Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Chemistry 2 Module 1: Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Name: - Section: - Exercise 1
General Chemistry 2 Module 1: Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Name: - Section: - Exercise 1
Uploaded by
SamhaeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Chemistry 2 Module 1: Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Name: - Section: - Exercise 1
General Chemistry 2 Module 1: Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Name: - Section: - Exercise 1
Uploaded by
SamhaeCopyright:
Available Formats
GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2
MODULE 1: INTERMOLECULAR FORCES OF ATTRACTION
Name: _______________________________ Section: ________________
Exercise 1
A. Read each question. Give what is being asked in each number.
1. Which of the substances, Ar, Hg, or I2 is most likely to be a gas at room temperature and
atmospheric pressure? Explain the basis of your answer. (3 points)
2. Which of the following molecules can experience dipole-dipole forces? Support your answer.
(2 points each)
a. NF3
b. CO2
c. CH3Cl
3. Which of the following pure substances can participate in hydrogen bonding? Support your
answer. (2 points each)
a. H2O
b. NH3
4. The physical properties of a substance depend on its intermolecular forces. The STRONGER
the forces between particles, …
a. the (higher, lower) the melting point
b. the (higher, lower) the boiling point
c. the (higher, lower) the vapor pressure
d. the (higher, lower) the viscosity
5. Arrange the following substances in order of increasing strength of intermolecular forces:
H2O, He, I2, and N2. (3 points)
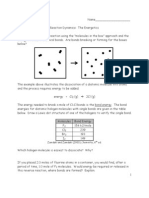
B. Study the table below. Put a check mark if the specific type of intermolecular force is present
in the given substances. (There can be more than 1 check mark for each substance.)
London Dispersion Dipole – dipole
Substance Hydrogen Bonding
Force Force
1. HCl
2. H2O
3. CH4
4. Kr
5. SO2
-STI/alma
You might also like
- Intermolecular Forces Worksheet With KeyDocument4 pagesIntermolecular Forces Worksheet With KeyNoreen ClarkNo ratings yet
- Print 1 PDFDocument2 pagesPrint 1 PDFBernadette NaulNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument3 pagesIntermolecular ForcesJoseph renz AndayaNo ratings yet
- 2021 IMF Packet WelchDocument9 pages2021 IMF Packet WelchbobNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Periodicity Worksheet PDFDocument5 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Periodicity Worksheet PDFAlejandra Barrera MNo ratings yet
- IMF Answer Keys Revised 2014Document6 pagesIMF Answer Keys Revised 2014Monia AliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document3 pagesLesson 4rhaineNo ratings yet
- Physical Science11 Q1 MODULE 6 Edited 08082020Document20 pagesPhysical Science11 Q1 MODULE 6 Edited 08082020Jennie Kim0% (1)
- GR 11 Physical Sciences P2 (English) November 2022 Question PaperDocument12 pagesGR 11 Physical Sciences P2 (English) November 2022 Question PaperpeterNo ratings yet
- HW Packet / Unit 7Document3 pagesHW Packet / Unit 7api-368121935No ratings yet
- Topic 4 Intermolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesTopic 4 Intermolecular ForcesNgoc TranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Problem Set 1Document2 pagesChapter 1 Problem Set 1Wendy SoyosaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry AssignmentDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry AssignmentCumar MaxamuudNo ratings yet
- PHYS SCIENCES P2 GR11 NOV2020 - English Exam Past PaperDocument18 pagesPHYS SCIENCES P2 GR11 NOV2020 - English Exam Past PaperScott FaurholmNo ratings yet
- End of IMF WorksheetDocument2 pagesEnd of IMF WorksheetAnshu MovvaNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Secunderabad: For The Questions (6) To (10), Find Out The Option From (A), (B), (C), (D)Document5 pagesDelhi Public School Secunderabad: For The Questions (6) To (10), Find Out The Option From (A), (B), (C), (D)Vedant SinghalNo ratings yet
- SCORING: 1: Less Than 65% // 2: 65-75% // 3:76-90% // 4: 91-100Document5 pagesSCORING: 1: Less Than 65% // 2: 65-75% // 3:76-90% // 4: 91-100Danna AguirreNo ratings yet
