Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
216 viewsHerpes Zoster
Herpes Zoster
Uploaded by
infectionmanHerpes zoster, also known as shingles, is caused by the varicella zoster virus which causes chickenpox. It occurs when the virus reactivates from nerve cells after a previous chickenpox infection. Signs and symptoms include a painful rash that follows nerve pathways and may include fever, headache, or malaise. Diagnosis is usually clinical but Tzanck testing of fluid from blisters can confirm. Treatment with acyclovir within 72 hours can reduce pain and speed healing. Nursing care focuses on preventing infection, managing pain and itching, and patient education.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- BRS PediatricsDocument825 pagesBRS PediatricsJsph Ldrn Rly93% (14)
- Communicable Diseases QuestionsDocument11 pagesCommunicable Diseases QuestionsChelleyOllitro100% (16)
- Chapter 19 Microbial Diseases of The Skin and WoundsDocument8 pagesChapter 19 Microbial Diseases of The Skin and WoundsGRACE MAR CABAHUG100% (1)
- Illustrated Guide To The Homoeopathic Treatment Harbaris Singh Khaneja.01169 3chestDocument7 pagesIllustrated Guide To The Homoeopathic Treatment Harbaris Singh Khaneja.01169 3chestMarija VelkoskiNo ratings yet
- Ob 1.05 Clinical Practice Guidelines On Immunization For Filipino WomenDocument7 pagesOb 1.05 Clinical Practice Guidelines On Immunization For Filipino Womenotartil_niman50% (2)
- Chicken Pox: BSN 1A Aquino, Cadaoas, Edic, Elegino, Dela Cruz, NepomucenoDocument20 pagesChicken Pox: BSN 1A Aquino, Cadaoas, Edic, Elegino, Dela Cruz, NepomucenoRayza MaglaqueNo ratings yet
- Immunocompromised Individuals That Is Characterized by Pain and Vesicular RashDocument2 pagesImmunocompromised Individuals That Is Characterized by Pain and Vesicular Rashadinda sandyaNo ratings yet
- Viral Disease 2021Document76 pagesViral Disease 2021Ageng betaNo ratings yet
- Patient Care Pathogen Reservoir Mode of Transmission: Viral Infections of HumansDocument21 pagesPatient Care Pathogen Reservoir Mode of Transmission: Viral Infections of HumansMark Vincent JanoyogNo ratings yet
- Herpes VirusDocument18 pagesHerpes VirusGrinty Babu BabuNo ratings yet
- Science Class Work 3 Virus and BacteriaDocument4 pagesScience Class Work 3 Virus and BacteriaJenia De La RosaNo ratings yet
- Viral InfectionsDocument110 pagesViral InfectionsMark Anthony CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Common Viral Infections - EditedDocument15 pagesCommon Viral Infections - EditedEcel AggasidNo ratings yet
- Spread Thru Olfactory BulbDocument2 pagesSpread Thru Olfactory BulbleoNo ratings yet
- Varicella Zoster VirusDocument11 pagesVaricella Zoster VirusJayaram SNo ratings yet
- VaricellaDocument4 pagesVaricellasingcojericho11No ratings yet
- Serological Diagnosis of Infectious DiseasesDocument38 pagesSerological Diagnosis of Infectious DiseasesPurple basketNo ratings yet
- Small Pox: General VirologyDocument24 pagesSmall Pox: General VirologyFahad HassanNo ratings yet
- Herpes ZosterDocument2 pagesHerpes ZosterJesselyn San PedroNo ratings yet
- Herpes: ALDEGUER, Gianina Emille HDocument13 pagesHerpes: ALDEGUER, Gianina Emille HgianinaemilleNo ratings yet
- Smallpox A Dead DiseaseDocument42 pagesSmallpox A Dead DiseasefarigNo ratings yet
- Scabies TreatmentDocument8 pagesScabies Treatmentheliana9107No ratings yet
- Dna Virus DNA Virus - Are Mostly Double Stranded DNA: BedielabzDocument2 pagesDna Virus DNA Virus - Are Mostly Double Stranded DNA: BedielabzDale SuanoNo ratings yet
- Viral Diseases With Rashes LastDocument46 pagesViral Diseases With Rashes LastHasan kahhalehNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease (Part 1) : Viral DiseasesDocument11 pagesInfectious Disease (Part 1) : Viral Diseasesmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- Efektivitas Vaksin VaricellaDocument21 pagesEfektivitas Vaksin VaricellaSul FadlyNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument2 pagesNSTPBernadette ArrojoNo ratings yet
- 10 - Herpes ZosterDocument2 pages10 - Herpes Zosteramen shanavasNo ratings yet
