Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Is This Accomplished?: Encoder Definitions
How Is This Accomplished?: Encoder Definitions
Uploaded by
Mahmoud AlaaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Is This Accomplished?: Encoder Definitions
How Is This Accomplished?: Encoder Definitions
Uploaded by
Mahmoud AlaaCopyright:
Available Formats
Encoder Definitions
How is this accomplished?
: As the code disc rotates, it shutters light from the LED and is received and
transmitted as square\sine waveforms
Receiver / Sensor
Code disc
Lens
Transmitter / LED
Shaft
: SICK, Inc. : Confidential 5
Incremental Encoders
Incremental
Produces electrical pulses or increments
with linear or rotary motion
Signals can be square or sinusoidal waves
Signals start over at power up, or after a
power failure. In other words, an incremental
encoder does not retain position after a
power cycle
Incremental encoders are typically used for
speed or applications that do not require
absolute position
: SICK, Inc. : Confidential 13
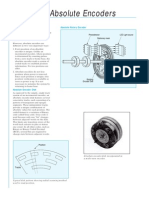
Absolute Encoders
Absolute
Provides a unique value for every shaft or
linear position
Code disc for absolute
encoders Absolute encoders retain their position after
a power cycle
Signals typically use SSI, parallel, or field bus
LED interfaces (Ethernet/IP, EtherCAT, Profinet,
Lens
Scanning mask Devicenet, CANopen, Profibus, etc)
Code disc Photo-
Elements Absolute encoders are used in applications
were position information is necessary
: SICK, Inc. : Confidential 14
Electrical Interface Summary
Things to know when choosing an encoder
: Incremental Encoders : Absolute Encoders
- Resolution (PPR) - Resolution (singleturn, multiturn)
- Supply Voltage - Output type
- Output Voltage (HTL, TTL or Open ▪ Parallel (output voltage needed)
Collector) ▪ SSI
▪ Fieldbus
- Programmable Encoders: - Programmable Encoders
DFS60 and DFS2x encoders let you Programmable options for SSI encoders to
program ALL electrical configurations program the resolution. All field bus
except an open collector output encoders are programmable over their
respective networks
: SICK, Inc. : Confidential : Name (Date) 28
You might also like
- P091 084 Ioiscm Um 1105Document30 pagesP091 084 Ioiscm Um 1105Badescu Ionut100% (1)
- E - EncodersDocument21 pagesE - EncodersAbdelrahman RagabNo ratings yet
- Encoders Basic TrainingDocument41 pagesEncoders Basic TrainingZyzerull Saad100% (1)
- Absolute Encoders: BasicsDocument2 pagesAbsolute Encoders: BasicsRamesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Sinyal Sistem w6 en ProjectsDocument113 pagesSinyal Sistem w6 en ProjectsbeyzaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial EncoderDocument3 pagesTutorial EncoderbequeNo ratings yet
- FPS110, FPS110B, FPS110E: Features ApplicationsDocument17 pagesFPS110, FPS110B, FPS110E: Features ApplicationsFrancisco HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Precision Hall-Effect Angle Sensor IC With I C, SPI, and SENT InterfacesDocument29 pagesPrecision Hall-Effect Angle Sensor IC With I C, SPI, and SENT InterfacesdsafasteasfNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Arduino BoardsDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Arduino BoardsRohit VarmaNo ratings yet
- Servo Parker PDFDocument8 pagesServo Parker PDFBeto HernándezNo ratings yet
- Basic Arduino ProgramsDocument25 pagesBasic Arduino ProgramsYogesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- IR117 RS-1 Remote Control ICDocument3 pagesIR117 RS-1 Remote Control IChandsome03No ratings yet
