Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Các Phương Pháp Gia Công Ngu I
Các Phương Pháp Gia Công Ngu I
Uploaded by
TRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢOOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Các Phương Pháp Gia Công Ngu I
Các Phương Pháp Gia Công Ngu I
Uploaded by
TRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢOCopyright:
Available Formats
BENCHWORK
1. BACKGROUND:
Slide 4: Is a method of mechanical process in which cutting by hand or using human power with the tool
being a benchwork tool and the workpiece not being heated.
has been around for a long time (about the 12th century)
Slide 5: after two methods of casting and forging processing it was born to provide mechanical products in
the form of mechanisms, equipment and machines that both methods the previous machining method
could not be performed.
2. MATERIALS:
Slide 6: There are 2 major types of materials to be considered:
+ Metal: metals that have lustrous sheen when cut, good heat conductor, electrical conductor
Ex: aluminum, copper, iron
+ Non-metal: can be elements or compounds of elements and mixtures of compounds.
Ex: wood, rubber, plastic, ceramic, glass
3. TOOLS:
Slide 7: According their purposes, we divide them into several groups presented here:
Slide 8: First of all, let talk about marking tools: Scriber is a very handy tool used for marking with the
structure alike a pen including two different ends shaped sharp point.
These two pictures as a description of how to use scriber to mark properly. As you can see, the right way
is to line the scriber along the straight edge.
Slide 9: Here are other types of scriber: For example, vernier caliper with a pen or using compass to
create a line marked parallel with edge.
Slide 10: Another way to mark is to create dots using dot punch, here we use the punch with a edge of
60 or 90 degree continue with the procedure to make dot marked: (đọc slide)
Slide 11: đọc slide
Slide 12: Next is measuring instruments (đọc slide)
Slide 13: We continue with cutting tool, beginning by hacksaw (đọc slide)
Slide 14: Other saws used in benchwork: đọc slide
To fix the blade, loosen one end and passing through a hole drilled in the work, then re-fix it in the frame
Slide 15: Cutting tools also include knives: đọc slide
Slide 16: A specific tool for cutting pipe: đọc slide
Slide 17: Đọc slide
Slide 18: Continued with the three steps
Slide 19: Lapping tool is also classified as cutting tool when it comes to cutting metal. (đọc slide)
Slide 20: Next part is about chipping. Chipping use involves forcing the blade into some material to cut it.
The driving force may be applied by pushing by hand, or by using a mallet or hammer. Chipping is a term
for wood while chiselling is used for metal.
Đọc slide
Slide 21: These pictures illustrate steps for chiselling (đọc slide)
Slide 22: The common types of chisels are:
+ flat chisel: it used for general – purpose chiseling
+ Cross-cut chisel: used for cutting grooves such as keyways, and for chipping
+ half – round round – nosed chisel: used for cutting grooves (which are either curved or half-round)
+ diamond – pointed chisel: used for working into corners and cutting small grooves
+ cow-mouth chisel
+ side cutting chisel: Where other types of chisel cannot be used easily, side cut chisels are used. The
keyway and cotter way is cleaned with this chisel. It is almost similar to the flat chisel but the part which
performs the function of cutting is turned to one side. It is turned at an angle and then forged. Its cutting
angle is generally at and forging angle at an angle.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rx_iiAnKanU
Slide 23: (đọc slide)
Slide 24: (đọc slide)
Slide 26: Here are several example of the file: File teeth are either single cut or double cut
Slide 27: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=32FUysj-Lu4
1:08
Slide 28: Next is drilling, boring, counter boring, spot-facing:
Slide 29: Different types of drilling machine. Due to its convenience, electric hand drill is the most
common used of all.
Slide 30: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DuewffX4eDo
Slide 31: With such big flat screw, we have to use countersinking and counterboring to create such hole
for fitting the triangle shape of it
Slide 32: (đọc slide)
Slide 33: (đọc slide)
Slide 34: Let ‘s me introduce several types of joint
Slide 35: Finally after all the mechanical process like weld or cutting, polish is the crucial step to produce
a shiny product. Mechanician use electrical polish tool to complete the workpieces.
CLASSIFICATION:
+ Tool quenching: bench work in which the worker only does one job, which is to use cutting tools
to make details in accordance with the technical requirements of the detailed drawings, the details can be
used to assemble into a structure, device or machine, those details can also be a finished product such
as mold making, when it comes to mold makers, it is people who refer to tool coolers.