- Gyne - Case 11 Lower Genital UTI PDFDocument2 pagesGyne - Case 11 Lower Genital UTI PDFcbac1990No ratings yet
- Chickenpox & ChlamydialDocument5 pagesChickenpox & ChlamydialEliezah RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Notes TuberculosisDocument5 pagesExam 2 Notes TuberculosisElizabeth McKeeNo ratings yet
- 8 Viral Exanthems of ChildhoodDocument9 pages8 Viral Exanthems of ChildhoodErik OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Virology Lecture 7 Viral DiseseDocument21 pagesVirology Lecture 7 Viral Diseseao868598No ratings yet
- Scabies Norwegian Presenting As Erythroderma in HIV A Case ReportDocument4 pagesScabies Norwegian Presenting As Erythroderma in HIV A Case ReportfakhrunnisaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Microbial Diseases of Man Let'S EngageDocument8 pagesLesson 2: Microbial Diseases of Man Let'S EngageJewel Berbano IINo ratings yet
- Disorders of Respiratory Function - Infections and Neoplasms - 2020Document17 pagesDisorders of Respiratory Function - Infections and Neoplasms - 2020Cres Padua QuinzonNo ratings yet
- Varicella Zoster Virus: Two Lives of A Pathogen: Clinical ReviewDocument5 pagesVaricella Zoster Virus: Two Lives of A Pathogen: Clinical ReviewVICKI ANDREANNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases Maam Ervina PDFDocument3 pagesCommunicable Diseases Maam Ervina PDFMary MisolaNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument13 pagesChickenpoxJoanne LagusadNo ratings yet
- Viral InfectionDocument15 pagesViral InfectionSivabalan RajagopalNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument23 pagesChickenpoxLukman HikimNo ratings yet
- Tugas BHS - Inggris Andi Siti KhadijahDocument2 pagesTugas BHS - Inggris Andi Siti Khadijahandi evi febriantiNo ratings yet
- VirologyDocument24 pagesVirologyRohama Qubra 279No ratings yet
- 11 Spirochetes 130520112830 Phpapp02Document61 pages11 Spirochetes 130520112830 Phpapp02Manisanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument2 pagesDengueAhana CherianNo ratings yet
- 22 Varicella Pink BookDocument24 pages22 Varicella Pink BookMohamad Syaikhul IslamNo ratings yet
- 2 Oral UlcersDocument27 pages2 Oral UlcersAhmed Abdelhady Mahmoud AbdelwahedNo ratings yet
- Herpes Zoster - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument6 pagesHerpes Zoster - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDhany karubuyNo ratings yet
- German Measles: DR Anwar AhmadDocument49 pagesGerman Measles: DR Anwar AhmadNoto SusantoNo ratings yet
- AkhdakaaaaaknuqmakaakddaDocument12 pagesAkhdakaaaaaknuqmakaakddaVICKI ANDREANNo ratings yet
- RabiesDocument4 pagesRabiesJamie FabianiaNo ratings yet
- K22 Variola KBKDocument12 pagesK22 Variola KBKedelinNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY - Docx Maam AlapDocument7 pagesCASE STUDY - Docx Maam AlapSam Aquino IINo ratings yet
- LalalaDocument4 pagesLalalanoreka azizahNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox 1Document7 pagesChickenpox 1Nica Joy CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Theory PointersDocument89 pagesTheory Pointerslala byuNo ratings yet
- CHN - Communicable DiseaseDocument117 pagesCHN - Communicable DiseaseGetom NgukirNo ratings yet
- CHICKENPOXDocument32 pagesCHICKENPOXCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Pinkbook: Herpes Zoster - CDCDocument8 pagesPinkbook: Herpes Zoster - CDCRezza PratamaNo ratings yet
- Macules Macules and Papules Papules VesiclesDocument6 pagesMacules Macules and Papules Papules VesiclesLanaAmerieNo ratings yet
- ManasDocument6 pagesManasjose randyNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument2 pagesChickenpoxapi-355830788No ratings yet
- Viral Exanthems ReviewerDocument4 pagesViral Exanthems ReviewerNicole TorralbaNo ratings yet
- NCP CholeDocument2 pagesNCP CholeinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument37 pagesThesisinfectionman100% (1)
