Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Business Blueprint Controlling: Synokem Pharmaceuticals LTD
Business Blueprint Controlling: Synokem Pharmaceuticals LTD
Uploaded by
Gudia SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Optional Unit 1 AssignmentDocument19 pagesOptional Unit 1 AssignmentTriet NguyenNo ratings yet
- Kraft-Foods Case StudyDocument18 pagesKraft-Foods Case StudyLevi Lazareno Eugenio50% (2)
- An Ethics Role Playing Case: Stockholders Vs StakeholdersDocument2 pagesAn Ethics Role Playing Case: Stockholders Vs StakeholderssNo ratings yet
- FDS0019 GAP0080 O2C GTS Commercial InvoiceDocument22 pagesFDS0019 GAP0080 O2C GTS Commercial Invoicesomusatish100% (1)
- Document: Uses of Special Period in SAP PDFDocument9 pagesDocument: Uses of Special Period in SAP PDFswainsatyaranjanNo ratings yet
- SAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsFrom EverandSAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsNo ratings yet
- International Trade - Chapt 9 Imports Tariff/ Quotas For Imperfect MarketsDocument10 pagesInternational Trade - Chapt 9 Imports Tariff/ Quotas For Imperfect MarketsglenlcyNo ratings yet
- Taller SAP Actividad 3Document67 pagesTaller SAP Actividad 3Daniel Ricardo Estupiñan Guzman100% (1)
- 1573561440-BP Conversion GuideDocument40 pages1573561440-BP Conversion GuideRuben CampoverdeNo ratings yet
- Brazil Accounting Tax Processes v1 PDFDocument163 pagesBrazil Accounting Tax Processes v1 PDFGustavo GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- 250open Text VIM For SAP SolutionsDocument2 pages250open Text VIM For SAP SolutionsTheo van BrederodeNo ratings yet
- Sap Fico Blue PrintDocument57 pagesSap Fico Blue Printuvtechdhananjay05100% (1)
- New Asset Accounting IntroductionDocument7 pagesNew Asset Accounting IntroductionCasimiro HernandezNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Refx Configuration Document PRDocument110 pagesToaz - Info Refx Configuration Document PRnew gstNo ratings yet
- Demo Script Planning and Consolidation (MS) Overview Demo: General InformationDocument44 pagesDemo Script Planning and Consolidation (MS) Overview Demo: General InformationbrainNo ratings yet
- Document and Reporting Compliance (5XU)Document43 pagesDocument and Reporting Compliance (5XU)Ind HashNo ratings yet
- Ifrs at Sap: Transition To IFRS: Implementation of IFRS As An Additional Set of Accounting Standards Alongside US GAAPDocument29 pagesIfrs at Sap: Transition To IFRS: Implementation of IFRS As An Additional Set of Accounting Standards Alongside US GAAPlsudhakarNo ratings yet
- IBM Review of Simple Finance 3.0 Process: Accounts ReceivableDocument9 pagesIBM Review of Simple Finance 3.0 Process: Accounts ReceivableMOORTHYNo ratings yet
- Define Functional AreaDocument1 pageDefine Functional AreaDipeshNo ratings yet
- Year End Closing Activities in Sap Fi CoDocument30 pagesYear End Closing Activities in Sap Fi Coansonyu305No ratings yet
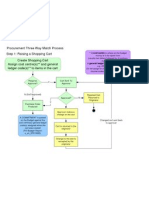
- 3 Way Match Process 1Document3 pages3 Way Match Process 1mkv428No ratings yet
- Ycoa Accdet Docu UsDocument72 pagesYcoa Accdet Docu UsSrinivas N GowdaNo ratings yet
- Accounts Payable: Global Process Management SystemDocument89 pagesAccounts Payable: Global Process Management SystemcybervistaNo ratings yet
- Funds Management Overview: © 2005 Intelligroup, IncDocument49 pagesFunds Management Overview: © 2005 Intelligroup, Incganesh gadeNo ratings yet
- SD RevRec MigrationDocument11 pagesSD RevRec MigrationAlina Cristina VranceanuNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of FICODocument149 pagesConceptual Design of FICOShree RamNo ratings yet
- COPADocument167 pagesCOPAAylene FloresNo ratings yet
- Project Management (PS) : Curriculum: Introduction To S/4HANA Using Global BikeDocument36 pagesProject Management (PS) : Curriculum: Introduction To S/4HANA Using Global BikeJuliusCesnakauskasNo ratings yet
- Fertilizers and Chemicals Travancore LTD: FACT ForwardDocument35 pagesFertilizers and Chemicals Travancore LTD: FACT ForwardfharooksNo ratings yet
- Sanad Wfrice Master List: SR No Object Id Object Object Purpose Tcode Object Sub CategoryDocument12 pagesSanad Wfrice Master List: SR No Object Id Object Object Purpose Tcode Object Sub CategoryAmr IsmailNo ratings yet
- BH5 S4hana1611 BPD en XXDocument23 pagesBH5 S4hana1611 BPD en XXIván Andrés Marchant NúñezNo ratings yet
- Column Fields Field: Additional Navigational AttributesDocument25 pagesColumn Fields Field: Additional Navigational AttributesSajanAndyNo ratings yet
- SAP Credit ManagementDocument6 pagesSAP Credit ManagementAvinash MalladhiNo ratings yet
- S4HANA RIG UX Lessons Learned 1909 PDFDocument42 pagesS4HANA RIG UX Lessons Learned 1909 PDFadelangel70No ratings yet
- S/4HANA Configuration Case Phase I - Handbook: Product Motivation PrerequisitesDocument75 pagesS/4HANA Configuration Case Phase I - Handbook: Product Motivation PrerequisitesDianPramana100% (2)
- Group Reporting (FIN-CS) : Public Document Version: SAP S/4HANA 2022 (October 2022) - 2022-10-03Document636 pagesGroup Reporting (FIN-CS) : Public Document Version: SAP S/4HANA 2022 (October 2022) - 2022-10-03Aymen AddouiNo ratings yet
- 2 Our HANA Capabilities PDFDocument17 pages2 Our HANA Capabilities PDFRueban manoharNo ratings yet
- Archit BBP CO V1 30.11.2010Document202 pagesArchit BBP CO V1 30.11.2010Subhash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Credit Limit On Customer Level v2Document9 pagesCredit Limit On Customer Level v2Durga SNo ratings yet
- Transition To The New Planning Solution in S/4Hana On PremiseDocument11 pagesTransition To The New Planning Solution in S/4Hana On PremiseNityaNo ratings yet
- HSPL Fi 06 House Bank v1.0Document18 pagesHSPL Fi 06 House Bank v1.0Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
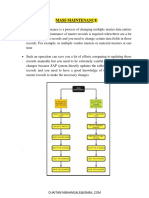
- Master Data Mass MaintenanceDocument12 pagesMaster Data Mass MaintenancePaul AlcosNo ratings yet
- SAP CO PPT'sDocument5 pagesSAP CO PPT'sTapas BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- ProjectPortfolioManagement CommercialProjectManagementDocument4 pagesProjectPortfolioManagement CommercialProjectManagementmohammad shaikNo ratings yet
- SAP FSCM Credit Management Config StepsDocument3 pagesSAP FSCM Credit Management Config StepsDamodar Naidu PaladuguNo ratings yet
- Vendor Recognition White PaperDocument9 pagesVendor Recognition White PaperAvinash MalladhiNo ratings yet
- Nota para Localização PDFDocument37 pagesNota para Localização PDFmarcosoliversilvaNo ratings yet
- SFIN - Documents Replication in CFINDocument25 pagesSFIN - Documents Replication in CFINmadhu100% (1)
- Sap (Fico) : SAP FI-Organization StructureDocument2 pagesSap (Fico) : SAP FI-Organization StructureChandrashekher EdumalaNo ratings yet
- Unity FSP MFG 06 V01R00Document83 pagesUnity FSP MFG 06 V01R00sowjanyaNo ratings yet
- Project System Module (PS) : CSU ChicoDocument38 pagesProject System Module (PS) : CSU ChicoKumar Venkat SNo ratings yet
- Design Document Co Profitabilty Analysis Author/ApproverDocument19 pagesDesign Document Co Profitabilty Analysis Author/ApproverAncuţa CatrinoiuNo ratings yet
- Transaction Code CESU Business Process Master List - FICODocument4 pagesTransaction Code CESU Business Process Master List - FICOJit GhoshNo ratings yet
- Ficobbpfinalone10022011 120815114154 Phpapp02Document146 pagesFicobbpfinalone10022011 120815114154 Phpapp02prashantaiwaleNo ratings yet
- 1qm S4hana1909 BPD en UsDocument46 pages1qm S4hana1909 BPD en UsMarceloNo ratings yet
- j62 S4hana2021 BPD en BRDocument76 pagesj62 S4hana2021 BPD en BRSandra Amadi100% (1)
- SAP BiddingDocument36 pagesSAP BiddingLakhya Pratim BaruahNo ratings yet
- Migrating Classic GL To S4 HANA Finance1Document10 pagesMigrating Classic GL To S4 HANA Finance1shaiNo ratings yet
- 1MV S4hana1909 BPD en XXDocument14 pages1MV S4hana1909 BPD en XXBiji RoyNo ratings yet
- Fica ExcelDocument171 pagesFica ExcelYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- OpenText VIM - Rollout Criteria and Event Linkages - SAP BlogsDocument9 pagesOpenText VIM - Rollout Criteria and Event Linkages - SAP BlogsDavid CoelhoNo ratings yet
- SAP GST Questionnaire-MesprosoftDocument3 pagesSAP GST Questionnaire-Mesprosoftnagesh99No ratings yet
- Sales Area: S / 4 HANA ContentDocument34 pagesSales Area: S / 4 HANA ContentEnrique Israel Flores ZúñigaNo ratings yet
- Detailed SAP Interface Design Fundamental DocumentDocument4 pagesDetailed SAP Interface Design Fundamental Documentamitava_bapiNo ratings yet
- First Nature, Second Nature and Metropolitan LocationDocument32 pagesFirst Nature, Second Nature and Metropolitan LocationCristóbal GuerraNo ratings yet
- Bechelor ThesisDocument71 pagesBechelor ThesisLê KiênNo ratings yet
- AppendixDocument4 pagesAppendixJayanga JayathungaNo ratings yet
- Multiattribute Utility FunctionsDocument25 pagesMultiattribute Utility FunctionssilentNo ratings yet
- Corporate Level Strategy Addresses The Entire Strategic Scope of The FirmDocument19 pagesCorporate Level Strategy Addresses The Entire Strategic Scope of The FirmOpshora AliNo ratings yet
- Diamond Strategy ModelDocument3 pagesDiamond Strategy ModelMERINANo ratings yet
- Economics of Strategy: The Vertical Boundaries of The FirmDocument49 pagesEconomics of Strategy: The Vertical Boundaries of The FirmVanessa HartonoNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Freedom To Trade by Edward L. HudginsDocument9 pagesThe Fundamental Freedom To Trade by Edward L. HudginsmirunelutuNo ratings yet
- Basic Economic ProblemsDocument146 pagesBasic Economic ProblemsRichard DancelNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Practice 101Document18 pagesWeek 7 Practice 101David LimNo ratings yet
- CH - 11 - Introduction To Supply Chain ManagementDocument72 pagesCH - 11 - Introduction To Supply Chain ManagementYogesh GirgirwarNo ratings yet
- Simu GuidelinesDocument54 pagesSimu Guidelinesniket mehtaNo ratings yet
- W08 - Managerial Decisions in Competitive Markets-FJODocument41 pagesW08 - Managerial Decisions in Competitive Markets-FJOGhasan Rasendriya PutraNo ratings yet
- Retail Management Black BookDocument82 pagesRetail Management Black BookShahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio Analysis As Determinant of Profitability in African Banking IndustryDocument10 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis As Determinant of Profitability in African Banking IndustryjaneNo ratings yet
- Analisis General CompetitivoDocument12 pagesAnalisis General CompetitivoluisNo ratings yet
- 1 Business ActivityDocument4 pages1 Business ActivityAnalía gonzalezNo ratings yet
- An Analysis and Valuation Of: Rak Ceramics (Bangladesh) LTDDocument30 pagesAn Analysis and Valuation Of: Rak Ceramics (Bangladesh) LTDFarzana Fariha LimaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Sees1Document19 pagesManagerial Economics Sees1doraline0911100% (2)
- Answer Key Bank Soal Micro UAS - Tutorku - 2020Document128 pagesAnswer Key Bank Soal Micro UAS - Tutorku - 2020Vriana ZenNo ratings yet
- XA Risk Reward RatioDocument4 pagesXA Risk Reward Ratiocarlos.ernesto.aa2023No ratings yet
- Performance Based PayDocument22 pagesPerformance Based PaySonam GondlekarNo ratings yet
- Kojima, K., Ozawa, T. (1984), Micro - and Macro-Economic Models of Direct Foreign InvestmentDocument21 pagesKojima, K., Ozawa, T. (1984), Micro - and Macro-Economic Models of Direct Foreign InvestmentGabriel MerloNo ratings yet
- MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS NOTES Unit-5 MBA 1stDocument6 pagesMANAGERIAL ECONOMICS NOTES Unit-5 MBA 1stRUBA NASIMNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: Cheat SheetDocument110 pagesManagerial Economics: Cheat SheetSushmitha KanasaniNo ratings yet
- Potato Corner Pestle AnalysisDocument2 pagesPotato Corner Pestle AnalysisJeremia DaNo ratings yet
Business Blueprint Controlling: Synokem Pharmaceuticals LTD
Business Blueprint Controlling: Synokem Pharmaceuticals LTD
Uploaded by
Gudia SharmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Business Blueprint Controlling: Synokem Pharmaceuticals LTD
Business Blueprint Controlling: Synokem Pharmaceuticals LTD
Uploaded by
Gudia SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Business Blueprint
Controlling
SAP S/4 HANA
Submitted to
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
14/486, Sundar Vihar, Outer Ring Road
Paschim Vihar, Delhi 110087
T: 011-25271800
Email: enquiry@synokempharma.com
Submitted by
Tables of Contents
Contents
INTRODUCTION............................................................................................................4
Confidential Document Page 1 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
2. ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE........................................................................................5
3. CONTROLLING MODULE INTRODUCTIONS........................................................................5
3.1 Functional Scope of CO Module.............................................................................7
3.2 Controlling Module Integration with other Modules....................................................8
4. SAP OVERVIEW......................................................................................................10
4.1 Client............................................................................................................10
4.2 Operating Concern.............................................................................................10
4.3 Controlling Area...............................................................................................10
4.4 Company Code..................................................................................................10
4.5 Controlling Structure.........................................................................................11
4.6 Profit Center Hierarchy.......................................................................................11
4.7 Cost Center Hierarchy........................................................................................11
5. MASTER RECORD.....................................................................................................12
5.1 Cost Element Master Data....................................................................................12
5.2 Cost Center Master Data:....................................................................................13
5.3 Activity Type:..................................................................................................14
5.4 Internal Order..................................................................................................14
5.5 Profit Center:..................................................................................................15
6. BUSINESS PROCESS LIST IN CONTROLLING.....................................................................15
6.1 Cost Element Accounting:....................................................................................15
6.2 Cost Center Accounting:......................................................................................17
6.3 Internal Order..................................................................................................22
6.4 Profit Center...................................................................................................25
6.5 Product Costing................................................................................................26
6.6 Profitability Analysis..........................................................................................39
..............................................................................................................................45
7. SAP REPORTS.........................................................................................................47
INTRODUCTION
This document summarizes the findings of the CSPL consulting team and Synokem Team, with respect
to SAP processes to be implemented in Synokem.
