Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sa 315
Sa 315
Uploaded by
shivam wadhwa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesThis document outlines the auditor's responsibilities for identifying and assessing risks of material misstatement in an entity's financial statements. It details the risk assessment procedures auditors must perform, including understanding the entity and its environment, internal controls, financial reporting processes and assessing risks at the assertion level. The auditor aims to identify significant risks and document the risk assessment process.
Original Description:
SA 315 from audit pronouncements
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the auditor's responsibilities for identifying and assessing risks of material misstatement in an entity's financial statements. It details the risk assessment procedures auditors must perform, including understanding the entity and its environment, internal controls, financial reporting processes and assessing risks at the assertion level. The auditor aims to identify significant risks and document the risk assessment process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesSa 315
Sa 315
Uploaded by
shivam wadhwaThis document outlines the auditor's responsibilities for identifying and assessing risks of material misstatement in an entity's financial statements. It details the risk assessment procedures auditors must perform, including understanding the entity and its environment, internal controls, financial reporting processes and assessing risks at the assertion level. The auditor aims to identify significant risks and document the risk assessment process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
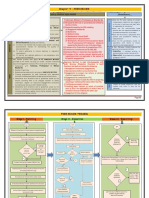
SA 315
IDENTIFYING AND ASSESSING THE RISK OF MATERIAL MISSTATEMENT
THROUGH UNDERSTANDING THE ENTITY AND ITS ENVIRONMENT
(1) Abbreviations Used:
FS Financial Statements
ROMMs Risks of Material Misstatements
Mgmt. Management
TCWG Those Charged with Governance
RAP Risk Assessment Procedures
EP Engagement Partner
ET Engagement Team
MM Material Misstatement
FRF Financial Reporting Framework
(2) Deals with <SA’s Title>
(3) Objective of auditor is to identify & assess ROMMs at assertion level, cause of
fraud or error.
(4) Definitions:
(a) Assertion: Representations by Mgmt. that are embodied in FS.
(b) Business Risk: Risk of not achieving Business Objective & Goal.
(c) Internal Control: Controls on preparation of FS by Mgmt.
(d) Risk Assessment Procedures: Audit procedures to <SA’s Title>
(e) Significant Risk: ROMMs which in auditors judgment requires special
consideration.
(5) Auditor shall perform RAP to provide basis for ROMM at Assertion Levels.
(6) RAP shall include:
(a) Inquiries of Mgmt. and Others
(b) Analytical Procedures
(c) Observation and Inspection
(7) Auditor shall consider if info. from client acceptance or continuation process is
relevant in identifying ROMM.
(8) If EP has performed other engagements for the entity, then consider if that info.
is relevant in identifying ROMM
(9) When auditor uses info. from previous audit experience, he shall evaluate if any
changes thereto.
(10) EP & ET shall discuss the susceptibility of FS for MM.
(11) Auditor shall obtain understanding of following:
(a) Relevant industry, regulatory factors of FRFs,
(b) Nature of entity including:
(i) its operations,
(ii) its ownership and governance structures,
(iii) the types of investments that the entity is making and plans to make
(iv) the way that the entity is structured and how it is financed,
(c) The entity’s selection and application of accounting policies,
(d) The entity’s objectives and strategies, and those related business risks that
may result in ROMM,
(e) Measurement & Review of entity’s Financial Performance.
(12) Obtain an understanding of internal control relevant to audit.
(13) Auditor shall evaluate the design of those controls and determine whether they
have been implemented, by performing procedures
(14) As part of understanding the control environment auditor shall evaluate if:
(a) Mgmt. with oversight of TCWG has created and maintained a culture of
honesty and ethical behavior,
(b) Strengths of control provide foundation for other components of internal
controls,
(15) Obtain an understanding if the entity has a process for:
(a) Identifying business risks relevant to financial reporting objectives,
(b) Estimating the significance of the risks,
(c) Assessing the likelihood of their occurrence,
(d) Deciding about actions to address those risks.
