Professional Documents
Culture Documents
First Term Strand Unit Topic Week
First Term Strand Unit Topic Week
Uploaded by
hafsahCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Gullivers TravelsDocument38 pagesGullivers TravelshafsahNo ratings yet
- First Term Strand Unit Topic WeekDocument6 pagesFirst Term Strand Unit Topic WeekStella ElytraNo ratings yet
- Bioscheme of Work Class 9Document7 pagesBioscheme of Work Class 9Stella ElytraNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination DPPDocument4 pagesControl and Coordination DPPkalanidhkaurNo ratings yet
- 5-Gr 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM SEC BDocument5 pages5-Gr 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM SEC BChloe HendricksNo ratings yet
- Humana Anatomy Q9Document2 pagesHumana Anatomy Q9Shiva GlennNo ratings yet
- Pointers Biology EASE 4Document4 pagesPointers Biology EASE 4Javier Rakha SulendraNo ratings yet
- Continuous Evaluation 3: 16 Coordination in HumansDocument12 pagesContinuous Evaluation 3: 16 Coordination in HumansLungNo ratings yet
- CytologyDocument8 pagesCytologyKin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- IX HalfYearly Dec21Document5 pagesIX HalfYearly Dec21Hasna Hena SarkerNo ratings yet
- Biology Ii: KARUNDURA TEST 2021 - 2022 District:Rwamagana Subject: Biology (Theory)Document8 pagesBiology Ii: KARUNDURA TEST 2021 - 2022 District:Rwamagana Subject: Biology (Theory)Mutaganda Ami fideleNo ratings yet
- CytologyDocument8 pagesCytologyNeetenin NeeteninNo ratings yet
- 1989 Paper 1 Question 5 (B)Document23 pages1989 Paper 1 Question 5 (B)Kin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- Third Term Biology TestDocument9 pagesThird Term Biology TestTheogene NTEGEREJIMANANo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemKin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- Bio Question 1Document9 pagesBio Question 1James ChauNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: The Foundation of Physiology Test Questions: Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesHomeostasis: The Foundation of Physiology Test Questions: Multiple ChoiceSenthereng MoaisiNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Nervous SystemsigwelanadacharityNo ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document4 pagesWa0004.nlipsa765No ratings yet
- Biology C-2 Syllabus Breakdown (2023-24) FinalDocument9 pagesBiology C-2 Syllabus Breakdown (2023-24) FinalMuhammad ShahswarNo ratings yet
- Coordination NervousDocument17 pagesCoordination NervousNeetenin NeeteninNo ratings yet
- Transport in Mammals: 1989 Paper 2 Question 6Document21 pagesTransport in Mammals: 1989 Paper 2 Question 6Kin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination - DPP 5.1 - (CDS - 2 Viraat 2023)Document5 pagesControl and Coordination - DPP 5.1 - (CDS - 2 Viraat 2023)tanwar9780No ratings yet
- FCA (SA) Part I Past Papers - 2014 1st Semester 2 10 2014 PDFDocument91 pagesFCA (SA) Part I Past Papers - 2014 1st Semester 2 10 2014 PDFkingbgmNo ratings yet
- Excretion As Part Of...Document2 pagesExcretion As Part Of...Andrew ColvilleNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument368 pagesBiologydamariskituku97No ratings yet
- CLASS XI BIo Question Paper 2019-20Document4 pagesCLASS XI BIo Question Paper 2019-20Lawrence GaikwadNo ratings yet
- HL Paper 3: Two Stimuli and The Receptors That Detect ThemDocument33 pagesHL Paper 3: Two Stimuli and The Receptors That Detect ThemUPBEAT VOIIDNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Aerobic and Anaerobic Questions MR MarecarDocument15 pagesCardiovascular, Respiratory, Aerobic and Anaerobic Questions MR MarecarMutaganda Ami fideleNo ratings yet
- 7-Gr 12 HOMEOSTASIS SEC BDocument4 pages7-Gr 12 HOMEOSTASIS SEC BChloe HendricksNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Quetion and AnswersDocument164 pagesAnatomy Quetion and AnswersericabayishimaNo ratings yet
