule Target 2021Document1 pageZenith Revision Schedule Target 2021SahilNo ratings yet
- N42EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN42EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- N42EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN42EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics: Reading ProblemsDocument6 pagesIntroduction & Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics: Reading Problemstpjoshi1No ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism Handouts 1Document5 pagesElectricity and Magnetism Handouts 1Homo CiderNo ratings yet
- N48SH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN48SH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: How Are Electric Charges and Magnetic Fields Related?Document4 pagesMagnetism: How Are Electric Charges and Magnetic Fields Related?INES MONTSERRAT VILLA VILLANo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Mind MapDocument1 pageElectromagnetism Mind Mapmaxine janorasNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation and Performance Testing of Heating Coil in Induction Surface Hardening MachineDocument5 pagesDesign Calculation and Performance Testing of Heating Coil in Induction Surface Hardening Machinebitconcepts9781No ratings yet
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry Theoretical Background: Galina KubyshkinaDocument34 pagesDifferential Scanning Calorimetry Theoretical Background: Galina KubyshkinaRizky Azizul AfniNo ratings yet
- Bitter ElectromagnetDocument5 pagesBitter ElectromagnetRishav KoiralaNo ratings yet
- N40EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN40EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- N40EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN40EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Electromechanical Printer VersionDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Electromechanical Printer VersionbellokhadijaadoNo ratings yet
- Physics Galaxy Advanced IllustrationsDocument2 pagesPhysics Galaxy Advanced Illustrationsshreyas shahNo ratings yet
- MM3010 - Mindmap 2: Maxwell Boltzmann DistributionDocument2 pagesMM3010 - Mindmap 2: Maxwell Boltzmann DistributionHardy SPNo ratings yet
- FACT SHEET - EM - Billets and Slabs - EnglishDocument2 pagesFACT SHEET - EM - Billets and Slabs - EnglishTowerNo ratings yet
- N42M Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN42M Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- M4 - Magnetic Domain Walls and Domains PDFDocument21 pagesM4 - Magnetic Domain Walls and Domains PDFGuille AngonaNo ratings yet
- N38EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN38EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- Ceramics, ElectronicDocument16 pagesCeramics, ElectronicjaimeNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 2: R.Rishaab Karthik MM19B046Document3 pagesMind Map 2: R.Rishaab Karthik MM19B046Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- Nanostructured Thermoelectrics: The New Paradigm?: Mercouri G. KanatzidisDocument12 pagesNanostructured Thermoelectrics: The New Paradigm?: Mercouri G. KanatzidisFrancisco NuñezNo ratings yet
- Class IX, X & X1 Monthly Breakup: Sr. No. Subjects Wee Ks Months August September October November DecemberDocument2 pagesClass IX, X & X1 Monthly Breakup: Sr. No. Subjects Wee Ks Months August September October November DecemberkazamNo ratings yet
- N42SH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN42SH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- Physics Updated SyllabusDocument7 pagesPhysics Updated Syllabusanubhav.bhardwaj0222No ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Materials: Chap 1Document19 pagesElectrical Properties of Materials: Chap 1Shuvro Sankar SenNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 13-10-2021: Hardhik Pinjala - MM19B043 - October 14, 2021Document2 pagesMind Map 13-10-2021: Hardhik Pinjala - MM19B043 - October 14, 2021Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 2: R.Rishaab Karthik MM19B046Document3 pagesMind Map 2: R.Rishaab Karthik MM19B046Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 09-09-2021: Hardhik Pinjala - MM19B043 - September 15, 2021Document2 pagesMind Map 09-09-2021: Hardhik Pinjala - MM19B043 - September 15, 2021Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- MM3010 - Mindmap 2: Maxwell Boltzmann DistributionDocument2 pagesMM3010 - Mindmap 2: Maxwell Boltzmann DistributionHardy SPNo ratings yet
- Mindmap 01Document2 pagesMindmap 01Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- DJ12 40Document2 pagesDJ12 40ParvezNo ratings yet
- CrankcaseDocument7 pagesCrankcaseCharlie BellNo ratings yet
- Ghid RO2019 RO WebDocument6 pagesGhid RO2019 RO WebAnonymous v5uipHNo ratings yet
- 文章评论apa格式Document11 pages文章评论apa格式cj8xkz6t100% (1)
- ModelEngineersWorkshopApril2021 Sanet ST Sanet STDocument68 pagesModelEngineersWorkshopApril2021 Sanet ST Sanet STAngelos Makris100% (1)
