Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
101 viewsDiagnostic Defibrillation
Diagnostic Defibrillation
Uploaded by
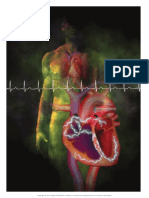
RobDefibrillation is a procedure used to stop ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia by delivering an electrical shock to the heart to reestablish an effective rhythm. The shock depolarizes the entire heart muscle so the sinoatrial node can regain control of the heart's rhythm. Nursing interventions before, during, and after the procedure include assessing for shockable rhythms, explaining the procedure to the patient, administering oxygen and medications, monitoring the patient, and providing education to the patient and family on heart health. Potential complications include decreased cardiac output, heart failure, and electrical burns.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Plabverse AllDocument316 pagesPlabverse AllFahad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Clinical Owl ECG Basics PreviewDocument3 pagesClinical Owl ECG Basics PreviewSalman khanNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation ChecklistDocument4 pagesDefibrillation ChecklistCzarina100% (1)
- PacemakerDocument48 pagesPacemakersoniya josephNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Pacing and ICDDocument74 pagesCardiac Pacing and ICDBernadixta Winda Dwi Cahyani100% (4)
- Acls Mega Code 1Document31 pagesAcls Mega Code 1mj8bfgxbyjNo ratings yet
- Defib ATI TemplateDocument1 pageDefib ATI Templatejoshua stapleNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorsDocument54 pagesDefibrillatorsAli Al-AhmedyNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument8 pagesDefibrillatorJisha JanardhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Ressucitation: Presented by Siwani Rai M.Sc. Nursing-IDocument39 pagesCardiopulmonary Ressucitation: Presented by Siwani Rai M.Sc. Nursing-ISiwani raiNo ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory Arrest (FS)Document55 pagesCardiorespiratory Arrest (FS)Ahmad AzharNo ratings yet
- Transposition of The Great VesselDocument30 pagesTransposition of The Great VesseljustinahorroNo ratings yet
- Ecg Dysrythmias Nursing Responsibilitu Sinus Node 1.) Sinus BradycardiaDocument2 pagesEcg Dysrythmias Nursing Responsibilitu Sinus Node 1.) Sinus BradycardiaNickha LazoNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation and CardioversionDocument28 pagesDefibrillation and CardioversionadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Ms4 Midterm Notesandreviewer PDFDocument24 pagesMs4 Midterm Notesandreviewer PDFNorbelisa Tabo-ac CadungganNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 DefibDocument60 pagesPresentation1 DefibRoshani sharmaNo ratings yet
- BCLS 2Document73 pagesBCLS 2Praveen Ravishankaran100% (1)
- Troubleshootingcardiac Monitor Problems: Don't Forget Toassess The Patient First!Document2 pagesTroubleshootingcardiac Monitor Problems: Don't Forget Toassess The Patient First!Melinia HdyNo ratings yet
- DEFIBRILLATIONDocument2 pagesDEFIBRILLATIONFuni PesNo ratings yet
- DefibrillationDocument13 pagesDefibrillationKristine VedadNo ratings yet
- 2 ArrhythmiasDocument18 pages2 Arrhythmiasset.b.rleNo ratings yet
- L Nursing2014 L AugustDocument7 pagesL Nursing2014 L AugustLuis Fernando Morales JuradoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PacingDocument4 pagesCardiac Pacingmrygnvll100% (1)
- Cardiology Medsurg LectureDocument9 pagesCardiology Medsurg LectureTine GuibaoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Ecg InterpretationDocument76 pagesBasics of Ecg InterpretationDennis MiritiNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 - Lesson 11 (Arrhythmia)Document5 pagesNCM 118 - Lesson 11 (Arrhythmia)Bobby Christian DuronNo ratings yet
- MS4 MidtermsDocument14 pagesMS4 Midtermsmendozajanice0601No ratings yet
- Cardiac PacingDocument4 pagesCardiac PacingmrygnvllNo ratings yet
- L2 ECG Monitoring I Moodle - 2023Document64 pagesL2 ECG Monitoring I Moodle - 2023Hailey YanNo ratings yet
- DC ShockDocument8 pagesDC Shockرافت العواضيNo ratings yet
- Diskusi Topik PacemakerDocument45 pagesDiskusi Topik PacemakerAl Hijjah FadhilahNo ratings yet
- IPD A Cardiovascular System Bates and and VideoDocument10 pagesIPD A Cardiovascular System Bates and and Videostar220498No ratings yet
- Early Management: Admit To Burns UnitDocument1 pageEarly Management: Admit To Burns UnitErica A. Gallegos AriasNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation in The Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome: ECG Recognition and Treatment in The EDDocument8 pagesAtrial Fibrillation in The Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome: ECG Recognition and Treatment in The EDyohanadebritarerekoliNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Rite Reviewer Part 1Document73 pagesCardiology Rite Reviewer Part 1Alvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Dvanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument72 pagesDvanced Cardiac Life Supportolivia100% (1)
