Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ELS Q1 M1 2 3 4activity Sheet
ELS Q1 M1 2 3 4activity Sheet
Uploaded by
Ljae NatinoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ELS Q1 M1 2 3 4activity Sheet
ELS Q1 M1 2 3 4activity Sheet
Uploaded by
Ljae NatinoCopyright:
Available Formats
2
EARTH & LIFE SCIENCE
Activity Sheets
Name: LJAE B. NATINO
Section: ABM
Date: October 18, 2020
General Direction: Use this activity sheet to answer the activities in your module.
QUARTER 1 MODULE 1: Origin and Structure of the Earth-Earth System
WHAT I KNOW
1) D
2) C
3) C
4) A
5) C
6) B
7) A
8) D
9) C
10) B
11) C
12) D
13) B
14) C
15) B
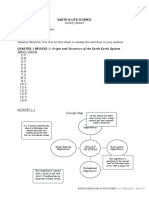
ACTIVITY 1.1
Concept Map
It describes the formation of
our solar system from
a nebula cloud made from a
collection of dust and gas.
SOLAR
NEBULA
A collision happened and huge HYPOTHESIS
amounts of gas from the sun
explode out of it but more in the
same directions around the sun
ENCOUNTER SOLAR NEBULAR
HYPOTHESIS
SYSTEM HYPOTHESIS
Our star system was formed 4.568
billion years ago when a small
part of a giant molecular cloud
experienced a gravitational
PROTOPLANET collapse.
HYPOTHESIS
It states that solar system begins by
forming out of the collapsing of either
cloud or a nebula, from here gravity play
its role by pulling material from the
cloud closer together to create a hot
dense core.
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
WHAT’S MORE/ Activity 1.2
1) Name the bodies involved in Encounter Hypothesis.
a) Sun
b) rogue star
2) Who are the scientists behind Nebular Hypothesis?
a) Immanuel Kant
b) Pierre Simon Laplace
3) Enumerate the four terrestrial planets.
a) Mercury
b) Venus
c) Earth
d) Mars
4) Differentiate Nebular Hypothesis and Solar Nebula Theory
-The difference between Nebular Hypothesis and Solar Nebula Theory is that
Nebular Hypothesis, it suggests that the Solar System formed from gas and dust
orbiting the Sun, while Solar Nebula Theory describes the formation of our solar
system from a nebula cloud made from a collection of dust and gas.
WHAT HAVE I LEARNED?
1) Name the theories/hypothesis that explain the origin of the solar system.
a) Encounter Hypothesis
b) Protoplanet Hypothesis
c) Nebular Hypothesis
d) Solar Nebula Theory
2) Describe each theory you answered in item # 1.
a) Encounter Hypothesis- is anchored to the concept that the Sun had come
across with a rogue star.
b) Protoplanet Hypothesis- is the hypothesis that suggests that a cloud of gas
and dust, about 10 million km in diameter rotated slowly
c) Nebular Hypothesis- theory proposed that the solar system formed from a
slowly rotating nebula that collapsed and flattened.
d) Solar Nebula Theory- this theory combined the idea of a flattening solar
nebula with that of a condensing interstellar dust as the nebula cooled, which served
as a condensation nuclei where matter is accumulated.
3) Why do you think it is called solar system?
- It is called the Solar System because it is composed of 8 planets
surrounding the Milky Way.
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
ACTIVITY 2.1
1) TRUE
2) FALSE – Earth is a terrestrial planet, it is small and rocky, Earth is located at
“goldilocks zone” it refers to habitable zone means it can support life.
3) TRUE
4) TRUE
5) FALSE – Ashes coming from volcanoes aren’t safe to be inhaled by humans
because it can lead us to respiratory diseases.
6) TRUE
7) TRUE
8) FALSE - Earth is located at Goldilocks zone which is the amount of heat and
solar energy it received is enough, not too hot nor too cold.