- Coordiantion in Humans LQ - Q&ADocument15 pagesCoordiantion in Humans LQ - Q&AChan Chun YanNo ratings yet
- Class XI Annual - 2022-23Document6 pagesClass XI Annual - 2022-23Farhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Extension Worksheet - Option HDocument2 pagesExtension Worksheet - Option HHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Cells - 1 V2 (Euks, Proks & Viruses)Document9 pagesCells - 1 V2 (Euks, Proks & Viruses)mormerodNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Specialist Biology Practice TestDocument7 pagesYear 10 Specialist Biology Practice TestSahana MEENACHISUNDARAMNo ratings yet
- Human Brain Biochemistry: American Journal of BioscienceDocument13 pagesHuman Brain Biochemistry: American Journal of BioscienceEugen MNo ratings yet
- Biology Class XDocument4 pagesBiology Class Xneha singhNo ratings yet
- Bio F1Document4 pagesBio F1milly khisaNo ratings yet
- HL Topic 11.3 KidneyDocument6 pagesHL Topic 11.3 KidneyPraveenNo ratings yet
- Biology CHP 1 Test Paper-20220127145424959329Document1 pageBiology CHP 1 Test Paper-20220127145424959329Asna NajeebNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Grade X Biology PT2Document4 pagesPractice Paper Grade X Biology PT2setidi1975No ratings yet
- Bio XiDocument3 pagesBio Xijackieaj093No ratings yet
- IGCSE Coordination and Response WsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Coordination and Response WsAnand Kumar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Panam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperDocument7 pagesPanam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- Panam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperDocument7 pagesPanam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- MB Biology MorningDocument7 pagesMB Biology MorningSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 10 AY 2023-24.PDFDocument8 pagesBiology Class 10 AY 2023-24.PDFhexrazorsharpNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Control and Coordination Test 05 PDFDocument1 page10 Science Control and Coordination Test 05 PDFKSP Classes GondiaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Co-Ordination, Response, Movement and HomeostasisDocument6 pagesUNIT 5 Co-Ordination, Response, Movement and HomeostasisDilan Hiroshana MendisNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Excretion, Control and Coordination PaperDocument2 pagesGrade 10 Excretion, Control and Coordination PaperMARIYAM NAVEDNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY MOCKS S1 QS(1)-1Document89 pagesBIOLOGY MOCKS S1 QS(1)-1gicherutony4No ratings yet
- Ans Paper 2 SelangorDocument12 pagesAns Paper 2 SelangorRozaini OthmanNo ratings yet
- Bio WorkDocument7 pagesBio WorkRiddhi TullooNo ratings yet
- Test Nervous System g12Document5 pagesTest Nervous System g12neanderbtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination PYQsDocument6 pagesChapter 7 - Control and Coordination PYQsrohanmurali8No ratings yet
- LSE-05 - ENG - Compressed PDFDocument4 pagesLSE-05 - ENG - Compressed PDFAashutosh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 S 202301Document4 pagesTutorial 4 S 202301subhadraNo ratings yet
- ICSE Biology (Sample Question Paper) Semester 2-1Document3 pagesICSE Biology (Sample Question Paper) Semester 2-1CCBUNo ratings yet
- First Term Strand Unit Topic WeekDocument8 pagesFirst Term Strand Unit Topic WeekhafsahNo ratings yet
- Accounting (7707) Topic WiseDocument3 pagesAccounting (7707) Topic WisehafsahNo ratings yet
- Accounting (7707) Scheme of WorkDocument52 pagesAccounting (7707) Scheme of WorkhafsahNo ratings yet
- Danny The Dog!: We Are Going To Have Help Learning About Adverbs FromDocument11 pagesDanny The Dog!: We Are Going To Have Help Learning About Adverbs FromhafsahNo ratings yet
- Danny The Dog!: We Are Going To Have Help Learning About Adverbs FromDocument11 pagesDanny The Dog!: We Are Going To Have Help Learning About Adverbs FromhafsahNo ratings yet
