Professional Documents
Culture Documents
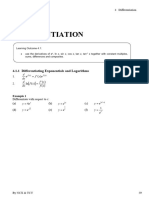
Differentiation Basic Mathematics 2022
Differentiation Basic Mathematics 2022
Uploaded by
ARJUN PATELCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
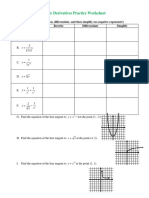
- Basic Derivatives Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesBasic Derivatives Practice WorksheetPhil harold Nera100% (1)
- 3.0 Differentiation of Exponential, Logarithmic and Trigonometric Functions (Topical Practice)Document3 pages3.0 Differentiation of Exponential, Logarithmic and Trigonometric Functions (Topical Practice)Shafiqa ShafiraNo ratings yet
- Exam2InClassReview2 PDFDocument1 pageExam2InClassReview2 PDFRicardo Bernardo RickyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1-Derivatives Jan 2010Document3 pagesWorksheet 1-Derivatives Jan 2010utpNo ratings yet
- WS - Basic DerivativesDocument2 pagesWS - Basic DerivativesMATEFISEDUNo ratings yet
- X y X X y y X y y X Y: Mf007 Calculus Tutorial 2Document1 pageX y X X y y X y y X Y: Mf007 Calculus Tutorial 2Lionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Ts JR Maths Ib Imp Questions-2023Document11 pagesTs JR Maths Ib Imp Questions-2023yashwanth2006.schoolNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 22 - Derivative Rules ReviewDocument1 pageWorksheet 22 - Derivative Rules ReviewHank JamesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Four Step Rule Differentiation Formulas2Document13 pagesLesson 7 - Four Step Rule Differentiation Formulas2Kent AvilaNo ratings yet
- First-Order Differential EquationsDocument37 pagesFirst-Order Differential Equationsمارتن بولسNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Four Step Rule Differentiation FormulasDocument59 pagesModule 6 - Four Step Rule Differentiation FormulasMackneal DuNo ratings yet
- Spring 2011 Quizes: Lim LimDocument3 pagesSpring 2011 Quizes: Lim LimMoh AmmNo ratings yet
- Taller Diagn Stico Ecuaiones DiferencialesDocument2 pagesTaller Diagn Stico Ecuaiones DiferencialesKAROL VANESA HOYOS CONTRERASNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 - Derivatives Jan 2010Document2 pagesWorksheet 2 - Derivatives Jan 2010utpNo ratings yet
- FX Egx y X X X: ChoicesDocument1 pageFX Egx y X X X: ChoicesRicardo Bernardo RickyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Multivariable FunctionsDocument10 pagesChapter 9 Multivariable FunctionsReza HusainiNo ratings yet
- Calculus Chapter 4 NotesDocument20 pagesCalculus Chapter 4 Notesian jheferNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument15 pagesChapter ThreeMustafa SagbanNo ratings yet
- Chain RuleDocument3 pagesChain RuleFrank MarshallNo ratings yet
- TS - JR - Maths - 1B - Imp Questions - 05-02-2024Document7 pagesTS - JR - Maths - 1B - Imp Questions - 05-02-2024nkkumawat0616No ratings yet
- TALLER #3 Funciones de Varias VariablesDocument7 pagesTALLER #3 Funciones de Varias Variablesmiguel rojas tonuscoNo ratings yet
- L7 Four Step Rule Differentiation FormulasDocument42 pagesL7 Four Step Rule Differentiation FormulasLinearNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 20-10-21Document3 pagesLecture 05 20-10-21Tayyab HusaainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Functions)Document6 pagesChapter 1 (Functions)XXUnknownNo ratings yet
- Partial Derivatives: Chapter 2: Function of Several VariablesDocument26 pagesPartial Derivatives: Chapter 2: Function of Several VariablesKhairunnisa ZakiriNo ratings yet
- Physics AssignmentsDocument3 pagesPhysics AssignmentshappytohelpNo ratings yet
- Demo DiffEQDocument26 pagesDemo DiffEQHarishNo ratings yet
- BT Chương 4 - TKTDocument8 pagesBT Chương 4 - TKTQuân VõNo ratings yet
