Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(Common To All Branches of Engineering) : (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing
(Common To All Branches of Engineering) : (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing
Uploaded by
ramu vasa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
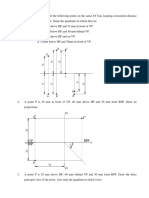
14 views3 pagesThe document contains 28 engineering drawing problems involving the projection of points, lines, and plane surfaces. The problems require drawing multi-view projections, determining true lengths and angles of inclined lines, and projecting various geometric shapes in different orientations relative to the horizontal and vertical planes. The shapes include points, lines, pentagons, semicircles, squares, and rectangles with specified dimensions and orientations. Solutions to the problems would involve precise technical drawing to depict the projections of the objects from different standard views.
Original Description:
Original Title
ED Unit 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document contains 28 engineering drawing problems involving the projection of points, lines, and plane surfaces. The problems require drawing multi-view projections, determining true lengths and angles of inclined lines, and projecting various geometric shapes in different orientations relative to the horizontal and vertical planes. The shapes include points, lines, pentagons, semicircles, squares, and rectangles with specified dimensions and orientations. Solutions to the problems would involve precise technical drawing to depict the projections of the objects from different standard views.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pages(Common To All Branches of Engineering) : (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing
(Common To All Branches of Engineering) : (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing
Uploaded by
ramu vasaThe document contains 28 engineering drawing problems involving the projection of points, lines, and plane surfaces. The problems require drawing multi-view projections, determining true lengths and angles of inclined lines, and projecting various geometric shapes in different orientations relative to the horizontal and vertical planes. The shapes include points, lines, pentagons, semicircles, squares, and rectangles with specified dimensions and orientations. Solutions to the problems would involve precise technical drawing to depict the projections of the objects from different standard views.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
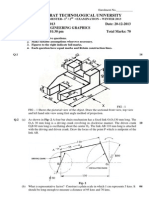
(20A03101T) ENGINEERING DRAWING
(Common to All Branches of Engineering)
UNIT-II
Syllabus: Projection of points, lines and planes: Projection of points in any quadrant, lines
inclined to one or both planes, finding true lengths, angle made by line. Projections of regular
plane surfaces
1. (a) A point A is on HP and 30 in front of VP. Draw its projections. (b) A point A is 20
above HP, 25 in front of VP. Draw its projections.
2. A line PQ has its end P, 10 mm above the HP and 20 mm infront of the VP, the end Q is 35
mm infront of the VP. The front view of the line measures 75 mm. The distance between the end
projectors is 50 mm. Draw the projections of the line and find its true length and its true
inclinations with the VP and HP.
3. A pentagon of side 30 mm rests on the ground on one of its corners with the sides
containing the corner being equally inclined to the ground. The side opposite to the corner on which
it rests is inclined at 30 to the VP and is parallel to the HP. The surface of the pentagon makes 50
with the ground. Draw the top and front views of the pentagon.
4. Semi-circular plate of 80 diameter, has its straight edge on VP and inclined at 30° to HP,
while the surface of the plate is inclined at 45° to VP. Draw the projections of the plate.
5. Draw the projections of the following points.
(i) A (+30 mm, +25mm). (ii) B (+28 mm, -22mm). (iii) C (-30 mm, -28mm).
6. (a) The FVs of two points P and Q coincide at 30 mm above XY. Their TVs are 30 mm
below and10mm above XY respectively. Draw the three views of each point and determine the
distance between them.
7. A point P is 10 mm above HP and 25 mm in front of VP. Point Q is 50 mm above HP and
45 mm in front of VP. The distance between the projectors is 55 mm. Draw the projections and
draw the projection of line joining P & Q.
8. A Rectangle of size 80 mm × 50 mm is seen as a square of 50 mm side in TV. Draw the
projections of rectangle if one of its diagonals is parallel to the VP. Find the angle made by the
rectangle with the VP.
9. Draw the projections of the following points on the same ground line, keeping the projectors
25 mm apart: (i) In the HP and 20 mm behind the VP. (ii) 40 mm above the HP and 25 mm in front
of the VP. (iii) In the VP and 40 mm above the HP. (iv) 25 mm below the HP and 25 mm behind
the VP . (v) 15 mm above the Hp and 50 mm behind the VP. (vi) 40 mm below the HP and 25 mm
in front of the VP. (vii) In both the HP and the VP.
10. A line measuring 80 mm long has one of its ends 60 mm above HP and 20 mm in front of
VP, the other end is 15 mm above HP. The front view of the line is 60 mm long. Draw the top view.
11. A circular plate of diameter 70mm has the end P of the diameter PQ in the HP, and the
plane is inclined at 40 0 to HP. Draw its projections when : (i) The top view of diameter PQ is
inclined at 45 ° to X Y line. (ii) The diameter PQ makes 45 0 with VP.
