Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Methodology 2.1 Modeling: Pak. J. Engg. Appl. Sci. Vol. 25, July., 2019
Methodology 2.1 Modeling: Pak. J. Engg. Appl. Sci. Vol. 25, July., 2019
Uploaded by
aunbhuttaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- JSSG-2006 1 PDFDocument1 pageJSSG-2006 1 PDFaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- PJE VOL2 Jul2022Document20 pagesPJE VOL2 Jul2022aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Associate Professor Alex NG Researcher ProfilesDocument6 pagesAssociate Professor Alex NG Researcher ProfilesaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Fig. 14: FRF For Beam With L 300 M and H 2 M: 3.2.1 Damping Ratios and Quality FactorDocument1 pageFig. 14: FRF For Beam With L 300 M and H 2 M: 3.2.1 Damping Ratios and Quality FactoraunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Rosettes: Ansys Composite Preppost Modeling Composites The Simple WayDocument9 pagesRosettes: Ansys Composite Preppost Modeling Composites The Simple WayaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- 02 Composite IntroductionDocument68 pages02 Composite IntroductionaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- 08 Oriented Element SetsDocument9 pages08 Oriented Element SetsaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Img 20180927 Wa0050Document1 pageImg 20180927 Wa0050aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- China's Top UniversitiesDocument4 pagesChina's Top UniversitiesaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Completing The E Conditions DossierDocument9 pagesCompleting The E Conditions DossieraunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- CAP 1220 Chapter 14: Flight DocumentationDocument13 pagesCAP 1220 Chapter 14: Flight DocumentationaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Wwwcsdgovpkoutlets 1 AspxDocument8 pagesWwwcsdgovpkoutlets 1 AspxaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Wwwcsdgovpkoutlets 1 AspxDocument8 pagesWwwcsdgovpkoutlets 1 AspxaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Reasons of Collapse of PassengerDocument5 pagesReasons of Collapse of PassengeraunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Air Headquarters Islamabad: (Acas Paca Sectt)Document1 pageAir Headquarters Islamabad: (Acas Paca Sectt)aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Civil Aviation AuthorityDocument5 pagesCivil Aviation AuthorityaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Computational Model and Solver SetupDocument11 pagesComputational Model and Solver SetupaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Headquarters Civil Aviation Authority: (Board of Inquiry)Document3 pagesHeadquarters Civil Aviation Authority: (Board of Inquiry)aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Headquarters Civil Aviation Authority: Reference: HQCAA/2388/511/HR (Inq) Date: December, 2018Document5 pagesHeadquarters Civil Aviation Authority: Reference: HQCAA/2388/511/HR (Inq) Date: December, 2018aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Table 4: General Characteristics of RD-93 EngineDocument11 pagesTable 4: General Characteristics of RD-93 EngineaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Headquarters Civil Aviation Authority: (Board of Inquiry)Document5 pagesHeadquarters Civil Aviation Authority: (Board of Inquiry)aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
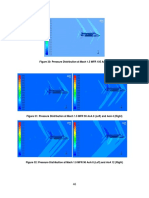
- Figure 30: Pressure Distribution at Mach 1.5 MFR 105 Aoa - 4Document11 pagesFigure 30: Pressure Distribution at Mach 1.5 MFR 105 Aoa - 4aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Thrust CalculationDocument10 pagesThrust CalculationaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Exhaust Nozzle and CharachteristicsDocument12 pagesChapter 2: Exhaust Nozzle and CharachteristicsaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
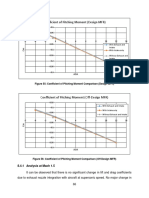
- Coefficient of Pitching Moment (Design MFR) : 8.4.1 Analysis at Mach 1.5Document17 pagesCoefficient of Pitching Moment (Design MFR) : 8.4.1 Analysis at Mach 1.5aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Cad AnalysisDocument10 pagesCad AnalysisaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Ficha Solarnova 550W - EngDocument2 pagesFicha Solarnova 550W - EngHugo AngelesNo ratings yet