- Midlands State University Faculty of Mining & Mineral Processing Engineering Hmte101 - Engineering Mathetatics I Worksheet 1Document3 pagesMidlands State University Faculty of Mining & Mineral Processing Engineering Hmte101 - Engineering Mathetatics I Worksheet 1Milton MoyoNo ratings yet
- Vector Function With Respect To Scalar VariableDocument4 pagesVector Function With Respect To Scalar Variablemonyeidavid13No ratings yet
- Lecture Note - Week 3 Ssce 1993Document48 pagesLecture Note - Week 3 Ssce 1993Paramoda TriangleNo ratings yet
- JIMBO Preboards 2 SolutionDocument3 pagesJIMBO Preboards 2 SolutionClark SibiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics4 (2) CHMEDocument40 pagesMathematics4 (2) CHMEcarleston thurgoodNo ratings yet
- Maths Practice SheetDocument3 pagesMaths Practice SheetParamveer SinghNo ratings yet
- TS JR Maths-1b Important Questions 1Document7 pagesTS JR Maths-1b Important Questions 1xaweta1770No ratings yet
- Quiz 1 FDocument1 pageQuiz 1 FLeslieNo ratings yet
- Math WorksheetDocument4 pagesMath Worksheettamenegezahegn645No ratings yet
- X G X F X G F: Composite of FunctionsDocument10 pagesX G X F X G F: Composite of FunctionsKim Seng OnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11-Higher Order and Implicit DifferentiationsDocument18 pagesLesson 11-Higher Order and Implicit DifferentiationsKyle Hanz AndayaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 DifferntiationDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 DifferntiationPro HackerNo ratings yet
- P3 Chapter4 Differentiation 2020Document15 pagesP3 Chapter4 Differentiation 2020Jonathan LeeNo ratings yet
- Sma 2270 Ass Tie, Abe July 2021Document3 pagesSma 2270 Ass Tie, Abe July 2021Davy einsteinNo ratings yet
- FX FX: XiniDocument6 pagesFX FX: XiniRyan TuyanNo ratings yet
- Differentiation QuestionsDocument24 pagesDifferentiation QuestionsSudha BabuNo ratings yet
- Antidifferentiation by SubstitutionDocument14 pagesAntidifferentiation by SubstitutionBretana joanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Differentiation Term 212Document2 pagesTutorial Differentiation Term 212Nidhi PatelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document18 pagesLecture 12ryan williamNo ratings yet
- Cal II Pretest NameDocument4 pagesCal II Pretest NameJames DabbsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Higher Order and Implicit DifferentiationsDocument18 pagesLesson 11 Higher Order and Implicit DifferentiationsCupackeNo ratings yet
- LCD-02-Solved ExampleDocument8 pagesLCD-02-Solved ExampleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - DERIVATIVES OF FUNCTIONSDocument13 pagesLesson 3 - DERIVATIVES OF FUNCTIONSNeo Garcera100% (1)
- Eliminate The Constant: Sheet (1) (BAS 126) DR: M.ShokryDocument1 pageEliminate The Constant: Sheet (1) (BAS 126) DR: M.ShokryMohamed rabeaaNo ratings yet
- PROBLEMS Antiderivatives and Indefinite IntegrationDocument13 pagesPROBLEMS Antiderivatives and Indefinite IntegrationCynthia PlazaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Homework - Curve Sketching WorksheetDocument1 page6 - Homework - Curve Sketching WorksheetSaad Hamoudi [Student]No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation: 5.1 Definition of The Partial DerivativeDocument21 pagesChapter 5 Partial Differentiation: 5.1 Definition of The Partial DerivativeDiptoNo ratings yet
- 微積分競賽題目Document6 pages微積分競賽題目0616chengNo ratings yet
- Math WorksheetDocument4 pagesMath WorksheetGumball 8No ratings yet
- TS - SR - Maths Iib - Imp Questions-2023-24Document6 pagesTS - SR - Maths Iib - Imp Questions-2023-24jaashwanand09No ratings yet
- C3 Differentiation A - QuestionsDocument1 pageC3 Differentiation A - QuestionsfelixacoolNo ratings yet