The information contained in this blue print was gathered through above activities during different
phases of the project i.e. Reviews of business processes, Business procedures, and documentation and
Confidential Document Page 2 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Relevant reports. These project results were devised and decided on by the project team and the
department experts from Synokem during the Business Blueprint project phase.
The purpose of Business Blueprint document is to form the basis and guidelines to move
forward to the Realization Phase. The information gathered and documented in the Blueprint is
sufficient for the team to go forward into the Realization phase.
This document aims to describe the future business solution based on SAP software. Any additional
explanations that are only relevant when the project is in progress will be provided in other form of
document like User Manual, Configuration Document etc.
2. Organization Structure
Confidential Document Page 3 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
3. Controlling Module Introductions
Controlling provides you with information for management decision-making. It facilitates coordination,
monitoring and optimization of all processes in an organization. This involves recording both the
consumption of production factors and the services provided by an organization.
As well as documenting actual events, the main task of controlling is planning. You can determine
variances by comparing actual data with plan data. These variance calculations enable you to control
business flows.
Income statements such as, contribution margin accounting, are used to control the cost efficiency of
individual areas of an organization, as well as the entire organization. The following are the basic
requirements of controlling module
Cost control
Costs are tracked at the origin
Responsibility is fixed for costs incurred.
Internal orders
Transparent costing system is maintained for internal jobs or responsible areas.
Budgetary control is exercised for operating and capital expenses.
Product costing
Confidential Document Page 4 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Product cost planning at the beginning of the year/period
Accurate product / process costing during the course of production
Report of cost in summarized form
Profitability Analysis
Analysis of reports on the basis of customer, country, product, plant,
Sales organization, company code.
Sales analysis
Features in Controlling Module
Controlling (CO) module is integral components of standard SAP S4 HANA system. Controlling module
provides information to the organization for managerial decision-making and facilitates
coordination, monitoring and optimization of processes in an organization.
The data update in controlling module is on line real time with any business transaction having
financial implication and processed in any other module. SAP S4 HANA achieves this through tight
integration of CO module with rest of the modules.
For the purpose of mapping various existing business processes along with improvements, if any the
following sub-modules within CO module in SAP S4 HANA are proposed to be considered for
implementation at Synokem in Controlling area - SYPL
Cost Element Accounting
Cost elements are no longer required in SAP S/4HANA Finance because they are created as G/L
accounts using Transaction FS00 and are part of the chart of accounts. A new field for the cost
element category has been introduced in the G/L master record. The default account
assignment is maintained using Trans- action OKB9 and not in the traditional cost element
master data. Customizing settings that require cost elements such as costing sheets or
settlement profiles and the business transactions where cost elements are used will continue to
be defined by the cost element category settings from the G/L master records. Cost element
groups continue to be available in SAP S/4HANA Finance for grouping the accounts and for
reporting purposes.
cost element accounting takes care of integrating FI general ledger accounts with CO. Cost
elements are a medium to update the data in CO with respect to posting of each business
transaction having financial implication and relevant to costing. In this component an enterprise
can get complete information about costs incurred within an enterprise during a period.
Cost Center Accounting
This functionality enables an enterprise to get information about the point of cost incurrence. It
provides information with respect to all costs assigned to their source, for management decision
making. It facilitates analysis of costs incurred for individual responsibility areas (cost centre).
Cost Centre Accounting facilitates the analysis of overhead costs according to where the costs
were incurred within the organization.
Internal Order
Confidential Document Page 5 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Internal orders are used to plan, collect, and settle the costs of event specific internal jobs and
tasks. The SAP system enables you to monitor your internal orders throughout their entire life-
cycle; from initial creation, through the planning and posting of actual costs, to the final
settlement. Internal order is also a powerful tool to collate expenses posted in FI for suitable
segregation, through creation and posting to statistical internal orders.
Profit Center Accounting
This sub-module offers the responsibility accounting function within an organization. Profit
Centre is an organizational unit similar to Cost Centre. Whereas the Cost Centre are for
analyzing and controlling costs, the objective of Profit Centre is to evaluate performance of
Profit Centre based on profitability and contribution analysis.
Dummy Profit Center
The dummy profit center is the default profit center to which data is posted when the
corresponding object has not been assigned to a profit center.
Product Costing
Product costing module of SAP has eased out all hassles of costing a manufactured Product.
Product Cost Controlling calculates the costs arising from the manufacture of a product or the
provision of a service. It enables you to calculate the minimum price at which a product can be
profitably marketed.
Profitability Analysis
Profitability Analysis (CO-PA) provides a focus on the results of a company’s doing business with
the external marketplace. It provides the ability to define which aspects or segments of that
market are relevant for analyzing operating results, such as profit by customer, product,
geographic area, sales organization, etc.
The aim of the system is to provide your sales, marketing, product management and corporate
planning departments with information to support internal accounting and decision-making.
3.1 Functional Scope of CO Module
The following Controlling sub-modules will be implemented during this implementation
Cost & Revenue Element Accounting
Master Data
Actual Posting
Information System
Cost Center Accounting
Master Data
Planning
Actual Posting
Information system
Internal Orders
Master Data
Planning & Budgeting
Confidential Document Page 6 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Statistical Actual Posting
Information system
Product Cost Planning
Standard Cost Estimate
Costing Variant
Cost Component Structure
Cost sheet for overhead
Information system
Product Cost by order
Basic Settings
Manufacturing Orders
Preliminary Costing
Period End Closing
Information system
Profit center accounting
Basic Settings
Master Data
Actual Postings
Information system
Profitability accounting
Structure
Master Data
Planning
Actual Postings
Information system
3.2 Controlling Module Integration with other Modules
Other SAP modules generate data that has a direct impact on CO. For example, when consumable items
are purchased, an expense is posted to the GL. At the same time, the expense is posted as a cost to the
cost center (or other object in CO) for which the items have been purchased. That cost centre’s costs
may later be passed on as overhead to a Cost Object. In addition to financial application Module,
following module integration are required.
Integration with FI
In SAP S/4HANA Finance, accounting documents are posted using a common document number. The FI
document for profit and loss (P&L) accounts still generates CO documents. To maintain consistency and
CO compatibility views, the document type and document number Customizing settings are maintained
for the internal CO postings and to assign the actual version of CO to the ledger. With the integration of
FI and CO, there is no requirement for a reconciliation ledger going forward. In the past, any CO-
related postings were updated in both the line item table (COEP) and totals table (COSP for
primary/COSS for secondary). With SAP S/4HANA Finance, the totals tables are no longer required
because data can be aggregated from the line item table, which is also used for reporting. This avoids
data redundancy. All actuals data continue to be stored in the line item table COEP.
Confidential Document Page 7 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Two new tables—COSP_BAK and COSS_BAK—have been created to store planned data related to primary
and secondary costs, respectively.
The Universal Journal has its own currency fields in FI while CO has its own currency settings. The
currency concept used separately in FI and CO has now been combined. You can enhance the journal
entry by adding the coding block and Profitability Analysis (CO-PA) characteristics. Access to old data in
tables is still possible via the compatibility views V_<table name>_ORI.
CO-FI Reconciliation
G/L account mapping of CO real-time integration with the new G/L is now obsolete. Secondary cost
elements are now created as G/L accounts and are part of the chart of accounts. On the configuration
side, document types that you want to use for posting in CO need to be defined and require the
indicator G/L to be set. These document types need to be linked to the CO business transaction via a
variant. The fiscal year variants of all controlling areas used by an organization and their assigned
company codes must be the same.
The Financial Accounting application area of SAP is a primary source of data for Controlling. The data
flow between the two components takes place on a regular basis. The relevant accounts in Financial
Accounting are managed in Controlling as cost elements or revenue elements. This enables us to
compare and reconcile the values from Controlling and Financial Accounting. Typically, most expense
postings to the General Ledger would result in a cost posting to CO. These expense postings to the G/L
could be manual journal entries, accounts payable postings, or depreciation postings from Asset
Accounting (FI-AA).
Integration with SD
Identification of Characteristics (E.g.: Product, Customer, Product Hierarchy, Division etc.) which will
flow from Sales Order to COPA. Identification of Value fields (E.g.: Sales Revenues, Discounts etc.)
which will flow to COPA through SD conditions. The SD module calculates revenues during billing with
the help of pricing mechanism and then enters it in the billing document. The billing document
transfers revenues directly to CO-PA.
Confidential Document Page 8 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Integration with MM
Identification of Characteristics Material Group and Manufacturer Code through MM Module. The
Logistics area of SAP also has numerous integration points with Controlling e.g. At the time of goods
receipt, the RM inventory will be valuated at moving average price, At the time of goods issue to
production order, the RM cost will be valuated at moving average price, At the time of goods receipt
from production, finished goods will be valued at standard price from standard cost estimate, the profit
center for materials is maintained in the material master.
Integration with PP
The Production Planning (PP) area of Logistics also works very closely with Controlling. Direct cost
would be absorbed through activity types where labor hours, Machine hours will be picked up from PP
master (Routing) and would be multiplied with the price which we maintain in the cost center
accounting in the combination of cost center and activity type.
Integration with PM
Organization should perform cost controlled activities for maintenance personnel time and material via
maintenance work orders. Technicians should enter actual hours for work orders and record all
part/service consumption on order. Costing department should perform regular cost settlement for
orders.
Integration with HR
The Human Resource application area of SAP is a primary source of data for Controlling. The data flow
between the two components takes place on a regular basis/month end /year end basis. The relevant
G/L’s are assigned in HR module for posting Salary & other costs and the same are managed in
Controlling as cost elements. This enables us to get data from HR module to Controlling module.
Confidential Document Page 9 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
4. SAP overview
4.1 Client
User working environment,in commercial, organizational, and technical terms, a self-contained unit in
SAP System with separate master records and its own set of tables. The Client is the highest level in the
SAP System hierarchy.