- Nokia Optical LAN Solution Brochure enDocument9 pagesNokia Optical LAN Solution Brochure enhugobiarNo ratings yet
- ExternalSpecialist SEARCH RESULTDocument6 pagesExternalSpecialist SEARCH RESULTSea RouteNo ratings yet
- Slide 7 FilterDocument66 pagesSlide 7 Filtermusa100% (1)
- Curriculum Vitae: A. Mohamed RawoofDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: A. Mohamed RawoofAnonymous ETBwIduGiNo ratings yet
- Rubycon (Radial Thru-Hole) YXG SeriesDocument3 pagesRubycon (Radial Thru-Hole) YXG SeriesOndrej LomjanskiNo ratings yet
- File 634 548Document20 pagesFile 634 548Dmitry PakhatovNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Provision - Electrical Installation ContinuedDocument2 pagesSolar Power Provision - Electrical Installation ContinuedKassim Nderi100% (1)
- Ealn-7g7k3r R5 enDocument2 pagesEaln-7g7k3r R5 enNguyễn Duy XuânNo ratings yet
- Scientech 2808Document138 pagesScientech 2808Divneet Singh KapoorNo ratings yet
- ADS Momentum Tutorial HL KY Final W09Document18 pagesADS Momentum Tutorial HL KY Final W09Pragash SangaranNo ratings yet
- GPS ArchitectureDocument13 pagesGPS ArchitectureMohamed ArifNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation and Maintenance Grade 11: Learning CompetencyDocument15 pagesElectrical Installation and Maintenance Grade 11: Learning CompetencyCristal Gumalang100% (6)
- Sample: 9.3 ElectromagnetsDocument10 pagesSample: 9.3 ElectromagnetshuongttNo ratings yet
- TMC2660 Datasheet Rev1.07Document52 pagesTMC2660 Datasheet Rev1.07Dima SlNo ratings yet
- CHO Conditional Handover in 5G NRDocument11 pagesCHO Conditional Handover in 5G NRfaiyaz432No ratings yet
- The Life Detection System Using L & S Band Microwaves in Space ApplicationsDocument34 pagesThe Life Detection System Using L & S Band Microwaves in Space Applicationsvenkat addepalliNo ratings yet
- Resume R DeshpandeDocument7 pagesResume R DeshpanderaghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- 2015 Substation Controls - HicksDocument54 pages2015 Substation Controls - HicksDave ChaudhuryNo ratings yet
- Figure 3-1 Basic ROM Structure: Decoder Memory Array 2n Words X M Bits N Input LinesDocument35 pagesFigure 3-1 Basic ROM Structure: Decoder Memory Array 2n Words X M Bits N Input LinesbikisahuNo ratings yet
- Scope of Works/Services 1.1 Comprehensive Maintenance LV Panels Maintenance Schedule S. No Test Carried Out Frequenc yDocument3 pagesScope of Works/Services 1.1 Comprehensive Maintenance LV Panels Maintenance Schedule S. No Test Carried Out Frequenc ySivabalan MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- M100 2G - Quick Start Guide & User Manual - v4 PDFDocument31 pagesM100 2G - Quick Start Guide & User Manual - v4 PDFRicardo AndradeNo ratings yet
- Gmid Methodology Using Evolutionary Algorithms andDocument5 pagesGmid Methodology Using Evolutionary Algorithms andwallace20071No ratings yet
- IP Rating Chart PDFDocument11 pagesIP Rating Chart PDFSameer PawarNo ratings yet
- Two PortDocument11 pagesTwo PortVasu KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- 7MBR100SB060 PDFDocument7 pages7MBR100SB060 PDFRobert CollinsNo ratings yet
- Man FXM FKM MotorsDocument166 pagesMan FXM FKM MotorsPaun AlNo ratings yet
- Proportional Pressure Relief Valve Poppet Type, Direct-Acting, Metric Cartridge - 350 BarDocument4 pagesProportional Pressure Relief Valve Poppet Type, Direct-Acting, Metric Cartridge - 350 BarSakahi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Soda Can Paper - TamannaDocument12 pagesSoda Can Paper - TamannaYoussef NasserNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Medgyn SD6 WirelessDocument3 pagesSpesifikasi Medgyn SD6 WirelessGray Dhaniar RistiyantiNo ratings yet
Methodology 2.1 Modeling: Pak. J. Engg. Appl. Sci. Vol. 25, July., 2019
Methodology 2.1 Modeling: Pak. J. Engg. Appl. Sci. Vol. 25, July., 2019
Uploaded by
aunbhuttaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Methodology 2.1 Modeling: Pak. J. Engg. Appl. Sci. Vol. 25, July., 2019
Methodology 2.1 Modeling: Pak. J. Engg. Appl. Sci. Vol. 25, July., 2019
Uploaded by
aunbhuttaCopyright:
Available Formats
Pak. J. Engg. Appl. Sci. Vol. 25, July.