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Real Printing Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation Process With Titanium and Zinc ElectrodesDocument9 pagesTreatment of Real Printing Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation Process With Titanium and Zinc ElectrodesCUEVA VASQUEZ BRYAN ALBERTONo ratings yet
- Nov 2001 p1Document15 pagesNov 2001 p1Wojtek BłażejNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PDFDocument51 pagesSyllabus PDFPalashNo ratings yet
- Shilpa PPT FinalDocument51 pagesShilpa PPT FinalDrakeNo ratings yet
- Genetics and InheritanceDocument78 pagesGenetics and Inheritanceapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Procedure For ConservationDocument10 pagesProcedure For ConservationabiramiNo ratings yet
- Requerimientos Nutricionales de EquinosDocument112 pagesRequerimientos Nutricionales de EquinosFaby DavalosNo ratings yet
- LOR ProfessorDocument1 pageLOR Professorapi-3845889100% (4)
- How To Draw and Read Line Diagrams Onboard Ships?: ShareDocument9 pagesHow To Draw and Read Line Diagrams Onboard Ships?: ShareShaif uddin rifatNo ratings yet
- SpecDocument70 pagesSpecLe HienNo ratings yet
- Waxes For PVC ProcessingDocument33 pagesWaxes For PVC ProcessingFrancisco Venegas Zuñiga100% (1)
- Final Construction Dossier HandoverDocument1 pageFinal Construction Dossier Handovercsc EXPERTISENo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing 10th Edition Cravens Test BankDocument9 pagesStrategic Marketing 10th Edition Cravens Test Bankdanielxavia55fok100% (17)
- Recovery of Pyrite From Copper Tailings by FlotationDocument6 pagesRecovery of Pyrite From Copper Tailings by FlotationDarwin Estrada SanchezNo ratings yet
- General Physics Lesson 1 Methods of Electrostatic ChargingDocument46 pagesGeneral Physics Lesson 1 Methods of Electrostatic ChargingLeoj Levamor D. AgumbayNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Real Estate Industry - Evolution and Trends - SAP Flexible Real Estate Management - InglesDocument5 pagesOverview of The Real Estate Industry - Evolution and Trends - SAP Flexible Real Estate Management - InglesAdriano MesadriNo ratings yet
- Nhóm 1 - Leadership Style of Jack MaDocument26 pagesNhóm 1 - Leadership Style of Jack MaNguyễn HoàiNo ratings yet
- 10002NB01510001Document12 pages10002NB01510001manoj6189No ratings yet
- Camera DesignDocument12 pagesCamera DesignSahil TiwariNo ratings yet
- Project 4Document6 pagesProject 4Trai TranNo ratings yet
- Understanding Feyerabend On GalileoDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Feyerabend On Galileorustycarmelina108No ratings yet
- H12 211-2Document24 pagesH12 211-2fraesser90% (10)
- Best Rosin Press of 2020 PDFDocument4 pagesBest Rosin Press of 2020 PDFdannie gaoNo ratings yet
- Nitro Nic 60Document4 pagesNitro Nic 60rizky efrinaldoNo ratings yet
- 9 St. Catherine Class ScheduleDocument1 page9 St. Catherine Class ScheduleAleah TungbabanNo ratings yet
- IV Eee 18 QT Sem-I Eed Lab External Attendence SheetDocument3 pagesIV Eee 18 QT Sem-I Eed Lab External Attendence SheetKLRCET ELECATRICAL ENGINEERSNo ratings yet
- Astm D2414-21Document9 pagesAstm D2414-21Rajdeep MalNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Job SatisfactionDocument4 pagesDeterminants of Job SatisfactionEINSTEIN2DNo ratings yet
- TarangMini ST13SMxxDocument1 pageTarangMini ST13SMxxPrasad ChabbiNo ratings yet
- DanielsDocument5 pagesDanielstv_whiteboyNo ratings yet
Differentiation Basic Mathematics 2022
Differentiation Basic Mathematics 2022
Uploaded by
ARJUN PATELOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Differentiation Basic Mathematics 2022
Differentiation Basic Mathematics 2022
Uploaded by
ARJUN PATELCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICS
JRS TUTORIALS
Basic Mathematics
Differentiation
1. DIFFERENTIATION OF ELEMENTRY FUNCTIONS
Find the derivative of given function w.r.t. corresponding independent variable.