- Phys Sciences p2 QP Gr11 Nov2023 - English DDocument24 pagesPhys Sciences p2 QP Gr11 Nov2023 - English DeducationsizweNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Provincial Examination Physical Sciences P2 (English) June 2023 Question PaperDocument7 pagesGrade 11 Provincial Examination Physical Sciences P2 (English) June 2023 Question PaperDick KaliatiNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Force Worksheet KeyDocument3 pagesIntermolecular Force Worksheet KeyBill alfonsoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1Document1 pageTutorial Chapter 1Afif Mah HassanNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Provincial Examination Physical Sciences P2 June 2017 Question PaperDocument16 pagesGrade 11 Provincial Examination Physical Sciences P2 June 2017 Question PaperNadia MurrayNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Intermolecular ForcesDocument2 pages3.4 Intermolecular ForcesRuoQi LeeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet QP 1Document3 pagesWorksheet QP 1Muhammed Muhasin. KNo ratings yet
- MARCH CONTROL TESTDocument11 pagesMARCH CONTROL TESTtabisamzalisiNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document11 pagesScience 10GeminiNo ratings yet
- Long Test ImfDocument1 pageLong Test ImfJoshua RomeaNo ratings yet
- Inter HWKDocument5 pagesInter HWKMohammed Elias AlamNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences P2 Sup 2018Document16 pagesPhysical Sciences P2 Sup 2018onalennapoha263No ratings yet
- Physc SC11-P2 Nov 2012 (Eng)Document24 pagesPhysc SC11-P2 Nov 2012 (Eng)Motlatso MaakeNo ratings yet
- 0609 GR10 FW (Eng) P2 DHDocument9 pages0609 GR10 FW (Eng) P2 DHbenjaminvanzyl996No ratings yet
- Test 2 Alternate AnswersDocument5 pagesTest 2 Alternate AnswersJames WongNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Section 2 Reaction TypesDocument2 pagesCH 6 Section 2 Reaction Typeskayla behlerNo ratings yet
- Ap Chemistry Unit 5 KeyDocument10 pagesAp Chemistry Unit 5 Keycookiesadries629No ratings yet
- 1 - Inter Molecular Forces Dipole MomentDocument4 pages1 - Inter Molecular Forces Dipole Momentjasonmichael75No ratings yet
- Year 11 2019 Chemistry QuizDocument9 pagesYear 11 2019 Chemistry Quizuyenkhuu06No ratings yet
- Class Xi Holiday Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesClass Xi Holiday Assignment PDF1234567No ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument4 pagesBalancing Chemical EquationsAndreNo ratings yet
- LAB#5 - Getting To Know Some Elements Students ReportDocument5 pagesLAB#5 - Getting To Know Some Elements Students Reportmario josephNo ratings yet
- PHYS SCIENCES P2 GR11 MEMO NOV2020 English Exam Past PaperDocument32 pagesPHYS SCIENCES P2 GR11 MEMO NOV2020 English Exam Past PaperScott FaurholmNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.1 Intermolecular Forces: Liquids, Solids, and Phase ChangesDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1.1 Intermolecular Forces: Liquids, Solids, and Phase ChangesRisciella 18No ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 10Document10 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 10tabisamzalisiNo ratings yet
- VII-Science-Matter and Chemical FormulaeDocument9 pagesVII-Science-Matter and Chemical FormulaeVrusti PatelNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Inorganic ChemistryDocument1 pageTutorial 1 Inorganic ChemistryDhania SorfinaNo ratings yet
- JR. CHEMISTRY Important QuestionsDocument8 pagesJR. CHEMISTRY Important QuestionsRocky Water0% (1)
- Mahgoub's Questions BankDocument31 pagesMahgoub's Questions BankYehia IbrahimNo ratings yet
- SNC2D - ReviewDocument4 pagesSNC2D - ReviewZeenat ShahidullahNo ratings yet
- Test Icse ChemistryDocument4 pagesTest Icse Chemistryvishudhanandchoudhary9056No ratings yet
- Science 10 Q4 Module 3Document21 pagesScience 10 Q4 Module 3Erika Nina Ceralde Granado100% (1)
- Zumdahl and Zumdahl (2003) Chemistry, 6 EdDocument4 pagesZumdahl and Zumdahl (2003) Chemistry, 6 Edpartho143No ratings yet
- Physical Science - Grade 11 Midyear Examination - Paper 2 14 JUNE 2021Document9 pagesPhysical Science - Grade 11 Midyear Examination - Paper 2 14 JUNE 2021soopfaceNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS - Intermolecular Forces 2021Document2 pagesANSWERS - Intermolecular Forces 2021Mikaela SteyerNo ratings yet
- Cbse Sample Paper For Class 11 ChemistryDocument11 pagesCbse Sample Paper For Class 11 ChemistryAshutosh RautNo ratings yet
- Chem Halfyrly 2020Document6 pagesChem Halfyrly 2020ShraddhaNo ratings yet
- Gr11 Phy P2 June 2017 Question PaperDocument16 pagesGr11 Phy P2 June 2017 Question Paperyoungmarley457No ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Gen Chem 1 Module 3 and 4Document2 pages2nd Quarter Gen Chem 1 Module 3 and 4DaveNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test in Physical Science - Gr.11Document3 pagesMastery Test in Physical Science - Gr.11kert mendozaNo ratings yet
- Science 2Document17 pagesScience 2Ralph NilloNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Chemical Equations and Hydrate Lab ReportDocument10 pagesUnit 3 Chemical Equations and Hydrate Lab ReportSophie DanhNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)