Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Post-Partum Care: TH TH
Post-Partum Care: TH TH
Uploaded by
Chay Rey Villahermosa Ahiyas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesThe document provides information on postpartum exercises, lactation, breastfeeding, and hygiene. It describes 5 postpartum exercises including abdominal breathing, chin-to-chest raises, perineal contractions, arm raises, and abdominal crunches. It also discusses breastfeeding positioning, initiation, engorgement, sore nipples, and hygienic measures such as perineal care. The goal is to strengthen the mother's muscles, promote lactation, and prevent issues like engorgement while maintaining hygiene.
Original Description:
chart
Original Title
Postpartum Care
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information on postpartum exercises, lactation, breastfeeding, and hygiene. It describes 5 postpartum exercises including abdominal breathing, chin-to-chest raises, perineal contractions, arm raises, and abdominal crunches. It also discusses breastfeeding positioning, initiation, engorgement, sore nipples, and hygienic measures such as perineal care. The goal is to strengthen the mother's muscles, promote lactation, and prevent issues like engorgement while maintaining hygiene.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesPost-Partum Care: TH TH
Post-Partum Care: TH TH
Uploaded by
Chay Rey Villahermosa AhiyasThe document provides information on postpartum exercises, lactation, breastfeeding, and hygiene. It describes 5 postpartum exercises including abdominal breathing, chin-to-chest raises, perineal contractions, arm raises, and abdominal crunches. It also discusses breastfeeding positioning, initiation, engorgement, sore nipples, and hygienic measures such as perineal care. The goal is to strengthen the mother's muscles, promote lactation, and prevent issues like engorgement while maintaining hygiene.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
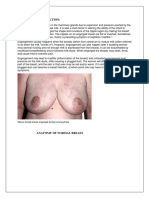
Post-partum Care - lying flat on her back with knees bent, a
Postpartum exercises woman folds her arms across her chest
Initiation of Lactation and raises herself to a sitting position
Relief of Discomforts - expends a great deal of effort/tires a
Hygienic measures postpartal woman easily
Maintaining adequate nutrition - begin gradually and work up slowly to
doing 10 times in a row
MUSCLE STRENGTHENING EXERCISES
Physiology of Breastfeeding
1. Abdominal breathing delivery of placenta causes decrease in
- started on first day after birth progesterone level, stimulating production
- lying flat on her back or sitting, a woman of prolactin
should breathe slowly and deeply in and breast milk formed in acinar and alveolar
out 5 times, using her abdominal cells
muscles Colostrum - 4th month of pregnancy
- check: watching her abdominal wall rise Transitional breast milk - 2nd-4th day
True or mature breast milk - 10th day
2. Chin-to-chest Milk flows from alveolar cells, where it is
- excellent for the second day produced, through small tubules to
- lying on her back with no pillow, a resevoirs for milk, the lactiferous sinuses.
woman raises her head and bends her This constantly forming milk is called
chin forward on her chest without foremilk. Its availability depends very little
moving any other part of her body while on the infant's sucking of the breast. As the
exhaling infant sucks at the breast, oxytocin causes
- should start gradually, repeat no more the collecting sinuses of the mammary
than 5 times the first time and then gland to contract, forcing milk forward
increasing it to 10-15 times in through the nipples. This is called the let-
succession down reflex.
- can be done 3-4 times a day A let-down reflex is also triggered by the
- check: woman will feel her abdominal sound of a baby crying or by thinking about
muscle pull and tighten the baby. New milk, called hind milk, is
formed after the let-down reflex.