- Charlie & The Chocolate Factory Guide - Vocabulary, QuestionsDocument21 pagesCharlie & The Chocolate Factory Guide - Vocabulary, QuestionshafsahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 LabDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 Labcess ignacioNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument35 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDiksha TNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life: 1 Mark QuestionsDocument3 pagesCh. 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life: 1 Mark QuestionsTanush RaghavNo ratings yet
- Indicators of Good Preparation Olevels 231 QuestionsDocument4 pagesIndicators of Good Preparation Olevels 231 QuestionsAteeb MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Life Full Lesson Plan PDFDocument50 pagesChemistry of Life Full Lesson Plan PDFbrain john dizonNo ratings yet
- Polygraphy 2022 ReadyDocument147 pagesPolygraphy 2022 ReadyDayana Marie100% (1)
- January 2022 QPDocument3 pagesJanuary 2022 QPWajid-ul-IslamNo ratings yet
- W2 - MEDSURG Guidelines For Nursing Interventions On Coma PatientsDocument6 pagesW2 - MEDSURG Guidelines For Nursing Interventions On Coma PatientsKyla L. Madjad100% (1)
- Science Reviewer 3RD QuarterDocument2 pagesScience Reviewer 3RD QuarterMica Simbajon (micay)No ratings yet
- Alimentary Tract-22073Document4 pagesAlimentary Tract-22073daniel balteanNo ratings yet
- Nutrigenomics Goals and StrategiesDocument8 pagesNutrigenomics Goals and StrategiesAmogh VatsNo ratings yet
- Early Method of Detecting DeceptionDocument6 pagesEarly Method of Detecting DeceptionTIPAY, EMELIE L.100% (2)
- Edexcel IAL Bio Mark Scheme (October 2020)Document27 pagesEdexcel IAL Bio Mark Scheme (October 2020)Meenakshie ChaudrieNo ratings yet
- S1 C2.1 Cell - Structure, Function and OrganisationDocument19 pagesS1 C2.1 Cell - Structure, Function and OrganisationANGELA HO SHU YEANNo ratings yet
- Tecnologí A Cosmé Tica 2020Document56 pagesTecnologí A Cosmé Tica 2020HAIDY FRANCONo ratings yet
- Peroxisome Diversity and EvolutionDocument10 pagesPeroxisome Diversity and EvolutionPaulius SungailaNo ratings yet
- Last Min. PT2 Rev.Document22 pagesLast Min. PT2 Rev.sumedhasaha09No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Physical ExaminationDocument8 pagesCardiovascular System: Physical ExaminationMiguel C. Dolot100% (1)
- Biology Notes Class 10Document2 pagesBiology Notes Class 10ParikshitNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Studies of Fragaria VescaDocument3 pagesIn Vitro Studies of Fragaria VescaMahnoor MansoorNo ratings yet
- (Dahlem Workshop Reports Life Sciences Research Report 20) T. a. Sears (Auth.), T. a. Sears (Eds.) - Neuronal-glial Cell Interrelationships_ Report of the Dahlem Workshop on Neuronal-glial Cell InterrDocument378 pages(Dahlem Workshop Reports Life Sciences Research Report 20) T. a. Sears (Auth.), T. a. Sears (Eds.) - Neuronal-glial Cell Interrelationships_ Report of the Dahlem Workshop on Neuronal-glial Cell InterrGustavo Sá MottaNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic System PDFDocument275 pagesHematopoietic System PDFXochitl ZambranoNo ratings yet
- BRAIN ASYMETRY Exp Rev ProtDocument11 pagesBRAIN ASYMETRY Exp Rev ProtChristina MountakiNo ratings yet
- Myology in Prosthodontics by PriyankaDocument43 pagesMyology in Prosthodontics by PriyankaPriya Prinku100% (1)
- Mok QuestionDocument28 pagesMok QuestionikaNo ratings yet
- NCM 3115 Care of The Elder Person Professor: Aissa R. Carlit, RN, Ohn, MN, DSCN Module 1: Principles of Gerontology/ Introduction of GerontologyDocument19 pagesNCM 3115 Care of The Elder Person Professor: Aissa R. Carlit, RN, Ohn, MN, DSCN Module 1: Principles of Gerontology/ Introduction of GerontologyKASSANDRA THERESE G. DAITOLNo ratings yet
- Phylum Rotifera: Body FormDocument4 pagesPhylum Rotifera: Body Formadeela akhterNo ratings yet