A. y x 2 x 8 B. s 5t 3 3t 5 C. y 5 sin x
D. y x 2 sin x E. y tan x cot x
Find the first derivative & second derivative of given functions w.r.t. corresponding independent variable.
12 4 1
F. y 6x 2 10x 5x 2 G. r 3 4 H. 3 z 7 7 z 3 21z 2
I. y sin x cos x J. y nx e x K. y nx 2 sin x
L. y 7 x tan x
2. DIFFERENTIATION BY PRODUCT RULE
Find derivative of given functions w.r.t. the independent variable .
A. x sin x B. y e x nx C. y ( x 1) ( x 2 x 1)
2 1
D. y ( x 1) x 5 x E. y sin x cos x F. y e x tan x
1 1
G. y x 2 sin4 x x cos 2 x H. y x x x x 1 I. y x 2 sin x 2x cos x 2 sin x
J. r (1 sec ) sin K. y x 2 cos x 2x sin x 2 cos x
3. DIFFERENTIATION BY QUOTIENT RULE
Find derivative of given function w.r.t. the independent variable.
sin x 2x 5 nx
A. y cos x B. y C. y
3x 2 x
t2 1 2x 1
D. f (t) , find f '(t) E. z F. y x 2 cot x
t2 t 2 x2 1
sin x cos x cot x tan q
G. y H. y I. p 1 tan q
cos x 1 cot x
cos x x
J. y x
cos x
JRS Tutorials, Durgakund, Varanasi-221005, Ph No.(0542) 2311922, 2311777
PHYSICS
4. DIFFERENTIATION BY CHAIN RULE
dy
Given y = f(u) and u = g(x) Find
dx
A. y 2u3 , u 8x 1 B. y sin u, u 3x 1 C. y 6u 9, u (1/ 2) x 4
x
D. y cos u, u E. y cos u, u sin x F. y sin u, u x cos x
3
dy
Find as a function of x
dx
7
x
G. y (2x 1)5 H. y (4 3x )9 I. y 1 7
10
x
J. y 2 1 K. y sin 5x L. y sin(x) ln( x 2 ) e 2 x
M. y 2 sin( x ) where and constants N. y sin3 x sin 3x
4
x2 1
O. sin ( x 1)
2 2
P. y x( x 1)
2 1 / 2
Q. y 8 x x
dq
R. q 2r r 2 , find
dr
5. Suppose u and v are functions of x that are differentiable at x = 0 and that
u (0) = 5 , u´(0) = – 3 , v( 0) = – 1 v´ (0) = 2
Find the values of the following derivatives at x = 0.
d d u d v d
(i) (uv) (ii) (iii) (iv) (7v – 2u)
dx dx v dx u dx
dy
6. Find if (i) x2y + xy2 = 6 (ii) x3 + y3 = 18 xy
dx
y
7. Find in the following
x
xz 2
(i) y 2x z 3
(ii) y x z 4
3 2
(iii) y
v
8. Find the slope of the tangent at the given points on the following curves:
(i) y = 2 – x2 at x = 0 (ii) y = 2x3 at x = 3
1
(iii) y = at x = 4 (iv) x2 + y2 – 4x – 1 = 0 at x = 3 at y = 2
x2
9. A force of 40 N is responsible for the motion of a body governed by the equation
s = 2t +2t2 where s is in meters and t in sec.
What is the momentum of the body at t = 2 sec?
JRS Tutorials, Durgakund, Varanasi-221005, Ph No.(0542) 2311922, 2311777
PHYSICS
1
10. The momentum of a particle moving in straight line is given by p ln t find the ( time t >0) at which
t
dp
the net force acting on particle is zero and its momentum at that time.
dt
2 3 25 2
11. The angle rotated by a disc is given by t t 77t 5 , where is in rad. And t in seconds.
3 2
d
(a) Find the time at which the angular velocity of the disc is zero.
dt
d 2
(b) Find the angular acceleration when the angular velocity of the disc is zero.
dt 2
12. The area of a blot of ink is growing such that after t seconds, its area is given by A = (3t 2+7) cm2
Calculate the rate of increase of area at t=5 second.