, 2019
and simulation tools. It is observed that increased
thickness requires higher actuation voltage while
increased length requires less voltage for actuation
[9]. Ansari studied sensitivity of MC with hole
near its fixed end using FEM simulation and found
thickness is directly related to sensitivity of MC of
this design [10]. Hawari studied the effects of
shape over sensitivity of MCs using ANSYS
simulations he obtained maximum deflections and
natural frequencies for 6 different shapes to study
their sensitivity [11]. Paul studied the effects of
substrate materials over sensitivity of MC and
concluded that it should be necessarily accounted Fig. 1: 2 sets of beams showing difference of gap
in sensitive applications [12]. height from beam to substrate
In the study of nonlinear dynamics of MCs
Another 2 sets of sketches are again drawn
it is seen that main cause of these non-linearity are
flexural rigidity especially these are occurring and extruded to remove the materials between the
because of varying lengths of the beams [13-16]. beams to give them the shape of cantilever. At the
end the sketches are drawn and extruded to get the
In the present study, effects of ambient different gap heights and thicknesses to make the
pressures, effects of this pressure over gap heights beams set different. Upper set is given the
of a micro cantilevers array and effects of thickness of 2.25 µm and gap height of 6.3 µm
substrate materials are studied. Modal Analysis while lower set is given gap height of 2.5µm and
and Transient Analysis are performed in Ansys thickness of beams is kept as 2.5µm as its cross-
Workbench to obtain the natural frequencies of the sectional view is shown in Fig.1 and an isometric
MC Array and FRF curves for two models having view is also shown in Fig. 2, difference of
difference in their substrate materials. These thickness and gap heights is indicated by arrows.
natural frequencies provided with a direct
comparison of sensitivity of two models while
FRF curves are analyzed to obtain damping ratios
and quality factors of both models. A comparison
of damping ratios and quality factor has been
made between two models to check for the more
sensitive model on these ambient pressures.
