Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ret Short Question
Ret Short Question
Uploaded by
Web FlowCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Advances in Solar Based Power GenerationDocument27 pagesAdvances in Solar Based Power GenerationSagar ShahNo ratings yet
- Ee1451-Electric Energy Generation Utilization and ConservationDocument21 pagesEe1451-Electric Energy Generation Utilization and ConservationDarwin JdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Power SystemDocument68 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Power SystemMonirul Islam100% (1)
- Green Power and Other Renewable Source of EnergyDocument24 pagesGreen Power and Other Renewable Source of EnergyPratyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit 1 GenerationDocument17 pagesQuestion Bank Unit 1 GenerationjothikumarNo ratings yet
- modeling and analysis of renewable energy systems المعدل pptxDocument37 pagesmodeling and analysis of renewable energy systems المعدل pptxanwar.23enp30No ratings yet
- Wind Solar Hybrid SystemDocument10 pagesWind Solar Hybrid SystemRavi Kiran GoudNo ratings yet
- Unit1 - Introduction To Electrical Power NotesDocument14 pagesUnit1 - Introduction To Electrical Power Notes1ms20ei002No ratings yet
- Ocean Thermal Energy ConversionDocument17 pagesOcean Thermal Energy ConversionVamsi Pelluru100% (1)
- Power System-L (3140914) Total ExperimentDocument54 pagesPower System-L (3140914) Total ExperimentAshutosh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Energy Harnessing - : SukritiDocument11 pagesEnergy Harnessing - : SukritiKumail BarafwalaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument10 pagesIntroductionmsmanojkumar763No ratings yet
- Wipo Idb Ip Ryd 07 2Document65 pagesWipo Idb Ip Ryd 07 2RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Power Systems: by Alebachew TDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Power Systems: by Alebachew TZerihun PaulosNo ratings yet
- EE1452 - Electric Energy Generation, Conservation and UtilizationDocument62 pagesEE1452 - Electric Energy Generation, Conservation and UtilizationKarthikeyan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy Generation Utilization and ConservationDocument24 pagesElectrical Energy Generation Utilization and Conservationarul skpNo ratings yet
- Files 1 2021 September NotesHubDocument 1632364811Document3 pagesFiles 1 2021 September NotesHubDocument 1632364811goels0798No ratings yet
- Ocean Thermal Power Plant ReportDocument10 pagesOcean Thermal Power Plant ReportMahmud L. MusaNo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument20 pagesPower Plantsjvharsha.sNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review On Distributed Power GenerationDocument5 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Distributed Power GenerationCésar Díaz LiberonaNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument18 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsMelvin Mendoza NocheNo ratings yet
- Principle of Power GenerationDocument36 pagesPrinciple of Power Generationbilyaminu hamisu b/zNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Part 2: Electrical Energy: EEEQ524 Energy Conservation and ManagementDocument9 pagesLecture 1-Part 2: Electrical Energy: EEEQ524 Energy Conservation and ManagementShahid AliNo ratings yet
- Mtechres PPT U 3 C 3Document15 pagesMtechres PPT U 3 C 3MounikaNo ratings yet
- 8269Document20 pages8269Vishnupriya VaradarajanNo ratings yet
- Desalination-Wind WaveDocument23 pagesDesalination-Wind WaveRubem MichelNo ratings yet
- Rotating GateDocument34 pagesRotating GateAlex MartynNo ratings yet
- 22 Solar Cell Challenges and New DevelopmentsDocument22 pages22 Solar Cell Challenges and New DevelopmentsPatrice ETEMENo ratings yet
- Svs College of Engineering: Name of The Faculty: S.KalaiarasiDocument23 pagesSvs College of Engineering: Name of The Faculty: S.KalaiarasiSudharsana ANo ratings yet