- Case Presentation On Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument64 pagesCase Presentation On Supraventricular TachycardiaHazel AsperaNo ratings yet
- Rate P Wave QRS Comple X PR Interval: ST RDDocument2 pagesRate P Wave QRS Comple X PR Interval: ST RDPat G.No ratings yet
- Tachycardia PDFDocument2 pagesTachycardia PDFubaidillah ubaiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument37 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life SupportRoy Acosta GumbanNo ratings yet
- Med II-LE1-1.03 Arrhythmia NotesDocument14 pagesMed II-LE1-1.03 Arrhythmia NotesAbigael SantosNo ratings yet
- Acls Algorithms Acls Algorithms: (Cardiac Arrest) (Bradycardia) Assessment ActionDocument5 pagesAcls Algorithms Acls Algorithms: (Cardiac Arrest) (Bradycardia) Assessment ActionCabales EmmanNo ratings yet
- Sinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementDocument4 pagesSinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementMargueretti Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation and Cardioversion: DescriptionDocument3 pagesDefibrillation and Cardioversion: DescriptionCristian RajagukgukNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest PDFDocument4 pagesCardiac Arrest PDFYogi drNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output Ready To PrintDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Ready To PrintAnne SedanzaNo ratings yet
- Cheat ECG-2Document3 pagesCheat ECG-2Neil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Assignment in NCM 112: Pilar College of Zamboanga CityDocument7 pagesAssignment in NCM 112: Pilar College of Zamboanga CityCake ManNo ratings yet
- Cardioversion and DefibrillationDocument24 pagesCardioversion and Defibrillationrona-chanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Anf Managing VertigoDocument67 pagesUnderstanding Anf Managing VertigoGede SuputraNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation TypedDocument8 pagesDefibrillation TypedValarmathiNo ratings yet
- ECG WorksheetDocument4 pagesECG WorksheetNikki GuisonNo ratings yet
- 7 Electrical Therapies Defib and PacingDocument16 pages7 Electrical Therapies Defib and PacingEricson LenovNo ratings yet
- ECG Description:: Ventricular FibrillationDocument2 pagesECG Description:: Ventricular FibrillationpsyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 Dysrhythmias Quizlet 4Document31 pagesChapter 26 Dysrhythmias Quizlet 4Marshin Thea CelociaNo ratings yet
- Bradycardia and TachycardiaDocument66 pagesBradycardia and TachycardiaKarissaNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesDecreased Cardiac Outputshuang81No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Groupings) - YASMIEN MARIEDocument21 pagesDRUG STUDY (Groupings) - YASMIEN MARIEYasmien MarieNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenDocument23 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenItsMe AJNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXFrom EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Classification of MurmursDocument2 pagesClassification of MurmursNazneen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- High Quality CPR, DR Ali Haedar PDFDocument45 pagesHigh Quality CPR, DR Ali Haedar PDFTaufik SuhendarNo ratings yet
- Arritmias Ventriculares en Corazones NormalesDocument14 pagesArritmias Ventriculares en Corazones Normalessanalejo0290No ratings yet
- Mattu Recent Cardiol Articles Youve Got To Know Icem 2023 LitupdatesDocument29 pagesMattu Recent Cardiol Articles Youve Got To Know Icem 2023 Litupdates85tq5nhsqbNo ratings yet
- Diastolic DysfunctionDocument6 pagesDiastolic DysfunctionMarina SecureanuNo ratings yet
- Ecg Indice 9788876407246Document12 pagesEcg Indice 9788876407246AndreaHistoryXNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument13 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life SupportEldonVinceIsidroNo ratings yet
- Erc - 2005Document58 pagesErc - 2005zulfantri1983No ratings yet
- Lead Avr PDFDocument9 pagesLead Avr PDFsiddharthNo ratings yet
- BagusDocument10 pagesBagusBelinda SuhuyanlyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Sports Cardiology and - ExerciseDocument80 pagesGuidelines On Sports Cardiology and - ExerciseBruno S. Homem De FariaNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Heart Sounds by Dr. RoomiDocument15 pagesLecture On Heart Sounds by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Ekg PJKDocument113 pagesEkg PJKdevipuspaNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia 6 YrDocument72 pagesArrhythmia 6 YrPiyush MalikNo ratings yet