- Andi Muh Octavian Pratama Et Anwar Lewa - Potential Tissue Repair of Salmon DNA As Additional Therapy For Improve Outcomes in Revision Rhinoplasty of Severely Contracted Nose A Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesAndi Muh Octavian Pratama Et Anwar Lewa - Potential Tissue Repair of Salmon DNA As Additional Therapy For Improve Outcomes in Revision Rhinoplasty of Severely Contracted Nose A Literature Reviewoctavian pratamaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Growth RequirementDocument12 pagesMicrobial Growth RequirementTalha HussainNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 5Document6 pagesScience Grade 5EARL MARCIAL CAINGCOYNo ratings yet
First Term Strand Unit Topic Week
First Term Strand Unit Topic Week
Uploaded by
hafsahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
First Term Strand Unit Topic Week
First Term Strand Unit Topic Week
Uploaded by
hafsahCopyright:
Available Formats
Subject: Biology 2019-2020
Scheme of work/Term wise syllabus breakup
Class Level: 10th O - LEVEL
FIRST TERM
Strand Unit Topic Objective Week
Excretion 9.1 Structure and (a) define excretion as the removal of toxic materials 1
function of kidneys and the waste products of metabolism from
9.2 Kidney dialysis organisms
(b) describe the removal of carbon dioxide from the
lungs
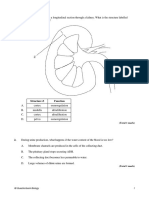
(c) identify on diagrams and name the kidneys,
ureters, bladder, urethra and state the function of
each (the function of the kidney should be described 1
simply as removing urea and excess salts and water
from the blood; details of kidney structure and
nephron are not required)
(d) describe dialysis in kidney machines as the
diffusion of waste products and salts (small
molecules) through a membrane; large molecules
(e.g. protein) remain in the blood. TOTAL: 2
10.1 Structure and (a) define homeostasis as the maintenance of a 1
function of the skin constant internal environment (b) explain the concept
of control by negative feedback
Homeostasis (c) identify, on a diagram of the skin, hairs, sweat
glands, temperature receptors, blood vessels and 1
fatty tissue
(d) describe the maintenance of a constant body
temperature in humans in terms of insulation and the
role of temperature receptors in the skin, sweating,
shivering, blood vessels near the skin surface and the TOTAL: 2
coordinating role of the brain
(a) state that the nervous system (brain, spinal cord 1
Coordination and 11.1 Nervous and nerves) serves to coordinate and regulate bodily
response system functions
11.2 Receptors (b) identify, on diagrams of the central nervous
11.3 Reflex action system, the cerebrum, cerebellum, pituitary gland and
11.4 Hormones hypothalamus, medulla, spinal cord and nerves
(c) describe the principal functions of the above
structures in terms of coordinating and regulating 1
bodily functions
(d) describe the gross structure of the eye as seen in
front view and in horizontal section
(e) state the principal functions of component parts 1
of the eye in producing a focused image of near and
distant objects on the retina
(f) describe the pupil reflex in response to bright and
dim light 1
(g) outline the functions of sensory neurones, relay
neurones and motor neurones
(h) discuss the function of the brain and spinal cord in
producing a coordinated response as a result of a
specific stimulus (reflex action)
(i) define a hormone as a chemical substance, 1
produced by a gland, carried by the blood, which
alters the activity of one or more specific target
organs and is then destroyed by the liver
(j) state the role of the hormone adrenaline in
boosting the blood glucose concentration and give
examples of situations in which this may occur
(k) state the role of the hormone insulin in controlling
blood glucose concentration
(l) describe the signs (increased blood glucose TOTAL ; 5
concentration and glucose in urine) and treatment
(administration of insulin) of diabetes mellitus.