4.2 Operating Concern
Profitability Analysis (CO-PA) enables you to evaluate market segments, which can be classified
according to products, customers, orders or any combination of these, or strategic business units, such
as sales organizations or business areas, with respect to your company's profit or contribution margin.
The aim of the system is to provide your sales, marketing, product management and corporate planning
departments with information to support internal accounting and decision-making.
Operating Operating Concern Name
Concern
SYPL Synokem - Operating Concern
4.3 Controlling Area
Controlling Area represents a closed system for cost accounting purposes. A controlling area includes
single or multiple company codes that may use different currencies. These company codes must use the
same operative chart of accounts.
There will be one controlling area for Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited and DNV Overseas Impex
Private Limited.
Controlling Area Controlling Area Name
SYPL Synokem - Controlling area
4.4 Company Code
The company code is the organizational unit that allows you to structure your enterprise from a
financial accounting perspective. The company code is an independent legal entity and it is the
smallest organizational unit of Financial Accounting for which a complete self-contained set of accounts
are drawn up for purposes of external reporting. This includes recording of all relevant transactions and
generating all supporting documents required for financial statements.
Company Code Company Name
9000 Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
9900 DNV Overseas Impex Private Limited
4.5 Controlling Structure
Confidential Document Page 10 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
The Controlling structure of Synokem Project is summarized as below:
Description Synokem Group Structure
Company code Cross-Company code cost
accounting
Chart of accounts SYPL
Company code currency INR
Filed status variant SYPL
Posting period variant 9000 & 9900
Fiscal year April to March (12 periods + 4
Special Periods)
Fiscal year variant V3
Operating Concern SYPL
Controlling area SYPL
Controlling area currency INR
4.6 Profit Center Hierarchy
Profit Center hierarchy is a tree structure which contains all profit centers in a controlling area and
reflects the organizational structure used in Profit Center Accounting. All the Profit Centers are
assigned to the Profit Center Groups and Profit Center Groups are assigned to Profit Center Hierarchy.
4.7 Cost Center Hierarchy
Cost Center Hierarchy is a tree structure representing all cost centers belonging to a controlling area,
Combining cost centers into cost center groups, and creating cost center hierarchies from these groups
by combining the groups according to decision-making area, area of responsibility, or management
area.
A cost center hierarchy comprises all cost centers for a given period and therefore represents the
whole enterprise. This hierarchy is known as the standard hierarchy.
5. Master Record
Master data determines the structure of the given application component in the SAP System and
remains essentially unchanged in a live system, that is, in the current settlement periods. Following
Master data will be created and maintained in the system. Authorized users will be able create,
change and maintain the master data.
The following are the Controlling Master Data is:
Cost Element Master data
Primary Cost Element
Travelling Expense
Selling Expense
Secondary Cost Element
Labor
Machine Hours
Cost Center Master data
Activity Type
Internal Order
Confidential Document Page 11 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Profit Center Master data
5.1 Cost Element Master Data
Cost and Revenue Element Accounting provides with an overview of the costs and revenues. Most of the
values are moved automatically from Financial Accounting to Controlling.
Cost Elements track the type of costs or spend. They form categories of costs that are independent
from external or financial reporting requirements, but helps management to track costs according to
internal accounting policies.
The primary Cost Elements are copy of P&L expense accounts from the financial chart of accounts.
Secondary Cost Elements are no longer tied to the accounts.
As per the SAP standard, all Income & Expenses related G/L must be created in system as a Cost
Element. And in Synokem we will follow the same.
Primary Cost Elements: A primary cost or revenue element is a cost or revenue-relevant item in the
chart of accounts, for which a corresponding general ledger (G/L) account exists in Financial Accounting
(FI).
Primary cost or Revenue element is created once if you define G/L account in the chart of accounts in
Financial Accounting (FI). At the time of creation of Primary Cost and Revenue Elements, the system
checks whether a corresponding G/L account exists in Financial Accounting.
Costs that are considered as primary cost elements include:
Consumption of Material costs
Production Direct cost
Admin Cost, Marketing Cost etc.
Costs for external procurement / External Services /external processing
Cost related to different Nature of Expenses
These costs are assigned to the order, for example, via primary costs, such as material withdrawals or
the purchasing of externally processed parts.
Secondary Cost Elements: Secondary cost elements are cost elements used to allocate costs for
internal activities. Secondary cost elements do not correspond to any G/L account in Financial
Accounting. They are only used in Controlling and consequently cannot be defined in FI as an account.
Costs that are considered to be secondary cost elements include:
Activity costs / Production Cost
Material overhead costs
Production overhead costs
Distribution of Cost to various Cost
These costs are allocated to the order via internal cost allocation.
Cost Element Group
The Cost Elements (both primary and secondary cost elements) with similar characteristics are
collected in Cost Element Groups. The cost element groups are used for the information system. The
cost element groups are used to process several cost elements in one transaction, such as in Cost
Center Planning, Distribution and Assessment. These groups are also used for report viewing purposes.
Confidential Document Page 12 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
The cost element group will facilitate better planning, allocation and reporting of costs. Using Cost
element Groups similar expense codes can be viewed in one group so that it will be possible to plan,
allocate and carry out analysis for a given cost object with ease and flexibility. For Example In case all
Personnel related costs are to be planned, displayed and analyzed in a single business transaction,
processing can be carried out using the Cost Element Group ‘Personnel Costs’ instead of choosing
repeatedly each of the numerous individual cost elements comprised in this group.
Production
Administration
Marketing
Dispatch
Accounts
HR
Sales Income
Other Income
5.2 Cost Center Master Data:
Cost centers in a controlling area represent a clearly delimited location where costs occur. The cost
centers are made on the basis of functional, settlement-related, activity-related, spatial, and/or
responsibility-related standpoints.
A cost center is assigned to exactly one profit center & one Business Area to which all costs of the cost
center can be attributed. By Assigning Profit Center and Business Area to Cost Center Master, system
updates automatically the Profit Center and Business Area, when any Cost is incurred in the cost
center.
Each Plant will be classified i nt o cost center Groups and further subdivided into cost Center
based on the services provided.
The entire cost center structure will be visible in a tree form on a single screen thus giving an overview
of the entire organization from the cost controlling perspective at a glance. Generally we can divide
the cost centers into two types i.e. production cost centers and service cost centers. Production cost
centers would be tied to work centers so as to use the activity types
Cost Center Group
Cost Center Groups are used to build cost center hierarchies, which summarize the decision-making,
responsibility, and control areas according to the particular requirements of the organization. The
individual cost centers form the lowest hierarchical level.
Cost Center Hierarchy are easily adapted and modified due to changes in the organization. New Cost
Centers are also added to the Hierarchy at any later date by creating the relevant Cost Center Master
Record and linking the Cost center to the relevant hierarchy area. Synokem Cost Center Group:
Production
Administration
Marketing
Sales
Accounts
HR
Cost Center Standard Hierarchy:
Cost Center Standard Hierarchy is a tree structure representing all cost centers belonging to a
controlling area from a Controlling perspective. There must be at least one group that contains all cost
centers and represents the entire business organization. This cost center group is described as the
standard hierarchy.
Confidential Document Page 13 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
At Synokem Project there is one Controlling Area & there will be one Standard Hierarchy, each
Company Code to which all the Cost Center groups & cost centers will be assigned.
5.3 Activity Type:
Activity Type is a unit that classifies the activities performed in a cost center with in the Controlling
Area. To plan and allocate the activities, the system records quantities that are measured in activity
units. Activity quantities are valuated using an activity price (allocation price).
The Activity Types at Synokem would help in categorizing production activities provided by a cost
center. These would be used for allocating costs of internal activities to the respective production
departments. The activity types would be defined in such a way that all activity types be measured in
terms of quantity and value.
5.4 Internal Order
Internal orders are used to plan, collect, and settle the costs of internal jobs and tasks. This component
enables to monitor internal orders throughout their entire life-cycle; from initial creation, through the
planning and posting of all the actual costs, to the final settlement. Internal orders are categorized in
to the following:
Overhead Cost: Orders used only for monitoring objects in Cost Accounting (such as, Conveyance,
Travelling Expenses, Employee Salary Expenses, Vehicle Maintenance cost etc.)
Investment Order: Productive orders that are value-added, that is, orders that can be capitalized
(such as in-house construction).
An Internal Order is assigned to exactly one profit center, one Business Area & one Cost Center to which
all costs of the Internal Order can be attributed. By Assigning Profit Center, Business Area & Cost
Center to Internal Order Master, system updates automatically the Profit Center, Business Area and
Cost Center when any Cost is incurred in the Internal Order.
5.5 Profit Center:
Profit Center Accounting evaluates the profit or loss of individual, independent areas within an
organization. These areas are responsible for their costs and revenues. Profit Center Accounting is a
statistical accounting component in the SAP system. This means that it takes place on a statistical basis
at the same time as true accounting. In addition to costs and revenues, Profit Center display key
figures, such as, return on investment, working capital or cash flow on a profit center.
A profit center is a management oriented organizational unit used for internal controlling purposes.
Dividing company up into profit centers allows to analyze areas of responsibility and to delegate
responsibility to decentralized units, thus treating them as “companies within the company”.
N.B.: Profit center code would be finalized at the time of master data training & realization.
Confidential Document Page 14 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Profit Center Group
A profit center group is a hierarchical structure of profit centers. Profit center groups are used for
reporting, allocations or in various planning functions, where it does not make sense to enter or display
data at the lowest level (with a high level of detail).
Additional Balance sheet and Profit & Loss Accounts
By default, all profit-related accounts as well as selected balance sheet accounts (payables and
receivables, assets, material stocks, and work in process) are transferred to Profit Center Accounting. If
no profit center is set for a specific transaction, the system will not allow the user to posts for any kind
of transactions. It requires greater flexibility in finding the profit centers, and also defines the
derivation rules for this purpose.
6. Business Process List in Controlling
The Following are the CO Business Process List available for Synokem Project:
Cost Element Accounting
Cost Center Accounting
Internal Order Planning & Actuals
Profit Center Accounting
Product Cost Controlling
Production Order Settlement
Profitability Analysis
6.1 Cost Element Accounting:
Cost Element Accounting provides you information or overview of all the Expenses and Revenues
incurred in the organization. All most all the values flow from Financial Accounting to Controlling. In
Synokem, use of Cost Element accounting will eliminate the need to enter cost data separately. Each
Cost or Revenue account in the organization flow from FI to CO through Cost & Revenue Element.
Primary Cost Element:
By using Primary Cost Element concept, the costs that originate outside of CO will be captured. Primary
cost elements correspond to all Profit & Loss G/L accounts in Financial Accounting. Using Secondary
Cost Element concept, the costs will be allocated for internal activities. Secondary cost elements do
not correspond to any G/L account in financial accounting. They are used only in Controlling.
The link between Finance and Controlling is General Ledger Account = Primary Cost element.
Secondary Cost Element:
Secondary cost elements are like production costs, material overheads, production overheads are
created and administered in only Controlling. Secondary Cost Elements are used for Reconciling the
internal cost allocation, overhead calculation, settlement of transaction, Reposting, Distribution and
Assessments.
Secondary Cost Element does not flow from FI to CO. During Month end activities internal cost
allocations like postings from one cost center to other cost centers for the exact expenses incurred by
each department during the period or year are done. Postings to these accounts do not affect the
Financial Accounting.
Confidential Document Page 15 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Secondary cost element belongs to internal settlements / Overhead Rates / Assessments is defined in
the Secondary cost Element master record.
Examples of secondary cost elements include:
Assessment & Distribution of cost elements
Cost elements for Internal Activity Allocation
Cost elements for Order Settlement
Cost Element Category
Cost element category determines which cost elements can be used for which business transactions.
SAP distinguishes between:
Primary Cost Element Categories.
Secondary Cost Element Categories.
The Primary Cost Element Categories:
01 General Primary Cost Element - This cost element category can be debited for all primary
postings.
11 Revenue Elements - This cost element category can be used to post revenues.
12 Sales Deductions - This cost element category can be used to post deductible items.
22 External Settlement - This cost element category can be used to settle order, Project to
objects outside of controlling. Ex: Settlement to Assets.
The Secondary Cost Element Categories:
21 Internal Settlement - Used to settle internal order costs to objects such as cost centers.
31 Order/Project Result Analysis - Used to calculate WIP
41 Overhead - Used to allocate from Cost Centers to production orders
42 Assessment - Used to allocate costs center to costs center during assessment
43 Activity type allocations - Used when activities are confirmed in PP.
In SAP cost elements can be created either manually or automatically( advisable manually).