- Cardiology USMLE 2CK (Cardio Clinical Care) Flashcards - MemorangDocument4 pagesCardiology USMLE 2CK (Cardio Clinical Care) Flashcards - MemorangMohamed Abbas0% (2)
- K - 7 Supraventrikular Takikardia (IKA)Document12 pagesK - 7 Supraventrikular Takikardia (IKA)thomasfelixNo ratings yet
- Kuliah EkgDocument30 pagesKuliah EkgMuhammad Ari AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Case 3: Aortic StenosisDocument11 pagesCase 3: Aortic StenosisfmNo ratings yet
- Heart Awareness Paula Cervera Joana Villanueva Regina IbarraDocument2 pagesHeart Awareness Paula Cervera Joana Villanueva Regina IbarraPaula CerveraNo ratings yet
- BSE A1 New Normal References Mar 20Document1 pageBSE A1 New Normal References Mar 20Roberta KalasauskaiteNo ratings yet
- Board Desember 2015 Fix Answer - BALIDocument67 pagesBoard Desember 2015 Fix Answer - BALIrahageng wida kusuma100% (1)
- Welly@unissula - Ac.id: Welly Anggarani, Sandy Christiono, Prima AgusmawantiDocument6 pagesWelly@unissula - Ac.id: Welly Anggarani, Sandy Christiono, Prima Agusmawantinabilah syahirahNo ratings yet
- CardiomegalyDocument6 pagesCardiomegalyChellamani UmakanthanNo ratings yet
- Ds Week 6 Nrg301 ValenzonaDocument2 pagesDs Week 6 Nrg301 ValenzonaJoshennaNo ratings yet
- 2 Midterm Exam Propedeutic-1: Attempt ReviewDocument8 pages2 Midterm Exam Propedeutic-1: Attempt ReviewYousra AhmedNo ratings yet
- Anjleena: Curriculum VitaeDocument2 pagesAnjleena: Curriculum Vitaetonny buddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 Management of Patients With StructuralDocument23 pagesChapter 28 Management of Patients With StructuralAbel C. Idusma Jr.No ratings yet
- 0421「心臟內科複習」講師盧雅雯醫師Document87 pages0421「心臟內科複習」講師盧雅雯醫師abc54115411.yNo ratings yet
Diagnostic Defibrillation
Diagnostic Defibrillation
Uploaded by
Rob0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
101 views1 pageDefibrillation is a procedure used to stop ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia by delivering an electrical shock to the heart to reestablish an effective rhythm. The shock depolarizes the entire heart muscle so the sinoatrial node can regain control of the heart's rhythm. Nursing interventions before, during, and after the procedure include assessing for shockable rhythms, explaining the procedure to the patient, administering oxygen and medications, monitoring the patient, and providing education to the patient and family on heart health. Potential complications include decreased cardiac output, heart failure, and electrical burns.
Original Description:
ATI Diagnostic-Defibrillation
Original Title
Diagnostic-Defibrillation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDefibrillation is a procedure used to stop ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia by delivering an electrical shock to the heart to reestablish an effective rhythm. The shock depolarizes the entire heart muscle so the sinoatrial node can regain control of the heart's rhythm. Nursing interventions before, during, and after the procedure include assessing for shockable rhythms, explaining the procedure to the patient, administering oxygen and medications, monitoring the patient, and providing education to the patient and family on heart health. Potential complications include decreased cardiac output, heart failure, and electrical burns.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
101 views1 pageDiagnostic Defibrillation
Diagnostic Defibrillation
Uploaded by
RobDefibrillation is a procedure used to stop ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia by delivering an electrical shock to the heart to reestablish an effective rhythm. The shock depolarizes the entire heart muscle so the sinoatrial node can regain control of the heart's rhythm. Nursing interventions before, during, and after the procedure include assessing for shockable rhythms, explaining the procedure to the patient, administering oxygen and medications, monitoring the patient, and providing education to the patient and family on heart health. Potential complications include decreased cardiac output, heart failure, and electrical burns.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Diagnostic Procedure
STUDENT NAME: PROCEDURE NAME _ defibrillation
Description of Procedure
Defibrillation is a direct shock delivered to the heart synchronized with the QRS complex. Defibrillation stops all electrical activity
which allows the SA node to take back control. Electrical current passed through the heart that causes the entire myocardium to
depolarize completely at the moment of shock. Produces a transient asystole and then allows the heart's SA node to gain
control.