- Bahir Dar Institute of Technology (Bit) : Faculty of Electrical & Computer EngineeringDocument20 pagesBahir Dar Institute of Technology (Bit) : Faculty of Electrical & Computer Engineeringtewachew alemNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument40 pagesEnergy ResourcesKim Howard CastilloNo ratings yet
- Electric Power GenerationDocument7 pagesElectric Power GenerationearhyathNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Ocean Thermal Energy ConversionDocument21 pagesSeminar Report On Ocean Thermal Energy ConversionHARENDRA BHINCHARNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument256 pagesRenewable Energy ResourcesshuklashreyanshuNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Power Systems: BY: Sarmishtha Satpathy REGD NO: 0701209432 Applied Electronics & Instrumentation EnggDocument18 pagesSeminar On Power Systems: BY: Sarmishtha Satpathy REGD NO: 0701209432 Applied Electronics & Instrumentation EnggSachin SrivastavNo ratings yet
- SKEE 4653 - Chapter 3 - Wind Energy SystemDocument149 pagesSKEE 4653 - Chapter 3 - Wind Energy Systemahmad azmirNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Renewable Resource: Presented byDocument24 pagesThe Ultimate Renewable Resource: Presented byMayukh Dutta ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Brainkart - 225 - EE8015, EE6801 Electric Energy Generation, Utilization and Conservation - 2 Marks With Answers - Bin-1Document23 pagesBrainkart - 225 - EE8015, EE6801 Electric Energy Generation, Utilization and Conservation - 2 Marks With Answers - Bin-1rithirithika2401No ratings yet
- For Power PlantDocument224 pagesFor Power PlantIrene Mununi100% (2)
- IEE Module 1 CompleteDocument25 pagesIEE Module 1 Completekamaxey638No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Unit - 1Document16 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Unit - 1S085 Pranav HNo ratings yet
- Unit III NotesDocument22 pagesUnit III NotesArun prakashNo ratings yet
- BY Maha Barathi Engineering College Ramanathan.R/Ap/EeeDocument224 pagesBY Maha Barathi Engineering College Ramanathan.R/Ap/EeeRaj RohitNo ratings yet
- Science 9-4-5Document6 pagesScience 9-4-5Kim ReiNo ratings yet
- Final Re ProtDocument59 pagesFinal Re Protkowsika rajaramNo ratings yet
- Renewable - Energy - SourcesDocument12 pagesRenewable - Energy - SourcesErRajeshNo ratings yet
- Ijisrt21oct009 PDFDocument32 pagesIjisrt21oct009 PDFwy9frghd7dNo ratings yet
- Solar Thesis PaperDocument4 pagesSolar Thesis Paperfc2fqg8j100% (2)
- First Presentation Under The Supervision Of: Prof - DR: Abdel Hamid GomaaDocument28 pagesFirst Presentation Under The Supervision Of: Prof - DR: Abdel Hamid GomaaahmedaboshadyNo ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument14 pagesRenewable EnergyMounikaNo ratings yet
- How To Generate Electricity in Your Respective Home Using The Available Resources in Your HomeDocument5 pagesHow To Generate Electricity in Your Respective Home Using The Available Resources in Your HomeGerryanna MagbitangNo ratings yet
- Research Paper About ElectricityDocument4 pagesResearch Paper About Electricitygz7vxzyz100% (1)
- Nuclear Power in UKDocument17 pagesNuclear Power in UKSmriti SinghNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantsDocument4 pagesNuclear Power PlantsJillianne PadilloNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy and Grid Integration: Submitted T0-Submitted byDocument12 pagesRenewable Energy and Grid Integration: Submitted T0-Submitted byTiya gonekarNo ratings yet
- XEIET132 Complete Presentation 0210Document61 pagesXEIET132 Complete Presentation 0210sulemankhalidNo ratings yet
- Solar Electricity Basics: Powering Your Home or Office with Solar EnergyFrom EverandSolar Electricity Basics: Powering Your Home or Office with Solar EnergyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- OrlanPellet BrochureDocument2 pagesOrlanPellet Brochuree-ComfortUSANo ratings yet