- CS NCPDocument2 pagesCS NCPinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Herpes ZosterDocument2 pagesHerpes ZosterinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- CVLSPMS Splash Screen: CVLSPMS Log-In FormDocument22 pagesCVLSPMS Splash Screen: CVLSPMS Log-In ForminfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Dosage & RouteDocument1 pageDosage & RouteinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Clonidine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageClonidine HydrochlorideLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNo ratings yet
- Adult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: ShockDocument1 pageAdult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: ShockinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DysrhythmiaDocument1 pageCardiac DysrhythmiainfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics: by DR - Mohammad Z. Abu Sheikha@Document101 pagesPediatrics: by DR - Mohammad Z. Abu Sheikha@صقر حوران100% (1)
- Cases in Medical EthicsDocument8 pagesCases in Medical EthicsOmarNo ratings yet
- Complicatii PneumonieDocument9 pagesComplicatii PneumonieTatiana JalbaNo ratings yet
- VaricellaDocument38 pagesVaricellapinanoeNo ratings yet
- Airborne Diseases 2Document143 pagesAirborne Diseases 2Karylle Petil100% (1)
- Sample MCQsDocument6 pagesSample MCQsRiyad AliNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mapeh 8Document13 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mapeh 8Jeoffrey ArceNo ratings yet
- NDA - BIO - CH 6 - DiseasesDocument4 pagesNDA - BIO - CH 6 - Diseaseshemanth varsanNo ratings yet
- Nle ReviewerdianemaydeeDocument170 pagesNle ReviewerdianemaydeeSucceed ReviewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Communicable Diseases 2ND Sem 2022 2023Document10 pagesChapter 1 Communicable Diseases 2ND Sem 2022 2023Lovelyn Cantollas EugenioNo ratings yet
- Chicken Fox, Cholera, Dengue FeverDocument2 pagesChicken Fox, Cholera, Dengue FeverAngel Joy CatalanNo ratings yet
- Parent Ver SCH 0 6yrsDocument2 pagesParent Ver SCH 0 6yrsunmundoextranopodcastNo ratings yet
- BETNESOL™ Tablets: Data SheetDocument4 pagesBETNESOL™ Tablets: Data Sheetsmargo171100% (1)
- Chicken PoxDocument6 pagesChicken Poxpiyushsukhija52No ratings yet
- Integumentary NCLEX PointsDocument6 pagesIntegumentary NCLEX PointsBrenda Bravo100% (1)
- UCLA VolunteerDocument23 pagesUCLA VolunteerSpencer NgNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Herpes PDFDocument9 pagesJurnal Herpes PDFIstianah EsNo ratings yet
- Random FactsDocument298 pagesRandom FactsglemeseNo ratings yet
- 9 Daftar Pustaka VaricelaDocument2 pages9 Daftar Pustaka VaricelaAfrina FaziraNo ratings yet
- Toefl Exercise Reading 1Document10 pagesToefl Exercise Reading 1GERIPATLI MALACOPPONo ratings yet
- WHO Med Guide 3 EdnDocument58 pagesWHO Med Guide 3 Ednmsk5in100% (1)
- Communicable Diseases GR.8 HealthDocument40 pagesCommunicable Diseases GR.8 HealthAiza May RosasNo ratings yet
- Mcqs in Rheumatology Inflammatory Arthritis Ms WordDocument10 pagesMcqs in Rheumatology Inflammatory Arthritis Ms WordTanvir Iqbal67% (3)
- (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) : CME For Family Physicians DermatologyDocument15 pages(A) (B) (C) (D) (E) : CME For Family Physicians DermatologyhashemNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument11 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingMelvinFabraÜ100% (1)
Herpes Zoster
Herpes Zoster
Uploaded by
infectionman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
216 views2 pagesHerpes zoster, also known as shingles, is caused by the varicella zoster virus which causes chickenpox. It occurs when the virus reactivates from nerve cells after a previous chickenpox infection. Signs and symptoms include a painful rash that follows nerve pathways and may include fever, headache, or malaise. Diagnosis is usually clinical but Tzanck testing of fluid from blisters can confirm. Treatment with acyclovir within 72 hours can reduce pain and speed healing. Nursing care focuses on preventing infection, managing pain and itching, and patient education.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHerpes zoster, also known as shingles, is caused by the varicella zoster virus which causes chickenpox. It occurs when the virus reactivates from nerve cells after a previous chickenpox infection. Signs and symptoms include a painful rash that follows nerve pathways and may include fever, headache, or malaise. Diagnosis is usually clinical but Tzanck testing of fluid from blisters can confirm. Treatment with acyclovir within 72 hours can reduce pain and speed healing. Nursing care focuses on preventing infection, managing pain and itching, and patient education.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