Indications CONSIDERATIONS
Nursing Interventions (pre, intra, post)
-Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia
-Determine the need for defibrillation (check for carotid pulse,
-Ventricular Fibrillation. apply conductive medium, use the quick look to evaluate rhythm)
-Asystole: if V-fib is considered. pre- Explain procedure, obtain consent, admin o2 ,
document procedure rhythm, have emergency equipment
available.
intra-Admin sedative, ensure proper lead placement,
monitor clients leads to ensure QRS complex is upright and
shockable, perform CPR, defibrillate immediately for v fib
post-Monitor VS, asses airway, document # of fibrillation
attempts, EKG, provide client & family education and
support.
Interpretation of Findings
-Client should have a reestablished regular rhythm. Client Education
-Educate client and family on how to assess for pulse.
-Client has no burns/skin irritation under
electrodes -Advise client to report palpitations or irregularities of heart
rate.
Potential Complications Nursing Interventions
-Offer emotional support to family.
-Decreased cardiac output
-Provide anticoagulation therapy.
-Heart Failure
-Monitor for signs of decrease cardiac output.
-Electrical burns under electrodes
-Provide medications to decrease workload and increase
-Failure of defibrillation
output.
-Embolism causing MI, CVA, & PE
-Asses burns & care for electrical burns
You might also like
- Plabverse AllDocument316 pagesPlabverse AllFahad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Clinical Owl ECG Basics PreviewDocument3 pagesClinical Owl ECG Basics PreviewSalman khanNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation ChecklistDocument4 pagesDefibrillation ChecklistCzarina100% (1)
- PacemakerDocument48 pagesPacemakersoniya josephNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Pacing and ICDDocument74 pagesCardiac Pacing and ICDBernadixta Winda Dwi Cahyani100% (4)
- Acls Mega Code 1Document31 pagesAcls Mega Code 1mj8bfgxbyjNo ratings yet
- Defib ATI TemplateDocument1 pageDefib ATI Templatejoshua stapleNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorsDocument54 pagesDefibrillatorsAli Al-AhmedyNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument8 pagesDefibrillatorJisha JanardhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Ressucitation: Presented by Siwani Rai M.Sc. Nursing-IDocument39 pagesCardiopulmonary Ressucitation: Presented by Siwani Rai M.Sc. Nursing-ISiwani raiNo ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory Arrest (FS)Document55 pagesCardiorespiratory Arrest (FS)Ahmad AzharNo ratings yet
- Transposition of The Great VesselDocument30 pagesTransposition of The Great VesseljustinahorroNo ratings yet
- Ecg Dysrythmias Nursing Responsibilitu Sinus Node 1.) Sinus BradycardiaDocument2 pagesEcg Dysrythmias Nursing Responsibilitu Sinus Node 1.) Sinus BradycardiaNickha LazoNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation and CardioversionDocument28 pagesDefibrillation and CardioversionadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Ms4 Midterm Notesandreviewer PDFDocument24 pagesMs4 Midterm Notesandreviewer PDFNorbelisa Tabo-ac CadungganNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 DefibDocument60 pagesPresentation1 DefibRoshani sharmaNo ratings yet
- BCLS 2Document73 pagesBCLS 2Praveen Ravishankaran100% (1)
- Troubleshootingcardiac Monitor Problems: Don't Forget Toassess The Patient First!Document2 pagesTroubleshootingcardiac Monitor Problems: Don't Forget Toassess The Patient First!Melinia HdyNo ratings yet
- DEFIBRILLATIONDocument2 pagesDEFIBRILLATIONFuni PesNo ratings yet
- DefibrillationDocument13 pagesDefibrillationKristine VedadNo ratings yet
- 2 ArrhythmiasDocument18 pages2 Arrhythmiasset.b.rleNo ratings yet
- L Nursing2014 L AugustDocument7 pagesL Nursing2014 L AugustLuis Fernando Morales JuradoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PacingDocument4 pagesCardiac Pacingmrygnvll100% (1)