3. Perineal contraction (Kegel exercises)
- add on the third day Advantages of breastfeeding for the mother
- woman tightens and relaxes her preventing breast cancer
perineal muscles 10-25 times in uterine involution
succession as if she were trying to stop empowering effect
voiding reduces cost of feeding and preparation
- check: will feel her perineal muscles time
working
bonding between mother and child
4. Arm raising
Advantages of breastfeeding to the infant
- helps both breast and abdomen return
breast milk contains IgA, which prevents
to good tone
the absorption of bacteria and viruses by
- add on the fourth day
the GI tract
- lying on her back, arms at her sides, a
Lactoferrin - interferes with the growth of
woman moves her arms out from her
bacteria
sides until they are perpendicular to her
body. She then raises them over her Lysosyme - enzyme that destroys bacteria
body until her hands touch and lowers L-bifidus - prevents diarrhea
them slowly to her sides ideal electrolyte and mineral composition
- should rest a moment, then repeat 5 Lactose - rapid brain growth
times Protein in milk is easily digested-rapid brain
growth
5. Abdominal crunches nutrients enough to supply infant's needs
- advisable to wait until 10th or 12th day avoid exposure to cow's milk (allergy)
after birth formation of dental arch
Beginning Breastfeeding
should begin as soon after birth as
possible, inside the birthing room
stimulates release of oxytocin
let-down of milk
uterine contraction
important for infants to open their mouths
wide enough to grasp both nipple and
areola
effective sucking
emptying of collecting sinuses
woman should place her infant first at the
breast at which the infant fed last in the
previous feeding
ensure breast is completely emptied at
every other feeding
do not offer bottles of breast milk until 4-
6 weeks of age
it takes less energy for an infant to suck
a bottle
Milk looks like nonfat milk, thin and almost
blue-tinged in appearance.
before breastfeeding - wash hands
Position: Promote Adequate Sucking
lying on her side with a pillow under her To stimulate milk production and ensure
head- relieves fatigue as it allows her to adequate fluid intake
rest on the bed keep infant awake – stroke the back,
football hold - with the baby supported on change baby’s position, rub the arms
a pillow and chest, change diapers, tick baby’s
feet
brushing infant's cheek - rooting reflex urge infant to suck
if woman has large breasts - grasp the If not sucking well
areolar margin between thumb and use breast massage
forefinger, holding the bulk of the breast Provide immediate support if problems
arise
First Few Days Provide information regarding techniques
babies fed every 2-3 hours for burping the breastfed baby
frequent feeding infants swallow air when breastfed
colostrum placing baby over one shoulder and
the more the breasts are emptied, the gently patting or stroking the back
more efficiently they fill holding the baby in sitting position on
the lap, leaning the child forward against
After Feeding: one hand, with the index finger and
TEACH mother to insert a finger in the thumb supporting the head. The other
corner of the infant’s mouth or pull down hand pat's the babies back
infant’s chin to release suction
Breast Engorgement
foremilk hindmilk 3rd or 4th day after birth, breast milk forms
breast distention
hardness
tenderness
heat in the breasts
skin appears red, tense and shiny
vascular and lymphatic congestion arising
from increased blood and lymph supply
infants have difficulty sucking on engorged
breasts because areola is too hard to grasp
6. avoid use of hand pump
Prevent/Relieve Engorgement pressure can cause fissures
empty breasts of milk - allow infant to suck use electric or batter-operated pump
often instead
firm-fitting bra Sore nipples are not a contraindication to
if infant cannot grasp a nipple - warm packs breastfeeding
or standing in warm shower minutes before
feeding combined with massage Hygienic Measures
manual expression or the use of breast include perineal care as part of her daily
pump after breastfeeding bath and after every voiding or bowel
symptom of engorgement is healthy, an movement
announcement her breasts are producing
milk Perineal care
subsides 24 hours Wash hands
Put on clean gloves
Sore Nipples Place a plastic -covered pad under the
strong sucking action of newborn woman's buttocks to protect the bed during
worsened by: the procedure.
improper positioning of infant With the woman in supine position, remove
forcefully pulling an infant from a breast the perineal pad from front to back, the
allowing an infant to suck too long at a direction is important to prevent the portion
breast after the breast is emptied of the pad that was over her rectal area
from sliding forward to contaminate the
permitting a nipple to remain wet from
vaginal opening.
leaking milk
If actual washing is to be done, use a clean
nipples are kept supple from the secretions
gauze square or a clean portion of a
of the Montgomery's tubercles
washcloth with soap and water to each
soreness - excessively dry or wet nipples
stroke, always washing from front to back,
from the pubis to the rectum. Rinse the
1. position baby slightly differently for each
area in the same manner and dry it.
