Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Revision-Unit 2: Organisation of The Organism
Biology Revision-Unit 2: Organisation of The Organism
Uploaded by
Alberto CasiniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Revision-Unit 2: Organisation of The Organism
Biology Revision-Unit 2: Organisation of The Organism
Uploaded by
Alberto CasiniCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Revision- Unit 2: Organisation of the Organism
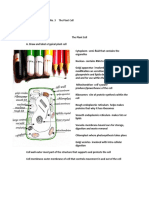
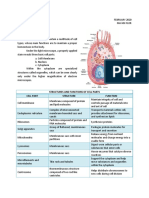
Cytoplasm Jelly-like with particles It’s enclosed by the Contains organelles,
and organelles in it. cell membrane. e.g. mitochondria,
nucleus.
It’s the site of chemical
reactions (metabolism)
Nucleus A oval structure which Inside cytoplasm Controls cell division
contains DNA
information, in form of Controls development
chromosomes
Controls cell activities
Cell membrane A partially permeable Around cytoplasm Prevents cell
layer that forms a contents from
boundary around the escaping.
cytoplasm.
Controls what
substances enter
and leave the cell.
Mitochondria Oval or slipper shaped Inside cytoplasm Responsible for
organelles aerobic respiration
Ribosomes Circular structure inside cytoplasm Protein synthesis
attached to
membranes or lying
free
Cell wall A tough, non living Around the Prevents plant cells
layer made of cellulose outside of plant from bursting
surrounding the cell cells
membrane Allows water and
salts to pass through
(freely permeable
Vacuole Fluid filled space Inside cytoplasm Contains salts and
surrounded by a of a plant cells sugars.
membrane
Helps keep plant
cells firm
Chloroplasts An organelle Inside the Traps light energy
containing chlorophyll cytoplasm of for photosynthesis
some plant cells
Magnification formula: Magnification= image size / actual size
Reverse formula (actual size): image size / magnification
Reverse formula (image size): magnification x actual size
There are:
1000 micrometres in a millimetre
10 000 micrometres in a centimetre
1 000 000 micrometres in a metre
1 000 000 nanometres in a millimetre
1000 nanometres in a micrometre
BACTERIA: Cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, single strand of DNA coiled up
to form nucleoide, plasmids, philis, sometimes flagellum
Multiple organelles> cell
Multiple cell> tissue
Multiple tissue> organ
Multiple organ> organ system
You might also like
- Lange Basic Histology Flashcards Lange PDFDocument412 pagesLange Basic Histology Flashcards Lange PDFMarcelo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- CytologyDocument20 pagesCytologykaziba stephen100% (1)
- 2017 OL Cell Cycle Exam ReviewDocument3 pages2017 OL Cell Cycle Exam ReviewAnne Romo50% (8)
- Cell Structure and Function ReviewerDocument4 pagesCell Structure and Function ReviewerLeandre Jasmine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and FunctionsKarren Ferrer-Mora Handayan100% (1)
- Biology Bmat Section 2Document20 pagesBiology Bmat Section 2celiNo ratings yet
- Notion 2 - Organization - of - The - OrganismDocument7 pagesNotion 2 - Organization - of - The - OrganismFadi AltananyNo ratings yet
- CellDocument9 pagesCellAlman AliNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureDocument31 pagesDokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureJairra Jae LunaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & OrganizationDocument7 pagesCell Structure & OrganizationMaryam ShahidNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Membrane and DivisionDocument15 pagesCell Structure Membrane and DivisionRawdatul JannahNo ratings yet
- Cell ComponentsDocument3 pagesCell Componentssu thadahtetNo ratings yet
- Organelle Present/Absent Description FunctionDocument5 pagesOrganelle Present/Absent Description FunctionTania BacsinNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument15 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesMai YoussifNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Organelle Diagram Where It's Found Role Cell Surface MembraneDocument6 pagesCell Organelles Organelle Diagram Where It's Found Role Cell Surface MembraneMoe SiNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie Jaiswal100% (1)
- 00 - Cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell WallDocument4 pages00 - Cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell WallJeremy TanNo ratings yet
- Cells VIS ChartDocument1 pageCells VIS Chartdidua08No ratings yet
- Cell Organelle CardsDocument6 pagesCell Organelle CardsVienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- Cells 240602 153233Document5 pagesCells 240602 153233mothusiamosselloNo ratings yet
- 02 Organization of The OrganismDocument10 pages02 Organization of The OrganismkaderovichNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2-SHORT NOTES Biology ALEVElSDocument38 pagesUNIT-2-SHORT NOTES Biology ALEVElSMohammed HasnatNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellElmer Tunggolh, Jr.No ratings yet
- Cytology 22Document20 pagesCytology 22lifeeternaltointerveneNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions (Flores)Document4 pagesEukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions (Flores)Dharyl FloresNo ratings yet
- The Voice of The GenomeDocument6 pagesThe Voice of The GenomeSeaCarrotNo ratings yet
- Bio 103 L1-2 - NiaDocument33 pagesBio 103 L1-2 - Niasubrotoghosh2001No ratings yet
- 00 - Cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell WallDocument4 pages00 - Cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell WallJeremy TanNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsjhabNo ratings yet
- Cytology and Chemicals of LifeDocument53 pagesCytology and Chemicals of LifeIVAN HUNCHONo ratings yet
- Gen Bio (Definitions) - Cell StructureDocument3 pagesGen Bio (Definitions) - Cell StructureMary Vhenn SamonteNo ratings yet
- A Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneDocument3 pagesA Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and Organization: Structur e FunctionDocument14 pages2.1 Cell Structure and Organization: Structur e Functionwafa eliasNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument16 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationanippoNo ratings yet