216 views2 pagesHerpes Zoster
Herpes Zoster
Uploaded by
infectionmanHerpes zoster, also known as shingles, is caused by the varicella zoster virus which causes chickenpox. It occurs when the virus reactivates from nerve cells after a previous chickenpox infection. Signs and symptoms include a painful rash that follows nerve pathways and may include fever, headache, or malaise. Diagnosis is usually clinical but Tzanck testing of fluid from blisters can confirm. Treatment with acyclovir within 72 hours can reduce pain and speed healing. Nursing care focuses on preventing infection, managing pain and itching, and patient education.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
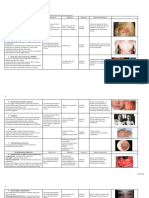
HERPES ZOSTER
I. Synonym 1. Shingles is not transmitted from
exposure to another infected person
1. Shingles so there is no applicable incubation
II. Definition period. Anyone who has recovered
from varicella may develop shingles.
Herpes zoster, also Shingles, gets its VI. Signs and Symptoms
name from both the Latin and French 1. Pain
words for belt or girdle and refers to 2. Itching
girdle-like skin eruptions that may occur 3. Tingling in the area where the rash
on the trunk of the body. Initially, red develops prior to blistering.
patches of rash develop into blisters. 4. Headache
Because the virus travels along the nerve 5. Fever
to the skin, it can damage the nerve and 6. Malaise
cause it to become inflamed. This 7. Chills
condition can be very painful. If
the pain persists long after the rash VII. Pathognomonic sign
disappears, it is known as 1. Regional Painful Rash
postherpetic neuralgia. 2. Lesions follow peripheral nerve
pathway of CN V and CN VII.
III. Etiologic Agents
VIII. Diagnostic test
1. The virus that causes chickenpox,
1. Tzanck testing can be used to
the Varicella Zoster Virus (VSV),
diagnose viral disease, such as
can become dormant in nerve cells
herpes simplex and herpes zoster,
after an episode of chickenpox and
and is done when active intact
later reemerge as shingles.
vesicles are present. Tzanck testing
cannot distinguish between herpes
IV. Mode of transmission
simplex and herpes zoster infections.
Transmission of the virus occurs
An intact blister is the preferred
through direct contact with the rash
lesion for examination. The blister
or fluid from the lesions. If the
roof is removed with a sharp blade,
person exposed has not previously
and the base of the unroofed vesicle
had chicken pox, that person would
is scraped with a #15 scalpel blade.
develop chicken pox, not shingles.
The scrapings are transferred to a
Therefore, shingles cannot be passed
slide and stained with Wright's stain
from one individual to another.
or Giemsa stain.
V. Incubation period Multinucleated giant cells are a sign of
herpes infection.
2. Culture of Wound Secretions 2. Acute pain related to the presence of
lesions and pruritus
IX. Drug of choice 3. Deficient knowledge of the cause of
the skin disorder and recommended.
1. Acyclovir hasten the healing and
decreases the pain if started within
72 hours of vesicle appearance
Submitted by:
X. Immunization Peter Francis O. Gonzaga
1. The varicella vaccine is a live 3 NRS-2 Group #4
(attenuated) vaccine that protects
against the viral disease commonly Submitted to:
known as chickenpox, Herpes zoster, Mr. Armando Delos Santos RN,
and Postherpetic neuralgia. MAN,
Clinical Instructor
XI. Prevention and control
1. People with shingles should keep
the rash covered and not touch or
scratch the rash.