13. If the radius of a spherical soap bubble is increasing at a constant rate of 0.4 ms–1, then determine the
2
rate of increase of its surface area when its radius is m.
14. The radius r and height h of a circular cylinder are related to the cylinder’s volume V by the formula
V = r2h. Find rate of increase of volume of cylinder..
(i) if height is increasing at a rate of 5 m/s while radius is constant,
(ii) if radius is increasing at a rate of 5 m/s while height is constant,
(iii) if height is increasing at a rate of 5 m/s and radius is increasing at a rate of 5 m/s,
15. The length, breadth & height of a cuboid depends on time t as
L = 1 + sin t
b = t2 – 1
h = (t + 1)
Find the rate of change of volume with time at t = sec.
2
16. MAXIMA & MINIMA
(i) Particle’s position as a function of time is given by x t 2 4t 4 find the maximum value of
position coordinate of particle.
(ii) Find the maximum and minimum values of y
(a) y = 2x 3 15x 2 36 x 11 (b) y x 4 62 x 2 120 x 9
(iii) Find two positive numbers x & y such that x + y = 60 and xy is maximum.
(iv) A sheet of area 40 m2 in used to make an open tank with a square base, then find the dimensions
of the base such that volume of this tank is maximum.
JRS Tutorials, Durgakund, Varanasi-221005, Ph No.(0542) 2311922, 2311777
PHYSICS
ANSWER KEY
dy ds dy
1. A. 2x 1 B. 15 t 2 15 t 4 C. 5 cos x
dx dt dx
dy
D. 2 x cos x E. sec 2 x cos ec 2 x
dx
dy d2 y
F. 12 x 10 10 x 3 , 12 30 x 4
dx dx 2
dr d 2r
G. 12 2 12 4 4 5 , 2 24 3 48 5 20 6
d d
d d2
H. 21z 6 21z 2 42 z , 2
126 z 5 42 z 42
dz dz
dy d2 y
I. cos x sin x, sin x cos x
dx dx 2
dy 1 d2 y 1
J. ex , 2
2 ex
dx x dx x
dy 2 d2 y –2
K. cos x , – sin x
dx x dx 2 x 2
6
– –13
7 d2 y –6
L. dy x sec 2 x 2 7 2 tan x sec 2 x
dx 7 dx 49
ex
2. A. sin x x cos x B. e x nx C. 3x 2
x
1
D. 3x 10x 2
2 2 2
E. cos x sin x F. ex(tanx + sec2x)
x2
2 1
G. 2xsin4x + 4x2 sin3x cosx + cos–2x + 2xcos–3xsinx H. 1 2x 3
– 2
x x
2
I. x2 cosx J. cos sec 2 K. –x sin x
19 1 nx
3. A. sec2 x B. y C.
( 3 x 2) 2 x 2
x2
t 2 2t 1 dz 2x 2 2x 2 dy
D. f ( t ) E. F. x 2 csc 2 x 2x cot x
( t 2 t 2)2 dx ( x 2 1)2 dx
dy – csc 2 x sec 2 q
G. sec 2 x H. I.
dx (1 cot x) 2 (1 tan q)2
dy – x sin x – cos x x sin x cos x
J. 2 +
dx x cos 2 x
JRS Tutorials, Durgakund, Varanasi-221005, Ph No.(0542) 2311922, 2311777
PHYSICS
dy
4. A. 48 (8 x 1) 2 B. 3 cos(3 x 1) C. 12x3
dx
dy 1 x dy
D. sin E. – sin (sinx) cos x. F. = cos (x – cosx) (1 + sinx)
dx 3 3 dx
8
x
G. 10(2x 1) 4
H. 27(4 3x) 8
I. 1
7
11
x 2
J. 5 1 K. 5 cos 5 x L. cos( x ) 2e 2 x
2 x
M. 2 cos( x ) N. 3sin2x cosx + 3cos3x O. 4x sin (x2 + 1) cos (x2 + 1)
3
1 x2 1 x 1 1– r
P. 2 3/2 Q. 4 x–
1 2 R.