At Synokem, Primary cost element category 01 would be using for all expense accounts (other than
those coming from SD module), 11 would be for Revenues, 12 would be for expenses which are coming
from SD module and 22 would be for Settlement to Asset Accounting & for Change in inventory GL
Accounts
Secondary Cost element category 21 would be using for settlement of internal order, Plant Maintenance
Order to cost center, 31 would be for calculation of WIP, 41 would be for overhead calculation, 42
would be for Assessment (from service cost center to production cost center) & 43 would be for Activity
type.
Confidential Document Page 16 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
6.2 Cost Center Accounting:
Cost Center Accounting is used for the purpose of controlling within the organization. The costs
incurred to the organization should be transparent. This enables to check the profitability of individual
functional areas and provide decision-making data for management. This requires that all costs are
assigned according to their source. However, source-related assignment is especially difficult for
overhead costs. Cost Center Accounting analyzes the overhead costs according to where they were
incurred within the organization. Cost centers are linked to profit centers in as many to one or a one on
one relationship such to allow for profit and loss reporting at the profit center level.
Dividing an organization into cost centers allows achieving several goals, depending on the cost
accounting method.
1. Assigning costs to cost centers determines where the costs are incurred within the organization.
2. Plan costs at cost center level; can check cost efficiency at the point where costs are incurred.
3. To assign overhead costs accurately to individual products, services, or market segments, it needs
further allocate the costs to those cost centers directly involved in the creation of the products or
services. From these cost centers it gives the use different methods to assign the activities and costs
to the relevant products, services, and market segments.
Confidential Document Page 17 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Cost center Accounting can be explained by the following points:
Master Data
Cost Center Planning
Manual Actual Posting
Period End Closing
Cost Center Planning
Cost center planning involves entering plan figures for costs, activities, prices for a particular cost
center and a particular planning period. It determines the variances from these figures when it is
compared these plan values with the costs actually incurred. These variances serve as a signal to make
the necessary changes to your business processes.
Cost center planning forms a part of the overall business planning process, and it is a prerequisite for
standard costing. The main characteristic of standard costing is that values and quantities are planned
for specified timeframes, independently of the actual values from previous periods.
The plan costs and plan activity quantities to determine the (activity) prices. These prices are used to
valuate internal activities during the ongoing period, i.e., before the actual costs are known.
Cost center planning has the following objectives:
To plan the structure of the organization’s future operations for a clearly defined time period.
It defines the performance targets and target achievement grades, and it should consider the
internal and external (market) factors affecting the organization.
To control business methods within the current settlement period. It ensures to keep as closely
as possible to the plan. Iterative planning lets adapt the target performance to reflect any
changes in the organizational environment.
Cost Center Planning can be done by the following methods:
a. General Cost Center Planning
b. Manufacturing Cost Center Planning
a. General Cost Center Planning
During the Cost Center budgeting process, the managers of non-operational cost centers such as sales,
marketing, administrative, research and development etc. plan the costs for various cost
types/elements on their respective cost centers .It gives Possibility to compare planned and actual
costs, monitoring of costs on cost centers.
Confidential Document Page 18 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Based on the General Cost Center Planning at the end of the Month / Year end system displays the
variances between standard cost center planning and Actual cost incurred during the period.
b. Manufacturing Cost Center Planning
The manufacturing cost centers plan the costs for various Activity types/elements for their respective
cost centers. In addition, the quantities of activity types needed for production and their prices are
determined.
At the month end there is a Possibilities to compare planned and actual costs, by monitoring the costs
on cost centers. Allocation of production & overhead costs to products (via activity types)
Cost Center Actuals Postings
The Actual posted values enables to monitor costs on an ongoing basis. These postings enable you to
recognize variances at an early stage, and to take the necessary counter measures.
Actual cost entry involves transferring primary costs to the Controlling (CO) application component. In
the CO component, this transfer occurs real-time from the components Financial Accounting (FI), Asset
Accounting (FI-AA), Materials Management (MM), Production Planning (PP) and Payroll Accounting (PA-
PA). This is achieved by entering a cost accounting object (such as a cost center or an internal order)
during account assignment.
Posting from MM
Certain material are not stocked but is charged off at the time of purchase itself. The item is assigned
to a cost center in the purchase order. In this case consumption is booked at the time of goods receipt.
For example: Printing & Stationery is issued and cost booked to Administration Cost Centre.
Posting from Asset Accounting
Each asset is assigned to a cost centre and depreciation is debited to it during Depreciation Run at
period end.
Confidential Document Page 19 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Posting from FI
During expense booking in FI the relevant Cost Centre is assigned which enables the flow of the expense
to the relevant cost centre. Note: Integrated value flow will happen to cost center when expenses are
posted in financial accounting general ledger account of expenses. Cost center line items with date and
value of posting will automatically updated in CO.
Note: Integrated value flow will happen to cost center when expenses are posted in financial
accounting general ledger account of expenses. Cost center line items with date and value of posting
will automatically updated in CO.
Allocation:
With the introduction of the new Universal Journal in SAP S/4HANA Finance, all the CO postings are
posted directly to the Universal Journal, Secondary cost elements are now part of G/L accounts in FI
and don’t require separate assignment in CO.
Cost Allocation:
Cost allocations will be performed under controlling area. Company code can allocate their costs using
the Standard allocation tools provided by SAP. Cost allocations in SAP shall be done using the procedure
of Distribution & Assessment.
Under this procedure, the costs collected on a cost center during the accounting period are allocated to
receivers. These are indirect allocation methods for which user-defined keys such as percentage rates,
amounts, or posted amounts provide the basis for cost/quantity assignment.
These methods are easy to use as the keys and the sender/receiver relationships are usually defined
only once.
For example, Salary costs are collected on a cost center for each period & then can be allocated using
the process of reposting or distribution/ assessment cycles at the end of the period according to the
number of employees in each cost center. Methods of cost allocation include:
Distribution which moves primary costs from one object to another using the original posted
primary cost elements.
Assessments which moves primary and secondary costs from one object to another using a
secondary cost element.
Reposting which moves primary costs from one object to another using the original posted
primary cost element.
Distribution:
Distribution is a method of internal cost allocation that allocates primary costs. Main feature of this
process is that the original cost element is retained in the receiver cost center. Information about the
sender and the receiver is documented in the Controlling document.
Features of Distribution-
The original, primary, cost element is retained.
Sender and receiver information is documented with line items in the CO document.
Distribution will work only for Primary Cost Elements and it will not work for Secondary Cost
Elements.
Assessment
Confidential Document Page 20 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Assessment is a method of internal cost allocation by which the costs of a sender cost center is
allocated (transferred) to receiver CO objects (orders, other cost centers, and so on) under an
assessment cost element (category 42). The method works according to the keys defined by the user. It
is used when it is unimportant for the user to know the breakdown of costs that a cost center will
receive in an allocation. Further analysis is available through CCA reporting.
Features of Assessment-
The original cost elements are grouped together into assessment cost elements (secondary cost
elements). The original cost elements are not displayed on the receivers.
Assessment will work both primary and secondary cost elements unlike Distribution
Periodic Reposting:
Primary posting such salaries are collected on an allocation object (cost center, overhead cost order) to
restrict the number of FI posting as much as possible. Later, these costs are allocated during the period
–end closing to the corresponding controlling objects. During this process, we can only repost primary
cost and the original cost element remains the same. Items required for manual reposting of cost:
Sending Cost center
Receiving cost center
Cost element
Manual Reposting of Cost:
We use the manual reposting of the cost function mainly to adjust (correct) posting errors.
When we make an internal reposting, the primary costs are reposted (under the original cost element)
to a receiving cost center. If the initial transaction is posted using an incorrect cost element, the
transaction must be corrected in the original application component in order to ensure reconciliation
between external and internal accounting.
Note that no sender check is made, in other words the system does not check whether the costs we
repost actually exist on the sending cost center. This means that negative costs may appear on the
sending cost center.
Items required for manual reposting of cost:
Sending Cost center (From we need to remove the cost)
Receiving cost center (to which we transfer the cost)
Cost element (From where we need to repost)
Reposting of Line Items:
The function for reposting line items enables us to repost specific line items from Management
accounting documents. This function is designed to enable us to correct primary postings that we
assigned to the wrong accounts. To do this, the Management Accounting document must contain a
reference to the original FI document.
Reposing line items is the equivalent of a reversal on the sender object. We can also enter more than
one receiver object.
Confidential Document Page 21 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
If we repost a line item in Management Accounting, the original account assignment object remains
noted in the FI document. To correct the account assignment object in the FI document, we will need
to reverse the FI document. If we have already carried out a line item reposting in Management
accounting for this document, we will first need to reverse this reposting before we can reverse the
document in FI.
Items required for manual reposting of cost:
Reference document number.
Receiving cost center (to which we repost the cost).
Document types for Cost Accounting
For every posting in CO the SAP System creates a numbered document. The document numbers are
unique to each controlling area since each number is assigned only once.
Every transaction that you carry out on the controlling area level has to be assigned to a number range
group. Each group is in turn attached to certain transaction(s). The document number range in CO
independently from the fiscal year.
A separate document number ranges for each transaction type has been created as follows:
Actual primary postings will have the number ‘1’ as the first digit of the document number.
Planning transactions will have the number ‘2’ as the first digit of the document number.
Actual secondary postings will have the number ‘3’ as the first digit of the document number.
Other transactions (e.g. variance calculation, activity allocation) will have the number ‘4’ as the first
digit of the document number.
Type of Transaction From To
Actual Primary Postings 10000000 19999999
Planning Transactions 20000000 29999999
Actual Secondary Postings 30000000 39999999
Other Transactions 40000000 49999999
N.B.: Number ranges would be decided at time of realization.
Confidential Document Page 22 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
6.3 Internal Order
Internal orders are cost objects in CO. They collect actual and plan revenues and cost, statistical and
activity data. Data is collected in the order at the transaction level. Based on the order’s purpose, the
values can be settled (periodically or all at once) to a final receiver such as a cost center, general
ledger account, asset, another internal order, profitability segment, etc. The order’s inflows as well as
outflows can be reported in the Internal Orders Information System. In the delivered reports, the user
can drill down through the original documents to the line item.
Order purpose is defined in order type. Standard order types that are required for our business scenario
are provided in the system. An Internal Order master record is created on the functional side and
includes the attributes established in the order type. Use a statistical order to manage statistical detail
with value detail posted to a cost center.
An internal order type provides the following default parameters to the orders:
1. Budget Profile
2. Settlement Profile
3. Planning Profile
4. Object Class
5. Functional area to be updated
6. Release Status
7. Control indicators for revenue postings
8. Commitment item & integrated Planning data
9. Field selection
10. Number Intervals
Confidential Document Page 23 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Internal Order Accounting
Internal orders are normally used to plan, collect, and settle the costs of internal jobs and tasks.
Internal orders can be effectively utilized for Capitalization Project the SAP system enables you to
monitor your internal orders throughout their entire life-cycle; from initial creation, through the
posting of all the actual costs, to the final settlement.
An Internal Order is also known as overhead orders and is used to monitor the costs of a Cost
restricted job (Project costs) or time-restricted job , such as marketing campaign, etc. where the
costs does not directly relate to a particular source object (cost center). In such cases, actual cost for
a particular project\event are recorded on the internal order, which on completion of the event are
analyzed with respect to the total costs incurred. Internal order can be a) Statistical or b) Real. The
real orders can be settled to AUC or the responsible cost objects (cost centers).
For each capitalization project Internal Order has to be created with budget and time schedule.
Budgetary control will be activated for certain order type. Order will be created for each asset or
even at lower level according to the need. Order type created for this type of order will be real in
nature. Cost incurred for the project will be initially captured on the internal orders and subsequently
settled it to an Asset that can be also AUC.
The authorized person would create the Internal Order under respective order type. The
mandatory information is:
Order type
Order number
Settlement rule
Name and Description of the orders
The general ledger postings in FI would be assigned to respective internal orders at the time
of transaction processing.
If the material consumption were required for the order, a reservation would be created.
MM will issue the material against the reservation and consumption would be booked on the
order.
In case of direct procurement, a purchase requisition would be raised. The stores will issue
a purchase order which will contain reference of internal order against the requisition and
procure the material. At the time of GR the consumption would be booked on the order.
Preliminary cost reports would be reviewed by the responsible person. The adjustments to
actual data, if any would be identified.
The adjustments should be identified with respect to GL correction or cost object
correction.
If GL correction is required, the same should be intimated to the FI department for
rectification.
Preliminary report of actual costs taken from the system. If approvals are required the
report is sent for approval. In case of adjustments suggested by the approving authority, the
same should be executed.
Confidential Document Page 24 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Once the order is complete, the status of the order would be set to technically close.
