Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 viewsV-Model: Kuliah Metode Dan Model Pengembangan Perangkat Lunak
V-Model: Kuliah Metode Dan Model Pengembangan Perangkat Lunak
Uploaded by
Fatih Cah JogjaThe V-Model is a sequential software development lifecycle model where each development phase has an associated testing phase. It is an extension of the waterfall model. In the V-Model, verification phases occur on one side of the "V" during development, while validation phases occur on the other side during testing. The V-Model is suitable for projects with well-defined requirements and fixed scope, but it is inflexible to changes and not well-suited for complex or long-term projects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Topographic Maps: Use The Following Hiking Map From Enchanted Rock To Complete The Following QuestionsDocument3 pagesTopographic Maps: Use The Following Hiking Map From Enchanted Rock To Complete The Following QuestionsVinujah Sukumaran50% (4)
- 2 Material HandlingDocument218 pages2 Material HandlingJon Blac100% (1)
- "The Mammogram Myth" by Rolf HeftiDocument3 pages"The Mammogram Myth" by Rolf HeftiRolf HeftiNo ratings yet
- Tropical SoilsDocument88 pagesTropical SoilsBernard Kipng'eno100% (1)
- Offshore Engineer-February 2015Document84 pagesOffshore Engineer-February 2015ilkerkozturk100% (2)
- V ModelDocument15 pagesV Modelmichael gordilloNo ratings yet
- SDLC - V-ModelDocument5 pagesSDLC - V-Modelpalvi kapurNo ratings yet
- SRE Chapter FiveDocument40 pagesSRE Chapter FiveDESEYALEW TAREKEGNNo ratings yet
- Basic Software Engineering: Prof. Vijya Tulsani, Assistant ProfessorDocument38 pagesBasic Software Engineering: Prof. Vijya Tulsani, Assistant ProfessorKuldeep ParekhNo ratings yet
- SDLC V ModelDocument3 pagesSDLC V ModelMukul Soni100% (1)
- Software Development Life CycleDocument14 pagesSoftware Development Life CycleKaushik RayNo ratings yet
- Software Requirement Class3Document41 pagesSoftware Requirement Class3farfromweakliteNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document13 pagesLec 4Ifra NoorNo ratings yet
- LaupDocument6 pagesLaupTK Lý Nguyễn Tuấn KiệtNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Lecture2Document64 pagesSoftware Engineering Lecture2vaishnavvarma2002No ratings yet
- SDLC (Software Development Lifecycle) - Is A Systematic Process For Building Software That Ensures The Quality and Correctness of The SoftwareDocument36 pagesSDLC (Software Development Lifecycle) - Is A Systematic Process For Building Software That Ensures The Quality and Correctness of The SoftwareqwertyNo ratings yet
- Link 1 For LS1 - LS2 - System Development Life CycleDocument8 pagesLink 1 For LS1 - LS2 - System Development Life Cycleodi.obiokalaNo ratings yet
- V-Model in Software EngineeringDocument16 pagesV-Model in Software EngineeringUn IntNo ratings yet
- He Waterfall Model Was First Process Model To Be Introduced-Tutorials PointDocument8 pagesHe Waterfall Model Was First Process Model To Be Introduced-Tutorials Pointmadhu_devu9837No ratings yet
- SDLC V ModelDocument4 pagesSDLC V Modelnet19b230No ratings yet
- AGILE (1 New)Document81 pagesAGILE (1 New)aswinNo ratings yet
- V ModelDocument14 pagesV ModelDiena Rauda Ramdania100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - 2 - Software Process ModelsDocument79 pagesLecture 2 - 2 - Software Process ModelsanteNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Document40 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Anonymous aQxekTRNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument37 pagesUnit Isantosh.kawadeNo ratings yet
- 1.what Is Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) ?Document9 pages1.what Is Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) ?masudNo ratings yet
- IT Proj SDLC ModelsDocument16 pagesIT Proj SDLC ModelsBaadal KathaitNo ratings yet
- Software ModelsDocument21 pagesSoftware ModelssudanharshpreetkaurNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: (SDLC & Software Process Model)Document44 pagesSoftware Engineering: (SDLC & Software Process Model)sayma meemNo ratings yet