+ Assembly cold profession: bench work in which the worker only does one job is to use
manufactured parts to assemble them together into a structure, equipment or machine in accordance with
the technical requirements of the assembly drawing. , in the process of performing work, assembly
workers sometimes need to repair and recalibrate details to suit the technical requirements of equipment
or machines. One can see a lot of cold assemblers in assembly companies and often refer to them as
machinists.
+ Repairing benchwork jobs: benchwork jobs where workers only work to maintain working
equipment of a certain production facility. The job of the repair cold worker is to maintain, repair and
restore the equipment: oiling, adjusting parameters, replacing damaged parts, disassembling the machine
and repairing and restoring damaged parts. In production facilities with technological equipment, there are
cold workers to repair in electromechanical groups and electromechanical rooms.
In addition, in order to serve the people, there are also cold-art crafts, it includes silversmiths,
locksmiths, motorcycle repairmen, gutters, buckets, buckets, etc. .
1. APPLICATION:
Theo tiêu chuẩn nào
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Liquid ChromatographyDocument12 pagesLiquid ChromatographyTRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- Franchise ContractDocument3 pagesFranchise Contractedward tablazon100% (2)
- Airline Needs To Check On Its Check in SystemDocument2 pagesAirline Needs To Check On Its Check in SystemAndrea FaicánNo ratings yet
- ESENECO (2) Interest Money Time RelationshipDocument50 pagesESENECO (2) Interest Money Time Relationshipjhonel guinto100% (3)
- 1BR - ANTIMONY SULFOIODIDE - SDS-US - EnglishDocument8 pages1BR - ANTIMONY SULFOIODIDE - SDS-US - EnglishTRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
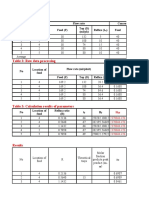
- Table 1: Raw Data: No Flow Rate Concentration Feed (F) Feed Location of Feed Top (D) (ML/PH) Reflux (L)Document9 pagesTable 1: Raw Data: No Flow Rate Concentration Feed (F) Feed Location of Feed Top (D) (ML/PH) Reflux (L)TRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology - VNU HCMC Faculty of Chemical EngineeringDocument52 pagesHo Chi Minh City University of Technology - VNU HCMC Faculty of Chemical EngineeringTRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Process Equipment Design Fundamentals of Process Equipment DesignDocument34 pagesFundamentals of Process Equipment Design Fundamentals of Process Equipment DesignTRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- Materials: Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology - VNU HCMC Faculty of Chemical EngineeringDocument37 pagesMaterials: Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology - VNU HCMC Faculty of Chemical EngineeringTRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- A. Absorption: B. Elution C. A and B D. None of ThisDocument7 pagesA. Absorption: B. Elution C. A and B D. None of ThisTRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- Total Distance Traveled by The Sample The Distance Traveled by The SolventDocument2 pagesTotal Distance Traveled by The Sample The Distance Traveled by The SolventTRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- Experimental Methods:: H C L L+2 X D L 2 X DDocument8 pagesExperimental Methods:: H C L L+2 X D L 2 X DTRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- PhyChem Lab ReportDocument12 pagesPhyChem Lab ReportTRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Lab Presentation: Group 4 - CC03Document28 pagesPhysical Chemistry Lab Presentation: Group 4 - CC03TRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- TNHL2 - Bài 2Document6 pagesTNHL2 - Bài 2TRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- Solution Solvent 0 SolventDocument7 pagesSolution Solvent 0 SolventTRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
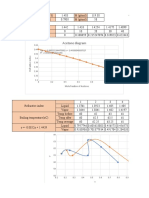