2. Methodology
2.1 Modeling
The comb like structure is modeled in
Ansys Design modeler in micro units. Base of the
structure (substrate) is modeled first so that other
Fig. 2: MCs Array; upper set have thickness of
beams structures may be constructed over it. Base
2.25µm and lower set has thickness of
has dimensions as 1000*300µm while its
2.5µm
thickness is kept as 30µm. 2 similar sets of
sketches are constructed, each set consisting of 4
beams of lengths 800,700,600 and 300 µm. The 2.2 Material Assignment
sketches are extruded later to get two set of beams. Simulations are done over 2 different
All the beams are having same width of 20µm. models having different substrates while the
These sketches are also used to print the faces beams material is same for both models. First
under the beams to get the perfect mesh. The two model is assigned material of N Type silicon while
sets are different in their gap heights from the 2nd is assigned as Quartz. Beams are made of
substrate and the thickness of the beams which polysilicon for both models. The materials
will be described later. properties are given in the table 1 below:
44
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- JSSG-2006 1 PDFDocument1 pageJSSG-2006 1 PDFaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- PJE VOL2 Jul2022Document20 pagesPJE VOL2 Jul2022aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Associate Professor Alex NG Researcher ProfilesDocument6 pagesAssociate Professor Alex NG Researcher ProfilesaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Fig. 14: FRF For Beam With L 300 M and H 2 M: 3.2.1 Damping Ratios and Quality FactorDocument1 pageFig. 14: FRF For Beam With L 300 M and H 2 M: 3.2.1 Damping Ratios and Quality FactoraunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Rosettes: Ansys Composite Preppost Modeling Composites The Simple WayDocument9 pagesRosettes: Ansys Composite Preppost Modeling Composites The Simple WayaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- 02 Composite IntroductionDocument68 pages02 Composite IntroductionaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- 08 Oriented Element SetsDocument9 pages08 Oriented Element SetsaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Img 20180927 Wa0050Document1 pageImg 20180927 Wa0050aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- China's Top UniversitiesDocument4 pagesChina's Top UniversitiesaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Completing The E Conditions DossierDocument9 pagesCompleting The E Conditions DossieraunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- CAP 1220 Chapter 14: Flight DocumentationDocument13 pagesCAP 1220 Chapter 14: Flight DocumentationaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Wwwcsdgovpkoutlets 1 AspxDocument8 pagesWwwcsdgovpkoutlets 1 AspxaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Wwwcsdgovpkoutlets 1 AspxDocument8 pagesWwwcsdgovpkoutlets 1 AspxaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Reasons of Collapse of PassengerDocument5 pagesReasons of Collapse of PassengeraunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Air Headquarters Islamabad: (Acas Paca Sectt)Document1 pageAir Headquarters Islamabad: (Acas Paca Sectt)aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Civil Aviation AuthorityDocument5 pagesCivil Aviation AuthorityaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Computational Model and Solver SetupDocument11 pagesComputational Model and Solver SetupaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Headquarters Civil Aviation Authority: (Board of Inquiry)Document3 pagesHeadquarters Civil Aviation Authority: (Board of Inquiry)aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Headquarters Civil Aviation Authority: Reference: HQCAA/2388/511/HR (Inq) Date: December, 2018Document5 pagesHeadquarters Civil Aviation Authority: Reference: HQCAA/2388/511/HR (Inq) Date: December, 2018aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Table 4: General Characteristics of RD-93 EngineDocument11 pagesTable 4: General Characteristics of RD-93 EngineaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Headquarters Civil Aviation Authority: (Board of Inquiry)Document5 pagesHeadquarters Civil Aviation Authority: (Board of Inquiry)aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Figure 30: Pressure Distribution at Mach 1.5 MFR 105 Aoa - 4Document11 pagesFigure 30: Pressure Distribution at Mach 1.5 MFR 105 Aoa - 4aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Thrust CalculationDocument10 pagesThrust CalculationaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Exhaust Nozzle and CharachteristicsDocument12 pagesChapter 2: Exhaust Nozzle and CharachteristicsaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of Pitching Moment (Design MFR) : 8.4.1 Analysis at Mach 1.5Document17 pagesCoefficient of Pitching Moment (Design MFR) : 8.4.1 Analysis at Mach 1.5aunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Cad AnalysisDocument10 pagesCad AnalysisaunbhuttaNo ratings yet
