Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Volumetric Analysis: Acid-Base: Analytical Chemistry I
Volumetric Analysis: Acid-Base: Analytical Chemistry I
Uploaded by
paulynnOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Volumetric Analysis: Acid-Base: Analytical Chemistry I
Volumetric Analysis: Acid-Base: Analytical Chemistry I
Uploaded by
paulynnCopyright:
Available Formats
ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY I
Volumetric Analysis: Acid-Base
I. Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer and write on the space provided for.
_A____1. A technique of measuring the volume of a reagent to react with analyte and is performed by slowly
adding the reagent from a measuring device.
A Titration C Titrant
B Standard Titrant D Direct titration
__A___2. The most common method of determining organic nitrogen content wherein sample is decomposed in
hot, concentrated sulfuric acid.
A Kjeldahl method C Ion Exchange
B Dumas Method D Winkler Method
___C__3. This represents the plot of a concentration-related variable as a function of reagent volume.
A Calibration curve C Titration curve
B pH curve D Linear Curve
___A__4. The following are characteristics of a primary standard except
A High molecular weight C High purity
B High stability D None of these
_____5. A titration techniques which involves a preliminary treatment of the analyte then titrating a product formed
from this reaction
A Back titration C Direct titration
B Indirect Titration D Gravimetric titration
_____6. A quantitative determination in which the volume of a reagent required to react completely with the
analyte is measured.
A Titrimetry C Volumetric titration
B Coulometric titration D Gravimetric titration
_____7. The point in a titration process when the amount of added reagent exactly equals the amount of analyte.
A Equivalence point C End point
B Standard point D All of these
_____8. The process of determining the exact concentration of a solution by using the solution to titrate a known
amount of a reagent
A Standardization C Standard solution
B Titration D Standard titrant
_____9. The number of equivalence of a solute in 1L of a solution
A Density C Normality
B Molality D Molarity
____10. The measured pH when the acid is exactly half neutralized is numerically equal to
A Pka C POH
B Ka D Kb
II. Solve the following Problems
1. Describe the preparation of the following solutions:
a) 500 ml of approximately 0.2M NaOH (40g/mol) from solid NaOH.
b) 1L of 0.5M HCl from concentrated solution of HCl that is 37.0% w/w and a density of 1.18 g/ml. MW
of HCl is 36.461
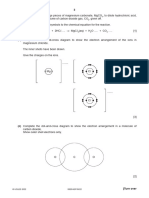
2. A 2.432 grams of primary standard Na 2CO3 (MW = 106) requires 47.26 mL of a H 2SO4 solution to reach
the end point in the reaction CO 32- + 2H+ H 2O + CO2(g). Calculate the molarity of the
H2SO4 solution.
3. A 25 ml of an HClO 4 solution was titrated with 0.1032 M NaOH solution, 28.06 ml was added in excess,
and it took 3.47 ml of 0.1094M HCl to back titrate the excess NaOH, calculate the molar concentration
of the HClO4.
4. A 25 ml sample of 0.2M NaOH was titrated with 0.2M HCl.
a) Calculate the pH of the solution before addition of any titrant and after the addition of 10 ml,
27 ml, and 30 ml of titrant.