Settlement rule would be processed and settlement transaction is executed in test run. If
the results are satisfactory on verification, the settlement is executed in update run. This
will result in transferring Project Cost to an Asset or to a CWIP for capitalization
The detailed steps involved are as under:
Activity Step Data input Data output Transaction Responsibility/ Remarks
Code in Authorization
SAP
Creation of 1 Order type, Creation of KO01
Internal Order company code, Internal Order
business area,
responsible
person, etc.
Creation of 2 Order group Internal KOH1
order group name, Orders can be
description, grouped
relevant order
numbers
Overall Planning 3 Order number, Plan data get KO12
against internal version, order generated
order type, amount
Cost Element 4 Version, period, Element wise KPF6
wise expense internal order planning at IO
planning no., cost element level
no. amount etc.
Individual 5 True Order no., IO get created KO88 For Real
Settlement of IO settlement Orders
period, only
processing type
Collective 6 True Order, IO group gets KO8G For Real
Settlement of IO Selection variant, settled Orders
period, only
processing type
Statistical Order
Statistical orders are used to collect costs to evaluate costs that cannot be itemized in detail in cost
element or cost center accounting. Costs could be booked only once to CO. When cost centers are real
cost objects, the internal orders serve as a statistical record. That means no further settlement from
the statistical order.
It is achieved by assigning the actual costs to a cost center and statistically to an internal order. The
costs will then appear under the original cost element both on the cost center (real costs) and on the
order (statistical, for information purposes only).
An example for statistical order is travelling, LTA, Conveyance, Mobile expenses incurred by each
employee can be tracked through internal Order. At the end of the month end once internal order
report is executed based on Primary Cost Element system gives the information about the person wise
details of his expenses during Travelling.
Confidential Document Page 25 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
S. No Internal Orders
1 Travelling Expenses
2 Telephone Expenses
3 Maintenance Expenses
4 Employee Salary Expenses
Investment Order
A tool used to monitor internal tasks whose costs are to be settled to a fixed asset account. It performs
preliminary costing on capital investment orders, make postings to them, and settle them to assets
under construction. On completion of the task, the order is settled to one or more assets.
An Example for Investment order is : At the time of project set up there would be some preoperative
expenses incurred, all those expenses has to be capitalized once the project is completed, For
Capitalizing the preoperative expenses SAP Provides to capitalize through Investment Order.
Internal Order Planning
Planning is the expected amount of spending during the lifetime of the internal order.Two ways of
planning are there. The first one is overall planning which does not require any detailed information
like cost elements etc. The overall amount will be broken for year-wise, if required
When it is required to have a detailed planning, the planning is carried out according to primary and
secondary cost elements.
6.4 Profit Center
A profit center is an organizational unit in accounting that reflects a management-oriented structure of
the organization for the purpose of internal control. Profit Center analyses internal profit or loss e.g.
for branch, line of business, site, etc. Profit Center Accounting is a statistical accounting component.
Confidential Document Page 26 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Because it takes all the transaction data postings in other components and represents it in the form of
profit center oriented point of view. The postings in profit center accounting are statistical postings,
since the profit center is not an account assignment object in Controlling.
Methods of Calculating Profits in Profit Centers:
● By Time Reference (periodic Calculation or transaction Based Calculation)
● By content of period accounting
In Profit Center Accounting, the data is stored and displayed by period and account. This corresponds to
the organizational principle in Financial Accounting. As a result, the uniform report structure in these
two components makes possible to reconcile the data in cost accounting and financial accounting based
on cost elements.
Profit center Assignment
In Customizing, Profit center are assign to all account assignment objects for which contain profit-
related data (such as cost centers, Internal Orders) to profit centers. By doing this, company is split
into profit centers.
These assignments make it no longer necessary to post data explicitly to profit centers. The system
automatically transfers the data to Profit center accounting when it is posted to the original object &
can reflect both actual and plan data from the assigned objects in Profit Center Accounting.
Integration
The following data is transferred to Profit Center Accounting:
Revenues and sales input - through assignment of sales document items
Direct costs - through assignment of production orders and cost objects
Overhead costs - through assignment of account assignment objects from Overhead Cost
Controlling (cost centers, orders etc.)
Profit centres are assigned to the following:
Assigning Materials:
Assignments of materials to profit centres provide the default values for assignment of Sales Orders
With internal goods movements also (such as stock transfers or material withdrawals) the profit centre
is derived from the material master. The assignment of materials also forms the basis for the transfer of
material stocks to Profit Centre Accounting. In order to assign materials to Profit Centres, it is
important that for each Profit Centre a separate Plant is created.
Assigning Sales Orders:
It is necessary to assign Sales Orders to profit centres in order to reflect sales revenues and sales
deductions. When the goods issue is posted, the cost of goods sold is also passed on to the profit centre
of the sales order.
Assigning Manufacturing Orders
Confidential Document Page 27 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
A manufacturing order is a PP production order, when we create a production order; the system
proposes the profit center from the master record (plant segment) of the material being produced.
Consequently, we usually do not have to enter it manually.
All the costs and internal cost allocations posted to the production order are passed on to the assigned
profit center, along with the credit posted when the production order is delivered or settled. The
assignment of production orders also lets us transfer work in process for open orders to Profit Center
Accounting.
Each production order is assigned to a plant. Each plant, in turn, is assigned to a company code, which
is assigned to a controlling area. This controlling area must be the same as that to which the profit
center is assigned.
Assigning Internal Orders
We need to assign internal orders to profit centers in order to be able to observe the flow of overhead
costs from Financial Accounting and their allocation through internal accounting from a profit center
point of view. Internal activities capitalized during order settlement are also assigned to the profit
center of the internal order.
Assigning Cost Centres
It is necessary to assign cost centres to profit centres so that we can reflect all the primary costs from
Financial Accounting and all secondary allocations from Cost Centre Accounting in Profit Centre
Accounting.
By Assigning Profit Center to different objects SAP System Provides solution for generation Profitability
and select balance sheet items balances at plant level and at each branch and grouping them together.
In Synokem the Profit Centers are defined at time of realisation:
Based on the Above Profit Center System generates automatically profit center wise Profit & Loss
Account and Balance sheet account.
6.5 Product Costing
It is a tool used to estimate standard cost per unit of a product & to determine the cost of goods
manufactured & cost of goods sold. This tool contains the following areas:
1. Product Cost Planning
2. Cost Object Controlling
3. Actual Costing or Material Ledger
4. Information Systems
Cost Components
5. Material Cost
6. Process or Conversion cost
7. Overheads
Manufacturing or Production Overheads
Administrative Overheads
Selling and Distribution Overheads
Product Cost Planning (CO-PC-PCP) is an area within Product Cost Controlling (CO-PC) where you can
plan costs for materials without reference to orders, and set prices for materials and other cost
accounting objects.
Confidential Document Page 28 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
You can use Product Cost Planning to analyze the costs of your company’s products such as:
Manufactured materials
Services
Other intangible goods
You can analyze costs to help provide answers to questions such as:
How high are the material, production, and overhead costs?
How can production efficiency be improved?
Can the product be supplied at a competitive price?
The following graphic provides an overview of the organizational structures required for costing:
AS-IS
1 Production Process – Make to Stock
2 Costing component:-
Raw Material
Packing Material
Allocation of expenses
(This cost is sum of all GLs which has relevance to product costing)
=====================
Total Manufacturing (Factory) Cost(COGM)
=====================
3 WIP Cost = Raw Material + Factory Overheads
4 Activity type = No Activity wise allocation is happening.
5 Standard cost Run – Monthly
Confidential Document Page 29 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
6 Costing should be Batch wise/Lot wise
7 Raw Material Moving Average cost (V) – During Standard cost updating what raw material cost system
will pick from raw material
TO-BE
Product Cost Controlling calculates the costs that occur during manufacture of a product. It enables us
to calculate the minimum price at which a product can be profitably marketed.
Product costing consists of two parts one is Product cost planning which talks about standard cost and
the other one is Cost Object Controlling which talks about actual costing.
Product costing is a tool for planning costs and establishing prices for materials. It is used to calculate
the costs of goods manufactured and the costs of goods sold for each product unit. Product costing
belongs to both the Production Planning (PP) Module and the Controlling (CO) Module. Product costing is
carried out at the plant level. All costing data is stored with reference to a plant. The system uses the
results of cost estimates to valuate material movements in Logistics. Material valuation is carried out at
the Plant level.
Valuation Methodology:
Moving Average Price
Price that change in consequence of usage and entry of invoices.
It is calculated by dividing the value of material by the quantity in stock.
Automatically recalculated based on activity.
Standard Price
Constant price without considering usage or invoices.
Material stock valued at the same price over an extended period.
Price variances are posted to price difference accounts; not affecting the standard price.
Standard Cost Estimate:
Material cost estimate used to calculate the standard price and update in the material master record.
The cost estimate must be executed with a costing variant that updates the material master, and the
cost estimate must be released.
Costing with a quantity structure is the tool for costing the product cost before it goes to production
order stage. It sets the price for the material at material master. These prices are used for valuating
material at standard price.
Each product shall have a Bill of Material & Routing which shall contain the standard material
requirement and process for production of a standard batch quantity. The cost of the finished product
will be made of the following:
Material cost
Activity costs
Confidential Document Page 30 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Overheads
Each cost estimate is based on costing variant. The costing variant contains settings and parameters for
costing. The settings decide how the costing is executed. Costing variant determines as how the prices
are to be taken from the system for materials and activities. Costing variant specifies particular
Valuation variant and costing type
The standard cost estimate will be calculated at the beginning of each month and shall be valid for the
month. The prices will be marked in the system, which will result in the prices to be written in the
material master as the future standard price. The prices will then be released in the system, which will
result in the prices to be written in the material master as the current standard price. The difference
between the earlier standard price and the current standard price for the quantity in stock will be
passed to the price difference account.
Cost Component Structure
In Product Costing, the costing results are displayed and saved using a structure which is termed as Cost
Component Structure. Cost component structure controls how the results of activity price calculation or
material costing are stored. In the cost component structure, we assign cost elements to cost
components to define a cost component split to our specific requirements.
In Product Cost Controlling (CO-PC), the cost component structure determines the attributes for passing
on the following costs:
Material costs passed on to material valuation as the standard price or inventory price
Cost of goods manufactured passed on to Profitability Analysis
The following graphic illustrates how cost components, cost component structures, and cost views are
follow.
Below is the proposed Cost Component Structure for Synokem Plant:
Raw Material
Packing Material
Labor
Power
Machine Cost (Consumables)
Factory Overheads
Admin. Overheads
=====================
Confidential Document Page 31 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Total Manufacturing Cost
=====================
Costing Variant
All Cost estimates are created with reference to a costing variant. A Costing variant contains important
parameters that drive the costing functionality. Costing Variant is a key that determines how a cost
estimate is performed and valuated.
Costing Variant
Quantity Structure Valuation
Determination Variant
Quantities Prices
Cost of Goods
Manufactured
In a cost estimate with a quantity structure, the costing variant determines the following:
Which dates are valid for the cost estimate itself and for exploding and valuating the
quantity structure
How the BOMs and routings are selected to create the quantity structure
Which prices are selected to valuate the quantity structure
How overhead is calculated
Cost Component Structure
A costing variant is linked to the following control parameters:
Costing type (which price and valuation view) is to be updated
Valuation variant (how to valuate materials, internal and external activities, assignment of
costing sheet)
Date control (date defaults)
Quantity structure control (BOM and Routing determination)
Transfer control (strategy sequences for transfer of the existing cost estimates into one
under calculation).
Confidential Document Page 32 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Strategy for Determination of :
Costing Sheet transfer of - Bills of Material
the existing - Routing
cost estimates
Determination of: Defaulted dates for
COSTING
- prices update costing
VARIANT
in material master
Valuation control for:
- materials
- internal activities
- external activities
- subcontracting
- overheads via
costing sheet
Components of Costing Variant
Following are the key components of Costing variant:
Costing type – The Costing type defines the purpose for which the cost estimate can be used. It
controls
To which field in the material master (standard price, planned price etc) the cost should be
transferred.
On what basis the overhead should be calculated
Synokem will use Standard SAP costing type – 01
Valuation Variant – Valuation variant controls how the materials and activities in the cost estimates are
valuated Synokem will valuate Raw materials and Packing materials at the moving average price and
Activities at the planned price on Cost Center through transaction code KP26.
Below is Synokem Strategy sequence for Material Valuation.
Planned price 1
Valuation price according to price control in Material Master
Moving Average Price
Date Control – Key that controls the dates for material cost estimates. The system will default current
date as costing from date, Maximum value as costing to date, current date will default into quantity
structure date and valuation date. For all costing runs, user will override all these dates with first day
of next month or next year.