- Ficha Solarnova 550W - EngDocument2 pagesFicha Solarnova 550W - EngHugo AngelesNo ratings yet
- Nokia Optical LAN Solution Brochure enDocument9 pagesNokia Optical LAN Solution Brochure enhugobiarNo ratings yet
- ExternalSpecialist SEARCH RESULTDocument6 pagesExternalSpecialist SEARCH RESULTSea RouteNo ratings yet
- Slide 7 FilterDocument66 pagesSlide 7 Filtermusa100% (1)
- Curriculum Vitae: A. Mohamed RawoofDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: A. Mohamed RawoofAnonymous ETBwIduGiNo ratings yet
- Rubycon (Radial Thru-Hole) YXG SeriesDocument3 pagesRubycon (Radial Thru-Hole) YXG SeriesOndrej LomjanskiNo ratings yet
- File 634 548Document20 pagesFile 634 548Dmitry PakhatovNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Provision - Electrical Installation ContinuedDocument2 pagesSolar Power Provision - Electrical Installation ContinuedKassim Nderi100% (1)
- Ealn-7g7k3r R5 enDocument2 pagesEaln-7g7k3r R5 enNguyễn Duy XuânNo ratings yet
- Scientech 2808Document138 pagesScientech 2808Divneet Singh KapoorNo ratings yet
- ADS Momentum Tutorial HL KY Final W09Document18 pagesADS Momentum Tutorial HL KY Final W09Pragash SangaranNo ratings yet
- GPS ArchitectureDocument13 pagesGPS ArchitectureMohamed ArifNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation and Maintenance Grade 11: Learning CompetencyDocument15 pagesElectrical Installation and Maintenance Grade 11: Learning CompetencyCristal Gumalang100% (6)
- Sample: 9.3 ElectromagnetsDocument10 pagesSample: 9.3 ElectromagnetshuongttNo ratings yet
- TMC2660 Datasheet Rev1.07Document52 pagesTMC2660 Datasheet Rev1.07Dima SlNo ratings yet
- CHO Conditional Handover in 5G NRDocument11 pagesCHO Conditional Handover in 5G NRfaiyaz432No ratings yet
- The Life Detection System Using L & S Band Microwaves in Space ApplicationsDocument34 pagesThe Life Detection System Using L & S Band Microwaves in Space Applicationsvenkat addepalliNo ratings yet
- Resume R DeshpandeDocument7 pagesResume R DeshpanderaghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- 2015 Substation Controls - HicksDocument54 pages2015 Substation Controls - HicksDave ChaudhuryNo ratings yet
- Figure 3-1 Basic ROM Structure: Decoder Memory Array 2n Words X M Bits N Input LinesDocument35 pagesFigure 3-1 Basic ROM Structure: Decoder Memory Array 2n Words X M Bits N Input LinesbikisahuNo ratings yet
- Scope of Works/Services 1.1 Comprehensive Maintenance LV Panels Maintenance Schedule S. No Test Carried Out Frequenc yDocument3 pagesScope of Works/Services 1.1 Comprehensive Maintenance LV Panels Maintenance Schedule S. No Test Carried Out Frequenc ySivabalan MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- M100 2G - Quick Start Guide & User Manual - v4 PDFDocument31 pagesM100 2G - Quick Start Guide & User Manual - v4 PDFRicardo AndradeNo ratings yet
- Gmid Methodology Using Evolutionary Algorithms andDocument5 pagesGmid Methodology Using Evolutionary Algorithms andwallace20071No ratings yet
- IP Rating Chart PDFDocument11 pagesIP Rating Chart PDFSameer PawarNo ratings yet
- Two PortDocument11 pagesTwo PortVasu KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- 7MBR100SB060 PDFDocument7 pages7MBR100SB060 PDFRobert CollinsNo ratings yet
- Man FXM FKM MotorsDocument166 pagesMan FXM FKM MotorsPaun AlNo ratings yet
- Proportional Pressure Relief Valve Poppet Type, Direct-Acting, Metric Cartridge - 350 BarDocument4 pagesProportional Pressure Relief Valve Poppet Type, Direct-Acting, Metric Cartridge - 350 BarSakahi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Soda Can Paper - TamannaDocument12 pagesSoda Can Paper - TamannaYoussef NasserNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Medgyn SD6 WirelessDocument3 pagesSpesifikasi Medgyn SD6 WirelessGray Dhaniar RistiyantiNo ratings yet