- Software DevelopmentDocument63 pagesSoftware DevelopmentVasanthi BojjaganiNo ratings yet
- Perspective ModelDocument8 pagesPerspective Modelomsuhagir123No ratings yet
- System Development Life CycleDocument8 pagesSystem Development Life CycleAyan MandalNo ratings yet
- V-Model: Team 2: Thi Thanh Chuong Le Ngoc Chinh To Hoai Quynh VyDocument13 pagesV-Model: Team 2: Thi Thanh Chuong Le Ngoc Chinh To Hoai Quynh VyDi ViếtNo ratings yet
- SE NotessDocument15 pagesSE NotessNidhin EdappalNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Document52 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Gm HarsshanNo ratings yet
- Waterfall ModelDocument19 pagesWaterfall Modelfindshubham73No ratings yet
- What You Mean by Software Engineering?Document15 pagesWhat You Mean by Software Engineering?dreem HunterNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four PMDocument35 pagesChapter Four PMSteve TekluNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 SDLCDocument59 pagesLec 2 SDLCMazhar BukhariNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life Cycle: Presented by V Tharun Kumar (17691A05F1)Document11 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycle: Presented by V Tharun Kumar (17691A05F1)Prince SivaNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Course MaterialDocument29 pagesSoftware Engineering Course Materialvikas desaleNo ratings yet
- Models in SEDocument6 pagesModels in SESarmi HarshaNo ratings yet
- WaterfallModelinSDLCDocument16 pagesWaterfallModelinSDLCHell GamingNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Computer Lesson 11 Completing An ApplicationDocument142 pagesGrade 10 Computer Lesson 11 Completing An Applicationabrielletan29No ratings yet
- Incremental Model: The Various Phases of Incremental Model Are As FollowsDocument5 pagesIncremental Model: The Various Phases of Incremental Model Are As FollowsAdeel CheemaNo ratings yet
- AssingmentDocument4 pagesAssingmentIslam SaleemNo ratings yet
- Slide 3Document45 pagesSlide 3masud ranaNo ratings yet
- Course Code: CSE3001 Course Name: Software Engineering Faculty Name: DR - Anand BihariDocument6 pagesCourse Code: CSE3001 Course Name: Software Engineering Faculty Name: DR - Anand BiharixyzNo ratings yet
- WaterfallModelinSDLCDocument15 pagesWaterfallModelinSDLCHell GamingNo ratings yet
- Unit 1seDocument40 pagesUnit 1semr. potterNo ratings yet
- SE Unit - I NotesDocument71 pagesSE Unit - I Notesokchaitanya568No ratings yet
- Ch. 2 Software Development Life CyclesDocument13 pagesCh. 2 Software Development Life Cyclesyashthakare9267No ratings yet
- Waterfall Model Prototyping ModelDocument26 pagesWaterfall Model Prototyping ModelAryan RathoreNo ratings yet
- Extreme Programming (XP)Document11 pagesExtreme Programming (XP)Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- Process Models Part 1Document26 pagesProcess Models Part 1haseebbaloch43No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Software Process ModelDocument101 pagesChapter 3 Software Process Modelsukhmanaulakh54No ratings yet
- Manual TestingDocument33 pagesManual TestingAnto Ramee100% (2)
- Software Engineering: Unit-2Document41 pagesSoftware Engineering: Unit-2Rameswar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument88 pagesUnit IiOnkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Software Process ModelDocument50 pagesChapter-3: Software Process ModelSaad Javaid SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument70 pagesSoftware EngineeringAnam TahirNo ratings yet
- Dpit 023 V-ModelDocument5 pagesDpit 023 V-Modeltoroitich Titus markNo ratings yet
- Waterfall ModelDocument19 pagesWaterfall Modelilias ahmed100% (2)
- V ModelsDocument8 pagesV ModelsRainNo ratings yet
- Software Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandSoftware Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Brake Valves: Z279180 Z101197 Z289395 Z102626 (ZRL3518JC02)Document5 pagesBrake Valves: Z279180 Z101197 Z289395 Z102626 (ZRL3518JC02)houssem houssemNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled DocumentLove Jirah JamandreNo ratings yet