- Cardiology Medsurg LectureDocument9 pagesCardiology Medsurg LectureTine GuibaoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Ecg InterpretationDocument76 pagesBasics of Ecg InterpretationDennis MiritiNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 - Lesson 11 (Arrhythmia)Document5 pagesNCM 118 - Lesson 11 (Arrhythmia)Bobby Christian DuronNo ratings yet
- MS4 MidtermsDocument14 pagesMS4 Midtermsmendozajanice0601No ratings yet
- Cardiac PacingDocument4 pagesCardiac PacingmrygnvllNo ratings yet
- L2 ECG Monitoring I Moodle - 2023Document64 pagesL2 ECG Monitoring I Moodle - 2023Hailey YanNo ratings yet
- DC ShockDocument8 pagesDC Shockرافت العواضيNo ratings yet
- Diskusi Topik PacemakerDocument45 pagesDiskusi Topik PacemakerAl Hijjah FadhilahNo ratings yet
- IPD A Cardiovascular System Bates and and VideoDocument10 pagesIPD A Cardiovascular System Bates and and Videostar220498No ratings yet
- Early Management: Admit To Burns UnitDocument1 pageEarly Management: Admit To Burns UnitErica A. Gallegos AriasNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation in The Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome: ECG Recognition and Treatment in The EDDocument8 pagesAtrial Fibrillation in The Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome: ECG Recognition and Treatment in The EDyohanadebritarerekoliNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Rite Reviewer Part 1Document73 pagesCardiology Rite Reviewer Part 1Alvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Dvanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument72 pagesDvanced Cardiac Life Supportolivia100% (1)
- Case Presentation On Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument64 pagesCase Presentation On Supraventricular TachycardiaHazel AsperaNo ratings yet
- Rate P Wave QRS Comple X PR Interval: ST RDDocument2 pagesRate P Wave QRS Comple X PR Interval: ST RDPat G.No ratings yet
- Tachycardia PDFDocument2 pagesTachycardia PDFubaidillah ubaiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument37 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life SupportRoy Acosta GumbanNo ratings yet
- Med II-LE1-1.03 Arrhythmia NotesDocument14 pagesMed II-LE1-1.03 Arrhythmia NotesAbigael SantosNo ratings yet
- Acls Algorithms Acls Algorithms: (Cardiac Arrest) (Bradycardia) Assessment ActionDocument5 pagesAcls Algorithms Acls Algorithms: (Cardiac Arrest) (Bradycardia) Assessment ActionCabales EmmanNo ratings yet
- Sinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementDocument4 pagesSinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementMargueretti Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation and Cardioversion: DescriptionDocument3 pagesDefibrillation and Cardioversion: DescriptionCristian RajagukgukNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest PDFDocument4 pagesCardiac Arrest PDFYogi drNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output Ready To PrintDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Ready To PrintAnne SedanzaNo ratings yet
- Cheat ECG-2Document3 pagesCheat ECG-2Neil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Assignment in NCM 112: Pilar College of Zamboanga CityDocument7 pagesAssignment in NCM 112: Pilar College of Zamboanga CityCake ManNo ratings yet
- Cardioversion and DefibrillationDocument24 pagesCardioversion and Defibrillationrona-chanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Anf Managing VertigoDocument67 pagesUnderstanding Anf Managing VertigoGede SuputraNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation TypedDocument8 pagesDefibrillation TypedValarmathiNo ratings yet
- ECG WorksheetDocument4 pagesECG WorksheetNikki GuisonNo ratings yet
- 7 Electrical Therapies Defib and PacingDocument16 pages7 Electrical Therapies Defib and PacingEricson LenovNo ratings yet
- ECG Description:: Ventricular FibrillationDocument2 pagesECG Description:: Ventricular FibrillationpsyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 Dysrhythmias Quizlet 4Document31 pagesChapter 26 Dysrhythmias Quizlet 4Marshin Thea CelociaNo ratings yet