- DATA Converter CircuitsDocument31 pagesDATA Converter CircuitsCharefNo ratings yet
- Siga CC1S PDFDocument4 pagesSiga CC1S PDFAngel DuarteNo ratings yet
- Intro To ArduinoDocument39 pagesIntro To ArduinoGkid GkidNo ratings yet
- Line Following Robot With Color Detection PDFDocument10 pagesLine Following Robot With Color Detection PDFpaishkepeng100% (1)
- EncodersDocument19 pagesEncodersadelsonpimentelNo ratings yet
- Workshop On Arduino VITDocument45 pagesWorkshop On Arduino VITLuqman SyedNo ratings yet
- PixArt PMW3310DH PDFDocument41 pagesPixArt PMW3310DH PDFfooobarNo ratings yet
- SN 65 Hvs 885Document28 pagesSN 65 Hvs 8851553No ratings yet
- Allegro A1335LLETR T Datasheet PDFDocument53 pagesAllegro A1335LLETR T Datasheet PDFeveraldoNo ratings yet
- Design GuideDocument8 pagesDesign Guideapi-3756260No ratings yet
- Ashida ADR141C & ADR214C Fix Type, 4 Element IDMT Relay PDFDocument13 pagesAshida ADR141C & ADR214C Fix Type, 4 Element IDMT Relay PDFachinta singhaNo ratings yet
- CCR204 - Lec05Document47 pagesCCR204 - Lec05Moni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Apds9960 PDFDocument38 pagesApds9960 PDFaraikNo ratings yet
- Encoders PDFDocument6 pagesEncoders PDFFernando Xavier Guanoluisa SolanoNo ratings yet
- Simplify Current and Voltage Monitoring With Isolated SPIDocument3 pagesSimplify Current and Voltage Monitoring With Isolated SPICarey JohnNo ratings yet
- Angle Analyzer Analyzer of An Encoder Using The Labview Using TheDocument4 pagesAngle Analyzer Analyzer of An Encoder Using The Labview Using TheChâu Tinh TrìNo ratings yet
- TM PRS PosterBook - Lowres - CleanedDocument16 pagesTM PRS PosterBook - Lowres - CleanedBiren Kumar PradhanNo ratings yet
- Encoder SDI To Analog Composite - Dual Reclocked Outputs: SpecificationsDocument1 pageEncoder SDI To Analog Composite - Dual Reclocked Outputs: SpecificationsJesus GarciaNo ratings yet
- Intro To ArduinoProgrammingDocument87 pagesIntro To ArduinoProgrammingAireen Galgo MargateNo ratings yet
- PR Interfaces ID1078628 enDocument40 pagesPR Interfaces ID1078628 enEdwars GuerreroNo ratings yet
- BuR X20 HardwareDocument14 pagesBuR X20 HardwarecelinNo ratings yet
- Manual - Drive - Is7 - ENG - KOR - Pulse Encoder Option PDFDocument22 pagesManual - Drive - Is7 - ENG - KOR - Pulse Encoder Option PDFFadFadNo ratings yet
- Fastest Finger First Game EE-121-L Lab Project Proposal: Submitted To: Mr. DanialDocument5 pagesFastest Finger First Game EE-121-L Lab Project Proposal: Submitted To: Mr. DanialHassaan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Absolute Encoders Principle of OperationDocument2 pagesAbsolute Encoders Principle of OperationSakhawat Hossain RonyNo ratings yet
- A1454 DatasheetDocument15 pagesA1454 DatasheetShawn JordanNo ratings yet
- Adr141c PDFDocument11 pagesAdr141c PDFNamrata Shetti100% (1)
- 1 - Micro C BASIC IO - LED AND SWITCHDocument90 pages1 - Micro C BASIC IO - LED AND SWITCHs221091638No ratings yet
- Bidirectional Visitor Counter With AutomDocument3 pagesBidirectional Visitor Counter With Automkaloy33No ratings yet
- Autonics Rotary Encoders (Technical Description) Data SheetDocument6 pagesAutonics Rotary Encoders (Technical Description) Data SheetTodi FindraNo ratings yet
- Contact Less Tachometer: IC 741c:an IC 741c Is Single Op-Amp Device. AnDocument6 pagesContact Less Tachometer: IC 741c:an IC 741c Is Single Op-Amp Device. Anravi prakashNo ratings yet