Respiration 8.1 Aerobic (a) define respiration as the release of energy from 1
respiration 8.2 food substances in all living cells
Anaerobic (b) define aerobic respiration as the release of a
respiration 8.3 relatively large amount of energy by the breakdown
Human gas of food substances in the presence of oxygen
exchange (c) state the equation (in words or symbols) for
aerobic respiration
(d) state the uses of energy in the human body:
muscle contraction, protein synthesis, cell division,
active transport, growth, the passage of nerve
impulses and the maintenance of a constant body 1
temperature (e) define anaerobic respiration as the
release of a relatively small amount of energy by the
breakdown of food substances in the absence of
oxygen
(f) state the equation (in words or symbols) for 1
anaerobic respiration in humans and in yeast
(g) describe the effect of lactic acid production in
muscles during exercise
(h) know the percentages of the gases in atmospheric
air and investigate and state the differences between
inspired and expired air 1
(i) investigate and state the effect of physical activity
on rate and depth of breathing
(j) identify on diagrams and name the larynx,
trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli and associated
capillaries
(k) state the characteristics of, and describe the role
of, the exchange surface of the alveoli in gas exchange
(l) describe the role of cilia, diaphragm, ribs and
intercostal muscles (external and internal) in
breathing. TOTAL: 4
ONE WEEK FOR REVISION
SECOND TERM
Strand Unit Topic Objective Week
Support, movement 12.1 Bones (a) identify and describe, from diagrams, photographs
and locomotion 12.2 Joints 12.3 and real specimens, the main bones of the forelimb 1
Antagonistic (humerus, radius, ulna and scapula) of a mammal
muscles (b) describe the type of movement permitted by the 1
ball and socket joint and the hinge joint of the
forelimb
(c) describe the action of the antagonistic muscles at TOTAL: 2
the hinge joint.
The use and abuse of 13.1 Antibiotics (a) define a drug as any externally administered
drugs 13.2 Effects of substance that modifies or affects chemical reactions 1
heroin in the body
13.3 Effects of (b) describe the medicinal use of antibiotics for the
alcohol treatment of bacterial infection
SS13.4 Effects of (c) describe the effects of the abuse of heroin: a
tobacco smoke powerful depressant, problems of addiction, severe 1
withdrawal symptoms and associated problems such
as crime and infection, e.g. AIDS
(d) describe the effects of excessive consumption of 1
alcohol: reduced self-control, depressant, effect on
reaction times, damage to liver and social implications 1
(e) describe the effects of tobacco smoke and its
major toxic components (nicotine, tar and carbon
monoxide) on health: strong association with 1
bronchitis, emphysema, lung cancer and heart
disease, and the association between smoking during
pregnancy and reduced birth weight of the baby
(f) recognise the fact that many people regard TOTAL: 5
smoking as no longer socially acceptable.
Microorganisms and 14.1 (a) list the main characteristics of the following 1
biotechnology Microorganisms groups: viruses, bacteria and fungi
14.2 Food (b) outline the role of microorganisms in 1
biotechnology decomposition
14.3 Industrial (c) explain the role of yeast in the production of 1
biotechnology bread and alcohol
l (d) outline the role of bacteria in yoghurt and cheese
production 1
(e) describe the use of fermenters for large-scale
production of antibiotics and single cell protein 1
(f) describe the role of the fungus Penicillium in the
production of penicillin. TOTAL: 5
TWO WEEKS REVISION
You might also like
- Gullivers TravelsDocument38 pagesGullivers TravelshafsahNo ratings yet
- First Term Strand Unit Topic WeekDocument6 pagesFirst Term Strand Unit Topic WeekStella ElytraNo ratings yet
- Bioscheme of Work Class 9Document7 pagesBioscheme of Work Class 9Stella ElytraNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination DPPDocument4 pagesControl and Coordination DPPkalanidhkaurNo ratings yet
