Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study - OB Ward
Drug Study - OB Ward
Uploaded by
Cheska Ysabelle0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
451 views8 pagesThis document provides information on the drug acetaminophen, including its mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, and nursing responsibilities. Acetaminophen is thought to produce analgesia by inhibiting prostaglandins and other substances that sensitize pain receptors. It is indicated for mild pain or fever and works by relieving fever through central action in the hypothalamic heat-regulating center. Adverse effects include CNS issues like agitation, cardiovascular issues like hypertension, and hepatic issues like jaundice. Nursing responsibilities include considering dose reductions in patients with hepatic or renal impairment and advising on proper use and signs of liver damage.
Original Description:
5
Original Title
Drug Study_OB Ward
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on the drug acetaminophen, including its mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, and nursing responsibilities. Acetaminophen is thought to produce analgesia by inhibiting prostaglandins and other substances that sensitize pain receptors. It is indicated for mild pain or fever and works by relieving fever through central action in the hypothalamic heat-regulating center. Adverse effects include CNS issues like agitation, cardiovascular issues like hypertension, and hepatic issues like jaundice. Nursing responsibilities include considering dose reductions in patients with hepatic or renal impairment and advising on proper use and signs of liver damage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
451 views8 pagesDrug Study - OB Ward
Drug Study - OB Ward
Uploaded by
Cheska YsabelleThis document provides information on the drug acetaminophen, including its mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, and nursing responsibilities. Acetaminophen is thought to produce analgesia by inhibiting prostaglandins and other substances that sensitize pain receptors. It is indicated for mild pain or fever and works by relieving fever through central action in the hypothalamic heat-regulating center. Adverse effects include CNS issues like agitation, cardiovascular issues like hypertension, and hepatic issues like jaundice. Nursing responsibilities include considering dose reductions in patients with hepatic or renal impairment and advising on proper use and signs of liver damage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
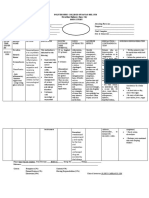
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF INDICATION / ADVERSE EFFECT NURSING
ACTION CONTRAINDICATION RESPONSIBILITIES
GENERIC: Acetaminophen Though to produce analgesia INDICATIONS: CNS: Consider reducing
by inhibiting prostaglandin Mild pain or fever Agitation (IV) total daily dose and
BRAND: Paracetamol and other substances that Rectal Anxiety increasing dosing
sensitize pain receptors. Drug Mild to moderate Fatigue intervals in patients
THERAPEUTIC CLASS: may relieve fever through pain; mild to Headache with hepatic or renal
NSAIDs central action in the moderate pain with Insomnia impairment.
hypothalamic heat-regulating adjunctive opioid Pyrexia Tell parents to
DOSAGE: center. analgesics; fever consult prescriber
CV:
Caplets: 500mg before giving drug to
HTN
Capsules: 325mg, children younger than
Hypotension
500mg age 2.
Peripheral edema
Oral solution: CONTRAINDICATIONS: Advise parents that
80mg/mL; Periorbital edema
Contraindicated in drug is only for short-
160mg/5mL; patients Tachycardia (IV)
term use; urge them
167mg/5mL hypersensitive to GI:
to consult prescriber
Suppositories: 80mg, drug. IV form is Nausea
if giving to infants
120mg, 160mg, contraindicated in Vomiting for longer than 3
325mg, 650mg patients with severe Abdominal pain days, children for
Tablets: 325mg, active liver disease. Diarrhea longer than 5 days, or
500mg, 650mg Use cautiously in Constipation (IV) adults for longer than
patients with any type GU: 10 days.