- Encoder CatalogDocument24 pagesEncoder CatalogCao Minh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Guddu PPT 1Document26 pagesGuddu PPT 1vikasNo ratings yet
- IK 220 CardDocument4 pagesIK 220 CardArthur TalibulinNo ratings yet
- 4 Adc/8 Dac With PLL, 192 KHZ, 24-Bit Codec Ad1939: Features General DescriptionDocument32 pages4 Adc/8 Dac With PLL, 192 KHZ, 24-Bit Codec Ad1939: Features General Descriptionsuan kwang TanNo ratings yet
- S&A Optical Encoders PDFDocument34 pagesS&A Optical Encoders PDFNiravNo ratings yet
- Interfaces: of HEIDENHAIN EncodersDocument25 pagesInterfaces: of HEIDENHAIN EncodersArturo FuentesNo ratings yet
- Si3216 15Document120 pagesSi3216 15Vasia DeminNo ratings yet
- Measuring Systems SIMODRIVE Sensor: 8/2 Built-On Optoelectronic Rotary EncodersDocument10 pagesMeasuring Systems SIMODRIVE Sensor: 8/2 Built-On Optoelectronic Rotary EncodersUlfran MedinaNo ratings yet
- Lec07 DS 2018Document76 pagesLec07 DS 2018Hưng PhạmNo ratings yet
- E85001-0543 - Synchronization Output ModuleDocument4 pagesE85001-0543 - Synchronization Output ModuleCoordinador TecnicoNo ratings yet
- Dide-Diode Opto IsolationDocument16 pagesDide-Diode Opto Isolationzivko.kokolanskiNo ratings yet
- K50 Pro Indicator With IO-Link: DatasheetDocument5 pagesK50 Pro Indicator With IO-Link: DatasheetRicardo Daniel Martinez HernandezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Arduino: // Basic Arduino Reference SheetDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Arduino: // Basic Arduino Reference SheetMOHD RASHIDNo ratings yet
- Protection Features: Relay Design Features:: Local Keys As Well As Remote Setting by Communication PortDocument17 pagesProtection Features: Relay Design Features:: Local Keys As Well As Remote Setting by Communication PortNamrata ShettiNo ratings yet
- Build A Video Switcher: Reprinted With Permission From September 1997 IssueDocument8 pagesBuild A Video Switcher: Reprinted With Permission From September 1997 IssueshajarajanNo ratings yet
- Exploring Arduino: Tools and Techniques for Engineering WizardryFrom EverandExploring Arduino: Tools and Techniques for Engineering WizardryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Inverter StartupDocument55 pagesInverter StartupMahmoud AlaaNo ratings yet
- Cat 3512 Sensor PositionDocument9 pagesCat 3512 Sensor PositionMahmoud AlaaNo ratings yet
- Module C4DW Control SystemsDocument34 pagesModule C4DW Control SystemsMahmoud AlaaNo ratings yet
- Analog Temperature SensorDocument1 pageAnalog Temperature SensorMahmoud AlaaNo ratings yet
- الخدمات التى تحتاج الى موافقه مسبقهDocument4 pagesالخدمات التى تحتاج الى موافقه مسبقهMahmoud AlaaNo ratings yet
- GTC Pub 030200Document2 pagesGTC Pub 030200Mahmoud AlaaNo ratings yet
- General Wiring and Installation Guidelines: Protecting Signals From Radiated and Conducted NoiseDocument2 pagesGeneral Wiring and Installation Guidelines: Protecting Signals From Radiated and Conducted NoiseMahmoud AlaaNo ratings yet
- Safety Relays C574: Ordering DetailsDocument1 pageSafety Relays C574: Ordering DetailsMahmoud AlaaNo ratings yet
- A Good Introduction To IPTVDocument2 pagesA Good Introduction To IPTVjumboseason7No ratings yet
- CmsDocument4 pagesCmsSinnarasa PratheepNo ratings yet
- M4-Internet Layer ProtokolDocument55 pagesM4-Internet Layer ProtokolAgung Budi CahyonoNo ratings yet
- OEO116120 LTE eRAN3.0 LTE TDD Subframe Configuration Feature ISSUE 1.00Document20 pagesOEO116120 LTE eRAN3.0 LTE TDD Subframe Configuration Feature ISSUE 1.00VinklerNo ratings yet