( x 1) 8 x 4 x 2r – r 2
7
5. (i) 13 (ii) – 7 (iii) (iv) 20
25
2xy y 2 18 y 3x 2
6. (i) 2 (ii)
x 2xy 3y 2 – 18x
z2
7. (i) 6x 2 (ii) 3z 2 x 2 (iii)
v
1 1
8. (i) 0 (ii) 54 (iii) (iv)
32 2
9. 100 kgm/s 10. 1 sec ; 1 kg m/sec
11. (a) 7sec , 5.5 sec (b) 3 rad/s2, –3 rad/s2
12. 30 cm2 s –1 13. 6.4 m2 s –1
14. (i) 5 r2 (ii) 10 rh (iii) 5 r2 + 10 rh
3 2
15. + 2 – 2
2
16. (i) 8 (ii) (a) ymax = 39, ymin = 38 (b) ymax = 68, ymin = 1647
40
(iii) x = 30 & y = 30 (iv) x = m
3
JRS Tutorials, Durgakund, Varanasi-221005, Ph No.(0542) 2311922, 2311777
You might also like
- Basic Derivatives Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesBasic Derivatives Practice WorksheetPhil harold Nera100% (1)
- 3.0 Differentiation of Exponential, Logarithmic and Trigonometric Functions (Topical Practice)Document3 pages3.0 Differentiation of Exponential, Logarithmic and Trigonometric Functions (Topical Practice)Shafiqa ShafiraNo ratings yet
- Exam2InClassReview2 PDFDocument1 pageExam2InClassReview2 PDFRicardo Bernardo RickyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1-Derivatives Jan 2010Document3 pagesWorksheet 1-Derivatives Jan 2010utpNo ratings yet
- WS - Basic DerivativesDocument2 pagesWS - Basic DerivativesMATEFISEDUNo ratings yet
- X y X X y y X y y X Y: Mf007 Calculus Tutorial 2Document1 pageX y X X y y X y y X Y: Mf007 Calculus Tutorial 2Lionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Ts JR Maths Ib Imp Questions-2023Document11 pagesTs JR Maths Ib Imp Questions-2023yashwanth2006.schoolNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 22 - Derivative Rules ReviewDocument1 pageWorksheet 22 - Derivative Rules ReviewHank JamesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Four Step Rule Differentiation Formulas2Document13 pagesLesson 7 - Four Step Rule Differentiation Formulas2Kent AvilaNo ratings yet
- First-Order Differential EquationsDocument37 pagesFirst-Order Differential Equationsمارتن بولسNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Four Step Rule Differentiation FormulasDocument59 pagesModule 6 - Four Step Rule Differentiation FormulasMackneal DuNo ratings yet
- Spring 2011 Quizes: Lim LimDocument3 pagesSpring 2011 Quizes: Lim LimMoh AmmNo ratings yet
- Taller Diagn Stico Ecuaiones DiferencialesDocument2 pagesTaller Diagn Stico Ecuaiones DiferencialesKAROL VANESA HOYOS CONTRERASNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 - Derivatives Jan 2010Document2 pagesWorksheet 2 - Derivatives Jan 2010utpNo ratings yet
- FX Egx y X X X: ChoicesDocument1 pageFX Egx y X X X: ChoicesRicardo Bernardo RickyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Multivariable FunctionsDocument10 pagesChapter 9 Multivariable FunctionsReza HusainiNo ratings yet
- Calculus Chapter 4 NotesDocument20 pagesCalculus Chapter 4 Notesian jheferNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument15 pagesChapter ThreeMustafa SagbanNo ratings yet
- Chain RuleDocument3 pagesChain RuleFrank MarshallNo ratings yet
- TS - JR - Maths - 1B - Imp Questions - 05-02-2024Document7 pagesTS - JR - Maths - 1B - Imp Questions - 05-02-2024nkkumawat0616No ratings yet
- TALLER #3 Funciones de Varias VariablesDocument7 pagesTALLER #3 Funciones de Varias Variablesmiguel rojas tonuscoNo ratings yet
- L7 Four Step Rule Differentiation FormulasDocument42 pagesL7 Four Step Rule Differentiation FormulasLinearNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 20-10-21Document3 pagesLecture 05 20-10-21Tayyab HusaainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Functions)Document6 pagesChapter 1 (Functions)XXUnknownNo ratings yet
- Partial Derivatives: Chapter 2: Function of Several VariablesDocument26 pagesPartial Derivatives: Chapter 2: Function of Several VariablesKhairunnisa ZakiriNo ratings yet