- Acetone Diagram: 1.44 1.46 F (X) 0.085221384475882 X + 1.44389548897517 R 0.996667758262254Document4 pagesAcetone Diagram: 1.44 1.46 F (X) 0.085221384475882 X + 1.44389548897517 R 0.996667758262254TRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- For The Case of V V, The Resultant Liquid Will Be Predominantly of Liquid B Containing Lesser Number of Globules of Liquid A Distributed RandomlyDocument2 pagesFor The Case of V V, The Resultant Liquid Will Be Predominantly of Liquid B Containing Lesser Number of Globules of Liquid A Distributed RandomlyTRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- Answers Practice - Questions - Chapters - 1 - and - 2 - GSCMDocument4 pagesAnswers Practice - Questions - Chapters - 1 - and - 2 - GSCMHardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Heichala Dream Enterprise (Ns0262486-H) : InvoiceDocument1 pageHeichala Dream Enterprise (Ns0262486-H) : InvoiceEmir NazrenNo ratings yet
- Door - Wilcon Depot IncDocument3 pagesDoor - Wilcon Depot IncSofiaJabadanEspulgarNo ratings yet
- The Secret of Boom and Crash Trading Sniper EntryDocument22 pagesThe Secret of Boom and Crash Trading Sniper Entryadvancedt24No ratings yet
- Reading: Benefits, Flexible Work Schedules and Bonus StructuresDocument3 pagesReading: Benefits, Flexible Work Schedules and Bonus StructuresKarem Yessenia OCHOCHOQUE SÁNCHEZNo ratings yet
- M-Jet 60 Basic ManualDocument5 pagesM-Jet 60 Basic ManualJordi Ferrer0% (1)
- Sworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net WorthDocument3 pagesSworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net WorthGen GenNo ratings yet
- Explain Entrepreneurship and Discuss Its ImportanceDocument3 pagesExplain Entrepreneurship and Discuss Its Importancesn nNo ratings yet
- LOI BINTANG-SOCAR. Rev-2Document5 pagesLOI BINTANG-SOCAR. Rev-2SyamNo ratings yet
- Mini Test 2 - Code 1 - INS1016 - HK2 - 2021-22Document4 pagesMini Test 2 - Code 1 - INS1016 - HK2 - 2021-2223. Lê Hải HươngNo ratings yet
- This Is An Auto-Generated Purchase Order Based On Online Tender DecisionDocument2 pagesThis Is An Auto-Generated Purchase Order Based On Online Tender DecisionTUff LabNo ratings yet
- HCF.013 - Asset Declaration FormDocument5 pagesHCF.013 - Asset Declaration Formozwin tikisaNo ratings yet
- Installation ManualDocument41 pagesInstallation ManualGabrielGrecoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Managerial Economics Applications Strategies and Tactics 13th EditionDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Managerial Economics Applications Strategies and Tactics 13th EditionJamesJohnsonqxcej100% (28)
- Deposit Slip ID: 192772 Deposit Slip ID: 192772: Fee Deposit Slip-Candidate Copy Fee Deposit Slip-BankDocument1 pageDeposit Slip ID: 192772 Deposit Slip ID: 192772: Fee Deposit Slip-Candidate Copy Fee Deposit Slip-BankAsim HussainNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA FATA TerbaruDocument2 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA FATA TerbaruFata JualanNo ratings yet
- Salary RegressionDocument5 pagesSalary RegressionSlipShod BonesNo ratings yet
- Defining Who Is A Volunteer ConceptualDocument21 pagesDefining Who Is A Volunteer ConceptualYosep Trisaputro WahyuNo ratings yet
- 3.urban Design ScalesDocument42 pages3.urban Design ScalessteveNo ratings yet
- MayaSavings SoA 2023AUGDocument1 pageMayaSavings SoA 2023AUGChrissandra BolarNo ratings yet
- AEAI Cina RE Invest Indonesia 2022 - TenggaraDocument33 pagesAEAI Cina RE Invest Indonesia 2022 - TenggaraIfnaldi SikumbangNo ratings yet
- Struktur Organisasi BTN KCS Makassar TMT Januari 2022Document1 pageStruktur Organisasi BTN KCS Makassar TMT Januari 2022sriwahyuningsih7656No ratings yet
- 03.00 - Welding Tables With Rotating Function enDocument1 page03.00 - Welding Tables With Rotating Function enMeisam Hosseinpour LahiciNo ratings yet
- Present Worth Method of Comparison Lecture 7&8Document20 pagesPresent Worth Method of Comparison Lecture 7&8Hammad SattiNo ratings yet
- 856 EconomicsDocument4 pages856 Economicsayushii kapurNo ratings yet
- P 6Document1 pageP 6REA CONSTRUCTIONNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of Marketing For Hospitality and Tourism 7th Edition Kotler Test Bank All ChapterDocument30 pagesFull Download PDF of Marketing For Hospitality and Tourism 7th Edition Kotler Test Bank All Chapteracistaqasih100% (6)