- Patton OS3300Document18 pagesPatton OS3300giannidieci010No ratings yet
- Laprf Personal Timing System: Operator'S ManualDocument22 pagesLaprf Personal Timing System: Operator'S Manualdbsi batamNo ratings yet
- An Adaptive Communication Architecture For Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument27 pagesAn Adaptive Communication Architecture For Wireless Sensor NetworksmouliomNo ratings yet
- PanasonicDocument362 pagesPanasonicComputer789No ratings yet
- 7ITHelpDesk PDFDocument30 pages7ITHelpDesk PDFiqbal raisnawanNo ratings yet
- 2G Call FlowDocument40 pages2G Call FlowPrincely JNo ratings yet
- Indoor/Outdoor Bidirectional Antenna 790-2700 MHZ: Product Data Sheet I-Atb1-790/2700Document2 pagesIndoor/Outdoor Bidirectional Antenna 790-2700 MHZ: Product Data Sheet I-Atb1-790/2700Сергей ФатхретдиновNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal 1Document14 pagesProject Proposal 1ammad ahmadNo ratings yet
- EcoStruxure Security Expert BrochureDocument8 pagesEcoStruxure Security Expert BrochureNguyen Van KhoiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 and 3Document12 pagesModule 2 and 3Jerome BarraNo ratings yet
- Wifi Hacking Rogue Access Points PreviewDocument38 pagesWifi Hacking Rogue Access Points PreviewJavierNo ratings yet
- Ieee PaperDocument6 pagesIeee PaperJayant OjhaNo ratings yet
- Field Trial of Automatic Bias Control Scheme For oDocument8 pagesField Trial of Automatic Bias Control Scheme For oansarixxxNo ratings yet
- Reconfigurable Stacked Microstrip Patch Antenna For Multi-Band ApplicationDocument5 pagesReconfigurable Stacked Microstrip Patch Antenna For Multi-Band ApplicationAmador Garcia IIINo ratings yet
- Venkateshwaran CV As On 25.11.2022Document5 pagesVenkateshwaran CV As On 25.11.2022huvenkateshNo ratings yet
- CSEC IT NOTES - Term 2 Week 11 - Computer Networks Lecture 1Document58 pagesCSEC IT NOTES - Term 2 Week 11 - Computer Networks Lecture 1kxng ultimateNo ratings yet
- New Perspectives Computer Concepts Enhanced Comprehensive 2016 19th Edition Parsons Test BankDocument25 pagesNew Perspectives Computer Concepts Enhanced Comprehensive 2016 19th Edition Parsons Test BankRichardHoweycgr100% (49)
- Price List - Service Packages & Plans Residential Services - Emerald Neopolis Karawang - 2021Document1 pagePrice List - Service Packages & Plans Residential Services - Emerald Neopolis Karawang - 2021Bernisela DamaraNo ratings yet
- JBL Live 300TWS Spec Sheet EnglishDocument2 pagesJBL Live 300TWS Spec Sheet EnglishCristian ZapataNo ratings yet
- Internet TechnologyDocument5 pagesInternet Technologyphilip abrahamsNo ratings yet
- HP Probook 4310s Laptop SchematicsDocument53 pagesHP Probook 4310s Laptop SchematicsAn TrầnNo ratings yet
- EEE225 - Pre-Final Exam Section 1 - Google FormsDocument11 pagesEEE225 - Pre-Final Exam Section 1 - Google FormsDavid Louie BediaNo ratings yet
- Management Information System: (Assignment)Document7 pagesManagement Information System: (Assignment)Arvin YadavNo ratings yet
- Tower Sharing-1Document8 pagesTower Sharing-1Amit GorkhaliNo ratings yet
- Huawei NE05E SE Routers DatasheetDocument35 pagesHuawei NE05E SE Routers DatasheetShahed IsrarNo ratings yet
- 6G The Next Horizon From Connected People and Things To Connected Intelligence 1St Edition Wen Tong Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pages6G The Next Horizon From Connected People and Things To Connected Intelligence 1St Edition Wen Tong Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFcassandra.delacruz689100% (16)