- 5-Gr 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM SEC BDocument5 pages5-Gr 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM SEC BChloe HendricksNo ratings yet
- Humana Anatomy Q9Document2 pagesHumana Anatomy Q9Shiva GlennNo ratings yet
- Pointers Biology EASE 4Document4 pagesPointers Biology EASE 4Javier Rakha SulendraNo ratings yet
- Continuous Evaluation 3: 16 Coordination in HumansDocument12 pagesContinuous Evaluation 3: 16 Coordination in HumansLungNo ratings yet
- CytologyDocument8 pagesCytologyKin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- IX HalfYearly Dec21Document5 pagesIX HalfYearly Dec21Hasna Hena SarkerNo ratings yet
- Biology Ii: KARUNDURA TEST 2021 - 2022 District:Rwamagana Subject: Biology (Theory)Document8 pagesBiology Ii: KARUNDURA TEST 2021 - 2022 District:Rwamagana Subject: Biology (Theory)Mutaganda Ami fideleNo ratings yet
- CytologyDocument8 pagesCytologyNeetenin NeeteninNo ratings yet
- 1989 Paper 1 Question 5 (B)Document23 pages1989 Paper 1 Question 5 (B)Kin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- Third Term Biology TestDocument9 pagesThird Term Biology TestTheogene NTEGEREJIMANANo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemKin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- Bio Question 1Document9 pagesBio Question 1James ChauNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: The Foundation of Physiology Test Questions: Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesHomeostasis: The Foundation of Physiology Test Questions: Multiple ChoiceSenthereng MoaisiNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Nervous SystemsigwelanadacharityNo ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document4 pagesWa0004.nlipsa765No ratings yet
- Biology C-2 Syllabus Breakdown (2023-24) FinalDocument9 pagesBiology C-2 Syllabus Breakdown (2023-24) FinalMuhammad ShahswarNo ratings yet
- Coordination NervousDocument17 pagesCoordination NervousNeetenin NeeteninNo ratings yet
- Transport in Mammals: 1989 Paper 2 Question 6Document21 pagesTransport in Mammals: 1989 Paper 2 Question 6Kin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination - DPP 5.1 - (CDS - 2 Viraat 2023)Document5 pagesControl and Coordination - DPP 5.1 - (CDS - 2 Viraat 2023)tanwar9780No ratings yet
- FCA (SA) Part I Past Papers - 2014 1st Semester 2 10 2014 PDFDocument91 pagesFCA (SA) Part I Past Papers - 2014 1st Semester 2 10 2014 PDFkingbgmNo ratings yet
- Excretion As Part Of...Document2 pagesExcretion As Part Of...Andrew ColvilleNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument368 pagesBiologydamariskituku97No ratings yet
- CLASS XI BIo Question Paper 2019-20Document4 pagesCLASS XI BIo Question Paper 2019-20Lawrence GaikwadNo ratings yet
- HL Paper 3: Two Stimuli and The Receptors That Detect ThemDocument33 pagesHL Paper 3: Two Stimuli and The Receptors That Detect ThemUPBEAT VOIIDNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Aerobic and Anaerobic Questions MR MarecarDocument15 pagesCardiovascular, Respiratory, Aerobic and Anaerobic Questions MR MarecarMutaganda Ami fideleNo ratings yet
- 7-Gr 12 HOMEOSTASIS SEC BDocument4 pages7-Gr 12 HOMEOSTASIS SEC BChloe HendricksNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Quetion and AnswersDocument164 pagesAnatomy Quetion and AnswersericabayishimaNo ratings yet
- Coordiantion in Humans LQ - Q&ADocument15 pagesCoordiantion in Humans LQ - Q&AChan Chun YanNo ratings yet
- Class XI Annual - 2022-23Document6 pagesClass XI Annual - 2022-23Farhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Extension Worksheet - Option HDocument2 pagesExtension Worksheet - Option HHellö PëachNo ratings yet
- Cells - 1 V2 (Euks, Proks & Viruses)Document9 pagesCells - 1 V2 (Euks, Proks & Viruses)mormerodNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Specialist Biology Practice TestDocument7 pagesYear 10 Specialist Biology Practice TestSahana MEENACHISUNDARAMNo ratings yet