- Siemens HedrichDocument51 pagesSiemens HedrichpabloalienadoNo ratings yet
- Internship Report 2019Document28 pagesInternship Report 2019Shivani YadavNo ratings yet
- Sunpower A Series Residential BLK DC A 390 A 400Document2 pagesSunpower A Series Residential BLK DC A 390 A 400Alex jonesNo ratings yet
- TE4a Solar Light Bank DatasheetDocument2 pagesTE4a Solar Light Bank Datasheetניסן בורוכובNo ratings yet
- Drum Control TheoryDocument9 pagesDrum Control TheoryRaju SkNo ratings yet
- DLF PresentationDocument9 pagesDLF PresentationhsparmarNo ratings yet
- EE 555 - Renewable Energy Systems - Hassan Abbas Khan PDFDocument3 pagesEE 555 - Renewable Energy Systems - Hassan Abbas Khan PDFWajahat Ullah Khan TareenNo ratings yet
- Tm2500 Mobile Gas TurbineDocument2 pagesTm2500 Mobile Gas TurbineMuhammad Syaifulhaq100% (1)
- 9 23Document2 pages9 23Sylaja GannavaramNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9Document4 pagesTutorial 9Jyoti Krishna PandaNo ratings yet
- HRSGDocument36 pagesHRSGDumitrescuNo ratings yet
- Pvsyst ReportDocument4 pagesPvsyst ReportZaman MoradiNo ratings yet
- Apr 88372Document2 pagesApr 88372N1234mNo ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument26 pagesRenewable EnergyPrakash KashyapNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant System and Operation PDFDocument161 pagesNuclear Power Plant System and Operation PDFelrajilNo ratings yet
- Manufacturer List New 2013Document75 pagesManufacturer List New 2013D.Muruganand100% (1)
- Bedienungsanleitung User Manual Manuale D'Uso Manuel de L'UtilisateurDocument2 pagesBedienungsanleitung User Manual Manuale D'Uso Manuel de L'Utilisateurmich2767No ratings yet
- Thermal EnggDocument2 pagesThermal EnggAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- A Review Paper On Solar Energy-Generated ElectricityDocument8 pagesA Review Paper On Solar Energy-Generated ElectricityIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- 1H99103 S-610M SchematicDocument9 pages1H99103 S-610M SchematicJesse chaseNo ratings yet
- Steam Boiler - DesignDocument44 pagesSteam Boiler - DesigntelldivyaNo ratings yet
- PV ModuleDocument2 pagesPV ModuleRoksana SobierajczykNo ratings yet
- Microhydro Power PlantDocument15 pagesMicrohydro Power Plantjeevana manjunathNo ratings yet
- Lycom - Ring - Apps SUPERIOR PARTS PDFDocument10 pagesLycom - Ring - Apps SUPERIOR PARTS PDFElmer VillegasNo ratings yet
- 24p AMMAR SALAH MAHDIDocument29 pages24p AMMAR SALAH MAHDIenta elektroNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Lecture Notes - CHAPTER-6 Gas Turbines & Combined CyclesDocument47 pagesPower Plant Lecture Notes - CHAPTER-6 Gas Turbines & Combined CyclesOtuagaNo ratings yet
- 1 KW Solar Power Plant Project ReportDocument3 pages1 KW Solar Power Plant Project ReportMohammd EssaNo ratings yet
- Eternal Hybrid Water Heater BrochureDocument2 pagesEternal Hybrid Water Heater Brochuree-ComfortUSANo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Hybrid Wind and Solar Energy System For Power GenerationDocument8 pagesDesign and Development of Hybrid Wind and Solar Energy System For Power GenerationBayu pradanaNo ratings yet
Ret Short Question
Ret Short Question
Uploaded by
Web FlowOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ret Short Question
Ret Short Question
Uploaded by
Web FlowCopyright:
Available Formats
Q2 What is the key factor on which drift current
depends?
The amount of drift current depends on the concentration of charge
carriers and their mobility in the material or medium.
Q3 What is the function of the diodes in a photovoltaic
installation
Diodes are extensively used in solar panel installations. Since the prevent
backflow of current (unidirectional flow of current), they are used as
blocking devices. They are also used as bypass devices to maintain the
reliability of the entire solar power system in the event of a solar panel
failure.
Q4 What happens to the current when PV cells are
connected in series and parallel?