(16) If such a process is established, auditor shall obtain an understanding of such
process and the results thereof.
(17) If such process has not been established, auditor shall discuss with mgmt. the
business risks relevant to financial reporting objectives and how mgmt. has
addressed such issues.
(18) Obtain understanding of Information system related to business process
relevant for financial reporting including following areas:
(a) Classes of Transactions significant to FS,
(b) Procedures within IT and manual systems by which initiated, recorded,
processed, corrected as necessary, transferred to the general ledger and
reported in FS (IRPCTR),
(c) Related accounting records and other supporting information,
(d) How the information system captures events & conditions,
(e) The financial reporting process used to prepare FS,
(f) Control surrounding journal entries.
(19) Understand how entity communicates financial reporting roles and
responsibilities to team.
(20) Understanding of control activities relevant for audit.
(21) Understanding of Control activities entity has taken in response to risks from IT.
(22) Obtain an understanding of the major activities that the entity uses to monitor
internal control over financial reporting.
(23) If there is internal audit function, Auditor shall determine if:
(a) NT&E of internal audit function,
(b) Activities performed in internal audit function,
(24) Understand the sources of info used in monitoring activities.
(25) Assess the ROMM at:
(a) FS level &
(b) Assertion level for Class of transaction, Account Balances and Disclosures.
(26) Auditor shall:
(a) Identify risks thought-out process by understanding,
(b) Assess the identified risks,
(c) Related the identified risks to what can go wrong,
(d) Consider the likelihood of what can go wrong,
(27) As part of identifying the risk under point 25, auditor shall determine whether in
auditor’s professional judgment they are significant risk.
(28) In exercising the Professional Judgement, auditor shall consider the
following:
(a) Is the risk being of fraud,
(b) Is it relating to recent significant economic, accounting developments or
changes.
(c) Complexity of transactions,
(d) Whether transactions with related parties involved.
(e) Degree of subjectivity involved
(f) Whether it involves significant transactions outside normal business.
(29) When Auditor determines that risk exists then, he shall understand the entities
controls relating to the risk.
(30) For some risk, it may not be possible to obtain sufficient & appropriate audit
evidence due to in routine nature of transaction, in such cases auditor shall obtain
understanding of them.
(31) Auditor’s assessment of ROMMs shall change during the audit.
(32) Document:
(a) Discussions done with ET,
(b) Key elements of understanding obtained regarding each aspect of entity,
(c) Identified and assesses ROMM,
(d) Risk identified and related controls.
You might also like
- DFCS Response To Ossoff ReportDocument11 pagesDFCS Response To Ossoff ReportLindsey BasyeNo ratings yet
- Annual MLRO Report TemplateDocument6 pagesAnnual MLRO Report TemplatePineung Mabok0% (1)
- Just For Feet, Inc.: CASE 1.3Document11 pagesJust For Feet, Inc.: CASE 1.3ffffffff dfdfdfNo ratings yet
- LS 2.80A - PSA 315 Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MisstatementDocument6 pagesLS 2.80A - PSA 315 Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MisstatementSkye LeeNo ratings yet
- CM 03 PsaDocument9 pagesCM 03 PsaLucy HeartfiliaNo ratings yet
- Sa - 300-499 Risk Assessment & Response To Assessed Risks PDFDocument11 pagesSa - 300-499 Risk Assessment & Response To Assessed Risks PDFsarvjeet_kaushal100% (1)