2. Wash hands properly and often.
3. There is no shingles vaccine
available for children; however,
administration of the varicella
vaccine will prevent infection if
contact with a shingles case occurs.
XII. Nursing management
1. Wear a clean cotton undershirt each
day.
2. Trim the fingernails short, and keep
the hands clean.
3. Wash the hands each time the area
is touched.
4. Wash any soiled clothes or linens in
hot water and soap.
5. Do not allow other family members
to use your towels.
6. Take medications as prescribed for
itching and pain.
7. Wash the sores and the skin around
them very gently with a soft
washcloth and a mild soap.
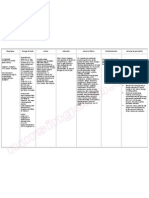
XIII. Possible nursing diagnosis
1. Risk For Infection r/t to disease
process
You might also like
- BRS PediatricsDocument825 pagesBRS PediatricsJsph Ldrn Rly93% (14)
- Communicable Diseases QuestionsDocument11 pagesCommunicable Diseases QuestionsChelleyOllitro100% (16)
- Chapter 19 Microbial Diseases of The Skin and WoundsDocument8 pagesChapter 19 Microbial Diseases of The Skin and WoundsGRACE MAR CABAHUG100% (1)
- Illustrated Guide To The Homoeopathic Treatment Harbaris Singh Khaneja.01169 3chestDocument7 pagesIllustrated Guide To The Homoeopathic Treatment Harbaris Singh Khaneja.01169 3chestMarija VelkoskiNo ratings yet
- Ob 1.05 Clinical Practice Guidelines On Immunization For Filipino WomenDocument7 pagesOb 1.05 Clinical Practice Guidelines On Immunization For Filipino Womenotartil_niman50% (2)
- Chicken Pox: BSN 1A Aquino, Cadaoas, Edic, Elegino, Dela Cruz, NepomucenoDocument20 pagesChicken Pox: BSN 1A Aquino, Cadaoas, Edic, Elegino, Dela Cruz, NepomucenoRayza MaglaqueNo ratings yet
- Immunocompromised Individuals That Is Characterized by Pain and Vesicular RashDocument2 pagesImmunocompromised Individuals That Is Characterized by Pain and Vesicular Rashadinda sandyaNo ratings yet
- Viral Disease 2021Document76 pagesViral Disease 2021Ageng betaNo ratings yet
- Patient Care Pathogen Reservoir Mode of Transmission: Viral Infections of HumansDocument21 pagesPatient Care Pathogen Reservoir Mode of Transmission: Viral Infections of HumansMark Vincent JanoyogNo ratings yet
- Herpes VirusDocument18 pagesHerpes VirusGrinty Babu BabuNo ratings yet
- Science Class Work 3 Virus and BacteriaDocument4 pagesScience Class Work 3 Virus and BacteriaJenia De La RosaNo ratings yet
- Viral InfectionsDocument110 pagesViral InfectionsMark Anthony CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Common Viral Infections - EditedDocument15 pagesCommon Viral Infections - EditedEcel AggasidNo ratings yet
- Spread Thru Olfactory BulbDocument2 pagesSpread Thru Olfactory BulbleoNo ratings yet
- Varicella Zoster VirusDocument11 pagesVaricella Zoster VirusJayaram SNo ratings yet
- VaricellaDocument4 pagesVaricellasingcojericho11No ratings yet
- Serological Diagnosis of Infectious DiseasesDocument38 pagesSerological Diagnosis of Infectious DiseasesPurple basketNo ratings yet
- Small Pox: General VirologyDocument24 pagesSmall Pox: General VirologyFahad HassanNo ratings yet
- Herpes ZosterDocument2 pagesHerpes ZosterJesselyn San PedroNo ratings yet
- Herpes: ALDEGUER, Gianina Emille HDocument13 pagesHerpes: ALDEGUER, Gianina Emille HgianinaemilleNo ratings yet
- Smallpox A Dead DiseaseDocument42 pagesSmallpox A Dead DiseasefarigNo ratings yet
- Scabies TreatmentDocument8 pagesScabies Treatmentheliana9107No ratings yet
- Dna Virus DNA Virus - Are Mostly Double Stranded DNA: BedielabzDocument2 pagesDna Virus DNA Virus - Are Mostly Double Stranded DNA: BedielabzDale SuanoNo ratings yet
- Viral Diseases With Rashes LastDocument46 pagesViral Diseases With Rashes LastHasan kahhalehNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease (Part 1) : Viral DiseasesDocument11 pagesInfectious Disease (Part 1) : Viral Diseasesmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- Efektivitas Vaksin VaricellaDocument21 pagesEfektivitas Vaksin VaricellaSul FadlyNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument2 pagesNSTPBernadette ArrojoNo ratings yet