b) Sketch the approximate titration curve
c) Suggest an appropriate visual indicator. Choose from the following:
Indicator pH range
Methyl orange 3.1 – 4.4
Bromothymol Blue 6.2 – 7.6
Thymolphthalein 9.3 – 10.5
You might also like
- Business Reporting July 2013 Exam PapersDocument16 pagesBusiness Reporting July 2013 Exam Paperskarlr9No ratings yet
- The Nomad Lore 1.31Document57 pagesThe Nomad Lore 1.31Rui HuNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology - Polyuria - SOAP Note - Jeanette GoguenDocument3 pagesEndocrinology - Polyuria - SOAP Note - Jeanette GoguenFrancieudo SampaioNo ratings yet
- ChemTech DiagnosticDocument3 pagesChemTech DiagnosticrickiegasparNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of The Flexor TendonsDocument21 pagesBiomechanics of The Flexor TendonsAlejandro PAEZ MONTESNo ratings yet
- Pre/Post-Assessment Answers: Food Safety in SchoolsDocument6 pagesPre/Post-Assessment Answers: Food Safety in SchoolsFlankzyNo ratings yet
- Qc1 Quiz CompilationsDocument8 pagesQc1 Quiz Compilationsprinz1mendezNo ratings yet
- Volumetric AnalysisDocument9 pagesVolumetric AnalysiszoeakatNo ratings yet
- 11th Experiment-5Document2 pages11th Experiment-5theinvisibleminecrafterNo ratings yet
- Unit X: Protein Nitrogen Determination by Kjeldahl Method 1. Warm-UpDocument8 pagesUnit X: Protein Nitrogen Determination by Kjeldahl Method 1. Warm-UpNgân Lê Thị ThảoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Titrimetric AnalysisDocument50 pagesIntroduction To Titrimetric AnalysisMartha Phasha100% (1)
- Chem Bio II Lecture 6 Titrimetry AutosavedDocument16 pagesChem Bio II Lecture 6 Titrimetry AutosavedKyrby CabalquintoNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Chemical AnalysisDocument5 pagesQuantitative Chemical AnalysisMae Christine PaduaNo ratings yet
- Abbyshaygayle Cape Chemistry Lab Full 22Document28 pagesAbbyshaygayle Cape Chemistry Lab Full 22Abby Shay GayleNo ratings yet
- Abbyshay Hayle Cape Chemistry Lab Full 2021Document22 pagesAbbyshay Hayle Cape Chemistry Lab Full 2021Abby Shay Gayle100% (1)
- Analytical Chemistry FinalsDocument9 pagesAnalytical Chemistry FinalsfayeNo ratings yet
- MCQ For Pharmaceutical Analysis-I (Bp102T) : Mrs. Namrata N. Patel Department of Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument17 pagesMCQ For Pharmaceutical Analysis-I (Bp102T) : Mrs. Namrata N. Patel Department of Pharmaceutical ChemistryNamrata patelNo ratings yet
- Question: The Following Primary Standards Can Be Used For The StandardiDocument5 pagesQuestion: The Following Primary Standards Can Be Used For The StandardiMustafa KhudhairNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document16 pagesChapter 13Banana QNo ratings yet
- Determination of Concentration of Acetic Acid in Vinegar Sample Using Titrimetric AnalysisDocument3 pagesDetermination of Concentration of Acetic Acid in Vinegar Sample Using Titrimetric AnalysisJoshua LimbagaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Determination of Solution ConcentrationDocument6 pagesLab 1 Determination of Solution ConcentrationMuhamad FarisNo ratings yet
- Informe Lab 3 Volumetria de NeutralizacionDocument4 pagesInforme Lab 3 Volumetria de NeutralizacionMiguel Angel Roldan MartinNo ratings yet
- Titrimetric Methods of AnalysisDocument82 pagesTitrimetric Methods of AnalysisMeseret KifileNo ratings yet
- 6-Titrimetric Methods of AnalysisDocument15 pages6-Titrimetric Methods of Analysisnids75% (4)
- Quantitative Chemistry PS 1 Answers 2022Document3 pagesQuantitative Chemistry PS 1 Answers 2022lyandle minNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Notes TitrationsDocument69 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Notes TitrationsAllen de Guzman80% (15)
- Unit 7 General Concept of Volumetric Titrimetry UST TemplateDocument22 pagesUnit 7 General Concept of Volumetric Titrimetry UST TemplateCess MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument95 pagesAnalytical ChemistryHugo WNo ratings yet
- Anachem Le1Document4 pagesAnachem Le1Bernard Jomari Blancada RazoteNo ratings yet
- Huy - lop TACN - in CNTP-đã Chuyển ĐổiDocument19 pagesHuy - lop TACN - in CNTP-đã Chuyển ĐổiNguyễn Thị Quỳnh HoaNo ratings yet