feeding
prevent same area of nipple from receiving
Post-partal menu
pressure
2200-2300 calories daily
2. expose nipples to air 10-15 minutes after
feeding high in protein, vitamins and minerals
3. discourage the use of plastic liners that needed for good tissue repair
come with nursing bras Roughage - peristaltic movement
4. apply vitamin E lotion Breastfeeding - additional 500 calories and
5. apply a few drops of breast milk to nipples 500 ml fluid
after feeding then massage into areola
Promote Adequate Fluid Intake
Montgomery’s tubercles The rapid diuresis and diaphoresis that
occur during the 2nd to 5th postpartal days
result in a weight loss of 5 lb in addition to
12 lb lost at childbirth.
Women feel thirsty during this period of
rapid fluid loss and want additional fluid.
woman needs to increase her fluid intake to
rid her body of wastes (catabolized uterine
cells)
You might also like
- NRPH BreastfeedingDocument8 pagesNRPH BreastfeedingDaphne PearlNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan (Breastfeeding)Document5 pagesHealth Teaching Plan (Breastfeeding)Zam Pamate100% (7)
- Mother's Class BFDocument55 pagesMother's Class BFriz04_fortitudessa5178100% (1)
- PostpartumDocument7 pagesPostpartummaryNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Presentation Breast FeedingDocument58 pagesMultimedia Presentation Breast Feedingsusie eusebius mudiNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding 120912050521 Phpapp01Document57 pagesBreastfeeding 120912050521 Phpapp01varshasharma05No ratings yet
- Breast FeedingDocument2 pagesBreast Feedingjessica queenNo ratings yet
- Learning ContentDocument5 pagesLearning ContentBernice Diana SalasaNo ratings yet
- Breast FeedingDocument41 pagesBreast FeedingLeena Pravil67% (3)
- Breast FeedingDocument33 pagesBreast Feedingjulie kisku100% (1)
- Breastfeeding OrientationDocument41 pagesBreastfeeding Orientationstudyyash100% (2)
- BreastfeedingDocument9 pagesBreastfeedingPriyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- MATERNAL RLE Second WeekDocument6 pagesMATERNAL RLE Second WeekEma HibayaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan For Proper Breast Feeding Begh ErDocument7 pagesTeaching Plan For Proper Breast Feeding Begh ErAmira Fatmah QuilapioNo ratings yet
- Teaching PlanDocument8 pagesTeaching PlanFranco Obedoza100% (1)
- Feeding of Normal AND Low Birth Weight Babies: Amola Khandwala Under Guidance of DR Dipen PatelDocument54 pagesFeeding of Normal AND Low Birth Weight Babies: Amola Khandwala Under Guidance of DR Dipen PatelDeep ShahNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan BreastfeedingDocument6 pagesHealth Teaching Plan BreastfeedingSandeepNo ratings yet
- (Doi 10.1016/B978!1!4377-0788-5.10014-8) Lawrence, Ruth A. - Breastfeeding - Breastfeeding Infants With ProblemsDocument41 pages(Doi 10.1016/B978!1!4377-0788-5.10014-8) Lawrence, Ruth A. - Breastfeeding - Breastfeeding Infants With ProblemsBray Yvc SaNo ratings yet
- Breast Feeding: Ns. Nur Falah Setyawati, S.Kep., MPHDocument28 pagesBreast Feeding: Ns. Nur Falah Setyawati, S.Kep., MPHNurfalah SetyawatiNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document55 pagesPresentation 1roshen02No ratings yet
- OB Stages of Labor and Care in The Stages of Labor With VideoDocument45 pagesOB Stages of Labor and Care in The Stages of Labor With VideodsmagallanesNo ratings yet
- Increase Supply 2021Document2 pagesIncrease Supply 2021Alaa MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding ManagementDocument16 pagesBreastfeeding ManagementggggangNo ratings yet
- The PostpartalDocument4 pagesThe PostpartalrahafNo ratings yet