ROUTE: Oral of liver disease, Oliguria (IV) Tell patient to consult
G6PD deficiency, Hematologic: prescriber for fever
chronic malnutrition, Hemolytic anemia lasting longer than 3
severe hypovolemia, Leukopenia days or recurrent
or severe renal Neutropenia fever.
impairment. Pancytopenia Caution patient to
Use cautiously in Anemia contact health care
patients with long- Hepatic: provider if signs and
term alcohol use Jaundice symptoms of liver
because therapeutic Musculoskeletal: damage occur.
doses cause Muscle spasms
hepatotoxicity in Extremity pain (IV)
these patients. Respiratory:
Chronic alcoholics Abnormal breath
shouldn’t take more sounds
than 2g of Dyspnea
acetaminophen every Hypoxia
24 hours. Atelectasis
Pleural effusion
Pulmonary edema
Stridor
Wheezing (IV)
Skin:
Rash
Urticaria
Infusion site pain
(IV)
Pruritus
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF INDICATION / ADVERSE EFFECT NURSING
ACTION CONTRAINDICATION RESPONSIBILITIES
GENERIC: Central dopamine receptor INDICATION: CNS: Report the beginning of
Metoclopramide antagonist with high Metoclopramide is a Mild sedation restlessness,
potency. Although medication used to treat Fatigue involuntary
BRAND: Reglan and structurally like the symptoms of sluggish Restlessness movements, facial
Metozolv ODT procainamide, it has stomach emptying Agitation grimacing, stiffness, or
minimal antiarrhythmic or (gastroparesis) in diabetic Headache tremors as soon as
THERAPEUTIC CLASS: anesthetic action. The patients. It acts by possible.
Insomnia
Prokinetic Agents precise method of action is enhancing the Extrapyramidal
Disorientation
unknown; however, it contractions or motions symptoms are
DOSAGE: 10-15 mg appears to sensitize GI of the stomach and Extrapyramidal particularly common in
smooth muscle to the intestines. It alleviates symptoms (acute dystonic children, young adults,
ROUTE: Oral effects of acetylcholine by symptoms such as type) and the elderly, as well
direct action. nausea, vomiting, Neurologic malignant as with high dose
heartburn, feeling full syndrome with injection. vomiting treatment
after meals, and loss of GI: related with cancer
appetite. Nausea chemotherapy. It might
Constipation take months for
CONTRAINDICATIONS: Diarrhea symptoms to subside.
Sensitivity or intolerance Dry mouth Be warned that serum
to metoclopramide; aldosterone may be
Altered drug absorption
allergy to sulfiting agents; raised during the early
Skin:
history of seizure treatment phase;
Urticarial or
disorders; concurrent use however, during
maculopapular rash.
of drugs that can cause lengthy administration
extrapyramidal periods, it returns to
Body as a Whole:
symptoms; pretreatment levels.
Glossal or periorbital
pheochromocytoma; Lab tests: Periodic
edema.
tactile GI obstruction or serum electrolyte.
perforation; ileus; history Monitor for
Hematologic:
of breast cancer; hypernatremia and
Methemoglobinemia.
pregnancy (category B), hypokalemia (see
lactation, children 6 years Appendix F),
CV:
and younger, infants, and particularly if the
Galactorrhea
neonates. patient has CHF or
Gynecomastia cirrhosis.
Amenorrhea Adverse responses
Impotence related with elevated
blood prolactin
concentrations
(galactorrhea,
menstrual problems,
gynecomastia)
normally resolve after a
few weeks or months
of discontinuing
medication therapy.
Avoid driving and
other potentially
dangerous activities for
a few hours after taking
the medication.
Avoid alcohol and
other CNS depressants.
Report to S&S any
signs of acute dystonia,
such as shaky hands
and facial grimacing
(see Appendix F), as
soon as possible.
Do not breastfeed if
you are on this
medication without
first seeing your
doctor.
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF INDICATION / ADVERSE EFFECT NURSING
ACTION CONTRAINDICATION RESPONSIBILITIES
GENERIC: Folic acid Vitamin B complex is INDICATION: [Reportedly non-toxic. Prior to beginning
required to produce Folic acid is Following IV administration, therapy, obtain a
BRAND: Folvite nucleoproteins and the commonly used to there is some flushing and a thorough history of
maintenance of normal treat megaloblastic sense of warmth.] nutritional consumption
THERAPEUTIC CLASS: erythropoiesis. Acts against anemias in as well as drug and
Vitamins, Water-Soluble. folic acid deficiency, which pregnancy. During alcohol use. Oral
inhibits thymidylate synthesis pregnancy, folic acid contraceptives, alcohol,
DOSAGE: 5 mg and results in the generation needs skyrocket, and barbiturates,
of faulty DNA, resulting in a lack will result in methotrexate, phenytoin,
ROUTE: Oral megaloblast development and fetal harm. primidone, and
bone marrow maturation trimethoprim have all
arrest. been linked to folate
CONTRAINDICATION: insufficiency. Folate
Folic acid alone is deficiency can also occur
used to treat because of renal dialysis.