- The Role of The School Psychologist in The Inclusive EducationDocument20 pagesThe Role of The School Psychologist in The Inclusive EducationCortés PameliNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Skeletal System Enhanced SciDocument126 pagesGrade 8 Skeletal System Enhanced SciCin TooNo ratings yet
- Time Clauses - That Vs Which-Relative ClausesDocument8 pagesTime Clauses - That Vs Which-Relative ClausesZuza AlexandrinaNo ratings yet
- English For Nursing Topic 12 Reinforcing A Dietary ProgramDocument6 pagesEnglish For Nursing Topic 12 Reinforcing A Dietary ProgramEha Huwaida HayatiNo ratings yet
- British HeritageDocument15 pagesBritish HeritageOksana BulhakovaNo ratings yet
- Abhinavagupta (C. 950 - 1016 CEDocument8 pagesAbhinavagupta (C. 950 - 1016 CEthewitness3No ratings yet
- Second Practice First Partial English IIIDocument5 pagesSecond Practice First Partial English IIICamiloNo ratings yet
- Knowledge of Cervical Cancer and Acceptance of HPVDocument6 pagesKnowledge of Cervical Cancer and Acceptance of HPVALIF FITRI BIN MOHD JASMINo ratings yet
- UIL Calculator Applications Study ListDocument7 pagesUIL Calculator Applications Study ListRocket FireNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Drug EducationDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Drug EducationCasandra CalacatNo ratings yet
- Jescspsu 08Document11 pagesJescspsu 08Alok RanjanNo ratings yet
- Individual Learning Monitoring Plan: San Benito Integrated SchoolDocument2 pagesIndividual Learning Monitoring Plan: San Benito Integrated SchoolAna Marie LedunaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Task 2 - Using Phones in SchoolDocument6 pagesIELTS Task 2 - Using Phones in SchoolUyên DiệpNo ratings yet
- μου κάνειDocument43 pagesμου κάνειΚατερίνα ΠαπαδάκηNo ratings yet
- Space Planning Guidelines: Edition 2Document29 pagesSpace Planning Guidelines: Edition 2Nur Nabilah SyazwaniNo ratings yet
- Nod 321Document12 pagesNod 321PabloAyreCondoriNo ratings yet
- Masterlist - Course - Offerings - 2024 (As at 18 July 2023)Document3 pagesMasterlist - Course - Offerings - 2024 (As at 18 July 2023)limyihang17No ratings yet
- Wedding Vows - What Do They Really MeanDocument28 pagesWedding Vows - What Do They Really Meanpsykosomatik0% (1)
- Systematix Sona BLW Initiates CoverageDocument32 pagesSystematix Sona BLW Initiates Coveragejitendra76No ratings yet
- Davis Michael 1A Resume 1Document1 pageDavis Michael 1A Resume 1Alyssa HowellNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment of Mandibular Anterior Crowding: Key Words: Crowding, Malocclusion, Labial FlaringDocument4 pagesOrthodontic Treatment of Mandibular Anterior Crowding: Key Words: Crowding, Malocclusion, Labial FlaringDunia Medisku OnlineShopNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Transportation: A Global Supply Chain Perspective, 8th Edition, John J. Coyle, Robert A. Novack, Brian Gibson, Edward J. BardiDocument34 pagesSolution Manual For Transportation: A Global Supply Chain Perspective, 8th Edition, John J. Coyle, Robert A. Novack, Brian Gibson, Edward J. Bardielizabethsantosfawmpbnzjt100% (21)
- Collection of Windows 10 Hidden Secret Registry TweaksDocument9 pagesCollection of Windows 10 Hidden Secret Registry TweaksLiyoNo ratings yet
V-Model: Kuliah Metode Dan Model Pengembangan Perangkat Lunak
V-Model: Kuliah Metode Dan Model Pengembangan Perangkat Lunak
Uploaded by
Fatih Cah Jogja0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views13 pagesThe V-Model is a sequential software development lifecycle model where each development phase has an associated testing phase. It is an extension of the waterfall model. In the V-Model, verification phases occur on one side of the "V" during development, while validation phases occur on the other side during testing. The V-Model is suitable for projects with well-defined requirements and fixed scope, but it is inflexible to changes and not well-suited for complex or long-term projects.