- 08 Identifying & Assessing The Risks of Material MisstatementDocument5 pages08 Identifying & Assessing The Risks of Material Misstatementrandomlungs121223No ratings yet
- Completing The AuditDocument21 pagesCompleting The AuditJb MejiaNo ratings yet
- AT 09 Identifying and Assessing The Risks of Material MisstatementDocument5 pagesAT 09 Identifying and Assessing The Risks of Material MisstatementPauline De VillaNo ratings yet
- Report On Audit Planning and Approach of QLD FitsDocument10 pagesReport On Audit Planning and Approach of QLD FitsAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chap 4567 AAADocument16 pagesChap 4567 AAAHà Phương TrầnNo ratings yet
- Session 7 - AUDITING AND ASSURANCE PRINCIPLESDocument31 pagesSession 7 - AUDITING AND ASSURANCE PRINCIPLESSharjaaahNo ratings yet
- Risk AsssesmentDocument13 pagesRisk Asssesmentutkarsh agarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 ReportDocument16 pagesChapter 19 ReportAmira SawadjaanNo ratings yet
- Isa 315Document3 pagesIsa 315Stefi Yunia SuwarlanNo ratings yet
- Risk of Material MisstatementDocument3 pagesRisk of Material Misstatementbobo kaNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Examination - Paper 2.6 (INT) Audit and Internal ReviewDocument12 pagesPart 2 Examination - Paper 2.6 (INT) Audit and Internal ReviewkhengmaiNo ratings yet
- EIS Booster Practice Session Questions CH 1 - MCQs May 23Document25 pagesEIS Booster Practice Session Questions CH 1 - MCQs May 23hdelibrate2019No ratings yet
- Module 1.3 Understanding The Entity and Its Environment Including IC - For POSTINGDocument12 pagesModule 1.3 Understanding The Entity and Its Environment Including IC - For POSTINGMae Gamit LaglivaNo ratings yet
- Scope of This ISADocument9 pagesScope of This ISAbaabasaamNo ratings yet
- Basic Acc Quiz1Document4 pagesBasic Acc Quiz1Angel BiernezaNo ratings yet
- ACC 139 - 15 Considering Certain Specific FS ItemsDocument13 pagesACC 139 - 15 Considering Certain Specific FS ItemsJomar RabiaNo ratings yet
- Gov BusDocument25 pagesGov Busctremaine072820No ratings yet
- Sulaiha Wati - Chapter 8 NewDocument6 pagesSulaiha Wati - Chapter 8 Newsulaiha watiNo ratings yet
- ERM Policy01 08 17Document4 pagesERM Policy01 08 17Mihir KumarNo ratings yet
- Assurance Answer Mock Test March 2021 (Final)Document10 pagesAssurance Answer Mock Test March 2021 (Final)Farjana AkterNo ratings yet
- Specialized Industries Final ExamDocument8 pagesSpecialized Industries Final Examlois martinNo ratings yet
- At Handouts 3Document18 pagesAt Handouts 3Jake MandapNo ratings yet
- Top10 Risk 2010Document44 pagesTop10 Risk 2010ghdavaNo ratings yet
- Audit Fraud MemoDocument16 pagesAudit Fraud MemoManish AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Trainings On 21 December 2023Document25 pagesTrainings On 21 December 2023ngabonziza samuelNo ratings yet
- (At) 03 PlanningDocument14 pages(At) 03 PlanningCykee Hanna Quizo LumongsodNo ratings yet
- Audit 1Document6 pagesAudit 1Yumna SalvatiraNo ratings yet
- Accounting Principles & Procedures MCQs (Set-I) For FPSC Senior Auditor TestsDocument11 pagesAccounting Principles & Procedures MCQs (Set-I) For FPSC Senior Auditor TestssangaYNo ratings yet
- CA Inter (QB) - Chapter 3Document101 pagesCA Inter (QB) - Chapter 3Siddhi ShahNo ratings yet
- PSA315Document6 pagesPSA315Klo MonNo ratings yet
- Auditing QuestionDocument7 pagesAuditing QuestionWaqar AmjadNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Overlooked and Under Tested : Robert J. Bradley, CAMSDocument12 pagesRisk Assessment: Overlooked and Under Tested : Robert J. Bradley, CAMSAleAleNo ratings yet