- Human Brain Biochemistry: American Journal of BioscienceDocument13 pagesHuman Brain Biochemistry: American Journal of BioscienceEugen MNo ratings yet
- Biology Class XDocument4 pagesBiology Class Xneha singhNo ratings yet
- Bio F1Document4 pagesBio F1milly khisaNo ratings yet
- HL Topic 11.3 KidneyDocument6 pagesHL Topic 11.3 KidneyPraveenNo ratings yet
- Biology CHP 1 Test Paper-20220127145424959329Document1 pageBiology CHP 1 Test Paper-20220127145424959329Asna NajeebNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Grade X Biology PT2Document4 pagesPractice Paper Grade X Biology PT2setidi1975No ratings yet
- Bio XiDocument3 pagesBio Xijackieaj093No ratings yet
- IGCSE Coordination and Response WsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Coordination and Response WsAnand Kumar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Panam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperDocument7 pagesPanam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- Panam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperDocument7 pagesPanam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- MB Biology MorningDocument7 pagesMB Biology MorningSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 10 AY 2023-24.PDFDocument8 pagesBiology Class 10 AY 2023-24.PDFhexrazorsharpNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Control and Coordination Test 05 PDFDocument1 page10 Science Control and Coordination Test 05 PDFKSP Classes GondiaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Co-Ordination, Response, Movement and HomeostasisDocument6 pagesUNIT 5 Co-Ordination, Response, Movement and HomeostasisDilan Hiroshana MendisNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Excretion, Control and Coordination PaperDocument2 pagesGrade 10 Excretion, Control and Coordination PaperMARIYAM NAVEDNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY MOCKS S1 QS(1)-1Document89 pagesBIOLOGY MOCKS S1 QS(1)-1gicherutony4No ratings yet
- Ans Paper 2 SelangorDocument12 pagesAns Paper 2 SelangorRozaini OthmanNo ratings yet
- Bio WorkDocument7 pagesBio WorkRiddhi TullooNo ratings yet
- Test Nervous System g12Document5 pagesTest Nervous System g12neanderbtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination PYQsDocument6 pagesChapter 7 - Control and Coordination PYQsrohanmurali8No ratings yet
- LSE-05 - ENG - Compressed PDFDocument4 pagesLSE-05 - ENG - Compressed PDFAashutosh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 S 202301Document4 pagesTutorial 4 S 202301subhadraNo ratings yet
- ICSE Biology (Sample Question Paper) Semester 2-1Document3 pagesICSE Biology (Sample Question Paper) Semester 2-1CCBUNo ratings yet
- First Term Strand Unit Topic WeekDocument8 pagesFirst Term Strand Unit Topic WeekhafsahNo ratings yet
- Accounting (7707) Topic WiseDocument3 pagesAccounting (7707) Topic WisehafsahNo ratings yet
- Accounting (7707) Scheme of WorkDocument52 pagesAccounting (7707) Scheme of WorkhafsahNo ratings yet
- Danny The Dog!: We Are Going To Have Help Learning About Adverbs FromDocument11 pagesDanny The Dog!: We Are Going To Have Help Learning About Adverbs FromhafsahNo ratings yet
- Danny The Dog!: We Are Going To Have Help Learning About Adverbs FromDocument11 pagesDanny The Dog!: We Are Going To Have Help Learning About Adverbs FromhafsahNo ratings yet
- Charlie & The Chocolate Factory Guide - Vocabulary, QuestionsDocument21 pagesCharlie & The Chocolate Factory Guide - Vocabulary, QuestionshafsahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 LabDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 Labcess ignacioNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument35 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDiksha TNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life: 1 Mark QuestionsDocument3 pagesCh. 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life: 1 Mark QuestionsTanush RaghavNo ratings yet