Original Description:
V model pengembangan perangkat lunak
Original Title
09. v model
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe V-Model is a sequential software development lifecycle model where each development phase has an associated testing phase. It is an extension of the waterfall model. In the V-Model, verification phases occur on one side of the "V" during development, while validation phases occur on the other side during testing. The V-Model is suitable for projects with well-defined requirements and fixed scope, but it is inflexible to changes and not well-suited for complex or long-term projects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views13 pagesV-Model: Kuliah Metode Dan Model Pengembangan Perangkat Lunak
V-Model: Kuliah Metode Dan Model Pengembangan Perangkat Lunak
Uploaded by
Fatih Cah JogjaThe V-Model is a sequential software development lifecycle model where each development phase has an associated testing phase. It is an extension of the waterfall model. In the V-Model, verification phases occur on one side of the "V" during development, while validation phases occur on the other side during testing. The V-Model is suitable for projects with well-defined requirements and fixed scope, but it is inflexible to changes and not well-suited for complex or long-term projects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 13
V-Model
Kuliah Metode dan Model
Pengembangan Perangkat
Lunak
V-Model
• The V-model is an SDLC model where execution of processes happens in
a sequential manner in a V-shape. It is also known as Verification and
Validation model.
• The V-Model is an extension of the waterfall model and is based on the
association of a testing phase for each corresponding development
stage. This means that for every single phase in the development cycle,
there is a directly associated testing phase. This is a highly-disciplined
model and the next phase starts only after completion of the previous
phase.
• Under the V-Model, the corresponding testing phase of the development
phase is planned in parallel. So, there are Verification phases on one side
of the ‘V’ and Validation phases on the other side. The Coding Phase
joins the two sides of the V-Model
Verification & Validation
Verification: “Are we building the product right “
• Software seharusnya sesuai dengan spesifikasinya
Validation:"Are we building the right product”.
• Software seharusnya melakukan apa yang benar-
benar disyaratkan oleh user.
Verifikasi Statik dan Dinamis
Software inspection. Berhubungan dengan analisis representasi
sistematatik untuk menemukan masalah (verifikasi statik)
• Dapat menjadi tambahan dari tool-based document dan code
analysis
Software testing. Berhubungan dengan pelaksanaan dan
memperhatikan perilaku produk (dinamik verifikasi)
• Sistem dijalankan dengan data tes dan perilaku operasionalnya
diperhatikan
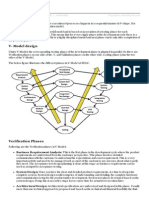
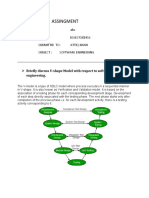
Ilustrasi V-Model
Model Kredibel karena V&V
Pengembangan Model Verifikasi
V-Model - Verification Phases
Business Requirement Analysis
• This is the first phase in the development cycle where the product requirements
are understood from the customer’s perspective. This phase involves detailed
communication with the customer to understand his expectations and exact
requirement. This is a very important activity and needs to be managed well, as
most of the customers are not sure about what exactly they need.
The acceptance test design planning is done at this stage as business
requirements can be used as an input for acceptance testing.
System Design
• Once you have the clear and detailed product requirements, it is time to design
the complete system. The system design will have the understanding and
detailing the complete hardware and communication setup for the product
under development. The system test plan is developed based on the system
design. Doing this at an earlier stage leaves more time for the actual test
execution later.
V-Model - Verification Phases (Lanjut)
Architectural Design
• Architectural specifications are understood and designed in this phase. Usually more than one technical
approach is proposed and based on the technical and financial feasibility the final decision is taken. The
system design is broken down further into modules taking up different functionality. This is also referred
to as High Level Design (HLD).
• The data transfer and communication between the internal modules and with the outside world (other
systems) is clearly understood and defined in this stage. With this information, integration tests can be
designed and documented during this stage.
Module Design
• In this phase, the detailed internal design for all the system modules is specified, referred to as Low Level
Design (LLD). It is important that the design is compatible with the other modules in the system
architecture and the other external systems. The unit tests are an essential part of any development
process and helps eliminate the maximum faults and errors at a very early stage. These unit tests can be
designed at this stage based on the internal module designs.
Coding Phase
• The actual coding of the system modules designed in the design phase is taken up in the Coding phase.
The best suitable programming language is decided based on the system and architectural requirements.
• The coding is performed based on the coding guidelines and standards. The code goes through
numerous code reviews and is optimized for best performance before the final build is checked into the
repository.
Validation Phases
Unit Testing
• Unit tests designed in the module design phase are executed on the code during this validation phase.
Unit testing is the testing at code level and helps eliminate bugs at an early stage, though all defects
cannot be uncovered by unit testing.
Integration Testing
• Integration testing is associated with the architectural design phase. Integration tests are performed to
test the coexistence and communication of the internal modules within the system.
System Testing
• System testing is directly associated with the system design phase. System tests check the entire system
functionality and the communication of the system under development with external systems. Most of the
software and hardware compatibility issues can be uncovered during this system test execution.