pernicious anemia or Keep the doctor up to
other vitamin B12 date on the patient's
deficient diseases, as reaction to therapy.
well as normocytic, Subtherapeutic plasma
refractory, aplastic, or levels in phenytoin
unexplained anemia. patients should be
monitored.
Patient & Family
Education
While on folic acid
treatment, keep a tight
eye on your doctor. If
there is a risk of relapse,
the maintenance dosage
should be adjusted.
Do not breastfeed if you
are on this medication
without first seeing your
doctor.
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF INDICATION / ADVERSE EFFECT NURSING
ACTION CONTRAINDICATION RESPONSIBILITIES
GENERIC: Antacid that acts INDICATION: GI: Take note of the number
Calcium quickly yet has a Calcium carbonate is used to treat Constipation or laxative and consistency of stools.
strong osteoporosis, osteomalacia, effect If constipation is a
BRAND: Tums neutralizing hypothyroidism, Acid rebound concern, the doctor may
capacity and a hypoparathyroidism, Nausea recommend alternate or
THERAPEUTIC reasonably pseudohypoparathyroidism, Eructation combination therapy with
CLASS: Antacids lengthy duration DiGeorge syndrome, kidney Flatulence a magnesium antacid, or
of action. dysfunction, pancreatitis, Vomiting the patient may be
DOSAGE: Reduces stomach rheumatoid arthritis, Fanconi advised to take a laxative
Fecal concretions
Calcium carbonate: acidity, syndrome, pregnancy, nursing or stool softener as
125 mg, 250 mg, decreasing mothers, and postmenopausal Metabolic: needed.
650 mg, 750 mg, pepsin's women who have low serum In patients on long-term
Hypercalcemia with
1.25 g, 1.5 g tablets. proteolytic calcium levels. treatment and those with
alkalosis
activity on renal impairment, serum
Calcium acetate: Metastatic calcinosis
gastric mucosa. CONTRAINDICATION: and urine calcium levels
667 mg tablets. Hypercalciuria
Increases the Hypercalcemia and should be determined on
tone of the lower Hypomagnesemia a weekly basis.
hypercalciuria (for example,
Calcium citrate: 950 esophageal hyperparathyroidism, vitamin D Hypophosphatemia Keep track of any
mg, 2376 mg sphincter as well. overdosage, decalcifying tumors, (when phosphate intake improvements in
tablets. Even though it is bone metastases), calcium loss is low). hypocalcemia symptoms.
categorized as a due to immobilization, severe Observe for signs and
Calcium phosphate non-systemic renal disease, renal calculi, GI CNS: symptoms of
tribasic: 1565.2 mg antacid, a mild to hemorrhage or obstruction, Mood and mental hypercalcemia in patients
tablets severe alkalosis dehydration, hypochloremic changes. who are taking frequent
frequently alkalosis, ventricular fibrillation, or large doses of
ROUTE: Oral develops with cardiac disease, pregnancy Urogenital: medication, or who have
extended use. (category C). Polyuria decreased renal function.
Acid rebound, Renal calculi. Do not use this drug for
which can occur more than 1–2 weeks
after even since it may produce acid
modest dosages, rebound, which usually
is mediated by happens after 1–2 weeks
gastrin release of recurrent usage and
driven by leads to chronic use.
calcium action in Self-medication has the
the small potential to be hazardous.
intestine. Without medical
supervision, do not use
antacids for more than 2
weeks.
Take calcium carbonate
with caution if you eat
cereals or other meals
high in oxalates.