When wiring solar panels in parallel, the amperage (current) is additive,
but the voltage remains the same. ... If you had 4 solar panels in a series
and each was rated at 12 volts and 5 amps, the entire array would be 48
volts and 5 amps.
Q5 Differentiate between dark and illuminated curves
The dark curve is a typical current vs. volt plot for a diode. A
reverse bias will produce very little or negligible current and a
forward bias will produce a very large current after a threshold.
The other lighter curve beneath the dark curve shows what
happens under illumination.
Q6 What is difference between Fresnel and Parabolic
troughs?
In general terms, we may say that Fresnel technology has more potential
for rooftop applications, while parabolic troughs can have a higher
potential when mounted on ground.
Q8 Why solar collectors are more efficient than PV cells?
It's a simple technology: the panels on your roof are the collectors of
sunlight, thus heating up the liquid in the tubes which is then transported
into your cylinder ready for use. ... They can be up to 70% more efficient
in collecting heat from sun rays than solar PV. The technology itself is
less complex than solar PV.
Q9 What is sustainability and how it can be achieved
through renewable energy technologies
Renewable energy sources such as wind, hydroelectric power, solar, and
geothermal energy are generally far more sustainable than fossil fuel sources.
However, some renewable energy projects, such as the clearing of forests to produce
biofuels, can cause severe environmental damage.
Q1010. What do you mean by chemical to physical energy
conversion?
Combustion reaction converts chemical energy into light and heat. ...
Biomass: Combustion reaction converts chemical energy into light and
heat. Natural gas: Combustion reaction converts chemical energy into light
and heat. Food: Digested to convert chemical energy into other forms of
energy used by cells.
Q11 What is Bitz limit and how it is determined?
The Betz limit is the theoretical maximum efficiency for a wind turbine,
conjectured by German physicist Albert Betz in 1919. Betz concluded that
this value is 59.3%, meaning that at most only 59.3% of the kinetic energy
from wind can be used to spin the turbine and generate electricity.
Q12 What is the key feasibly areas of wind energy in
Pakistan?
Pakistan has immense wind potential in Sindh, Balochistan, and Khyber
Pakhtun Khwa (KPK).
The Gharo-Jhimpir wind corridor in Sindh was identified as the most
lucrative site for wind power plants. The wind power potential covered an
area of 9700 km2 with a gross wind power potential of 43000 MW.
Q13 What is the difference between upwind and
horizontal wind turbines?
As already mentioned, the horizontal axis wind turbine is the most common
design of wind turbine. The axis of rotation is parallel to the ground.
Upwind machines have the rotor facing the wind. In addition, an upwind
machine needs a yaw mechanism to keep the rotor facing the wind.
Q14 What is difference between Fuel Cell and battery?
The biggest difference between the two is that a battery stores energy,
while a fuel cell generates energy by converting available fuel. ... It takes
an energy source, such as propane, diesel or natural gas, and converts it
into electrical energy.
Q15 What are key applications of fuel cells according to
various types of fuel cells.
Fuel cells are used for primary and backup power for commercial,
industrial and residential buildings and in remote or inaccessible
areas. They are also used to power fuel cell vehicles, including forklifts,
automobiles, buses, boats, motorcycles and submarines.
Q16 What is difference among undershot, breast shot and
overshot water wheels?
Overshot and backshot water wheels are typically used where the available
height difference is more than a couple of meters. Breastshot wheels are
more suited to large flows with a moderate head. Undershot and stream
wheel use large flows at little or no head.
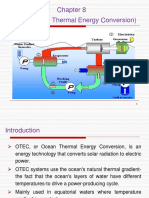
Q17 What is working principle of OTEC?
OTEC uses the ocean's warm surface water with a temperature of
around 25°C to vaporize a working fluid, which has a low-boiling point,
such as ammonia. The vapor expands and spins a turbine coupled to a
generator to produce electricity. ... The bigger the temperature difference,
the higher the efficiency.
Q18 What is earth’s temperature gradient?
The geothermal gradient is the amount that the Earth's temperature
increases with depth. It indicates heat flowing from the Earth's warm interior
to its surface. On average, the temperature increases by about 25°C for
every kilometer of depth.