12. The top view of a 75 mm long line AB measures 65 mm, while its front view measures 50
mm. It’s one end A is in HP and 12 mm in front of VP. Draw the projections of AB and determine
it’s with HP and VP.
13. Draw the projections of the following point on a common reference line: (i) Point A is 40
mm above HP and 60 mm in front of VP (ii) Point A lying on HP and 25 mm in front of VP. (iii)
Point A lying on VP and 70 mm above HP. (iv) Point C is 40 mm below HP and 30 mm behind VP.
(v) Point A is in V.P and 55 mm above H.P
14. Draw the projections of straight line AB 60 mm long parallel to HP and inclined at an angle
of 40 ° to VP. The end A is 30 mm above HP and 20 mm in front of VP.
15. A pentagonal plane ABCDE 35 mm side has its plane inclined 50 ° to H.P. Its diameter
joining the vertex B to the midpoint F of the base DE is inclined at 25 ° to the xy -line. Draw its
projections keeping the corner B nearer to VP.
16. A point P is 20 mm above HP and 15 mm in front of VP. Draw the front view, top view and
left side view.
17. A point P is 10 mm above HP and 25 mm in front of VP. Point Q is 50 mm above HP and
45 mm in front of VP. The distance between the projectors is 55 mm. Draw the projections and
draw the projection of line joining P &Q.
18. A 60 mm long line AB is parallel to VP and inclined at 30 ° to HP. One end A is 30 mm
above HP and 15 mm in front of VP. Draw the projections of the line.
19. Draw the projections of a point Q, which is 45 mm above HP and 15 mm behind VP.
20. Draw the projections of a point R, which is 40 mm below HP and 15 mm behind VP.
21. Draw the projections of a line CD 60 mm long parallel to HP and inclined at 35 to VP. C is
20 mm above HP and 15 mm in front of VP.
22. The line EF 60 mm long is in VP and inclined HP. The top view measures 45 mm. The end
E is 15 mm above HP. Draw the projections of the line. Find it inclination with HP.
23. A line AB 60 mm long is parallel to HP. The point P is 20 mm above HP and 35 mm in
front of VP. The length of the front view is 50 mm. Determine its true inclination with VP.
24. A square plate of side 30 mm is perpendicular to V.P and inclined at 30 0 to H.P Draw it
projections.
25. The front view of a line, inclined at 30 0 to the V.P. is 65 mm long. Draw the projection of
the line, when it is parallel to and 40 mm above the VP, its one end being 30 mm in front of the
V.P.
26. A regular pentagon of 25 mm side has one side on the ground. Its plane is inclined to H.P at
450 and perpendicular to V.P. Draw its projections.
27. A line PQ 75 mm long has its end P in both HP and VP. It is inclined at an angle of 30 0 to
HP and 450 to VP. Draw projections of the line.
28. A rectangular plane of 60 mm 40 mm is resting on shorter edge on the ground and inclined
at 450 to V.P. The plane surface is inclined at 30 0 to H.P. Draw its projections.
You might also like
- Elementary Geometry For College Students 6th Edition Alexander Solutions Manual DownloadDocument38 pagesElementary Geometry For College Students 6th Edition Alexander Solutions Manual DownloadCharles Vanhorne100% (30)
- Problems On Engineering Drawing 1st YearDocument30 pagesProblems On Engineering Drawing 1st YearKrishna AsharNo ratings yet
- Architectural Graphics Shades and ShadowsDocument17 pagesArchitectural Graphics Shades and ShadowsEllixerxes Channel33% (3)
- Engineering Graphics Question Bank 2021-22Document15 pagesEngineering Graphics Question Bank 2021-22asjadpathan0770No ratings yet
- GEC 1101 - Engineering Graphics: Tutorial-Module - 3 Projection of Straight Lines and PlanesDocument3 pagesGEC 1101 - Engineering Graphics: Tutorial-Module - 3 Projection of Straight Lines and PlanesG. RajeshNo ratings yet
- EG TutorialDocument20 pagesEG TutorialSubramanian ManivelNo ratings yet
- Caed - Question Bank - 2023-2024Document29 pagesCaed - Question Bank - 2023-2024Anand BalaganurNo ratings yet
- Caed QB-2022Document9 pagesCaed QB-2022kalyanivishal777No ratings yet
- Anna Edusat Course On " Engineering Graphics Lecture - 4 Projections of LinesDocument38 pagesAnna Edusat Course On " Engineering Graphics Lecture - 4 Projections of LinesAntonetteNo ratings yet
- Caed Manual-Apr2823Document45 pagesCaed Manual-Apr2823Aditya KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Assignment QuestionDocument3 pagesAssignment Questionharshitsingh5225No ratings yet
- 6 1Document5 pages6 1S.C. HaneeshNo ratings yet