Oxalates and calcium
carbonate mix to
generate insoluble,
nonabsorbable
molecules.
Calcium carbonate
should not be combined
with foods high in
vitamin D (such as milk)
or sodium bicarbonate on
a regular basis because it
can cause milk-alkali
syndrome, which
includes hypercalcemia,
food aversion, headache,
confusion, nausea,
vomiting, abdominal
pain, metabolic alkalosis,
hypercalciuria, polyuria,
soft tissue calcification
(calcinosis),
hyperphosphatemia, and
renal insufficiency.
Renal failure,
dehydration, electrolyte
imbalance, and
hypertension are all risk
factors.
Do not breastfeed if you
are on this medication
without first seeing your
doctor.
You might also like
- The Complete Book of VitaminsDocument582 pagesThe Complete Book of VitaminsMarko JovanovicNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Introduction To Pharmacology 11th Edition Mary Kaye Asperheim DownloadDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Introduction To Pharmacology 11th Edition Mary Kaye Asperheim Downloadchristinespencerxwerdqmpoc100% (29)
- The Complete Book of VitaminsDocument856 pagesThe Complete Book of Vitaminsmvrht100% (4)
- Vitamin Case Study Fall 2019 PDFDocument7 pagesVitamin Case Study Fall 2019 PDFapi-484960148100% (1)
- Quick Bites Dietary ComputationsDocument22 pagesQuick Bites Dietary ComputationsCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- B Complex Patient HandoutDocument1 pageB Complex Patient HandoututglibNo ratings yet
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CDocument6 pagesDRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- Dexamethasone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDexamethasone Drug StudyVIDMENTON PHNo ratings yet
- Docu - Tips Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDocu - Tips Drug StudyArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Diethystilbestrol)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Diethystilbestrol)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFINAL Drug StudycasedraftNo ratings yet
- Methyldopa, Losartan K, Ascorbic AcidDocument4 pagesMethyldopa, Losartan K, Ascorbic AcidRico Mae ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDocument1 pageDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- DS PiptazDocument1 pageDS PiptazCristel Z. Gabuco100% (1)
- Drug Study Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ferrous SulfatePauline AnesNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDocument4 pagesMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenNo ratings yet
- IbuprofenDocument1 pageIbuprofenDherick RosasNo ratings yet
- Carboprost TromethamineDocument2 pagesCarboprost TromethamineDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- Aspirin: Generic NameDocument4 pagesAspirin: Generic NameGwww BabababaNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument1 pageOMEPRAZOLERheza0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyZia CaldozaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Metoclopramide Brand Name: Reglan and Metozolv ODTDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Metoclopramide Brand Name: Reglan and Metozolv ODTJohn Paolo Tamayo OrioNo ratings yet
- Leoprolide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLeoprolide Drug Studyhappymee927No ratings yet
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Drug Name Classification/ Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument1 pageDrug Name Classification/ Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameRheza AltimoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyHerwincayeNo ratings yet
- MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesMetronidazoleJm RomancapNo ratings yet
- DS HydralazineDocument3 pagesDS HydralazineGe LoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument4 pagesDrug Study OrthoJhessa Curie Pitagan100% (1)
- Drug Study ICUDocument5 pagesDrug Study ICUEcko MoawiaNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cushing's SyndromeDocument5 pagesDrug Study Cushing's SyndromeSelena MarieNo ratings yet
- HYOSCINEDocument1 pageHYOSCINEzyr2189No ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument5 pagesDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatNo ratings yet
- OB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesOB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidJustin Ancog100% (1)