Confidential Document Page 33 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Quantity Structure Control - Automatic process by which the system determines the quantity structure
(such as the BOM and routing) when materials are costed. Production BOM and routing will always be
selected for Cost estimate
Costing Run
You can use the costing run to process mass data. It enables you to cost, mark, and release
more than one material at the same time.
Every processing step involved in costing with quantity structure is performed by the costing
run, from the same screen.
Costing run consists of
General data (organizational units, selection criteria).
Selected materials.
Exploded BOMs.
Costing run results.
Price updates results.
Costing Run Creation
Company Code Costing
Costing variant Run
Dates
Partial selection
of materials
Selection
of
all materials BOM explosion
$ $
Execute costing run
$ $ $ $
$ $ $
Marking and releasing costing run results
(price update) Materials
Confidential Document Page 34 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Costing Run – Price update
Once the cost estimate is carried out, costing results needs to be transferred to material
master for updating prices
When the cost estimate is ‘marked’, Future Standard price in the material master is
updated
After ‘marking’, Cost estimate is ‘released’. The new released standard price becomes the
‘Current Standard price’ and standard price previously updated in the ‘Current standard
price’ is updated as the ‘previous standard price’
The existing inventory gets revalued at the new current standard prices and system passes
following accounting entry for revaluation:
Inventory FG/SFG Dr/Cr
Revaluation Inventory FG/SFG Dr/Cr
Material Master Data
Analysis of Costing Results
Standard Price
Future Current Previous
10
Future Current Previous
Marking Standard
Cost Estimate 15 10
Future Current Previous
Releasing Standard
Cost Estimate 15 10
Stock Revaluation
Standard price:
Only one validated standard price per product per period
The price represents most desired (or most likely) costs
Costing run at each month will update a new standard price for each FG/SFG
Base for variance calculation; which is then posted to FI and CO-PA
Used for stock valuation of finished goods and semi-finished products
Confidential Document Page 35 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Stored in material master data (accounting and costing view) after releasing the cost
estimate
Future Standard price:
Stored in material master data (accounting & costing view) after marking the cost estimate
Previous Standard price:
Replaced standard price by current one due to releasing the cost estimate
Stored in material master data (accounting & costing view)
Synokem will run standard cost Estimate every month.
By-Product
At every stage there is some useable and non-useable waste produced. The useable waste generated in
the process shall be treated as a By-Product in SAP to make its reusability and also to ensure
accountability.
The By-Product could be used as raw material in other lines for Mixing; the Non-usable material is sold
to the market in different grades.
A by-product is a product that is produced in conjunction with other products. The system does not
create a separate order item for each by-product. The material valuation of a by-product is always
based on the price specified by price control in the material master.
By-product will be valuated at net releasable value which needs to be updated in planned price 1 in the
material master. Once standard cost runs for this material the value given in planned price 1 field, gets
updated in standard price field in the material master.
Confidential Document Page 36 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Create Standard Cost for Individual Material
t
en New Material Created for a Plant
Ev Needs to have a Standard Cost
Create
Bill of
Material
ng
eri
ne Create
gi Routing
En
Create
Purchasing
Info
Release Cost
nt Correct Mark Cost Estimate for End Process
ta Source of Estimate for Material
Inaccuracy No Material
un
co
Yes
Ac Is
Create Cost Cost
st Estim
Estimate for
Co Material ate
Accur
ate?
Overhead (Costing Sheet)
The costing sheet integrates all elements of overhead costing.
You can take the overheads directly from the costing sheet and then maintain them as necessary, or
define them separately in the steps Define percentage overhead or Define quantity-based overhead.
The overhead row contains a credit key that defines which object (cost center or order) is credited
during the overhead calculation.
You can either take the credit keys directly from the costing sheet and then maintain them as
necessary, or define them separately in the step Define credit.
Rework order
Sometimes there would be operation deviation; in that case they may add some chemicals. If this is the
scenario rework order needs to be created without material, and this rework production order needs to
be settled to the main production order.
If whole material is reprocessed or reworked, rework order with materials needs to be created as
normal production order and the settlement process is the same as that of normal production order.
Product Costing - Make to Stock
As per production target plan monthly production will be planned through shop floor production
control.
Make to Stock Costing Cycle involves the following steps:
Confidential Document Page 37 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Determining the Actual Cost of Product
Variance Calculation
Production Order Settlement
Determine the Actual Cost of Product
Actual Postings to the Production Order which includes
Goods Issue to Production Order.
Confirmations of the actual activities at the planned rate will be done in the production
order this will calculate the cost for operations.
Goods Receipt from the Production Order.
Following master data would be used for product costing
Bill Of Materials (BOM)
Work Center
Routing
Material Master
Cost Center
Activity Type
Work in Process (WIP)
The WIP batch is a batch that you can create for a production order and for a process order to
document the properties of a material during the manufacturing process (e.g. after individual
worksteps). It also represents a link between input batches and goods receipt batches.
You can use the WIP batch in manufacturing not only to document the steps in production on a quantity
basis (confirmations) but also to record the current properties of the material that is to be produced.
Furthermore, the WIP batch ensures that end-to-end batch tracing is possible, because with this
function the system can automatically record n:m relationships between input and goods receipt
batches.
Following master data would be used for product costing
Result analysis Keys
Cost element for WIP Calculation
Result Analysis version
Valuation Method
Line IDs
Assignment
Update
Posting Rules for settling WIP
Number Ranges
Result Analysis Keys
Result analysis keys contains the control parameter for calculation of WIP. You can calculate WIP for
the following orders :
Production order with quantity structure(PP)
Confidential Document Page 38 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Production order without quantity structure(CO)
Run schedule headers, if reporting point quantities can be entered.
Process order, if the confirmation is made separately for each operation and not at header level.
WIP is the total actual costs posted to Production order( in make to stock e..g). the actual can be goods
issue, activities confirmation, overhead posting as well as goods receipts.
At the month end when you calculate WIP, as long as the status of the production order is nither TECO
or DLV, total cost ed will be treated as WIP. When settled, the posting will be made to FI and to Profit
center if used.
The presence of result analysis key in the production order means that the order is included in WIP
calculation during the period end closing.
Variance Calculation
Comparison of actual costs and planned costs at order level provides the result of variance calculation.
There may be a number of reasons for both positive and negative plan variances.
There may be difference between the planned quantities and actual quantities consumed. This is known
as usage variance. When target costs are compared with charged actual costs, it provides the amount of
volume variance.
In SAP system the variances are determined for each cost element and assigned to number of variance
categories. Variance categories specify the cause of a variance such as price variance or quantity
variance.
When the order is completed and delivered, the difference between the actual cost posted to the order
and the standard cost estimate of the quantity produced is the order balance. The order balance is
settled in accordance with the control parameters in the settlement structure.
Target cost versions determine which values are compared in order to determine the variance.
If the price control is ‘S’, that is controlled by standard cost price, then the variance is posted to price
difference account in GL and settled to the CO-PA.
In Synokem, we follow the price control ‘S’
In all the situations, the PA transfer structure provides such settlement to CO-PA.
Confidential Document Page 39 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Settlement of Production Orders
When production is completed, the order is settled. There are order debits due to issue of raw
material, components and activities or processes to the production. The outward movement of goods
from the order is the delivery of finished goods to the inventory. The amount of delivery of goods is
credited to the production order. It happens every time the deliveries of finished goods are taking place
from production order.
The credit value is based on the price control of the finished product of the production order. After due
credit for the delivery of goods from the production order, the difference between the debits and
credits of the production order is the variance. The variance amount is transferred to Price difference
account or Inventory account in accordance with price control of the material. The variance is also
settled to the profitability analysis.
The settlement parameters are defined in settlement profile and settlement structure.
CO PC : Product Cost Controlling
Confidential Document Page 40 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Accounting Entries in Cost Object Controlling
Raw Material Consumption
Raw Material Consumption A/c Dr
To Inventory of Raw Material A/c
Activities confirmation
Note: At the time of activities confirmation there won’t be any FI entry rather there would be CO
entry.
Production Order Dr
To Production Cost Center
Goods Receipt from Production
SFG/FG Inventory A/c Dr.
To Change in stock of SFG/FG A/c
Variance Calculation
If the Variance between the Standard and Actual Cost is favorable the following entry gets generated.
Production variance A/c Dr.
To Price difference A/c
Note: Primary cost element would be created for Production variance A/c but not for price difference
account
If the Variance between the Standard and Actual Cost is unfavorable the following entry gets generated
Confidential Document Page 41 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Price Difference A/c Dr.
To Production variance A/c
Direct Cost and Indirect Cost absorption:
Direct costs like Machine cost, labor cost and Consumables would be absorbed through activity types.
Indirect costs would be divided into Factory over heads and Administrative Overheads and these would
be absorbed based on the given percentage by Synokem.
Maintenance Cost:
For maintenance there would be plant maintenance order or Cost center. If consumables are issued
against plant maintenance order, those would be settled to the receiver cost center in turn these would
be transferred to Factory over heads pooling cost center.
Power Cost, Machine Hours, Labor Cost etc.
Power Cost, Machine Hours, Labor Cost etc. will be absorbed through activity type and it would be with
standard price which is maintained in KP26. Production orders should not be revaluated with Power
Cost hence over absorption/under absorption should be transferred to COPA.
S. No Description TCODE
1 Variances Calculation periodic KSS5
2 Settlement of Orders - Individual Processing KO88
3 Settlement of Orders – Collective Processing KO8G
4 Cost Estimate with Quantity Structure CK11N
5 Price Update for FG materials CK24
6 Standard Costing Run CK40N
7 Actual Activity price calculation KSII
8 Revaluation of orders CON2
Reports Description TCODE
Costing Run To analyze costing run S_ALR_87099930
To analyze variances between costing
Variances runs S_ALR_87099932
Cost components Used for cost component comparison S_ALR_87013047
Cost components Used for cost elements comparison S_ALR_87013048
To display list of existing material cost
Cost estimates estimates S_P99_41000111
Used for comparison of material
Itemization itemization CK79_99
Itemization Used for analyzing itemizations CK84_99
Material cost
Components Used to analyze cost component split CK80_99
Used to view multi-level BOM for material
Multilevel BOM in a Plant CK86_99
Confidential Document Page 42 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Product Costing - Make to ORDER
Make-to-order production is a process in which a product is individually manufactured for a particular
customer. Stock keeping is not usually carried out for products that are made to order. The primary
benefits of this process are the ability to track the progress for the sales order and the flexibility to
offer to the customer the products to meet their specific requirements. The benefit also lies in tracking
the costs incurred in the servicing of the sales order in the manufacturing of the goods and the ability
of arrive at a profitability of the sales order.
This Business Scenario Map shows how enterprises work together to complete a make to order scenario.
The planning and manufacturing process is initiated after receiving the sales orders from the customer..
There is a constant link between the sales order and the production order. This leads to the tracking of
the progress on the customer order. The material stock is seen as customer stock.
6.6 Profitability Analysis
Business Process Requirements
Most organizations have financial reporting systems that measure the overall financial performance of
the organization. Often, these reporting systems fall short in their ability to provide critical financial
performance information regarding specific business segments of the organization, including Region,
products, divisions, and customers. Without this information, management may not be able to maximize
profit by reallocating its resources to those segments that can contribute most to company profit.
Profitability Analysis offer Contribution and Profitability Analysis Studies to provide you with critical
financial performance information on specific business of Synokem segments of your organization.
Profitability Analysis (CO-PA) enables you to evaluate market segments, which can be classified
according to products, customers or any combination of these, or strategic business units, such as sales
organizations with respect to your company's profit or contribution margin
The aim of the system is to provide your sales, marketing, product management and corporate planning
departments with information to support internal accounting and decision-making.
Confidential Document Page 43 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
The Business Process Describes the Profitability reporting.
Purpose : View Profitability reports based on various segments.
Benefits : Helps in decision making.
Key Process Steps: Execute Reports.
SAP-Profitability Analysis (PA) is the module in SAP designed to provide users with an external view of
multi-dimensional, cost of sales (COS) analysis. The strength of PA lies in its tight integration with the
other SAP modules that feed PA data. Depending on the modules installed, data is fed into PA
automatically at the time of transaction execution. For example, if the Sales module (SD) is active,
whenever the sale order is invoiced, the revenues and standard costs for the products listed are posted
into PA.
Two forms of Profitability Analysis are supported: costing-based and account-based.
In the past, SAP advised companies to use costing-based CO-PA rather than, account-based CO-PA. The
main reason for this was:
Companies wanted a contribution-margin report with a breakdown of their cost-of-sales down to
the cost components level for each cost bucket
They wanted a production variance report by variance categories
They wanted a breakdown of the individual cost buckets beyond the total value that was posted
to the general ledger.
This functionality was not available in COPA account base before and therefor did the most
companies use Cost Base COPA.