Acceptance Testing
• Acceptance testing is associated with the business requirement analysis phase and involves testing the
product in user environment. Acceptance tests uncover the compatibility issues with the other systems
available in the user environment. It also discovers the non-functional issues such as load and
performance defects in the actual user environment.
V- Model ─ Application
• V- Model application is almost the same as the waterfall model, as both
the models are of sequential type. Requirements have to be very clear
before the project starts, because it is usually expensive to go back and
make changes. This model is used in the medical development field, as it
is strictly a disciplined domain.
• The following pointers are some of the most suitable scenarios to use the
V-Model application.
• Requirements are well defined, clearly documented and fixed.
• Product definition is stable.
• Technology is not dynamic and is well understood by the project team.
• There are no ambiguous or undefined requirements.
• The project is short.
V-Model - Advantages
The advantage of the V-Model method is that it is very easy to understand
and apply. The simplicity of this model also makes it easier to manage. The
disadvantage is that the model is not flexible to changes and just in case
there is a requirement change, which is very common in today’s dynamic
world, it becomes very expensive to make the change.
• The advantages of the V-Model method are as follows −
• This is a highly-disciplined model and Phases are completed one at a time.
• Works well for smaller projects where requirements are very well understood.
• Simple and easy to understand and use.
• Easy to manage due to the rigidity of the model. Each phase has specific
deliverables and a review process.
The disadvantages of the V-Model method
• High risk and uncertainty.
• Not a good model for complex and object-oriented projects.
• Poor model for long and ongoing projects.
• Not suitable for the projects where requirements are at a moderate
to high risk of changing.
• Once an application is in the testing stage, it is difficult to go back
and change a functionality.
• No working software is produced until late during the life cycle
You might also like
- Topographic Maps: Use The Following Hiking Map From Enchanted Rock To Complete The Following QuestionsDocument3 pagesTopographic Maps: Use The Following Hiking Map From Enchanted Rock To Complete The Following QuestionsVinujah Sukumaran50% (4)
- 2 Material HandlingDocument218 pages2 Material HandlingJon Blac100% (1)
- "The Mammogram Myth" by Rolf HeftiDocument3 pages"The Mammogram Myth" by Rolf HeftiRolf HeftiNo ratings yet
- Tropical SoilsDocument88 pagesTropical SoilsBernard Kipng'eno100% (1)
- Offshore Engineer-February 2015Document84 pagesOffshore Engineer-February 2015ilkerkozturk100% (2)
- V ModelDocument15 pagesV Modelmichael gordilloNo ratings yet
- SDLC - V-ModelDocument5 pagesSDLC - V-Modelpalvi kapurNo ratings yet
- SRE Chapter FiveDocument40 pagesSRE Chapter FiveDESEYALEW TAREKEGNNo ratings yet
- Basic Software Engineering: Prof. Vijya Tulsani, Assistant ProfessorDocument38 pagesBasic Software Engineering: Prof. Vijya Tulsani, Assistant ProfessorKuldeep ParekhNo ratings yet
- SDLC V ModelDocument3 pagesSDLC V ModelMukul Soni100% (1)
- Software Development Life CycleDocument14 pagesSoftware Development Life CycleKaushik RayNo ratings yet
- Software Requirement Class3Document41 pagesSoftware Requirement Class3farfromweakliteNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document13 pagesLec 4Ifra NoorNo ratings yet
- LaupDocument6 pagesLaupTK Lý Nguyễn Tuấn KiệtNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Lecture2Document64 pagesSoftware Engineering Lecture2vaishnavvarma2002No ratings yet
- SDLC (Software Development Lifecycle) - Is A Systematic Process For Building Software That Ensures The Quality and Correctness of The SoftwareDocument36 pagesSDLC (Software Development Lifecycle) - Is A Systematic Process For Building Software That Ensures The Quality and Correctness of The SoftwareqwertyNo ratings yet
- Link 1 For LS1 - LS2 - System Development Life CycleDocument8 pagesLink 1 For LS1 - LS2 - System Development Life Cycleodi.obiokalaNo ratings yet
- V-Model in Software EngineeringDocument16 pagesV-Model in Software EngineeringUn IntNo ratings yet