- 10 - Herpes ZosterDocument2 pages10 - Herpes Zosteramen shanavasNo ratings yet
- Gyne - Case 11 Lower Genital UTI PDFDocument2 pagesGyne - Case 11 Lower Genital UTI PDFcbac1990No ratings yet
- Chickenpox & ChlamydialDocument5 pagesChickenpox & ChlamydialEliezah RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Notes TuberculosisDocument5 pagesExam 2 Notes TuberculosisElizabeth McKeeNo ratings yet
- 8 Viral Exanthems of ChildhoodDocument9 pages8 Viral Exanthems of ChildhoodErik OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Virology Lecture 7 Viral DiseseDocument21 pagesVirology Lecture 7 Viral Diseseao868598No ratings yet
- Scabies Norwegian Presenting As Erythroderma in HIV A Case ReportDocument4 pagesScabies Norwegian Presenting As Erythroderma in HIV A Case ReportfakhrunnisaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Microbial Diseases of Man Let'S EngageDocument8 pagesLesson 2: Microbial Diseases of Man Let'S EngageJewel Berbano IINo ratings yet
- Disorders of Respiratory Function - Infections and Neoplasms - 2020Document17 pagesDisorders of Respiratory Function - Infections and Neoplasms - 2020Cres Padua QuinzonNo ratings yet
- Varicella Zoster Virus: Two Lives of A Pathogen: Clinical ReviewDocument5 pagesVaricella Zoster Virus: Two Lives of A Pathogen: Clinical ReviewVICKI ANDREANNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases Maam Ervina PDFDocument3 pagesCommunicable Diseases Maam Ervina PDFMary MisolaNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument13 pagesChickenpoxJoanne LagusadNo ratings yet
- Viral InfectionDocument15 pagesViral InfectionSivabalan RajagopalNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument23 pagesChickenpoxLukman HikimNo ratings yet
- Tugas BHS - Inggris Andi Siti KhadijahDocument2 pagesTugas BHS - Inggris Andi Siti Khadijahandi evi febriantiNo ratings yet
- VirologyDocument24 pagesVirologyRohama Qubra 279No ratings yet
- 11 Spirochetes 130520112830 Phpapp02Document61 pages11 Spirochetes 130520112830 Phpapp02Manisanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument2 pagesDengueAhana CherianNo ratings yet
- 22 Varicella Pink BookDocument24 pages22 Varicella Pink BookMohamad Syaikhul IslamNo ratings yet
- 2 Oral UlcersDocument27 pages2 Oral UlcersAhmed Abdelhady Mahmoud AbdelwahedNo ratings yet
- Herpes Zoster - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument6 pagesHerpes Zoster - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDhany karubuyNo ratings yet
- German Measles: DR Anwar AhmadDocument49 pagesGerman Measles: DR Anwar AhmadNoto SusantoNo ratings yet
- AkhdakaaaaaknuqmakaakddaDocument12 pagesAkhdakaaaaaknuqmakaakddaVICKI ANDREANNo ratings yet
- RabiesDocument4 pagesRabiesJamie FabianiaNo ratings yet
- K22 Variola KBKDocument12 pagesK22 Variola KBKedelinNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY - Docx Maam AlapDocument7 pagesCASE STUDY - Docx Maam AlapSam Aquino IINo ratings yet
- LalalaDocument4 pagesLalalanoreka azizahNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox 1Document7 pagesChickenpox 1Nica Joy CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Theory PointersDocument89 pagesTheory Pointerslala byuNo ratings yet
- CHN - Communicable DiseaseDocument117 pagesCHN - Communicable DiseaseGetom NgukirNo ratings yet
- CHICKENPOXDocument32 pagesCHICKENPOXCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Pinkbook: Herpes Zoster - CDCDocument8 pagesPinkbook: Herpes Zoster - CDCRezza PratamaNo ratings yet
- Macules Macules and Papules Papules VesiclesDocument6 pagesMacules Macules and Papules Papules VesiclesLanaAmerieNo ratings yet