The biggest issue with Cost based was the reconciliation effort, because cost base COPA did not use a
direct alignment to the general ledger accounts.
SAP’s latest SAP Simple Finance product , uses SAP HANA as its primary database, and opened up new
options to build a COPA structures aligned with the general ledger. Due to this SAP enhanced Account-
based CO-PA in SAP Simple Finance to provide:
Detailed information on the cost of goods, break down cost-of-sales to the cost component of
each cost bucket
Production variances by variance categories
Invoice quantities
Reconciliation between COPA and the GL at Account level
Costing-based Profitability Analysis is the form of profitability analysis that groups costs and
revenues according to value fields and costing-based valuation approaches, both of which
you can define yourself. It guarantees you access at all times to a complete, short-term
profitability report.
Account-based Profitability Analysis is a form of profitability analysis organized in accounts
and using an account-based valuation approach. The distinguishing characteristic of this
form is its use of cost and revenue elements. It provides you with a profitability report that
is permanently reconciled with financial accounting.
Functional Solution Design
Organization Structure - Operating Concern:
Confidential Document Page 44 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Represents a part of an organization for which the sales market is structured in a uniform manner By
setting off the costs against the revenues, you can calculate an operating profit for the individual
market segments, which are defined by a combination of classifying characteristics (such as Customer,
customer group, country, or distribution channel). You can assign multiple controlling areas to one
operating concern.
Operating Concern SYPL will be defined for Synokem Pharmaceuticals Ltd and DNV Overseas Impex
Pvt Ltd.
Synokem will be using both operating concern currency and company code currency for reporting
purpose in profitability analysis.
Operating currency in COPA will be represented as ‘B0’, here in Synokem.
operating concern currency will be INR
Fiscal year variant in COPA will be same as controlling Area.
The characteristics in Profitability Analysis represent those criteria according to which you analyze your
operating results. Valid values of these characteristics are combined to form profitability segments.
Fixed characteristics:
A number of fundamental characteristics are automatically predefined in every operating concern.
These include the product, company code, billing type, sales order, customer, and the controlling area,
to name a few. You can define your operating concerns by using characteristics that already exist in
other applications.
Customer-Defined Characteristics:
If the characteristic categories are insufficient for your needs, you can define completely new
characteristics from scratch for exclusive use in Profitability Analysis.
Synokem will use the following characteristics
S. NO Characteristics
1 Sales Person
2 Agent
3 CO Area
4 Company Code
5 Plant
6 Sales Organization
7 Division
8 Distribution Channel
9 Profit Center
Confidential Document Page 45 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
10 Product
11 Customer
12 Billing Type
13 Sales Order
Characteristic Derivation:
Characteristic derivation is the attempt to determine the characteristic values for all CO-PA
characteristics in a given profitability-relevant business transaction. The characteristic values that are
transferred automatically are used to determine other logically dependent characteristics. For this, the
system can access information contained in the source document as well as that existing outside it.
The profitability segment to which the account assignments are to be made is determined using the
quantity of characteristic values drawn from characteristic derivation.
For Synokem Characteristics – Sales Person and Area, Zone will be derived from the Customer master by
using derivation rules
Profitability Segments
The combination of the values for the characteristics in an operating concern is called a Profitability
Segment. These are object within Profitability Analysis to which costs and revenues are assigned. A
profitability segment corresponds to a market segment. You can calculate the profitability of a
profitability segment by setting off its sales revenues against its costs. A profitability segment in an
operating concern is defined by a combination of characteristic values.
Characteristic Description
Sales Person
Agent
CO Area
Company Code
Plant All the characteristics will be defined as Segment level
characteristics
Profit Center
Product
Customer
Billing Type
The following characteristics are not used to form the profitability segments:
Sales order
Confidential Document Page 46 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
Sales order item
Order
Cost Object
Value Fields
Question: "What performance measures do I want to track and analyze?"
Examples: Gross Sales, Discounts, Cost-of-Sales.
Synokem will use below format for Contribution margin reporting. Value fields will be based on the
below table.
S. No Value Field
1 Sales Quantity
2
Sales Revenue
3 Net Sales Revenue
4 Cost of goods sold (COGS)
5 Production variance
6 Discount
7
Rebate
8 Admin, Selling and Finance Cost
9 Net Profit
This part can be changed at the time of realization phase as per management requirement
Value Flow in Profitability analysis
Once Profitability Analysis is active, you can transfer the following actual postings to profitability
segments:
Automatic transfer of billing document data from SD.
Direct postings from Financial Accounting (FI).
Settlement of Production Orders.
Period-based allocations, such as the transfer of overhead.
Automatic transfer of billing document data from SD
The actual postings represent the most important source of information in CO-PA. In CO-PA (Costing
Based,) the COGS entry as well as the Sales entry flow only at the time of Billing and not separately at
the time of Delivery and Billing.
Confidential Document Page 47 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
CO
V NO POSTING PA
A
L
U Inventory Inventory
E - Finished Product (FG)
119430
F Stock
4,975.00-
L
O FI
W
Cost of Goods Sold
462002
Change Stock
4,975.00
Business Goods Issue
process
MM
The goods issue is triggered by a delivery in SD. This affects the values in Materials
Management and Financial Accounting. Balance sheet and stock change postings are made in
FI when the goods issue is posted according to a price in material master.
Note that the goods issue posting does not cause any data to be posted in costing-based CO-
PA. The cost of goods sold is only transferred to costing-based
CO-PA when the billing document is transferred.
CO
V PA
A
L
U
E
FI Receivables Standard Cost of Goods
… Price Sold
F
L 10,000 +
O Product
W Sales Cost
810000 Estimate
10,000 -
Business Sales/Billing
process
SD
The following data is transferred from billing document to CO-PA.
Revenues
Sales deductions (shipping, discounts, and so on)
The cost of goods sold is only transferred to costing-based CO-PA when the billing document
is transferred according to a price in material master and a material cost estimate valid on
the date of a delivery.
Direct postings from Financial Accounting and Materials Management
You can transfer direct primary postings from Financial Accounting (FI) and Materials Management (MM)
to profitability segments.
Confidential Document Page 48 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
V
A
L
U
E
F FI
L
O
W
CO
PA
You assign the values to a profitability segment directly in the FI posting transaction. There
you can call up a special assignment dialog box for each posting line by clicking the Prof.
Segment field.
In this dialog box the system displays the characteristics that you can choose from the
operating concern you are working in
Typical business transactions for which a profitability segment is found automatically
include:
Price differences that are posted in purchasing due to differing order prices or differing
prices in invoice receipt (as period costs).
Revaluation of material stocks (as period costs) - expenses or revenues.
Settlement of Production Variances
When you settle the Production Order, you can transfer Production Variance to separate value fields in
Profitability Analysis
Goods Issues
of materials from
CO stock
PC ‘Production Order’
Product Costing Plan costs + Actual costs
...
... Confirmations/
activity allocation
Delivery
Variances
to stock
Deliver
Confidential Document Page 49 of 53 CO
Calculate FI
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
variances
MM Business Blueprint Document
Controlling Settlement
Warehouse CO
PA
Allocation from Cost Center
Admin, Selling and Finance costs will be transferred from Cost Center Accounting to COPA. The process
for this allocation is currently being discussed.
Below table shows source for actual value flows in COPA
S. No. Value Fields Source
1 Sales Quantity SD – Billing document
2 Sales Revenue SD – Condition type
3 Sales discount SD – Condition type
4 Net Sales Revenue NA
5 Cost of goods sold (COGS) SD - Condition type
7 Production variance Product Costing
10 Discount SD – Condition type
11 Rebate SD – Condition type
12 Selling Marketing, Admin, Finance Expenses Cost Center accounting
13 Net Profit
Planning
Planning in Profitability Analysis allows you to plan sales, revenue and profitability data for any
selected profitability segments. You can display the entire planning process of your company in
different ways, depending on your business demands.
Synokem can use Planning concept in COPA for Revenue Planning.
Top –Down Distribution
In Profitability Analysis, sales revenues, sales deductions, and costs of goods manufactured are
generally stored at the customer/product level. However, many business transactions - such as freight
invoices, insurance expenses, or advertising - cannot easily be assigned to such a detailed level in CO-
PA. Consequently, these need to be posted at a summarized level, such as the division, sales
organization, or company code level.
Top-down distribution of actual data is a periodic function that lets you distribute this aggregated data
to more detailed levels in CO-PA on the basis of reference information (such as the data from the
previous year).
Confidential Document Page 50 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
You can perform distribution in any of the following ways:
You can select values posted to any profitability segments and in any value fields, and then
distribute this data to a specified distribution level.
You can use existing actual or planning data as the basis for this distribution. The basis can
be the values in a single value field (such as revenue) or a calculated value (such as
contribution margin 1) or occur by value fields.
You can select several record types for the data to be distributed and the reference data.
You can summarize the different record types in the reference data, which means that the
reference data is treated as if it had the same record type.
You can also distribute period by period, or aggregate the period values to smooth out
variances.
Synokem will be using Top-Down distribution method to distribute production order
variance, Sales and Marketing Expenses.
Valuation strategy
Cost of goods manufactured for every finished product need to be transferred to COPA to obtain
contribution margin. For this existing standard cost estimate of that particular period will be
transferred to COPA for valuation of finished products
Line Item Reporting
A report based on line items allows you to display the line items you have in Profitability Analysis. This
type of report always reads the line items directly. Unlike the profitability report, it never accesses
data from the segment level. In this way, you can analyze characteristics that are contained in line
items but were locked out of the segment level in Customizing under segment-level characteristics.
Confidential Document Page 51 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
It makes most sense to use reports based on line items when you analyze a relatively small amount of
line items, such as when analyzing sales for a given day. More extensive analyses cause very long
runtimes.
In contrast to line item lists, which offer you only a limited number of functions, reports based on line
items allow you to use all of the navigation and display functions available in drilldown reporting.