- Indicators of Good Preparation Olevels 231 QuestionsDocument4 pagesIndicators of Good Preparation Olevels 231 QuestionsAteeb MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Life Full Lesson Plan PDFDocument50 pagesChemistry of Life Full Lesson Plan PDFbrain john dizonNo ratings yet
- Polygraphy 2022 ReadyDocument147 pagesPolygraphy 2022 ReadyDayana Marie100% (1)
- January 2022 QPDocument3 pagesJanuary 2022 QPWajid-ul-IslamNo ratings yet
- W2 - MEDSURG Guidelines For Nursing Interventions On Coma PatientsDocument6 pagesW2 - MEDSURG Guidelines For Nursing Interventions On Coma PatientsKyla L. Madjad100% (1)
- Science Reviewer 3RD QuarterDocument2 pagesScience Reviewer 3RD QuarterMica Simbajon (micay)No ratings yet
- Alimentary Tract-22073Document4 pagesAlimentary Tract-22073daniel balteanNo ratings yet
- Nutrigenomics Goals and StrategiesDocument8 pagesNutrigenomics Goals and StrategiesAmogh VatsNo ratings yet
- Early Method of Detecting DeceptionDocument6 pagesEarly Method of Detecting DeceptionTIPAY, EMELIE L.100% (2)
- Edexcel IAL Bio Mark Scheme (October 2020)Document27 pagesEdexcel IAL Bio Mark Scheme (October 2020)Meenakshie ChaudrieNo ratings yet
- S1 C2.1 Cell - Structure, Function and OrganisationDocument19 pagesS1 C2.1 Cell - Structure, Function and OrganisationANGELA HO SHU YEANNo ratings yet
- Tecnologí A Cosmé Tica 2020Document56 pagesTecnologí A Cosmé Tica 2020HAIDY FRANCONo ratings yet
- Peroxisome Diversity and EvolutionDocument10 pagesPeroxisome Diversity and EvolutionPaulius SungailaNo ratings yet
- Last Min. PT2 Rev.Document22 pagesLast Min. PT2 Rev.sumedhasaha09No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Physical ExaminationDocument8 pagesCardiovascular System: Physical ExaminationMiguel C. Dolot100% (1)
- Biology Notes Class 10Document2 pagesBiology Notes Class 10ParikshitNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Studies of Fragaria VescaDocument3 pagesIn Vitro Studies of Fragaria VescaMahnoor MansoorNo ratings yet
- (Dahlem Workshop Reports Life Sciences Research Report 20) T. a. Sears (Auth.), T. a. Sears (Eds.) - Neuronal-glial Cell Interrelationships_ Report of the Dahlem Workshop on Neuronal-glial Cell InterrDocument378 pages(Dahlem Workshop Reports Life Sciences Research Report 20) T. a. Sears (Auth.), T. a. Sears (Eds.) - Neuronal-glial Cell Interrelationships_ Report of the Dahlem Workshop on Neuronal-glial Cell InterrGustavo Sá MottaNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic System PDFDocument275 pagesHematopoietic System PDFXochitl ZambranoNo ratings yet
- BRAIN ASYMETRY Exp Rev ProtDocument11 pagesBRAIN ASYMETRY Exp Rev ProtChristina MountakiNo ratings yet
- Myology in Prosthodontics by PriyankaDocument43 pagesMyology in Prosthodontics by PriyankaPriya Prinku100% (1)
- Mok QuestionDocument28 pagesMok QuestionikaNo ratings yet
- NCM 3115 Care of The Elder Person Professor: Aissa R. Carlit, RN, Ohn, MN, DSCN Module 1: Principles of Gerontology/ Introduction of GerontologyDocument19 pagesNCM 3115 Care of The Elder Person Professor: Aissa R. Carlit, RN, Ohn, MN, DSCN Module 1: Principles of Gerontology/ Introduction of GerontologyKASSANDRA THERESE G. DAITOLNo ratings yet
- Phylum Rotifera: Body FormDocument4 pagesPhylum Rotifera: Body Formadeela akhterNo ratings yet
- Andi Muh Octavian Pratama Et Anwar Lewa - Potential Tissue Repair of Salmon DNA As Additional Therapy For Improve Outcomes in Revision Rhinoplasty of Severely Contracted Nose A Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesAndi Muh Octavian Pratama Et Anwar Lewa - Potential Tissue Repair of Salmon DNA As Additional Therapy For Improve Outcomes in Revision Rhinoplasty of Severely Contracted Nose A Literature Reviewoctavian pratamaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Growth RequirementDocument12 pagesMicrobial Growth RequirementTalha HussainNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 5Document6 pagesScience Grade 5EARL MARCIAL CAINGCOYNo ratings yet