- Strategic Business Management July 18 Mark PlanDocument22 pagesStrategic Business Management July 18 Mark PlanWong AndrewNo ratings yet
- Week 4 HomeworkDocument5 pagesWeek 4 HomeworkchaitrasuhasNo ratings yet
- Accounting Principles #038 Procedures MCQs (Set-I) For FPSC Senior AuditoDocument10 pagesAccounting Principles #038 Procedures MCQs (Set-I) For FPSC Senior AuditoAdiBalochNo ratings yet
- AML ChecklistDocument9 pagesAML ChecklistVu Nguyen AnhNo ratings yet
- Aud 1.3Document12 pagesAud 1.3Marjorie BernasNo ratings yet
- VIII. Consideration of Internal ControlDocument15 pagesVIII. Consideration of Internal ControlKrizza MaeNo ratings yet
- CGRE Asynchronous Assignment - 11Document5 pagesCGRE Asynchronous Assignment - 11Treesa JogiNo ratings yet
- Audit Process - Psba PDFDocument46 pagesAudit Process - Psba PDFMariciele Padaca AnolinNo ratings yet
- Control Testing and Control RiskDocument48 pagesControl Testing and Control Riskaleahrey monganganNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PolicyDocument10 pagesRisk Management Policyvinal.sharmaNo ratings yet
- Citibank N.A. - Pakistan BranchesDocument10 pagesCitibank N.A. - Pakistan Branchesflavendar178No ratings yet
- Rrpa 9Document8 pagesRrpa 9mr rahulNo ratings yet
- FT Audit QPDocument7 pagesFT Audit QPmewtwovarceusNo ratings yet
- Almednralejo Chap7 DiscussionDocument10 pagesAlmednralejo Chap7 DiscussionRhywen Fronda GilleNo ratings yet
- 05 - Part 1-Control and Accounting Information SystemsDocument16 pages05 - Part 1-Control and Accounting Information SystemsQuỳnh NhưNo ratings yet
- Accounting Principles and ProceduresDocument8 pagesAccounting Principles and ProceduresAdnan DaniNo ratings yet
- Audit New July 21 Suggested Ans InterDocument15 pagesAudit New July 21 Suggested Ans InterPriyansh KhatriNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice. Write Your Answer On The Space Provided Before Each NumberDocument12 pagesMultiple Choice. Write Your Answer On The Space Provided Before Each NumberKathleenNo ratings yet
- Audit and Risk Committee TorDocument4 pagesAudit and Risk Committee TorYasser BashaNo ratings yet
- Auditing Quiz TestDocument2 pagesAuditing Quiz Testrathaloz777No ratings yet
- CFAS Questions Chaps 1 and 2Document13 pagesCFAS Questions Chaps 1 and 2King SigueNo ratings yet
- 04 Audit Planning and Risk AssessmentDocument12 pages04 Audit Planning and Risk AssessmentaibsNo ratings yet
- Perform Auditing and ReportingDocument65 pagesPerform Auditing and ReportingMulugeta GebinoNo ratings yet
- SFM CA Final (New) Block Test Series: Total Marks: 30 Time: 1 HourDocument2 pagesSFM CA Final (New) Block Test Series: Total Marks: 30 Time: 1 Hourshivam wadhwaNo ratings yet
- Rohit Chaurasia: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesRohit Chaurasia: Objectiveshivam wadhwaNo ratings yet
- Compulsory MCQS: (Just Select The Correct Answer, No Need For Reasoning)Document17 pagesCompulsory MCQS: (Just Select The Correct Answer, No Need For Reasoning)shivam wadhwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - PEER REVIEWDocument2 pagesChapter 17 - PEER REVIEWshivam wadhwaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Bajaj Allianz FamilyDocument7 pagesWelcome To Bajaj Allianz Familyshivam wadhwaNo ratings yet
- SA 330 The Auditor's Responses To Assessed Risks: Scope of This SA: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesSA 330 The Auditor's Responses To Assessed Risks: Scope of This SA: Objectiveshivam wadhwaNo ratings yet
- Rahul MadaanDocument3 pagesRahul Madaanshivam wadhwaNo ratings yet