Q19 What is difference between temperature and salinity
gradients ocean energy
Salinity gradient technologies generate electricity from the chemical
pressure differential created by differences in ionic concentration
between freshwater and seawater. Seawater has a higher osmotic
pressure than freshwater due to its high concentration of salt.
Ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) is a process or technology for
producing energy by harnessing the temperature differences (thermal
gradients) between ocean surface waters and deep ocean waters. Energy
from the sun heats the surface water of the ocean.
Q20 What are main Biomass Energy Resources in
Pakistan?
Rural areas of Pakistan are replete with a variety of biomass resources
(animal dung waste, MSW, agri-industrial, and agricultural waste),
which can be used to produce about 12 million cubic meters of biogas per
day, which is enough to fulfill the energy requirements of 28 million rural
people.
You might also like
- Advances in Solar Based Power GenerationDocument27 pagesAdvances in Solar Based Power GenerationSagar ShahNo ratings yet
- Ee1451-Electric Energy Generation Utilization and ConservationDocument21 pagesEe1451-Electric Energy Generation Utilization and ConservationDarwin JdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Power SystemDocument68 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Power SystemMonirul Islam100% (1)
- Green Power and Other Renewable Source of EnergyDocument24 pagesGreen Power and Other Renewable Source of EnergyPratyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit 1 GenerationDocument17 pagesQuestion Bank Unit 1 GenerationjothikumarNo ratings yet
- modeling and analysis of renewable energy systems المعدل pptxDocument37 pagesmodeling and analysis of renewable energy systems المعدل pptxanwar.23enp30No ratings yet
- Wind Solar Hybrid SystemDocument10 pagesWind Solar Hybrid SystemRavi Kiran GoudNo ratings yet
- Unit1 - Introduction To Electrical Power NotesDocument14 pagesUnit1 - Introduction To Electrical Power Notes1ms20ei002No ratings yet
- Ocean Thermal Energy ConversionDocument17 pagesOcean Thermal Energy ConversionVamsi Pelluru100% (1)
- Power System-L (3140914) Total ExperimentDocument54 pagesPower System-L (3140914) Total ExperimentAshutosh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Energy Harnessing - : SukritiDocument11 pagesEnergy Harnessing - : SukritiKumail BarafwalaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument10 pagesIntroductionmsmanojkumar763No ratings yet
- Wipo Idb Ip Ryd 07 2Document65 pagesWipo Idb Ip Ryd 07 2RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Power Systems: by Alebachew TDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Power Systems: by Alebachew TZerihun PaulosNo ratings yet
- EE1452 - Electric Energy Generation, Conservation and UtilizationDocument62 pagesEE1452 - Electric Energy Generation, Conservation and UtilizationKarthikeyan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy Generation Utilization and ConservationDocument24 pagesElectrical Energy Generation Utilization and Conservationarul skpNo ratings yet
- Files 1 2021 September NotesHubDocument 1632364811Document3 pagesFiles 1 2021 September NotesHubDocument 1632364811goels0798No ratings yet
- Ocean Thermal Power Plant ReportDocument10 pagesOcean Thermal Power Plant ReportMahmud L. MusaNo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument20 pagesPower Plantsjvharsha.sNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review On Distributed Power GenerationDocument5 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Distributed Power GenerationCésar Díaz LiberonaNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument18 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsMelvin Mendoza NocheNo ratings yet