- Projetion of Straight Line ProblemDocument3 pagesProjetion of Straight Line ProblemRajesh JunghareNo ratings yet
- Projection of LinesDocument2 pagesProjection of LinesSakthikumar ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3Shivansh SahuNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Engg Graphics 1Document15 pagesQuestion Bank Engg Graphics 1yuvashreesharmiNo ratings yet
- Eg Que BankDocument10 pagesEg Que BankAmey ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- BCEDK103 Points Lines Question BankDocument2 pagesBCEDK103 Points Lines Question Bankwameb49109No ratings yet
- Caed Question BankDocument28 pagesCaed Question BankSafeer MNo ratings yet
- Graphics Assignment LINESDocument2 pagesGraphics Assignment LINESAbdul NazarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Question Bank by (MUSA)Document5 pagesEngineering Graphics Question Bank by (MUSA)Sunita DangarNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Projections of LineDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank: Projections of LineDevil GameNo ratings yet
- Caed FinalDocument30 pagesCaed Finalk19101829No ratings yet
- EG Question Bank PDFDocument22 pagesEG Question Bank PDFManish DVNo ratings yet
- Projection of Straight LinesDocument63 pagesProjection of Straight LinesYash Fifa0% (1)
- Engineering Graphics and Computer Drafting: Assignment - 3Document1 pageEngineering Graphics and Computer Drafting: Assignment - 3Sandhya RaniNo ratings yet
- Drawing I TutorialDocument23 pagesDrawing I TutorialManoj Paudel100% (2)
- Classwork Problems TcetDocument1 pageClasswork Problems TcetrsdeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Eg - Cat1Document1 pageEg - Cat1Bertram Nirmal PhilipNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - 2Document2 pagesPractice Problems - 2Daksh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Projection of LinesDocument2 pagesProjection of LinesSmd nazeeb100% (1)
- Answer Any Two QuestionsDocument1 pageAnswer Any Two QuestionscnjoyusNo ratings yet
- 03 - Projections of LinesDocument2 pages03 - Projections of LinesSumukh KiniNo ratings yet
- Lines Homework Questions From Previous QPDocument2 pagesLines Homework Questions From Previous QPwafflerick69No ratings yet
- A2 LinesDocument2 pagesA2 Linessriram.gate.iiscNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem EG-Questions 7 SheetsDocument7 pages2nd Sem EG-Questions 7 Sheetssunny045No ratings yet
- ED Classwork Problems TcetDocument1 pageED Classwork Problems TcetrsdeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Qus PaperDocument6 pagesQus PaperBalamurugan KarnanNo ratings yet
- Lines 2Document2 pagesLines 2sandeep_gaikwad2No ratings yet
- Lines QuestionsDocument1 pageLines QuestionsAbinayaNo ratings yet
- Projection of Lines PDFDocument5 pagesProjection of Lines PDFVicky ŔòýNo ratings yet
- Engineering GraphicsDocument18 pagesEngineering GraphicsPraveen MathiNo ratings yet
- EG TutorialsDocument1 pageEG Tutorialsdhana555No ratings yet
- Anna University Question Bank For Engineering GraphicsDocument11 pagesAnna University Question Bank For Engineering GraphicsRajkumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Part 4Document26 pagesEngineering Graphics Part 4Deekshith DileepNo ratings yet
- EGDocument11 pagesEGvivekselvan2No ratings yet
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question Bank Unit1 Unit5Document7 pagesAnna University Engineering Graphics Question Bank Unit1 Unit5florenceprasadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledSuyog ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Kings: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument11 pagesKings: Department of Mechanical Engineeringrammit2007No ratings yet
- GE6152 EngineeringGraphicsquestionbankDocument11 pagesGE6152 EngineeringGraphicsquestionbankNatarajan AgoramNo ratings yet
- Sheet ProblemsDocument1 pageSheet ProblemsPrashant UbarhandeNo ratings yet
- ME1120 - Midsem PaperDocument1 pageME1120 - Midsem Paperamitbagarwal5930No ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Calicut Department of Mechanical Engineering ZZ 1002 Engineering Graphics Batch E, Class Work: 4Document1 pageNational Institute of Technology Calicut Department of Mechanical Engineering ZZ 1002 Engineering Graphics Batch E, Class Work: 4RaghuNo ratings yet
- GE2111 QB Unit 1 To 5Document7 pagesGE2111 QB Unit 1 To 5meckup123No ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics - Question BankDocument15 pagesEngineering Graphics - Question BankimamuddeenNo ratings yet