- Sa 402Document2 pagesSa 402shivam wadhwaNo ratings yet
- Auditing & Assurance Services, 6eDocument26 pagesAuditing & Assurance Services, 6ehuma1208No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Global, Ethics, and Security Management: Enterprise Systems For Management, 2e (Motiwalla/Thompson)Document13 pagesChapter 10 Global, Ethics, and Security Management: Enterprise Systems For Management, 2e (Motiwalla/Thompson)Uts HughNo ratings yet
- Case Studies On Threats To Audit IndependenceDocument3 pagesCase Studies On Threats To Audit IndependencedemolaojaomoNo ratings yet
- Cost and Management Accounting OverviewDocument40 pagesCost and Management Accounting OverviewpRiNcE DuDhAtRaNo ratings yet
- Outsourcing Internal AuditDocument12 pagesOutsourcing Internal AuditDr-Mohammed FaridNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 GEDocument37 pagesChapter 15 GEKholoud LabadyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document5 pagesLecture 1eyooloNo ratings yet
- Notes Ais615Document28 pagesNotes Ais615Bucko BarnesNo ratings yet
- 6502 - Assignment 2Document10 pages6502 - Assignment 2aamirshehzad1383010No ratings yet
- 2011 ICQ BandCDocument117 pages2011 ICQ BandCPastidjaNo ratings yet
- Audit Checklist Example - Medical DevicesDocument20 pagesAudit Checklist Example - Medical DevicesVickysh MevawalaNo ratings yet
- Approved - Guidance: GNB-CPDDocument17 pagesApproved - Guidance: GNB-CPDAnonymous G6ceYCzwtNo ratings yet
- CERT-SC-F 01-G Self Assessment Checklist GMP GHPDocument23 pagesCERT-SC-F 01-G Self Assessment Checklist GMP GHPAsma DahaboNo ratings yet
- PSA-720 (Revised) PDFDocument98 pagesPSA-720 (Revised) PDFehlayzaaNo ratings yet
- FULL REPORT - Audit of Polk County, Tennessee For FY22Document229 pagesFULL REPORT - Audit of Polk County, Tennessee For FY22Dan Lehr100% (1)
- 5S Routine Audit Form: Quit Created by Javier RubioDocument7 pages5S Routine Audit Form: Quit Created by Javier Rubioadnan iqbalNo ratings yet
- Study Case - Assessing Information Technology General Control RiskDocument15 pagesStudy Case - Assessing Information Technology General Control RiskGerardo Ruíz BazánNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Summary TaskDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Summary TaskRinchi MatsuokaNo ratings yet
- Supplier Questionnaire - Supplier FormDocument5 pagesSupplier Questionnaire - Supplier FormSunday Augustine Chibuzo100% (1)
- Chapter 17 Basic Audit Sampling ConceptsDocument32 pagesChapter 17 Basic Audit Sampling ConceptsClar Aaron Bautista100% (1)
- Kcs Act 1969Document187 pagesKcs Act 1969HvffNo ratings yet
- Isca MCQ PDFDocument5 pagesIsca MCQ PDFAnnu JyotiNo ratings yet
- QP-GEN-03 Prosedur Internal AuditDocument9 pagesQP-GEN-03 Prosedur Internal AuditFendiNo ratings yet
- Naukri SANJAYJAIN (27y 0m)Document4 pagesNaukri SANJAYJAIN (27y 0m)Amit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Determinants of The Effectiveness of Audit Procedures in Revealing Fraud: Attribution Theory Approach With Time Pressure As An Intervening VariableDocument18 pagesDeterminants of The Effectiveness of Audit Procedures in Revealing Fraud: Attribution Theory Approach With Time Pressure As An Intervening VariableIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Exam Reviwer in GbermicDocument23 pagesExam Reviwer in GbermicMary Elisha PinedaNo ratings yet
- 20J E1 Addendum 1Document3 pages20J E1 Addendum 1AshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Auditing IT Governance ControlsDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Auditing IT Governance ControlsKim Cristian MaañoNo ratings yet