- Buku+Petunjuk+Prak+KA InterDocument49 pagesBuku+Petunjuk+Prak+KA InterAjeng NadiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.1. Fundamentals of Volumetric AnalysisDocument7 pagesChapter 5.1. Fundamentals of Volumetric AnalysisAmir KasimNo ratings yet
- Exit inDocument4 pagesExit inMegersa ChaliNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument12 pagesAnalytical ChemistryArjayle Airobail LlevadoNo ratings yet
- Titrimetric Methods of AnalysisDocument23 pagesTitrimetric Methods of Analysissarifah supriNo ratings yet
- CMC Chapter 11Document58 pagesCMC Chapter 11Marah Omar50% (2)
- QuestionsDocument17 pagesQuestionsAbhishek SunaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base TitrationDocument2 pagesAcid Base TitrationRangerNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemDocument18 pagesAnalytical Chemziya75100% (1)
- Compiled Past Board Exam Questions: Licensure Examination For Chemical Technicians October 29, 2021Document15 pagesCompiled Past Board Exam Questions: Licensure Examination For Chemical Technicians October 29, 2021Jhema Mae Eco AguilarNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chem Chap11Document18 pagesAnalytical Chem Chap11Nicole Ann PedriñaNo ratings yet
- Titrations: Taking Advantage of Stoichiometric ReactionsDocument18 pagesTitrations: Taking Advantage of Stoichiometric ReactionsAngelica Camille B. AbaoNo ratings yet
- Campion College 6B Chemistry ' LaboratoryDocument3 pagesCampion College 6B Chemistry ' LaboratoryNickolai AntoineNo ratings yet
- Module4 - Volumetric Method of AnalysisDocument18 pagesModule4 - Volumetric Method of AnalysisJoyce Mariele RomeroNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Shahjalal University of Science & Technology, SylhetDocument6 pagesLab Report: Shahjalal University of Science & Technology, SylhetMd Afif AbrarNo ratings yet
- Chem MCQDocument11 pagesChem MCQnahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- Titration Notes: MethodDocument3 pagesTitration Notes: MethodArSlanRahatNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chem-Unit 5Document18 pagesAnalytical Chem-Unit 5Jayson Polinar100% (1)
- 205-W13-Acid-base Titrations-Instant Notes - Analytical ChemistryDocument7 pages205-W13-Acid-base Titrations-Instant Notes - Analytical ChemistrykhujastakhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Review On Basic Principles Applied in Analytical ChemistryDocument12 pagesUnit 4 - Review On Basic Principles Applied in Analytical ChemistryJayson PolinarNo ratings yet
- Chapter II: Titrimetric Method of AnalysisDocument36 pagesChapter II: Titrimetric Method of AnalysisHenok Girma100% (1)
- Analytical ChemistryDocument4 pagesAnalytical ChemistryJewls HatudNo ratings yet
- 2017 Unit 2 Chemistry KTT 6 Volumetric Analysis - Question BookDocument12 pages2017 Unit 2 Chemistry KTT 6 Volumetric Analysis - Question Bookfrank sinatraaNo ratings yet
- Titrimetric Methods of AnalysesDocument10 pagesTitrimetric Methods of AnalysesJason BakerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab# 3 (Completed)Document3 pagesChemistry Lab# 3 (Completed)tahjsalmon100% (2)
- Chem2 Ch13 Skoog Lab Volumetric Analysis TitrationDocument40 pagesChem2 Ch13 Skoog Lab Volumetric Analysis TitrationBochibo Snatch100% (1)
- QC Blue Pacop QuestionsDocument26 pagesQC Blue Pacop QuestionsSophia AndresNo ratings yet
- Question Bank PA I CBCS R-2019 Sem IDocument13 pagesQuestion Bank PA I CBCS R-2019 Sem IArthor KingNo ratings yet
- Some Laboratory Errors Are More Obvious Than OthersDocument64 pagesSome Laboratory Errors Are More Obvious Than Othersahmad FouadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Titrimetric MethodsDocument31 pagesChapter 6 Titrimetric MethodsNapi D. LuffyNo ratings yet
- 01 - Solution Concentrations-Chem22Document4 pages01 - Solution Concentrations-Chem22EJ RamirezNo ratings yet
- Analytical Stream Model QuestionsDocument4 pagesAnalytical Stream Model Questionsdanimiresa961No ratings yet
- Practical Manual of Analytical ChemistryFrom EverandPractical Manual of Analytical ChemistryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Date Submitted: Course / Section: Activity Title: Realization, Insight and LearningsDocument3 pagesDate Submitted: Course / Section: Activity Title: Realization, Insight and LearningspaulynnNo ratings yet