- Act Rapid 2Document2 pagesAct Rapid 2Leah Torcelino-InfanteNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsDocument18 pagesDrug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsJenica ManuntagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SARAHDocument2 pagesDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument1 pageAtropine SulfateTrishaaMayolNo ratings yet
- Stugeron® TabletsDocument3 pagesStugeron® TabletsmahgadNo ratings yet
- Pseudoephedrine HydrochlorideDocument6 pagesPseudoephedrine HydrochlorideAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study QIDocument8 pagesDrug Study QImaeDonitaNo ratings yet
- PantoprazoleDocument1 pagePantoprazolehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine CPDocument2 pagesAmlodipine CPRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- TrimetazidineDocument2 pagesTrimetazidinemasheennavirgoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AzithromycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study AzithromycinYamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 04-21-09Document2 pagesDrug Study 04-21-09obietobiNo ratings yet
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFADocument3 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- BactidolDocument1 pageBactidolRryje SallevaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug Studyzjoshuac100% (1)
- NCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFKimNo ratings yet
- Tramadol (Dolcet)Document1 pageTramadol (Dolcet)Beverly Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- MefenamicDocument1 pageMefenamicChristian Clyde N. ApigoNo ratings yet
- ZafirlukastDocument3 pagesZafirlukastapi-379794167% (3)
- Drug Mechanis MOF Action Indicatio N Contraindicatio N Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilit YDocument1 pageDrug Mechanis MOF Action Indicatio N Contraindicatio N Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilit YNica RodriguezNo ratings yet
- BNP (C)Document2 pagesBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- MedroxyprogesteroneDocument5 pagesMedroxyprogesteroneunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarNo ratings yet
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyGrace CadawasNo ratings yet
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocument2 pagesDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Chlorthalidone HygrotonDocument2 pagesChlorthalidone HygrotonLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Observe and Docume NT Stool Frequen Cy, Characte RisticsDocument11 pagesObserve and Docume NT Stool Frequen Cy, Characte RisticsCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Defense MechanismDocument3 pagesDefense MechanismCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Application 6 - PEDocument2 pagesApplication 6 - PECheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- JournalDocument1 pageJournalCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Nutri Lab 5 1Document5 pagesNutri Lab 5 1Cheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 8749 Philippines Clean Air Act of 1999Document1 pageRepublic Act 8749 Philippines Clean Air Act of 1999Cheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- NCM 114-TelehealthDocument2 pagesNCM 114-TelehealthCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Recommended DietDocument3 pagesRecommended DietCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- FNCPDocument6 pagesFNCPCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Group 4: Ahmed, Hani Cac, Frances Corpuz, Adrae Kiwang, Peter Mata, Gerlyn Ann Oviedo, Kayzee Tawaken LopinaDocument72 pagesGroup 4: Ahmed, Hani Cac, Frances Corpuz, Adrae Kiwang, Peter Mata, Gerlyn Ann Oviedo, Kayzee Tawaken LopinaCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- I. Title: Author: Source: YEAR OF PUBLICATION: (For The Past 3 Years)Document2 pagesI. Title: Author: Source: YEAR OF PUBLICATION: (For The Past 3 Years)Cheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan and FdarDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan and FdarCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Care NotesDocument13 pagesPrenatal Care NotesCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- 13 Areas of Assessment 1. Psychosocial StatusDocument3 pages13 Areas of Assessment 1. Psychosocial StatusCheska Ysabelle100% (1)