- Water Activity and PH MeasurementDocument51 pagesWater Activity and PH MeasurementEnekwa AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Consumer Pricelist April 2014Document44 pagesConsumer Pricelist April 2014prakash_garudNo ratings yet
- Europe's Onshore and Offshore Wind Energy PotentialDocument91 pagesEurope's Onshore and Offshore Wind Energy PotentialSuDokuNo ratings yet
- Power WizardDocument80 pagesPower Wizarddoce12100% (1)
- L293D Motor Driver DatasheetDocument14 pagesL293D Motor Driver DatasheetAnkit Daftery100% (3)
- Module 5 - Rotodynamic Pumps-Part 1Document28 pagesModule 5 - Rotodynamic Pumps-Part 1ASHITA K B100% (1)
- A2 5 Lifecycle Flow TemplatemanufactureDocument1 pageA2 5 Lifecycle Flow Templatemanufactureapi-247436935No ratings yet
- Turbo-Driven Boiler Feed Pump: 1. Turbine Information CasingDocument15 pagesTurbo-Driven Boiler Feed Pump: 1. Turbine Information Casingparthibanemails5779No ratings yet
- Weld Summary ReportDocument80 pagesWeld Summary ReportBinu SulochananNo ratings yet
- PP ProjectDocument23 pagesPP ProjectAbrhaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Laboratory Aim:: SVKM'S Nmims Mukesh Patel School of Technology Management & EngineeringDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Laboratory Aim:: SVKM'S Nmims Mukesh Patel School of Technology Management & EngineeringronakNo ratings yet
- The Building Blocks of Life NotebookDocument4 pagesThe Building Blocks of Life NotebookosamaNo ratings yet
- Tier 4 PM Agreements Jan 2012Document46 pagesTier 4 PM Agreements Jan 2012Sixto Guarniz AnticonaNo ratings yet
- IEEE Guide For Seismic Qualification of Class 1E Metal-Enclosed Power Switchgear AssembliesDocument23 pagesIEEE Guide For Seismic Qualification of Class 1E Metal-Enclosed Power Switchgear AssembliesukritNo ratings yet
- IEEE STD 1584A 2004 Guide For Performing Arc Flash Hazard Calculations Amendment 1 PDFDocument9 pagesIEEE STD 1584A 2004 Guide For Performing Arc Flash Hazard Calculations Amendment 1 PDFjose manuel valle fabianNo ratings yet
- PMFDocument2 pagesPMFSyedNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analytical Chemistry and Its Importance of Pharmaceutical Field1Document9 pagesQuantitative Analytical Chemistry and Its Importance of Pharmaceutical Field1cyper zoonNo ratings yet
- A320 Overhead PanelDocument1 pageA320 Overhead PanelMartha B. de Lima100% (4)
- Biobor JF PdsDocument19 pagesBiobor JF PdsHozifa Krar100% (1)
Mechanical Properties Material Properties Optical Properties
Mechanical Properties Material Properties Optical Properties
Uploaded by
Hardy SPOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mechanical Properties Material Properties Optical Properties
Mechanical Properties Material Properties Optical Properties
Uploaded by
Hardy SPCopyright:
Available Formats
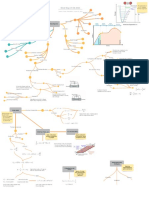
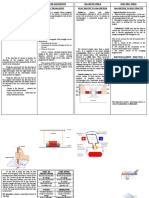
Modulus of Elasticity, Yield Strength,
Tensile strength, Ductility, Resilience, Physics of Materials - Mindmap 1
Toughness, Hardness Mechanical Properties Material Properties Optical properties
Shreya Smitha mm19b054 | August 24, 2021
Chemical Properties
Bond strenght, Ionization
Energy, Electron Affinity
Refractive Index, Reflectivity,
No thermal expansion
Electrical Properties Absorptivity, Transmitivity
Magnetic properties Large coefficient of
thermal expansion
Thermal Properties
If symmetric
Electrical Conductivity,
If shallow and wide
Dielectric constant, Band
structure, Electron mobility
Curie temperature, Remanence, Need to raise
Coercivity, Soft Magnetic materials, temperature
If deep significantly before
Hard Magneitc materials
Thermal Expansion, Conductivity, any thermal
Specific heat Graph of Energy vs interatomic spacing expansion is noticed
Properties Thermal Expansion
Heat Shrinks
Electric Conductivity Conduction: Lattice
2 probe and 4 probe (more accurate) Measuring Conductivity
measurement vibrations (No large scale
DC
movement of atoms)
Thermal conductivity
Using impedence, Z
There is no net transfer of
Convection: In ligwuids and
For pure capacitor in AC, Z=-j/(wL) AC gases (Large scale movement of
Drude Model electrons but transfer of Energy Types of heat transfer
For pure inductor in AC, Z= jwL atoms)
Free electron gas Radiation: Electromagnetic
Waves (heat from Sun to Earth)
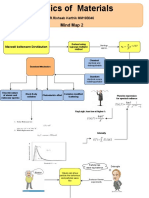
Particle density of electrons three orders of
magnitude greater than ideal gas
Ohms Law
Drude Model
1. Electrons undergo instantaneous collisions Rules
leading to their scattering
2. Average resistive term used to account for the
interaction between collisions
3. Mean free time between collisions (Tau),
independent of position and velocity of electron
4. Electrons attain equilibrium with their Wiedermann - Franz Law
surroundings through collisions with other e-
(Experimental)
Nf= Number of particles per
unit volume (From Drude model)
Cv= Specific heat at
constant volume
Average translational Kinetic Energy per ideal gas
atom/ molecule in a system at equilibrium.