- Physics AssignmentsDocument3 pagesPhysics AssignmentshappytohelpNo ratings yet
- Demo DiffEQDocument26 pagesDemo DiffEQHarishNo ratings yet
- BT Chương 4 - TKTDocument8 pagesBT Chương 4 - TKTQuân VõNo ratings yet
- Midlands State University Faculty of Mining & Mineral Processing Engineering Hmte101 - Engineering Mathetatics I Worksheet 1Document3 pagesMidlands State University Faculty of Mining & Mineral Processing Engineering Hmte101 - Engineering Mathetatics I Worksheet 1Milton MoyoNo ratings yet
- Vector Function With Respect To Scalar VariableDocument4 pagesVector Function With Respect To Scalar Variablemonyeidavid13No ratings yet
- Lecture Note - Week 3 Ssce 1993Document48 pagesLecture Note - Week 3 Ssce 1993Paramoda TriangleNo ratings yet
- JIMBO Preboards 2 SolutionDocument3 pagesJIMBO Preboards 2 SolutionClark SibiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics4 (2) CHMEDocument40 pagesMathematics4 (2) CHMEcarleston thurgoodNo ratings yet
- Maths Practice SheetDocument3 pagesMaths Practice SheetParamveer SinghNo ratings yet
- TS JR Maths-1b Important Questions 1Document7 pagesTS JR Maths-1b Important Questions 1xaweta1770No ratings yet
- Quiz 1 FDocument1 pageQuiz 1 FLeslieNo ratings yet
- Math WorksheetDocument4 pagesMath Worksheettamenegezahegn645No ratings yet
- X G X F X G F: Composite of FunctionsDocument10 pagesX G X F X G F: Composite of FunctionsKim Seng OnnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11-Higher Order and Implicit DifferentiationsDocument18 pagesLesson 11-Higher Order and Implicit DifferentiationsKyle Hanz AndayaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 DifferntiationDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 DifferntiationPro HackerNo ratings yet
- P3 Chapter4 Differentiation 2020Document15 pagesP3 Chapter4 Differentiation 2020Jonathan LeeNo ratings yet
- Sma 2270 Ass Tie, Abe July 2021Document3 pagesSma 2270 Ass Tie, Abe July 2021Davy einsteinNo ratings yet
- FX FX: XiniDocument6 pagesFX FX: XiniRyan TuyanNo ratings yet
- Differentiation QuestionsDocument24 pagesDifferentiation QuestionsSudha BabuNo ratings yet
- Antidifferentiation by SubstitutionDocument14 pagesAntidifferentiation by SubstitutionBretana joanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Differentiation Term 212Document2 pagesTutorial Differentiation Term 212Nidhi PatelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document18 pagesLecture 12ryan williamNo ratings yet
- Cal II Pretest NameDocument4 pagesCal II Pretest NameJames DabbsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Higher Order and Implicit DifferentiationsDocument18 pagesLesson 11 Higher Order and Implicit DifferentiationsCupackeNo ratings yet
- LCD-02-Solved ExampleDocument8 pagesLCD-02-Solved ExampleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - DERIVATIVES OF FUNCTIONSDocument13 pagesLesson 3 - DERIVATIVES OF FUNCTIONSNeo Garcera100% (1)
- Eliminate The Constant: Sheet (1) (BAS 126) DR: M.ShokryDocument1 pageEliminate The Constant: Sheet (1) (BAS 126) DR: M.ShokryMohamed rabeaaNo ratings yet
- PROBLEMS Antiderivatives and Indefinite IntegrationDocument13 pagesPROBLEMS Antiderivatives and Indefinite IntegrationCynthia PlazaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Homework - Curve Sketching WorksheetDocument1 page6 - Homework - Curve Sketching WorksheetSaad Hamoudi [Student]No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation: 5.1 Definition of The Partial DerivativeDocument21 pagesChapter 5 Partial Differentiation: 5.1 Definition of The Partial DerivativeDiptoNo ratings yet
- 微積分競賽題目Document6 pages微積分競賽題目0616chengNo ratings yet
- Math WorksheetDocument4 pagesMath WorksheetGumball 8No ratings yet