- Pregnancy, Lactation, InfancyDocument32 pagesPregnancy, Lactation, InfancyCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Anti HelminticsDocument7 pagesNCM 106 Anti HelminticsCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- NCM 108 (BIOETHICS) As A Course in The Nursing CurriculumDocument1 pageNCM 108 (BIOETHICS) As A Course in The Nursing CurriculumCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- pptGroup4-Water NCM105 BSN2Document21 pagespptGroup4-Water NCM105 BSN2Cheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Diagnostic TestingDocument4 pagesAntepartum Diagnostic TestingCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Culture - Health Beliefs and PracticesDocument2 pagesCulture - Health Beliefs and PracticesCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- AOGD Bulletin December 2019Document68 pagesAOGD Bulletin December 2019Abhilekh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Vitamins, Trace Minerals, and Other Micronutrients Mason JDocument10 pagesVitamins, Trace Minerals, and Other Micronutrients Mason JLeonardo RanderNo ratings yet
- Williams Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy 15th Edition Nix Test BankDocument10 pagesWilliams Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy 15th Edition Nix Test Bankanthelioncingulumgvxq100% (29)
- The Bioaccessibility of Water-Soluble VitaminsDocument12 pagesThe Bioaccessibility of Water-Soluble Vitaminsxxghostwarrior13No ratings yet
- 32 LN Water Soluble Vitamins II BLGDocument45 pages32 LN Water Soluble Vitamins II BLGDakshitha DharmakeerthiNo ratings yet
- InfantFeedingGuidelinesDocument68 pagesInfantFeedingGuidelinesivabogNo ratings yet
- Water-Soluble VitaminsDocument32 pagesWater-Soluble VitaminsHomed OpriNo ratings yet
- Manual of High Risk Pregnancy and DeliveryDocument736 pagesManual of High Risk Pregnancy and DeliveryVioly CabigatNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Health and Child Care: Pharmacognosy 28 January 2020Document7 pagesMinistry of Health and Child Care: Pharmacognosy 28 January 2020Von Valentine MhuteNo ratings yet
- Coenzyme CofactorDocument13 pagesCoenzyme CofactorGabriel RamosNo ratings yet
- Formerly: Notre Dame Hospital and School of Midwifery: 2. Identify and Discuss The Function of Macro and Micro NutrientsDocument20 pagesFormerly: Notre Dame Hospital and School of Midwifery: 2. Identify and Discuss The Function of Macro and Micro NutrientsMhianne SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Pharma E5 Ratio PDFDocument35 pagesPharma E5 Ratio PDFJoey RosalesNo ratings yet
- Synopsis PresentationDocument15 pagesSynopsis PresentationANKU GAMITNo ratings yet
- The Relevance of Nutrition To Pediatric Oncology - A Cancer Control Perspective - PEDIATRIC BLOODDocument8 pagesThe Relevance of Nutrition To Pediatric Oncology - A Cancer Control Perspective - PEDIATRIC BLOODGUSTAVO BELLONo ratings yet
- Infographic VitaminsDocument1 pageInfographic VitaminsRafaqat AliNo ratings yet
- Medicine: Effect of Vitamin B Supplementation On Cancer Incidence, Death Due To Cancer, and Total MortalityDocument9 pagesMedicine: Effect of Vitamin B Supplementation On Cancer Incidence, Death Due To Cancer, and Total MortalityClarsafNo ratings yet
- Antenatal CareDocument46 pagesAntenatal CareKIPA SHRESTHANo ratings yet
- The Dental Hygienists Guide To Nutritional Care 5Th Edition Cynthia A Stegeman Full ChapterDocument67 pagesThe Dental Hygienists Guide To Nutritional Care 5Th Edition Cynthia A Stegeman Full Chapterhope.staubin69386% (7)
- Dy Nutrition The Creatine 316 G StrawberryDocument2 pagesDy Nutrition The Creatine 316 G StrawberryIgregNo ratings yet
- 2) Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument17 pages2) Megaloblastic AnemiaAndrea Aprilia100% (1)
- Nutritional Guidelines For Spinal Cord InjuryDocument19 pagesNutritional Guidelines For Spinal Cord InjuryChris Theberge100% (3)
- Arrigo F.G. Cicero, Alessandro Colletti (Auth.) - Handbook of Nutraceuticals For Clinical Use-Springer International Publishing (2018)Document213 pagesArrigo F.G. Cicero, Alessandro Colletti (Auth.) - Handbook of Nutraceuticals For Clinical Use-Springer International Publishing (2018)Võ Đức Trọng100% (2)
- Vitamins For Babies and Young Children: ReviewDocument5 pagesVitamins For Babies and Young Children: ReviewELIDA NOEMI SANTISTEBANNo ratings yet
- 7-Ingredient Healthy Pregnancy Cookbook 75 Easy Recipes For Every Stage of PregnancyDocument279 pages7-Ingredient Healthy Pregnancy Cookbook 75 Easy Recipes For Every Stage of Pregnancyadina.manuela.ionitaNo ratings yet
- USP Dietary Supplements Reference Standards CatalogDocument50 pagesUSP Dietary Supplements Reference Standards CatalogJonathan EdwardNo ratings yet