- Bradycardia and TachycardiaDocument66 pagesBradycardia and TachycardiaKarissaNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesDecreased Cardiac Outputshuang81No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Groupings) - YASMIEN MARIEDocument21 pagesDRUG STUDY (Groupings) - YASMIEN MARIEYasmien MarieNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenDocument23 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenItsMe AJNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXFrom EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Classification of MurmursDocument2 pagesClassification of MurmursNazneen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- High Quality CPR, DR Ali Haedar PDFDocument45 pagesHigh Quality CPR, DR Ali Haedar PDFTaufik SuhendarNo ratings yet
- Arritmias Ventriculares en Corazones NormalesDocument14 pagesArritmias Ventriculares en Corazones Normalessanalejo0290No ratings yet
- Mattu Recent Cardiol Articles Youve Got To Know Icem 2023 LitupdatesDocument29 pagesMattu Recent Cardiol Articles Youve Got To Know Icem 2023 Litupdates85tq5nhsqbNo ratings yet
- Diastolic DysfunctionDocument6 pagesDiastolic DysfunctionMarina SecureanuNo ratings yet
- Ecg Indice 9788876407246Document12 pagesEcg Indice 9788876407246AndreaHistoryXNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument13 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life SupportEldonVinceIsidroNo ratings yet
- Erc - 2005Document58 pagesErc - 2005zulfantri1983No ratings yet
- Lead Avr PDFDocument9 pagesLead Avr PDFsiddharthNo ratings yet
- BagusDocument10 pagesBagusBelinda SuhuyanlyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Sports Cardiology and - ExerciseDocument80 pagesGuidelines On Sports Cardiology and - ExerciseBruno S. Homem De FariaNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Heart Sounds by Dr. RoomiDocument15 pagesLecture On Heart Sounds by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Ekg PJKDocument113 pagesEkg PJKdevipuspaNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia 6 YrDocument72 pagesArrhythmia 6 YrPiyush MalikNo ratings yet
- Cardiology USMLE 2CK (Cardio Clinical Care) Flashcards - MemorangDocument4 pagesCardiology USMLE 2CK (Cardio Clinical Care) Flashcards - MemorangMohamed Abbas0% (2)
- K - 7 Supraventrikular Takikardia (IKA)Document12 pagesK - 7 Supraventrikular Takikardia (IKA)thomasfelixNo ratings yet
- Kuliah EkgDocument30 pagesKuliah EkgMuhammad Ari AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Case 3: Aortic StenosisDocument11 pagesCase 3: Aortic StenosisfmNo ratings yet
- Heart Awareness Paula Cervera Joana Villanueva Regina IbarraDocument2 pagesHeart Awareness Paula Cervera Joana Villanueva Regina IbarraPaula CerveraNo ratings yet
- BSE A1 New Normal References Mar 20Document1 pageBSE A1 New Normal References Mar 20Roberta KalasauskaiteNo ratings yet
- Board Desember 2015 Fix Answer - BALIDocument67 pagesBoard Desember 2015 Fix Answer - BALIrahageng wida kusuma100% (1)
- Welly@unissula - Ac.id: Welly Anggarani, Sandy Christiono, Prima AgusmawantiDocument6 pagesWelly@unissula - Ac.id: Welly Anggarani, Sandy Christiono, Prima Agusmawantinabilah syahirahNo ratings yet
- CardiomegalyDocument6 pagesCardiomegalyChellamani UmakanthanNo ratings yet
- Ds Week 6 Nrg301 ValenzonaDocument2 pagesDs Week 6 Nrg301 ValenzonaJoshennaNo ratings yet
- 2 Midterm Exam Propedeutic-1: Attempt ReviewDocument8 pages2 Midterm Exam Propedeutic-1: Attempt ReviewYousra AhmedNo ratings yet
- Anjleena: Curriculum VitaeDocument2 pagesAnjleena: Curriculum Vitaetonny buddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 Management of Patients With StructuralDocument23 pagesChapter 28 Management of Patients With StructuralAbel C. Idusma Jr.No ratings yet
- 0421「心臟內科複習」講師盧雅雯醫師Document87 pages0421「心臟內科複習」講師盧雅雯醫師abc54115411.yNo ratings yet