Drawbacks of Drude Model
Cv is 2 orders of magnitude higher than what is experimentally observed
Hall effect: RH limitation (for +ve charge carriers)
Maxwell - Boltzmann distribution Macrostate: Specifies T, V, total E
Classical particle - Particles following Maxwell-
Boltzmann distribution (non interacting) Microstate: Details on how many particles are
occupying each enetgy level For more than 2 particles, a
microstate ioccurs more than the
others (higher probability)
You might also like
- Pumps Problems 20 ItemsDocument11 pagesPumps Problems 20 ItemsMahmoud Mahmoud100% (1)
- MOB - 655 Mako Waterjet Versjon-SteyrDocument24 pagesMOB - 655 Mako Waterjet Versjon-SteyrDavid Mattos100% (1)
- Speck Perangkat Smart 3Document6 pagesSpeck Perangkat Smart 3indahdchyn100% (1)
- Thermador PRG484ECGDocument1 pageThermador PRG484ECGPurcellMurrayNo ratings yet
- ECISGROUP - Cooling Tower Water Treatment - Rev1Document31 pagesECISGROUP - Cooling Tower Water Treatment - Rev1Ecisgroup100% (2)
- Soot BlowerDocument9 pagesSoot BlowerParmeshwar Nath Tripathi100% (1)
- Mindmap 01Document2 pagesMindmap 01Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- Thermal ResistanceDocument1 pageThermal ResistanceLOPEZ BARAJAS GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Ashby Method - SM - 2.1Document25 pagesAshby Method - SM - 2.1Anand BhiseNo ratings yet
- Materials SelectionDocument29 pagesMaterials Selectionfikri wahyu pratamaNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Material SelectionDocument41 pages8.1 Material Selectiondina gunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Preumont Chapter 4Document36 pagesMechatronics Preumont Chapter 4ibrahim el hajjNo ratings yet
- L01 RN-Ch1Document8 pagesL01 RN-Ch1Chamille LescottNo ratings yet
- Physics 2023 CRDocument1 pagePhysics 2023 CRRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Junior Level Physics ScheduleDocument2 pagesJunior Level Physics ScheduleeltytanNo ratings yet
- 2022 Study Plan 11th Jan'22 - 27th Feb'22Document11 pages2022 Study Plan 11th Jan'22 - 27th Feb'22Abhigyan Mohan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Equivalent of HeatDocument5 pagesMechanical Equivalent of HeatJose GalvanNo ratings yet
- Electrodinamika-PETA KONSEPDocument1 pageElectrodinamika-PETA KONSEPMelfi NenchiNo ratings yet
- Meet00 1Document42 pagesMeet00 1Cj TilamNo ratings yet
- Magnetism - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesMagnetism - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedianirb2010No ratings yet
- UAITS Tests PlannerDocument2 pagesUAITS Tests Plannershashwat holkarNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties of SolidsDocument1 pageMagnetic Properties of SolidsRitu B.ANo ratings yet
- M5 - Magnetostriction and Magnetizaton Process PDFDocument14 pagesM5 - Magnetostriction and Magnetizaton Process PDFGuille AngonaNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 09-09-2021: Hardhik Pinjala - MM19B043 - September 15, 2021Document2 pagesMind Map 09-09-2021: Hardhik Pinjala - MM19B043 - September 15, 2021Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 2Document2 pagesActivity No. 2klaudevincent.cullaNo ratings yet
- Welding An OverviewDocument14 pagesWelding An OverviewAgus WidyiantoNo ratings yet
- Material Science Lec ExamDocument141 pagesMaterial Science Lec ExamCayle MalitNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument7 pagesPhysicsMurtaza AbbasNo ratings yet
- 12th Grade Chemistry by Byju'sDocument54 pages12th Grade Chemistry by Byju'srohan rajNo ratings yet
- Physics Galaxy Advanced Illustrations - CompressDocument2 pagesPhysics Galaxy Advanced Illustrations - Compressshreyas shahNo ratings yet
- Syllabus-CLASS 13TH-minDocument1 pageSyllabus-CLASS 13TH-minKartikey SengarNo ratings yet
- Paramagnetism and Conduction ElectronsDocument3 pagesParamagnetism and Conduction Electronsjose miranda100% (1)
- DMA PowerPoint Presentation Prepared by Yared FikreDocument24 pagesDMA PowerPoint Presentation Prepared by Yared FikreYAREDNo ratings yet