- Eg QPDocument5 pagesEg QPSurulivelrajantNo ratings yet
- CAD Assignment LinesDocument2 pagesCAD Assignment Linesapi-3723664No ratings yet
- .Sheet 2 and 3Document2 pages.Sheet 2 and 3Rudra SathwaraNo ratings yet
- Eg Question Bank - 2013Document18 pagesEg Question Bank - 2013kgmaheswaranNo ratings yet
- EGD Assignment 2 NCUDocument2 pagesEGD Assignment 2 NCUartyNo ratings yet
- Projection of LinesDocument2 pagesProjection of LinesanandandmeenaNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering I B.Tech-I SEM (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing Unit-VDocument2 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering I B.Tech-I SEM (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing Unit-Vramu vasaNo ratings yet
- (Common To All Branches of Engineering) : (20A03101T) Engineering DrawingDocument2 pages(Common To All Branches of Engineering) : (20A03101T) Engineering Drawingramu vasaNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering I B.Tech - I Sem (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing Unit-Iii Syllabus: Question Bank-AY: 2020-21Document2 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering I B.Tech - I Sem (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing Unit-Iii Syllabus: Question Bank-AY: 2020-21ramu vasaNo ratings yet
- Geethanjali Institute of Science & Technology: NelloreDocument2 pagesGeethanjali Institute of Science & Technology: Nelloreramu vasaNo ratings yet
- Volume and Surface Area PracticeDocument3 pagesVolume and Surface Area Practiceapi-1679240860% (1)
- Circular Measure (Exercise)Document5 pagesCircular Measure (Exercise)Zaweyah SulaimanNo ratings yet
- SMC 2017 Paper PDFDocument4 pagesSMC 2017 Paper PDFCubeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Answers Chapter62Document106 pagesWorksheet Answers Chapter62Sarah Olive-SmithNo ratings yet
- Maths Practical File Project T2Document7 pagesMaths Practical File Project T2samahadadilkhanNo ratings yet
- 110013Document2 pages110013AMIT SOLANKINo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS 8 4thLTDocument4 pagesMATHEMATICS 8 4thLTCarl (Carl)No ratings yet
- Distance and MidpointsDocument6 pagesDistance and MidpointsMohamed YousryNo ratings yet
- 3 Math 10 - Q2 - Week 6Document20 pages3 Math 10 - Q2 - Week 6Ralph Marcus ValdezNo ratings yet
- Math 4 Q4 Week 1 DLLDocument6 pagesMath 4 Q4 Week 1 DLLJulie LescanoNo ratings yet
- Pà Áðlpà Ëæqsà Pàët Àjãpáë Àäaqà : General Instructions To The CandidateDocument9 pagesPà Áðlpà Ëæqsà Pàët Àjãpáë Àäaqà : General Instructions To The CandidateHarish RNo ratings yet
- CPM Precalculus Chapter 01 SolutionsDocument34 pagesCPM Precalculus Chapter 01 SolutionsBTS ARMY BTS100% (1)
- Class X Term I Exam (2021-22) - MathsDocument5 pagesClass X Term I Exam (2021-22) - Mathspuneet manglaNo ratings yet
- 2017 AMC 10A Problems: Problem 1Document4 pages2017 AMC 10A Problems: Problem 1mmmmmNo ratings yet
- StudenttextDocument26 pagesStudenttextapi-195130729No ratings yet
- Warm-Up Exercise: TextbookDocument37 pagesWarm-Up Exercise: Textbook2C 29黃嘉朗No ratings yet
- Mastery Test in Mathq3Document5 pagesMastery Test in Mathq3Criselda Bacatan VarcaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - Maths - QuadrilateralsDocument25 pagesClass 9 - Maths - Quadrilateralselajchet senniNo ratings yet
- Support Grade 7 Second Final Exam 2024Document8 pagesSupport Grade 7 Second Final Exam 202442h47n5zvrNo ratings yet
- Roll and Cover Community Helper MatsDocument6 pagesRoll and Cover Community Helper Matsalbina milieNo ratings yet
- CSEC Study Guide (Revised 2016)Document92 pagesCSEC Study Guide (Revised 2016)EMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- FemsDocument12 pagesFemswylliexhanNo ratings yet
- Algorithms For Geodesics: Charles F. F. KarneyDocument12 pagesAlgorithms For Geodesics: Charles F. F. KarneyYu KYNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure - HL MathDocument13 pagesCircular Measure - HL MathPrakash PhilipNo ratings yet
- Pretest Math 2Document5 pagesPretest Math 2wyxrvwbqgdNo ratings yet
- Project On CircleDocument8 pagesProject On CircleGourav Patidar100% (1)
- Mariano Marcos State University: College of EngineeringDocument7 pagesMariano Marcos State University: College of EngineeringLyka Jane Tapia OpeñaNo ratings yet