- ManasDocument6 pagesManasjose randyNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument2 pagesChickenpoxapi-355830788No ratings yet
- Viral Exanthems ReviewerDocument4 pagesViral Exanthems ReviewerNicole TorralbaNo ratings yet
- NCP CholeDocument2 pagesNCP CholeinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument37 pagesThesisinfectionman100% (1)
- CS NCPDocument2 pagesCS NCPinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Herpes ZosterDocument2 pagesHerpes ZosterinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- CVLSPMS Splash Screen: CVLSPMS Log-In FormDocument22 pagesCVLSPMS Splash Screen: CVLSPMS Log-In ForminfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Dosage & RouteDocument1 pageDosage & RouteinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Clonidine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageClonidine HydrochlorideLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNo ratings yet
- Adult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: ShockDocument1 pageAdult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: ShockinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DysrhythmiaDocument1 pageCardiac DysrhythmiainfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics: by DR - Mohammad Z. Abu Sheikha@Document101 pagesPediatrics: by DR - Mohammad Z. Abu Sheikha@صقر حوران100% (1)
- Cases in Medical EthicsDocument8 pagesCases in Medical EthicsOmarNo ratings yet
- Complicatii PneumonieDocument9 pagesComplicatii PneumonieTatiana JalbaNo ratings yet
- VaricellaDocument38 pagesVaricellapinanoeNo ratings yet
- Airborne Diseases 2Document143 pagesAirborne Diseases 2Karylle Petil100% (1)
- Sample MCQsDocument6 pagesSample MCQsRiyad AliNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mapeh 8Document13 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mapeh 8Jeoffrey ArceNo ratings yet
- NDA - BIO - CH 6 - DiseasesDocument4 pagesNDA - BIO - CH 6 - Diseaseshemanth varsanNo ratings yet
- Nle ReviewerdianemaydeeDocument170 pagesNle ReviewerdianemaydeeSucceed ReviewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Communicable Diseases 2ND Sem 2022 2023Document10 pagesChapter 1 Communicable Diseases 2ND Sem 2022 2023Lovelyn Cantollas EugenioNo ratings yet
- Chicken Fox, Cholera, Dengue FeverDocument2 pagesChicken Fox, Cholera, Dengue FeverAngel Joy CatalanNo ratings yet
- Parent Ver SCH 0 6yrsDocument2 pagesParent Ver SCH 0 6yrsunmundoextranopodcastNo ratings yet
- BETNESOL™ Tablets: Data SheetDocument4 pagesBETNESOL™ Tablets: Data Sheetsmargo171100% (1)
- Chicken PoxDocument6 pagesChicken Poxpiyushsukhija52No ratings yet
- Integumentary NCLEX PointsDocument6 pagesIntegumentary NCLEX PointsBrenda Bravo100% (1)
- UCLA VolunteerDocument23 pagesUCLA VolunteerSpencer NgNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Herpes PDFDocument9 pagesJurnal Herpes PDFIstianah EsNo ratings yet
- Random FactsDocument298 pagesRandom FactsglemeseNo ratings yet
- 9 Daftar Pustaka VaricelaDocument2 pages9 Daftar Pustaka VaricelaAfrina FaziraNo ratings yet
- Toefl Exercise Reading 1Document10 pagesToefl Exercise Reading 1GERIPATLI MALACOPPONo ratings yet
- WHO Med Guide 3 EdnDocument58 pagesWHO Med Guide 3 Ednmsk5in100% (1)
- Communicable Diseases GR.8 HealthDocument40 pagesCommunicable Diseases GR.8 HealthAiza May RosasNo ratings yet
- Mcqs in Rheumatology Inflammatory Arthritis Ms WordDocument10 pagesMcqs in Rheumatology Inflammatory Arthritis Ms WordTanvir Iqbal67% (3)
- (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) : CME For Family Physicians DermatologyDocument15 pages(A) (B) (C) (D) (E) : CME For Family Physicians DermatologyhashemNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument11 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingMelvinFabraÜ100% (1)