Process Steps Detailed Requirements and Solutions
Process Steps TCODE Expected Result
Maintain Realignments KEND Posted data is corrected
Top down distribution KE28 Costs are distributed
Line item display actual KE24 Line item data is displayed
data
Execute COPA report KE30 Report is displayed
Change COPA report KE32 Report is changed
7. SAP Reports
S. No. Transaction Code Description
Cost Element wise Controlling Documents:
1 KSB5
Actual Costs
2 S_ALR_87013611 Cost Centers: Actual/Plan/Variance
3 S_ALR_87013612 Cost Centers Actuals
4 S_ALR_87013623 Cost Centers: Quarterly Comparison
5 S_ALR_87013624 Cost Centers: Fiscal Year Comparison
6 S_ALR_87013625 Cost Centers: Actual/Target/Variance
7 S_ALR_87013627 Cost Centers: Variances
8 KSB1 Cost Centers: Actual Line Items
9 S_ALR_87012993 Internal Orders: Actual/Plan/Variance
10 S_ALR_87012994 Internal Orders: Current Period/Cumulative
11 S_ALR_87012997 Cost Elements by Internal Order
12 S_ALR_87013001 Internal Orders: Actual Yearly Comparison
13 KOB1 Internal Orders: Actual Line Items
14 S_ALR_87013011 Internal Orders: Actual/Plan/Price Variance
15 KOC4 Cost Analysis
16 S_ALR_87099932 Variances Between Costing Runs
17 S_P99_41000111 Analyze/Compare Material Cost Estimates
18 CKAPP01 Display Materials to be Costed
19 S_ALR_87013139 Target/Actual/Production Variances
Target/Actual Comparison Variance
20 S_ALR_87013143
Analysis
21 S_ALR_87013148 Variance Categories of Production Orders
22 S_ALR_87013151 Production Order Actual WIP
23 S_ALR_87013095 Target/Actual/Production Variance
Confidential Document Page 52 of 53
Synokem Pharmaceuticals Limited
Business Blueprint Document
Controlling
24 S_ALR_87013098 Production Variance Categories
25 S_ALR_87013094 Actual Production Costs
26 KE5Z Profit Center: Actual Line Items
BBP Process Sign Off
Power Project
Business Process Consultant - Project Manager -
Users/Core Team Manager
CorporateServe CorporateServe
Owner (Synokem)
Members
Mr. Sumit Mr. Danveer Mr. Anup Pratap
Mr. Sumit Gupta Singh
Mr. Raj Kumar
Singh
Sharma
Confidential Document Page 53 of 53
You might also like
- Optional Unit 1 AssignmentDocument19 pagesOptional Unit 1 AssignmentTriet NguyenNo ratings yet
- Kraft-Foods Case StudyDocument18 pagesKraft-Foods Case StudyLevi Lazareno Eugenio50% (2)
- An Ethics Role Playing Case: Stockholders Vs StakeholdersDocument2 pagesAn Ethics Role Playing Case: Stockholders Vs StakeholderssNo ratings yet
- FDS0019 GAP0080 O2C GTS Commercial InvoiceDocument22 pagesFDS0019 GAP0080 O2C GTS Commercial Invoicesomusatish100% (1)
- Document: Uses of Special Period in SAP PDFDocument9 pagesDocument: Uses of Special Period in SAP PDFswainsatyaranjanNo ratings yet
- SAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsFrom EverandSAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsNo ratings yet
- International Trade - Chapt 9 Imports Tariff/ Quotas For Imperfect MarketsDocument10 pagesInternational Trade - Chapt 9 Imports Tariff/ Quotas For Imperfect MarketsglenlcyNo ratings yet
- Taller SAP Actividad 3Document67 pagesTaller SAP Actividad 3Daniel Ricardo Estupiñan Guzman100% (1)
- 1573561440-BP Conversion GuideDocument40 pages1573561440-BP Conversion GuideRuben CampoverdeNo ratings yet
- Brazil Accounting Tax Processes v1 PDFDocument163 pagesBrazil Accounting Tax Processes v1 PDFGustavo GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- 250open Text VIM For SAP SolutionsDocument2 pages250open Text VIM For SAP SolutionsTheo van BrederodeNo ratings yet
- Sap Fico Blue PrintDocument57 pagesSap Fico Blue Printuvtechdhananjay05100% (1)
- New Asset Accounting IntroductionDocument7 pagesNew Asset Accounting IntroductionCasimiro HernandezNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Refx Configuration Document PRDocument110 pagesToaz - Info Refx Configuration Document PRnew gstNo ratings yet
- Demo Script Planning and Consolidation (MS) Overview Demo: General InformationDocument44 pagesDemo Script Planning and Consolidation (MS) Overview Demo: General InformationbrainNo ratings yet
- Document and Reporting Compliance (5XU)Document43 pagesDocument and Reporting Compliance (5XU)Ind HashNo ratings yet
- Ifrs at Sap: Transition To IFRS: Implementation of IFRS As An Additional Set of Accounting Standards Alongside US GAAPDocument29 pagesIfrs at Sap: Transition To IFRS: Implementation of IFRS As An Additional Set of Accounting Standards Alongside US GAAPlsudhakarNo ratings yet
- IBM Review of Simple Finance 3.0 Process: Accounts ReceivableDocument9 pagesIBM Review of Simple Finance 3.0 Process: Accounts ReceivableMOORTHYNo ratings yet
- Define Functional AreaDocument1 pageDefine Functional AreaDipeshNo ratings yet
- Year End Closing Activities in Sap Fi CoDocument30 pagesYear End Closing Activities in Sap Fi Coansonyu305No ratings yet
- 3 Way Match Process 1Document3 pages3 Way Match Process 1mkv428No ratings yet
- Ycoa Accdet Docu UsDocument72 pagesYcoa Accdet Docu UsSrinivas N GowdaNo ratings yet
- Accounts Payable: Global Process Management SystemDocument89 pagesAccounts Payable: Global Process Management SystemcybervistaNo ratings yet
- Funds Management Overview: © 2005 Intelligroup, IncDocument49 pagesFunds Management Overview: © 2005 Intelligroup, Incganesh gadeNo ratings yet
- SD RevRec MigrationDocument11 pagesSD RevRec MigrationAlina Cristina VranceanuNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of FICODocument149 pagesConceptual Design of FICOShree RamNo ratings yet
- COPADocument167 pagesCOPAAylene FloresNo ratings yet
- Project Management (PS) : Curriculum: Introduction To S/4HANA Using Global BikeDocument36 pagesProject Management (PS) : Curriculum: Introduction To S/4HANA Using Global BikeJuliusCesnakauskasNo ratings yet
- Fertilizers and Chemicals Travancore LTD: FACT ForwardDocument35 pagesFertilizers and Chemicals Travancore LTD: FACT ForwardfharooksNo ratings yet
- Sanad Wfrice Master List: SR No Object Id Object Object Purpose Tcode Object Sub CategoryDocument12 pagesSanad Wfrice Master List: SR No Object Id Object Object Purpose Tcode Object Sub CategoryAmr IsmailNo ratings yet
- BH5 S4hana1611 BPD en XXDocument23 pagesBH5 S4hana1611 BPD en XXIván Andrés Marchant NúñezNo ratings yet
- Column Fields Field: Additional Navigational AttributesDocument25 pagesColumn Fields Field: Additional Navigational AttributesSajanAndyNo ratings yet
- SAP Credit ManagementDocument6 pagesSAP Credit ManagementAvinash MalladhiNo ratings yet
- S4HANA RIG UX Lessons Learned 1909 PDFDocument42 pagesS4HANA RIG UX Lessons Learned 1909 PDFadelangel70No ratings yet
- S/4HANA Configuration Case Phase I - Handbook: Product Motivation PrerequisitesDocument75 pagesS/4HANA Configuration Case Phase I - Handbook: Product Motivation PrerequisitesDianPramana100% (2)
- Group Reporting (FIN-CS) : Public Document Version: SAP S/4HANA 2022 (October 2022) - 2022-10-03Document636 pagesGroup Reporting (FIN-CS) : Public Document Version: SAP S/4HANA 2022 (October 2022) - 2022-10-03Aymen AddouiNo ratings yet
- 2 Our HANA Capabilities PDFDocument17 pages2 Our HANA Capabilities PDFRueban manoharNo ratings yet
- Archit BBP CO V1 30.11.2010Document202 pagesArchit BBP CO V1 30.11.2010Subhash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Credit Limit On Customer Level v2Document9 pagesCredit Limit On Customer Level v2Durga SNo ratings yet
- Transition To The New Planning Solution in S/4Hana On PremiseDocument11 pagesTransition To The New Planning Solution in S/4Hana On PremiseNityaNo ratings yet
- HSPL Fi 06 House Bank v1.0Document18 pagesHSPL Fi 06 House Bank v1.0Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Master Data Mass MaintenanceDocument12 pagesMaster Data Mass MaintenancePaul AlcosNo ratings yet
- SAP CO PPT'sDocument5 pagesSAP CO PPT'sTapas BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- ProjectPortfolioManagement CommercialProjectManagementDocument4 pagesProjectPortfolioManagement CommercialProjectManagementmohammad shaikNo ratings yet
- SAP FSCM Credit Management Config StepsDocument3 pagesSAP FSCM Credit Management Config StepsDamodar Naidu PaladuguNo ratings yet
- Vendor Recognition White PaperDocument9 pagesVendor Recognition White PaperAvinash MalladhiNo ratings yet
- Nota para Localização PDFDocument37 pagesNota para Localização PDFmarcosoliversilvaNo ratings yet
- SFIN - Documents Replication in CFINDocument25 pagesSFIN - Documents Replication in CFINmadhu100% (1)
- Sap (Fico) : SAP FI-Organization StructureDocument2 pagesSap (Fico) : SAP FI-Organization StructureChandrashekher EdumalaNo ratings yet
- Unity FSP MFG 06 V01R00Document83 pagesUnity FSP MFG 06 V01R00sowjanyaNo ratings yet
- Project System Module (PS) : CSU ChicoDocument38 pagesProject System Module (PS) : CSU ChicoKumar Venkat SNo ratings yet
- Design Document Co Profitabilty Analysis Author/ApproverDocument19 pagesDesign Document Co Profitabilty Analysis Author/ApproverAncuţa CatrinoiuNo ratings yet
- Transaction Code CESU Business Process Master List - FICODocument4 pagesTransaction Code CESU Business Process Master List - FICOJit GhoshNo ratings yet
- Ficobbpfinalone10022011 120815114154 Phpapp02Document146 pagesFicobbpfinalone10022011 120815114154 Phpapp02prashantaiwaleNo ratings yet
- 1qm S4hana1909 BPD en UsDocument46 pages1qm S4hana1909 BPD en UsMarceloNo ratings yet
- j62 S4hana2021 BPD en BRDocument76 pagesj62 S4hana2021 BPD en BRSandra Amadi100% (1)
- SAP BiddingDocument36 pagesSAP BiddingLakhya Pratim BaruahNo ratings yet
- Migrating Classic GL To S4 HANA Finance1Document10 pagesMigrating Classic GL To S4 HANA Finance1shaiNo ratings yet
- 1MV S4hana1909 BPD en XXDocument14 pages1MV S4hana1909 BPD en XXBiji RoyNo ratings yet
- Fica ExcelDocument171 pagesFica ExcelYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- OpenText VIM - Rollout Criteria and Event Linkages - SAP BlogsDocument9 pagesOpenText VIM - Rollout Criteria and Event Linkages - SAP BlogsDavid CoelhoNo ratings yet
- SAP GST Questionnaire-MesprosoftDocument3 pagesSAP GST Questionnaire-Mesprosoftnagesh99No ratings yet
- Sales Area: S / 4 HANA ContentDocument34 pagesSales Area: S / 4 HANA ContentEnrique Israel Flores ZúñigaNo ratings yet
- Detailed SAP Interface Design Fundamental DocumentDocument4 pagesDetailed SAP Interface Design Fundamental Documentamitava_bapiNo ratings yet
- First Nature, Second Nature and Metropolitan LocationDocument32 pagesFirst Nature, Second Nature and Metropolitan LocationCristóbal GuerraNo ratings yet
- Bechelor ThesisDocument71 pagesBechelor ThesisLê KiênNo ratings yet
- AppendixDocument4 pagesAppendixJayanga JayathungaNo ratings yet
- Multiattribute Utility FunctionsDocument25 pagesMultiattribute Utility FunctionssilentNo ratings yet
- Corporate Level Strategy Addresses The Entire Strategic Scope of The FirmDocument19 pagesCorporate Level Strategy Addresses The Entire Strategic Scope of The FirmOpshora AliNo ratings yet
- Diamond Strategy ModelDocument3 pagesDiamond Strategy ModelMERINANo ratings yet
- Economics of Strategy: The Vertical Boundaries of The FirmDocument49 pagesEconomics of Strategy: The Vertical Boundaries of The FirmVanessa HartonoNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Freedom To Trade by Edward L. HudginsDocument9 pagesThe Fundamental Freedom To Trade by Edward L. HudginsmirunelutuNo ratings yet
- Basic Economic ProblemsDocument146 pagesBasic Economic ProblemsRichard DancelNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Practice 101Document18 pagesWeek 7 Practice 101David LimNo ratings yet
- CH - 11 - Introduction To Supply Chain ManagementDocument72 pagesCH - 11 - Introduction To Supply Chain ManagementYogesh GirgirwarNo ratings yet
- Simu GuidelinesDocument54 pagesSimu Guidelinesniket mehtaNo ratings yet
- W08 - Managerial Decisions in Competitive Markets-FJODocument41 pagesW08 - Managerial Decisions in Competitive Markets-FJOGhasan Rasendriya PutraNo ratings yet
- Retail Management Black BookDocument82 pagesRetail Management Black BookShahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio Analysis As Determinant of Profitability in African Banking IndustryDocument10 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis As Determinant of Profitability in African Banking IndustryjaneNo ratings yet
- Analisis General CompetitivoDocument12 pagesAnalisis General CompetitivoluisNo ratings yet
- 1 Business ActivityDocument4 pages1 Business ActivityAnalía gonzalezNo ratings yet
- An Analysis and Valuation Of: Rak Ceramics (Bangladesh) LTDDocument30 pagesAn Analysis and Valuation Of: Rak Ceramics (Bangladesh) LTDFarzana Fariha LimaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Sees1Document19 pagesManagerial Economics Sees1doraline0911100% (2)
- Answer Key Bank Soal Micro UAS - Tutorku - 2020Document128 pagesAnswer Key Bank Soal Micro UAS - Tutorku - 2020Vriana ZenNo ratings yet
- XA Risk Reward RatioDocument4 pagesXA Risk Reward Ratiocarlos.ernesto.aa2023No ratings yet
- Performance Based PayDocument22 pagesPerformance Based PaySonam GondlekarNo ratings yet
- Kojima, K., Ozawa, T. (1984), Micro - and Macro-Economic Models of Direct Foreign InvestmentDocument21 pagesKojima, K., Ozawa, T. (1984), Micro - and Macro-Economic Models of Direct Foreign InvestmentGabriel MerloNo ratings yet
- MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS NOTES Unit-5 MBA 1stDocument6 pagesMANAGERIAL ECONOMICS NOTES Unit-5 MBA 1stRUBA NASIMNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: Cheat SheetDocument110 pagesManagerial Economics: Cheat SheetSushmitha KanasaniNo ratings yet
- Potato Corner Pestle AnalysisDocument2 pagesPotato Corner Pestle AnalysisJeremia DaNo ratings yet