- Principle of Power GenerationDocument36 pagesPrinciple of Power Generationbilyaminu hamisu b/zNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Part 2: Electrical Energy: EEEQ524 Energy Conservation and ManagementDocument9 pagesLecture 1-Part 2: Electrical Energy: EEEQ524 Energy Conservation and ManagementShahid AliNo ratings yet
- Mtechres PPT U 3 C 3Document15 pagesMtechres PPT U 3 C 3MounikaNo ratings yet
- 8269Document20 pages8269Vishnupriya VaradarajanNo ratings yet
- Desalination-Wind WaveDocument23 pagesDesalination-Wind WaveRubem MichelNo ratings yet
- Rotating GateDocument34 pagesRotating GateAlex MartynNo ratings yet
- 22 Solar Cell Challenges and New DevelopmentsDocument22 pages22 Solar Cell Challenges and New DevelopmentsPatrice ETEMENo ratings yet
- Svs College of Engineering: Name of The Faculty: S.KalaiarasiDocument23 pagesSvs College of Engineering: Name of The Faculty: S.KalaiarasiSudharsana ANo ratings yet
- Bahir Dar Institute of Technology (Bit) : Faculty of Electrical & Computer EngineeringDocument20 pagesBahir Dar Institute of Technology (Bit) : Faculty of Electrical & Computer Engineeringtewachew alemNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument40 pagesEnergy ResourcesKim Howard CastilloNo ratings yet
- Electric Power GenerationDocument7 pagesElectric Power GenerationearhyathNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Ocean Thermal Energy ConversionDocument21 pagesSeminar Report On Ocean Thermal Energy ConversionHARENDRA BHINCHARNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument256 pagesRenewable Energy ResourcesshuklashreyanshuNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Power Systems: BY: Sarmishtha Satpathy REGD NO: 0701209432 Applied Electronics & Instrumentation EnggDocument18 pagesSeminar On Power Systems: BY: Sarmishtha Satpathy REGD NO: 0701209432 Applied Electronics & Instrumentation EnggSachin SrivastavNo ratings yet
- SKEE 4653 - Chapter 3 - Wind Energy SystemDocument149 pagesSKEE 4653 - Chapter 3 - Wind Energy Systemahmad azmirNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Renewable Resource: Presented byDocument24 pagesThe Ultimate Renewable Resource: Presented byMayukh Dutta ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Brainkart - 225 - EE8015, EE6801 Electric Energy Generation, Utilization and Conservation - 2 Marks With Answers - Bin-1Document23 pagesBrainkart - 225 - EE8015, EE6801 Electric Energy Generation, Utilization and Conservation - 2 Marks With Answers - Bin-1rithirithika2401No ratings yet
- For Power PlantDocument224 pagesFor Power PlantIrene Mununi100% (2)
- IEE Module 1 CompleteDocument25 pagesIEE Module 1 Completekamaxey638No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Unit - 1Document16 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Unit - 1S085 Pranav HNo ratings yet
- Unit III NotesDocument22 pagesUnit III NotesArun prakashNo ratings yet
- BY Maha Barathi Engineering College Ramanathan.R/Ap/EeeDocument224 pagesBY Maha Barathi Engineering College Ramanathan.R/Ap/EeeRaj RohitNo ratings yet
- Science 9-4-5Document6 pagesScience 9-4-5Kim ReiNo ratings yet
- Final Re ProtDocument59 pagesFinal Re Protkowsika rajaramNo ratings yet
- Renewable - Energy - SourcesDocument12 pagesRenewable - Energy - SourcesErRajeshNo ratings yet
- Ijisrt21oct009 PDFDocument32 pagesIjisrt21oct009 PDFwy9frghd7dNo ratings yet
- Solar Thesis PaperDocument4 pagesSolar Thesis Paperfc2fqg8j100% (2)
- First Presentation Under The Supervision Of: Prof - DR: Abdel Hamid GomaaDocument28 pagesFirst Presentation Under The Supervision Of: Prof - DR: Abdel Hamid GomaaahmedaboshadyNo ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument14 pagesRenewable EnergyMounikaNo ratings yet
- How To Generate Electricity in Your Respective Home Using The Available Resources in Your HomeDocument5 pagesHow To Generate Electricity in Your Respective Home Using The Available Resources in Your HomeGerryanna MagbitangNo ratings yet
- Research Paper About ElectricityDocument4 pagesResearch Paper About Electricitygz7vxzyz100% (1)