- Technique of Breast Feeding (Position of Breast Feeding)Document17 pagesTechnique of Breast Feeding (Position of Breast Feeding)Rajeev NepalNo ratings yet
- East FeedingDocument5 pagesEast FeedingJeya vanithaNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding: PurposesDocument6 pagesBreastfeeding: PurposesAlex BasadaNo ratings yet
- AsiDocument30 pagesAsikholifahnwNo ratings yet
- 3 - Aasisting With FeedingDocument23 pages3 - Aasisting With Feeding.No ratings yet
- Learning GuideDocument3 pagesLearning GuideErica Ruth CabrillasNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding SeminarDocument37 pagesBreastfeeding SeminarAlfreda MeggyNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan For BreastfeedingDocument2 pagesTeaching Plan For BreastfeedingEmerson Sambo100% (6)
- Breast Care and Assisting in BreastfeedingDocument7 pagesBreast Care and Assisting in BreastfeedingBJ FernandezNo ratings yet
- BreastfeedingDocument3 pagesBreastfeedingapi-316378224No ratings yet
- V NB HMN MNM BHDocument111 pagesV NB HMN MNM BHKYLE MITZIE SENGCONo ratings yet
- Breast EngorgeDocument16 pagesBreast EngorgeNadiya RashidNo ratings yet
- BREASTFEEDINGDocument49 pagesBREASTFEEDINGAurora Doris BatagaNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 6Document13 pagesKelompok 6betty gindiNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding Counselling: Pediatric Department Hasan Sadikin Hospital - University of PadjadjaranDocument28 pagesBreastfeeding Counselling: Pediatric Department Hasan Sadikin Hospital - University of Padjadjarantammy_tataNo ratings yet
- Mother's Class BFDocument55 pagesMother's Class BFriz04_fortitudessa5178No ratings yet
- Breastfeeding FinalDocument25 pagesBreastfeeding FinalWengel RedkissNo ratings yet
- Breast Care SoftDocument53 pagesBreast Care SoftMiraflor BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding 121023054344 Phpapp01Document36 pagesBreastfeeding 121023054344 Phpapp01Jose Miguel Granados GalvanNo ratings yet
- What You Should Know: Irene Joy R. Lubrino BSN 4-2, Group 5Document7 pagesWhat You Should Know: Irene Joy R. Lubrino BSN 4-2, Group 5irene joyNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding - de Castro and DecenaDocument21 pagesBreastfeeding - de Castro and DecenaAiley DumpNo ratings yet
- Breast Feeding Autosaved SDocument48 pagesBreast Feeding Autosaved Syuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Manual Breast Manual ExpressionDocument9 pagesManual Breast Manual ExpressionhoneykrizelNo ratings yet
- Mobbs Et Al-2016-Acta PaediatricaDocument6 pagesMobbs Et Al-2016-Acta Paediatricamhelanhie_09No ratings yet
- Breastfeeding LectDocument26 pagesBreastfeeding LectJan Erika AlmeronNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding: Colostrum, The Yellowish, Sticky Breast Milk Produced at The End of Pregnancy, IsDocument12 pagesBreastfeeding: Colostrum, The Yellowish, Sticky Breast Milk Produced at The End of Pregnancy, IsPaolo ZabatNo ratings yet
- Breast FeedingDocument4 pagesBreast FeedingSweetie PieNo ratings yet
- PCBF KpjrawangDocument48 pagesPCBF KpjrawangDr Puteri Nur Sabrina Binti Mohd HanapiNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Health TeachingDocument6 pagesPostpartum Health TeachingAnn Michelle TarrobagoNo ratings yet
- Breast Feeding Tec.Document9 pagesBreast Feeding Tec.Chairali DodiyaNo ratings yet
- Lactation ManagementDocument13 pagesLactation ManagementNadia Nur Salsabila50% (2)
- Procedure On Techniques of BreastfeedingDocument5 pagesProcedure On Techniques of BreastfeedingPabhat Kumar100% (2)