- Thermal Cracking in BeamsDocument5 pagesThermal Cracking in BeamsdikshithNo ratings yet
- Hysteresis (M-H) Curve: Domains in Ferromagnetic & Ferrimagnetic MaterialsDocument7 pagesHysteresis (M-H) Curve: Domains in Ferromagnetic & Ferrimagnetic MaterialsMukesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Welding Metallurgy, Part 1: Understanding Mechanical PropertiesDocument4 pagesWelding Metallurgy, Part 1: Understanding Mechanical PropertiesMau Atenas PerezNo ratings yet
- Zenith Revision Schedule Target 2021Document1 pageZenith Revision Schedule Target 2021SahilNo ratings yet
- N42EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN42EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- N42EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN42EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics: Reading ProblemsDocument6 pagesIntroduction & Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics: Reading Problemstpjoshi1No ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism Handouts 1Document5 pagesElectricity and Magnetism Handouts 1Homo CiderNo ratings yet
- N48SH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN48SH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: How Are Electric Charges and Magnetic Fields Related?Document4 pagesMagnetism: How Are Electric Charges and Magnetic Fields Related?INES MONTSERRAT VILLA VILLANo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Mind MapDocument1 pageElectromagnetism Mind Mapmaxine janorasNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation and Performance Testing of Heating Coil in Induction Surface Hardening MachineDocument5 pagesDesign Calculation and Performance Testing of Heating Coil in Induction Surface Hardening Machinebitconcepts9781No ratings yet
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry Theoretical Background: Galina KubyshkinaDocument34 pagesDifferential Scanning Calorimetry Theoretical Background: Galina KubyshkinaRizky Azizul AfniNo ratings yet
- Bitter ElectromagnetDocument5 pagesBitter ElectromagnetRishav KoiralaNo ratings yet
- N40EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN40EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- N40EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN40EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Electromechanical Printer VersionDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Electromechanical Printer VersionbellokhadijaadoNo ratings yet
- Physics Galaxy Advanced IllustrationsDocument2 pagesPhysics Galaxy Advanced Illustrationsshreyas shahNo ratings yet
- MM3010 - Mindmap 2: Maxwell Boltzmann DistributionDocument2 pagesMM3010 - Mindmap 2: Maxwell Boltzmann DistributionHardy SPNo ratings yet
- FACT SHEET - EM - Billets and Slabs - EnglishDocument2 pagesFACT SHEET - EM - Billets and Slabs - EnglishTowerNo ratings yet
- N42M Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN42M Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- M4 - Magnetic Domain Walls and Domains PDFDocument21 pagesM4 - Magnetic Domain Walls and Domains PDFGuille AngonaNo ratings yet
- N38EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN38EH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- Ceramics, ElectronicDocument16 pagesCeramics, ElectronicjaimeNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 2: R.Rishaab Karthik MM19B046Document3 pagesMind Map 2: R.Rishaab Karthik MM19B046Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- Nanostructured Thermoelectrics: The New Paradigm?: Mercouri G. KanatzidisDocument12 pagesNanostructured Thermoelectrics: The New Paradigm?: Mercouri G. KanatzidisFrancisco NuñezNo ratings yet
- Class IX, X & X1 Monthly Breakup: Sr. No. Subjects Wee Ks Months August September October November DecemberDocument2 pagesClass IX, X & X1 Monthly Breakup: Sr. No. Subjects Wee Ks Months August September October November DecemberkazamNo ratings yet