- Nuclear Power in UKDocument17 pagesNuclear Power in UKSmriti SinghNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantsDocument4 pagesNuclear Power PlantsJillianne PadilloNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy and Grid Integration: Submitted T0-Submitted byDocument12 pagesRenewable Energy and Grid Integration: Submitted T0-Submitted byTiya gonekarNo ratings yet
- XEIET132 Complete Presentation 0210Document61 pagesXEIET132 Complete Presentation 0210sulemankhalidNo ratings yet
- Solar Electricity Basics: Powering Your Home or Office with Solar EnergyFrom EverandSolar Electricity Basics: Powering Your Home or Office with Solar EnergyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- OrlanPellet BrochureDocument2 pagesOrlanPellet Brochuree-ComfortUSANo ratings yet
- Siemens HedrichDocument51 pagesSiemens HedrichpabloalienadoNo ratings yet
- Internship Report 2019Document28 pagesInternship Report 2019Shivani YadavNo ratings yet
- Sunpower A Series Residential BLK DC A 390 A 400Document2 pagesSunpower A Series Residential BLK DC A 390 A 400Alex jonesNo ratings yet
- TE4a Solar Light Bank DatasheetDocument2 pagesTE4a Solar Light Bank Datasheetניסן בורוכובNo ratings yet
- Drum Control TheoryDocument9 pagesDrum Control TheoryRaju SkNo ratings yet
- DLF PresentationDocument9 pagesDLF PresentationhsparmarNo ratings yet
- EE 555 - Renewable Energy Systems - Hassan Abbas Khan PDFDocument3 pagesEE 555 - Renewable Energy Systems - Hassan Abbas Khan PDFWajahat Ullah Khan TareenNo ratings yet
- Tm2500 Mobile Gas TurbineDocument2 pagesTm2500 Mobile Gas TurbineMuhammad Syaifulhaq100% (1)
- 9 23Document2 pages9 23Sylaja GannavaramNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9Document4 pagesTutorial 9Jyoti Krishna PandaNo ratings yet
- HRSGDocument36 pagesHRSGDumitrescuNo ratings yet
- Pvsyst ReportDocument4 pagesPvsyst ReportZaman MoradiNo ratings yet
- Apr 88372Document2 pagesApr 88372N1234mNo ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument26 pagesRenewable EnergyPrakash KashyapNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant System and Operation PDFDocument161 pagesNuclear Power Plant System and Operation PDFelrajilNo ratings yet
- Manufacturer List New 2013Document75 pagesManufacturer List New 2013D.Muruganand100% (1)
- Bedienungsanleitung User Manual Manuale D'Uso Manuel de L'UtilisateurDocument2 pagesBedienungsanleitung User Manual Manuale D'Uso Manuel de L'Utilisateurmich2767No ratings yet
- Thermal EnggDocument2 pagesThermal EnggAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- A Review Paper On Solar Energy-Generated ElectricityDocument8 pagesA Review Paper On Solar Energy-Generated ElectricityIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- 1H99103 S-610M SchematicDocument9 pages1H99103 S-610M SchematicJesse chaseNo ratings yet
- Steam Boiler - DesignDocument44 pagesSteam Boiler - DesigntelldivyaNo ratings yet
- PV ModuleDocument2 pagesPV ModuleRoksana SobierajczykNo ratings yet
- Microhydro Power PlantDocument15 pagesMicrohydro Power Plantjeevana manjunathNo ratings yet
- Lycom - Ring - Apps SUPERIOR PARTS PDFDocument10 pagesLycom - Ring - Apps SUPERIOR PARTS PDFElmer VillegasNo ratings yet
- 24p AMMAR SALAH MAHDIDocument29 pages24p AMMAR SALAH MAHDIenta elektroNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Lecture Notes - CHAPTER-6 Gas Turbines & Combined CyclesDocument47 pagesPower Plant Lecture Notes - CHAPTER-6 Gas Turbines & Combined CyclesOtuagaNo ratings yet
- 1 KW Solar Power Plant Project ReportDocument3 pages1 KW Solar Power Plant Project ReportMohammd EssaNo ratings yet
- Eternal Hybrid Water Heater BrochureDocument2 pagesEternal Hybrid Water Heater Brochuree-ComfortUSANo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Hybrid Wind and Solar Energy System For Power GenerationDocument8 pagesDesign and Development of Hybrid Wind and Solar Energy System For Power GenerationBayu pradanaNo ratings yet