- Breast Feeding Teaching ToolDocument5 pagesBreast Feeding Teaching ToolRene ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Breast Feeding Made Easy: How To Breastfeed For Mothers Of NewbornsFrom EverandBreast Feeding Made Easy: How To Breastfeed For Mothers Of NewbornsNo ratings yet
- Review Article On Tarpanadi Samsarjana KramaDocument5 pagesReview Article On Tarpanadi Samsarjana KramaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- FSchapter 1Document7 pagesFSchapter 1Danna Mae R. MagapanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Neet Chapter 31Document16 pagesChemistry Notes For Neet Chapter 31harshadmaharajthiruvenkadamNo ratings yet
- Women's Fitness - February UKDocument168 pagesWomen's Fitness - February UKFizza RaufNo ratings yet
- Gulayan NurseryDocument6 pagesGulayan NurseryJoshteKunNo ratings yet
- Nutrients 14 00427 v3Document14 pagesNutrients 14 00427 v3Edson HilárioNo ratings yet
- College of Human Kinetics: Cagayan State UniversityDocument20 pagesCollege of Human Kinetics: Cagayan State UniversityRUSSEL AQUINONo ratings yet
- Zaxbys Nutrition Trifold 2022 P3 Web 83a6cecd01 Rotated 215301d30fDocument2 pagesZaxbys Nutrition Trifold 2022 P3 Web 83a6cecd01 Rotated 215301d30ftye mooreNo ratings yet
- Lawler 2019Document15 pagesLawler 2019Ulul AzmiNo ratings yet
- Science 10 CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesScience 10 Carbohydrateskarizajean desalisaNo ratings yet
- Wupp emDocument15 pagesWupp emGuesrim LallogoNo ratings yet
- AaharDocument30 pagesAaharAnju SahaNo ratings yet
- Trends & Patterns of Child Malnutrition in India-Case StudyDocument20 pagesTrends & Patterns of Child Malnutrition in India-Case Studybagadbilla1612No ratings yet
- Food Nutrition & Dietetics: Study MaterialDocument21 pagesFood Nutrition & Dietetics: Study MaterialGloria JaisonNo ratings yet
- Child Health Nursing 3rd Edition Bindler Solutions ManualDocument19 pagesChild Health Nursing 3rd Edition Bindler Solutions Manualbeyradicantdays100% (33)
- Diet Plan For Weight LossDocument4 pagesDiet Plan For Weight LossTEJA HOSPITAL TEJANo ratings yet
- ISGH Project Presentation - Eka Mardiana ADocument9 pagesISGH Project Presentation - Eka Mardiana AEka AfriliaNo ratings yet
- Q1-Module-Cookery 10Document80 pagesQ1-Module-Cookery 10athea garciaNo ratings yet
- A Zil A Fermented Coconut Book ChapterDocument13 pagesA Zil A Fermented Coconut Book ChapterEdsel Willyanto PutraNo ratings yet
- Final Research PaperDocument12 pagesFinal Research PapermargiNo ratings yet
- 2015 Updating of Nutritional Status of Filipino Children and Other Population GroupsDocument9 pages2015 Updating of Nutritional Status of Filipino Children and Other Population GroupsAlthea Marie AlmadenNo ratings yet
- Untitled 2Document2 pagesUntitled 2api-533509430No ratings yet
- CC and Mortality ICUDocument8 pagesCC and Mortality ICUSimone BernardesNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Nutritioan Practices and Associated FactorsYigremachewDocument24 pagesAssessment of Nutritioan Practices and Associated FactorsYigremachewZayed AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Flavor Fatigue in Cats: A Long Term StudyDocument3 pagesFlavor Fatigue in Cats: A Long Term StudyCaroline TeodoroNo ratings yet
- A PDFDocument2 pagesA PDFBauroNo ratings yet
- Diet On Milk QualityDocument2 pagesDiet On Milk QualityEndale BalchaNo ratings yet
- Pear Extract and Malaxinic AcidDocument10 pagesPear Extract and Malaxinic AcidShruti PatelNo ratings yet
- Testing Amount of Casein in Milk (Draft) (Ashwin)Document7 pagesTesting Amount of Casein in Milk (Draft) (Ashwin)Ashwinashishashwathy KumarNo ratings yet
- Social Practice of The Language 6Document9 pagesSocial Practice of The Language 6Brenda LizarragaNo ratings yet