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocument37 pages2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- Cambridge o Level Biology Revision GuideDocument10 pagesCambridge o Level Biology Revision GuideAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells NotesDocument7 pagesBio Cells Notesnabita20211No ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer 2Document3 pagesAnaphy Reviewer 2Christopher Valle ArgelNo ratings yet
- Act 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesAct 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportRicky SalazarNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells PDFDocument4 pagesAnimal Cells PDFFalah HabibNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology-1 (The Cell) BS ZOL 3rdDocument93 pagesCell Biology-1 (The Cell) BS ZOL 3rdNadir BashirNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and TaxonomyCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesRahul ManhasNo ratings yet
- DR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Document14 pagesDR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Cole- Min Khant KyawNo ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- Activity Ii The Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument7 pagesActivity Ii The Cellular Level of OrganizationRjosheNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyJasmin Pearl AndayaNo ratings yet
- Act 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportDocument7 pagesAct 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- CELulas 2Document21 pagesCELulas 2lizetteNo ratings yet
- NatSci2 Chapter 3Document33 pagesNatSci2 Chapter 3kayNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDocument49 pagesEukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDaezel Deux100% (1)
- Chapter 2 & 3 - ZoologyDocument4 pagesChapter 2 & 3 - ZoologyAngel MerilloNo ratings yet
- Module I-Cocepts in BiologyDocument46 pagesModule I-Cocepts in BiologyManan MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Biology: MicrosDocument17 pagesBiology: MicrosEANo ratings yet
- 2 Organisation of the organismDocument10 pages2 Organisation of the organismac24jwNo ratings yet
- B M Subramanya Swamy CIE Co Ordinator & Examination Officer Kanaan Global School Jakarta Indonesia Swamy@kanaanglobal - Sch.idDocument42 pagesB M Subramanya Swamy CIE Co Ordinator & Examination Officer Kanaan Global School Jakarta Indonesia Swamy@kanaanglobal - Sch.idB M Subramanya SwamyNo ratings yet
- Histology AssignmentDocument6 pagesHistology AssignmentBryan LebasnonNo ratings yet
- Introduction CellDocument48 pagesIntroduction CellabdNo ratings yet
- Lesso N 2: Organe LlesDocument19 pagesLesso N 2: Organe LlesMicha E.No ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of CellsDocument7 pagesParts and Functions of CellsKate Aireen JerezNo ratings yet
- DP1 BIO - Test - Topic 1 Paper 1 PDFDocument6 pagesDP1 BIO - Test - Topic 1 Paper 1 PDFSaima SyedaNo ratings yet
- L041 - Laboratory Exercise No. 1B - Dautil JastineDocument2 pagesL041 - Laboratory Exercise No. 1B - Dautil JastineJastine Managbanag DautilNo ratings yet
- Cell Model Ornament PDFDocument3 pagesCell Model Ornament PDFapi-354423730No ratings yet
- Digestive System ExamDocument3 pagesDigestive System ExamRouse Leanne NicolasNo ratings yet
- Google Forms: Organelle Quiz DataDocument44 pagesGoogle Forms: Organelle Quiz DataElizabeth DavisNo ratings yet
- Lab+Exam+1+Worksheet+ +terminology 1Document11 pagesLab+Exam+1+Worksheet+ +terminology 1jharvillgreeneNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument4 pagesMitosisstudent10100No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells: Module in Science 7Document21 pagesPlant and Animal Cells: Module in Science 7Sarah Darriguez100% (1)
- Exp No 7 Meiosis in Onion Bud CellDocument3 pagesExp No 7 Meiosis in Onion Bud CellShadab AhmadNo ratings yet
- MCQs & QUs On Fsirst Year First ComDocument74 pagesMCQs & QUs On Fsirst Year First Commaisara10No ratings yet
- Lesson - 2 - Cell TheoryDocument28 pagesLesson - 2 - Cell Theoryafif kaziNo ratings yet
- Lbybio4 Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesLbybio4 Cell DivisionAlyssaNo ratings yet
- Essay Prokaryotic vs. EukaryoticDocument2 pagesEssay Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryoticctramel001No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Study GuideDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Study GuideNihalAbou-Ghaly0% (1)
- Question Bank Cell Division and Structure of Chromosome: 1. Name The Following: (I) The Suicidal Bag of The CellDocument33 pagesQuestion Bank Cell Division and Structure of Chromosome: 1. Name The Following: (I) The Suicidal Bag of The CellAnoopNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument23 pagesCell Structure and FunctionsMEOW41No ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Document12 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Farman MunawarNo ratings yet
- AY 2020 Sem 1 A104 P01 WS Team 2Document7 pagesAY 2020 Sem 1 A104 P01 WS Team 2Lim Liang XuanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - Cells and Membrane TransportDocument3 pagesMODULE 3 - Cells and Membrane TransportAnne Therese / Annie KanaanNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionsDocument44 pagesPlant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionsClara MaeNo ratings yet
- CellDocument37 pagesCellAmber ZahidNo ratings yet
- Biologia A ColorDocument2 pagesBiologia A ColorJorge Andres Vasquez Avila100% (1)
- Worksheet On CellsDocument6 pagesWorksheet On CellshatchdogNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Protein LocalizationDocument54 pagesPowerpoint Protein LocalizationJoseph BenaiahNo ratings yet
- CellsStudyGuide 2Document13 pagesCellsStudyGuide 2heyimiki1No ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 3 MicrobiologyDocument8 pagesTUTORIAL 3 MicrobiologyJOSEPH TING FU KIONGNo ratings yet
- Sadava MSCDocument118 pagesSadava MSCNikkizGogasNo ratings yet