- Introductory Statement - : Results and DiscussionDocument12 pagesIntroductory Statement - : Results and DiscussionpaulynnNo ratings yet
- Form - Case Analysis Essay No Read, No Write - Story of Mang DeolitoDocument1 pageForm - Case Analysis Essay No Read, No Write - Story of Mang DeolitopaulynnNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.3.aDocument2 pagesExercise 2.3.apaulynnNo ratings yet
- Form - CWTS102 Essay #1Document2 pagesForm - CWTS102 Essay #1paulynnNo ratings yet
- Form - CWTS102 Term-End Essay Part-1Document3 pagesForm - CWTS102 Term-End Essay Part-1paulynnNo ratings yet
- Expansion ValvesDocument19 pagesExpansion ValvesMostafa ZaytounNo ratings yet
- TRG2 ReportDocument2 pagesTRG2 ReportWET WATERNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review 2Document82 pagesMidterm Review 2middletown njNo ratings yet
- Fakir Apparels LTD Final Credit ReportDocument5 pagesFakir Apparels LTD Final Credit Reportfarabi1984No ratings yet
- Management Operating System Auckland CityDocument20 pagesManagement Operating System Auckland CityVasilis PolykarpidisNo ratings yet
- PVSyst Loss Description - by Filipe AndradeDocument12 pagesPVSyst Loss Description - by Filipe AndradeMezrag mohamedNo ratings yet
- Httpswww-Clinicalkey-Es Pbidi Unam Mx2443servicecontentpdfwatermarked3-S2 0-B9780323680134000195 Pdflocale Es - ES&searcDocument18 pagesHttpswww-Clinicalkey-Es Pbidi Unam Mx2443servicecontentpdfwatermarked3-S2 0-B9780323680134000195 Pdflocale Es - ES&searcDafne TeranNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument41 pagesRate of ReactionHala NajiNo ratings yet
- Organizational Development & Change Of: Presented By: Kamal Lochan BeheraDocument17 pagesOrganizational Development & Change Of: Presented By: Kamal Lochan BeheraKamalLochanBehera0% (1)
- Confined Space Hazards Assessment FormDocument3 pagesConfined Space Hazards Assessment FormAhmed El-sherpiniNo ratings yet
- Corken CompressorI100Document16 pagesCorken CompressorI100adriansya7No ratings yet
- The Health Anxiety Inventory Development and Validation of Scales For The Measurement of Health Anxiety and HypochondriasisDocument11 pagesThe Health Anxiety Inventory Development and Validation of Scales For The Measurement of Health Anxiety and HypochondriasisJan LAWNo ratings yet
- Bomba SKC 222 ManualDocument11 pagesBomba SKC 222 ManualEderson GuimaraesNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 8749Document77 pagesRepublic Act No. 8749Jey RhyNo ratings yet
- Entry Level English AssessmentDocument16 pagesEntry Level English AssessmentRosa-Marie RamkissoonNo ratings yet
- PROCESS in RAW SUGAR Production of FFHCDocument27 pagesPROCESS in RAW SUGAR Production of FFHCTenebroso Pevie Anne100% (1)
- Essay On Cigarette SmokingDocument6 pagesEssay On Cigarette Smokingfz5s2avw100% (2)
- Checklist For Internal PlasteringDocument2 pagesChecklist For Internal Plasteringyash shah100% (1)
- Ruwais Refinery Expansion Project Project No. 5578 Epc Package - 6 (Non Process Building)Document32 pagesRuwais Refinery Expansion Project Project No. 5578 Epc Package - 6 (Non Process Building)Mohammed AzharNo ratings yet
- LO1Clean The Bar AreasDocument27 pagesLO1Clean The Bar AreasEiszel CadacioNo ratings yet
- Pumpkin Rogan Josh With Cumin RaitaDocument1 pagePumpkin Rogan Josh With Cumin RaitawatkinsbbNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch02 Solutions PDFDocument5 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch02 Solutions PDFSahilGuptaNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Studies of Bats in Captivity: Methodology, Training, and Experimental DesignDocument20 pagesBehavioral Studies of Bats in Captivity: Methodology, Training, and Experimental DesignIslam Ausraf RajibNo ratings yet
- A GCE Biology 2805 03 January 2008 Question PaperDocument16 pagesA GCE Biology 2805 03 January 2008 Question PaperVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- Structure of Human Eye DipiyDocument10 pagesStructure of Human Eye Dipiyvineet_knwrNo ratings yet