- He Waterfall Model Was First Process Model To Be Introduced-Tutorials PointDocument8 pagesHe Waterfall Model Was First Process Model To Be Introduced-Tutorials Pointmadhu_devu9837No ratings yet
- SDLC V ModelDocument4 pagesSDLC V Modelnet19b230No ratings yet
- AGILE (1 New)Document81 pagesAGILE (1 New)aswinNo ratings yet
- V ModelDocument14 pagesV ModelDiena Rauda Ramdania100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - 2 - Software Process ModelsDocument79 pagesLecture 2 - 2 - Software Process ModelsanteNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Document40 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Anonymous aQxekTRNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument37 pagesUnit Isantosh.kawadeNo ratings yet
- 1.what Is Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) ?Document9 pages1.what Is Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) ?masudNo ratings yet
- IT Proj SDLC ModelsDocument16 pagesIT Proj SDLC ModelsBaadal KathaitNo ratings yet
- Software ModelsDocument21 pagesSoftware ModelssudanharshpreetkaurNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: (SDLC & Software Process Model)Document44 pagesSoftware Engineering: (SDLC & Software Process Model)sayma meemNo ratings yet
- Software DevelopmentDocument63 pagesSoftware DevelopmentVasanthi BojjaganiNo ratings yet
- Perspective ModelDocument8 pagesPerspective Modelomsuhagir123No ratings yet
- System Development Life CycleDocument8 pagesSystem Development Life CycleAyan MandalNo ratings yet
- V-Model: Team 2: Thi Thanh Chuong Le Ngoc Chinh To Hoai Quynh VyDocument13 pagesV-Model: Team 2: Thi Thanh Chuong Le Ngoc Chinh To Hoai Quynh VyDi ViếtNo ratings yet
- SE NotessDocument15 pagesSE NotessNidhin EdappalNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Document52 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Gm HarsshanNo ratings yet
- Waterfall ModelDocument19 pagesWaterfall Modelfindshubham73No ratings yet
- What You Mean by Software Engineering?Document15 pagesWhat You Mean by Software Engineering?dreem HunterNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four PMDocument35 pagesChapter Four PMSteve TekluNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 SDLCDocument59 pagesLec 2 SDLCMazhar BukhariNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life Cycle: Presented by V Tharun Kumar (17691A05F1)Document11 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycle: Presented by V Tharun Kumar (17691A05F1)Prince SivaNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Course MaterialDocument29 pagesSoftware Engineering Course Materialvikas desaleNo ratings yet
- Models in SEDocument6 pagesModels in SESarmi HarshaNo ratings yet
- WaterfallModelinSDLCDocument16 pagesWaterfallModelinSDLCHell GamingNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Computer Lesson 11 Completing An ApplicationDocument142 pagesGrade 10 Computer Lesson 11 Completing An Applicationabrielletan29No ratings yet
- Incremental Model: The Various Phases of Incremental Model Are As FollowsDocument5 pagesIncremental Model: The Various Phases of Incremental Model Are As FollowsAdeel CheemaNo ratings yet
- AssingmentDocument4 pagesAssingmentIslam SaleemNo ratings yet
- Slide 3Document45 pagesSlide 3masud ranaNo ratings yet
- Course Code: CSE3001 Course Name: Software Engineering Faculty Name: DR - Anand BihariDocument6 pagesCourse Code: CSE3001 Course Name: Software Engineering Faculty Name: DR - Anand BiharixyzNo ratings yet
- WaterfallModelinSDLCDocument15 pagesWaterfallModelinSDLCHell GamingNo ratings yet
- Unit 1seDocument40 pagesUnit 1semr. potterNo ratings yet
- SE Unit - I NotesDocument71 pagesSE Unit - I Notesokchaitanya568No ratings yet
- Ch. 2 Software Development Life CyclesDocument13 pagesCh. 2 Software Development Life Cyclesyashthakare9267No ratings yet
- Waterfall Model Prototyping ModelDocument26 pagesWaterfall Model Prototyping ModelAryan RathoreNo ratings yet
- Extreme Programming (XP)Document11 pagesExtreme Programming (XP)Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- Process Models Part 1Document26 pagesProcess Models Part 1haseebbaloch43No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Software Process ModelDocument101 pagesChapter 3 Software Process Modelsukhmanaulakh54No ratings yet