- N42SH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN42SH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- Physics Updated SyllabusDocument7 pagesPhysics Updated Syllabusanubhav.bhardwaj0222No ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Materials: Chap 1Document19 pagesElectrical Properties of Materials: Chap 1Shuvro Sankar SenNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 13-10-2021: Hardhik Pinjala - MM19B043 - October 14, 2021Document2 pagesMind Map 13-10-2021: Hardhik Pinjala - MM19B043 - October 14, 2021Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 2: R.Rishaab Karthik MM19B046Document3 pagesMind Map 2: R.Rishaab Karthik MM19B046Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 09-09-2021: Hardhik Pinjala - MM19B043 - September 15, 2021Document2 pagesMind Map 09-09-2021: Hardhik Pinjala - MM19B043 - September 15, 2021Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- MM3010 - Mindmap 2: Maxwell Boltzmann DistributionDocument2 pagesMM3010 - Mindmap 2: Maxwell Boltzmann DistributionHardy SPNo ratings yet
- Mindmap 01Document2 pagesMindmap 01Hardy SPNo ratings yet
- DJ12 40Document2 pagesDJ12 40ParvezNo ratings yet
- CrankcaseDocument7 pagesCrankcaseCharlie BellNo ratings yet
- Ghid RO2019 RO WebDocument6 pagesGhid RO2019 RO WebAnonymous v5uipHNo ratings yet
- 文章评论apa格式Document11 pages文章评论apa格式cj8xkz6t100% (1)
- ModelEngineersWorkshopApril2021 Sanet ST Sanet STDocument68 pagesModelEngineersWorkshopApril2021 Sanet ST Sanet STAngelos Makris100% (1)
- Water Activity and PH MeasurementDocument51 pagesWater Activity and PH MeasurementEnekwa AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Consumer Pricelist April 2014Document44 pagesConsumer Pricelist April 2014prakash_garudNo ratings yet
- Europe's Onshore and Offshore Wind Energy PotentialDocument91 pagesEurope's Onshore and Offshore Wind Energy PotentialSuDokuNo ratings yet
- Power WizardDocument80 pagesPower Wizarddoce12100% (1)
- L293D Motor Driver DatasheetDocument14 pagesL293D Motor Driver DatasheetAnkit Daftery100% (3)
- Module 5 - Rotodynamic Pumps-Part 1Document28 pagesModule 5 - Rotodynamic Pumps-Part 1ASHITA K B100% (1)
- A2 5 Lifecycle Flow TemplatemanufactureDocument1 pageA2 5 Lifecycle Flow Templatemanufactureapi-247436935No ratings yet
- Turbo-Driven Boiler Feed Pump: 1. Turbine Information CasingDocument15 pagesTurbo-Driven Boiler Feed Pump: 1. Turbine Information Casingparthibanemails5779No ratings yet
- Weld Summary ReportDocument80 pagesWeld Summary ReportBinu SulochananNo ratings yet
- PP ProjectDocument23 pagesPP ProjectAbrhaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Laboratory Aim:: SVKM'S Nmims Mukesh Patel School of Technology Management & EngineeringDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Laboratory Aim:: SVKM'S Nmims Mukesh Patel School of Technology Management & EngineeringronakNo ratings yet
- The Building Blocks of Life NotebookDocument4 pagesThe Building Blocks of Life NotebookosamaNo ratings yet
- Tier 4 PM Agreements Jan 2012Document46 pagesTier 4 PM Agreements Jan 2012Sixto Guarniz AnticonaNo ratings yet
- IEEE Guide For Seismic Qualification of Class 1E Metal-Enclosed Power Switchgear AssembliesDocument23 pagesIEEE Guide For Seismic Qualification of Class 1E Metal-Enclosed Power Switchgear AssembliesukritNo ratings yet
- IEEE STD 1584A 2004 Guide For Performing Arc Flash Hazard Calculations Amendment 1 PDFDocument9 pagesIEEE STD 1584A 2004 Guide For Performing Arc Flash Hazard Calculations Amendment 1 PDFjose manuel valle fabianNo ratings yet
- PMFDocument2 pagesPMFSyedNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analytical Chemistry and Its Importance of Pharmaceutical Field1Document9 pagesQuantitative Analytical Chemistry and Its Importance of Pharmaceutical Field1cyper zoonNo ratings yet
- A320 Overhead PanelDocument1 pageA320 Overhead PanelMartha B. de Lima100% (4)
- Biobor JF PdsDocument19 pagesBiobor JF PdsHozifa Krar100% (1)