- TS - SR - Maths Iib - Imp Questions-2023-24Document6 pagesTS - SR - Maths Iib - Imp Questions-2023-24jaashwanand09No ratings yet
- C3 Differentiation A - QuestionsDocument1 pageC3 Differentiation A - QuestionsfelixacoolNo ratings yet
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Real Printing Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation Process With Titanium and Zinc ElectrodesDocument9 pagesTreatment of Real Printing Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation Process With Titanium and Zinc ElectrodesCUEVA VASQUEZ BRYAN ALBERTONo ratings yet
- Nov 2001 p1Document15 pagesNov 2001 p1Wojtek BłażejNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PDFDocument51 pagesSyllabus PDFPalashNo ratings yet
- Shilpa PPT FinalDocument51 pagesShilpa PPT FinalDrakeNo ratings yet
- Genetics and InheritanceDocument78 pagesGenetics and Inheritanceapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Procedure For ConservationDocument10 pagesProcedure For ConservationabiramiNo ratings yet
- Requerimientos Nutricionales de EquinosDocument112 pagesRequerimientos Nutricionales de EquinosFaby DavalosNo ratings yet
- LOR ProfessorDocument1 pageLOR Professorapi-3845889100% (4)
- How To Draw and Read Line Diagrams Onboard Ships?: ShareDocument9 pagesHow To Draw and Read Line Diagrams Onboard Ships?: ShareShaif uddin rifatNo ratings yet
- SpecDocument70 pagesSpecLe HienNo ratings yet
- Waxes For PVC ProcessingDocument33 pagesWaxes For PVC ProcessingFrancisco Venegas Zuñiga100% (1)
- Final Construction Dossier HandoverDocument1 pageFinal Construction Dossier Handovercsc EXPERTISENo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing 10th Edition Cravens Test BankDocument9 pagesStrategic Marketing 10th Edition Cravens Test Bankdanielxavia55fok100% (17)
- Recovery of Pyrite From Copper Tailings by FlotationDocument6 pagesRecovery of Pyrite From Copper Tailings by FlotationDarwin Estrada SanchezNo ratings yet
- General Physics Lesson 1 Methods of Electrostatic ChargingDocument46 pagesGeneral Physics Lesson 1 Methods of Electrostatic ChargingLeoj Levamor D. AgumbayNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Real Estate Industry - Evolution and Trends - SAP Flexible Real Estate Management - InglesDocument5 pagesOverview of The Real Estate Industry - Evolution and Trends - SAP Flexible Real Estate Management - InglesAdriano MesadriNo ratings yet
- Nhóm 1 - Leadership Style of Jack MaDocument26 pagesNhóm 1 - Leadership Style of Jack MaNguyễn HoàiNo ratings yet
- 10002NB01510001Document12 pages10002NB01510001manoj6189No ratings yet
- Camera DesignDocument12 pagesCamera DesignSahil TiwariNo ratings yet
- Project 4Document6 pagesProject 4Trai TranNo ratings yet
- Understanding Feyerabend On GalileoDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Feyerabend On Galileorustycarmelina108No ratings yet
- H12 211-2Document24 pagesH12 211-2fraesser90% (10)
- Best Rosin Press of 2020 PDFDocument4 pagesBest Rosin Press of 2020 PDFdannie gaoNo ratings yet
- Nitro Nic 60Document4 pagesNitro Nic 60rizky efrinaldoNo ratings yet
- 9 St. Catherine Class ScheduleDocument1 page9 St. Catherine Class ScheduleAleah TungbabanNo ratings yet
- IV Eee 18 QT Sem-I Eed Lab External Attendence SheetDocument3 pagesIV Eee 18 QT Sem-I Eed Lab External Attendence SheetKLRCET ELECATRICAL ENGINEERSNo ratings yet
- Astm D2414-21Document9 pagesAstm D2414-21Rajdeep MalNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Job SatisfactionDocument4 pagesDeterminants of Job SatisfactionEINSTEIN2DNo ratings yet
- TarangMini ST13SMxxDocument1 pageTarangMini ST13SMxxPrasad ChabbiNo ratings yet
- DanielsDocument5 pagesDanielstv_whiteboyNo ratings yet