- Manual TestingDocument33 pagesManual TestingAnto Ramee100% (2)
- Software Engineering: Unit-2Document41 pagesSoftware Engineering: Unit-2Rameswar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument88 pagesUnit IiOnkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Software Process ModelDocument50 pagesChapter-3: Software Process ModelSaad Javaid SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument70 pagesSoftware EngineeringAnam TahirNo ratings yet
- Dpit 023 V-ModelDocument5 pagesDpit 023 V-Modeltoroitich Titus markNo ratings yet
- Waterfall ModelDocument19 pagesWaterfall Modelilias ahmed100% (2)
- V ModelsDocument8 pagesV ModelsRainNo ratings yet
- Software Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandSoftware Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Brake Valves: Z279180 Z101197 Z289395 Z102626 (ZRL3518JC02)Document5 pagesBrake Valves: Z279180 Z101197 Z289395 Z102626 (ZRL3518JC02)houssem houssemNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled DocumentLove Jirah JamandreNo ratings yet
- The Role of The School Psychologist in The Inclusive EducationDocument20 pagesThe Role of The School Psychologist in The Inclusive EducationCortés PameliNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Skeletal System Enhanced SciDocument126 pagesGrade 8 Skeletal System Enhanced SciCin TooNo ratings yet
- Time Clauses - That Vs Which-Relative ClausesDocument8 pagesTime Clauses - That Vs Which-Relative ClausesZuza AlexandrinaNo ratings yet
- English For Nursing Topic 12 Reinforcing A Dietary ProgramDocument6 pagesEnglish For Nursing Topic 12 Reinforcing A Dietary ProgramEha Huwaida HayatiNo ratings yet
- British HeritageDocument15 pagesBritish HeritageOksana BulhakovaNo ratings yet
- Abhinavagupta (C. 950 - 1016 CEDocument8 pagesAbhinavagupta (C. 950 - 1016 CEthewitness3No ratings yet
- Second Practice First Partial English IIIDocument5 pagesSecond Practice First Partial English IIICamiloNo ratings yet
- Knowledge of Cervical Cancer and Acceptance of HPVDocument6 pagesKnowledge of Cervical Cancer and Acceptance of HPVALIF FITRI BIN MOHD JASMINo ratings yet
- UIL Calculator Applications Study ListDocument7 pagesUIL Calculator Applications Study ListRocket FireNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Drug EducationDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Drug EducationCasandra CalacatNo ratings yet
- Jescspsu 08Document11 pagesJescspsu 08Alok RanjanNo ratings yet
- Individual Learning Monitoring Plan: San Benito Integrated SchoolDocument2 pagesIndividual Learning Monitoring Plan: San Benito Integrated SchoolAna Marie LedunaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Task 2 - Using Phones in SchoolDocument6 pagesIELTS Task 2 - Using Phones in SchoolUyên DiệpNo ratings yet
- μου κάνειDocument43 pagesμου κάνειΚατερίνα ΠαπαδάκηNo ratings yet
- Space Planning Guidelines: Edition 2Document29 pagesSpace Planning Guidelines: Edition 2Nur Nabilah SyazwaniNo ratings yet
- Nod 321Document12 pagesNod 321PabloAyreCondoriNo ratings yet
- Masterlist - Course - Offerings - 2024 (As at 18 July 2023)Document3 pagesMasterlist - Course - Offerings - 2024 (As at 18 July 2023)limyihang17No ratings yet
- Wedding Vows - What Do They Really MeanDocument28 pagesWedding Vows - What Do They Really Meanpsykosomatik0% (1)
- Systematix Sona BLW Initiates CoverageDocument32 pagesSystematix Sona BLW Initiates Coveragejitendra76No ratings yet
- Davis Michael 1A Resume 1Document1 pageDavis Michael 1A Resume 1Alyssa HowellNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment of Mandibular Anterior Crowding: Key Words: Crowding, Malocclusion, Labial FlaringDocument4 pagesOrthodontic Treatment of Mandibular Anterior Crowding: Key Words: Crowding, Malocclusion, Labial FlaringDunia Medisku OnlineShopNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Transportation: A Global Supply Chain Perspective, 8th Edition, John J. Coyle, Robert A. Novack, Brian Gibson, Edward J. BardiDocument34 pagesSolution Manual For Transportation: A Global Supply Chain Perspective, 8th Edition, John J. Coyle, Robert A. Novack, Brian Gibson, Edward J. Bardielizabethsantosfawmpbnzjt100% (21)
- Collection of Windows 10 Hidden Secret Registry TweaksDocument9 pagesCollection of Windows 10 Hidden Secret Registry TweaksLiyoNo ratings yet