9) TRUE
10) FALSE – Mercury and Venus have the most extreme temperature planets in our
solar system which is very impossible to support life.
WHAT’S MORE/Activity 2.2
1) Name three characteristics of the Earth making it the only livable planet in
the solar system.
a) Earth is placed in the “Goldilocks Zone”.
b) It has the right chemical ingredients for life, including water and carbon.
c) Earth is just at the right distance from the Sun. It receives enough energy to
allow water to exist as a liquid on its surface.
2) What made Mercury and Venus unfit to nurture life?
Mercury – it is the first planet in the solar system and it is the nearest planet in
the sun. Earth is just at a right distance, unlike Mercury, it is very near that had
hot temperature. Also, Mercury doesn’t have thick atmosphere that will protect
living organisms from temperature extremes and excessive UV radiation.
Venus – its atmosphere is very hot and thick. It is the hottest planet even
though it isn’t the nearest one.
3) Enumerate the four gas planets.
a) Jupiter
b) Saturn
c) Uranus
d) Neptune
4) What is so called ‘goldilocks zone’?
- The Goldilocks Zone refers to the habitable zone around a star where the
temperature is just right - not too hot and not too cold - for liquid water to exist on
a planet.
5) What is the role of the Sun in making a planet suitable for life?
- It makes life possible to exist on Earth because it emits solar energy. Living
things like us, humans need enough light and heat in order to gain energy as well
as plants, in order for them to grow. Moreover, Earth would be in its lowest
temperature without Sun.
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
WHAT HAVE I LEARNED?
1) Why do you think life do not exist in planets such as Saturn, Uranus and
Neptune?
- They are called the “Jovian Planets”, where life is impossible to exist there because
they are mainly composed of gases, that is why they are also called gas giants. In
short, there is no gravity and oxygen in these planets.
2) How the amount of heat received by the Earth from the Sun able it to
support life?
- Earth is found to be located in such region where due to its distance from the sun,
the amount of heat and solar energy it receives is just enough to keep it Earth neither
too hot nor too cold.
3) Is the location of the Earth from the Sun can be a reason that it can
nurture life? Why?
-Yes, because in its distance, Earth can receive proper and appropriate
temperature and heat from the sun that lets us exist in it.
4) List at least three characteristics of the Earth and discuss each of their
importance in the existence of life.
a) It has gaseous atmosphere that contains 21% oxygen, which is necessary for
us to breathe, 78% nitrogen, and, 9% argon.
b) Earth is composed of 70% water. Without water, we cannot live, for water is
life. Living things need water in order to survive.
c) Earth orbits in the so-called Goldilocks zone, where the planet receives
enough energy to allow water to exist as a liquid on its surface.
WHAT I CAN DO
Skip this task.
ASSESSMENT/Post Test
1) C
2) A
3) A
4) B
5) C
6) A
7) D
8) C
9) A
10) D
11) C
12) D
13) B
14) A
15) B
QUARTER 1 – MODULE 2: Earth and Earth System
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
PRETEST
1) A
2) D
3) A
4) C
5) D
6) C
7) B
8) D
9) A
10) A
11) D
12) C
13) C
14) B
15) D
16) B
17) C
18) B
19) A
20) C
WHAT IS IT: Think Globally, Act Locally
Observation System
1) Humans are planting flowers Biosphere
and trees.
2) Plants giving off oxygen inhaled Atmosphere
by humans.
3) Burning of dry leaves. Atmosphere
4) Water flowing form the water Hydrosphere
pump.
5) Raining Connection between hydrosphere and
atmosphere
WHAT’S MORE
Name something from each spheres of the Earth system (lithosphere,
hydrosphere, biosphere, atmosphere) that you interact with every day.
Lithosphere = Using garden soil for planting plants in our yard
Hydrosphere = Filling our pails with water from the water pump
Biosphere = Planting flowers and trees
Atmosphere = Inhaling oxygen, and exhaling Carbon dioxide
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
EXPLAIN
How do those things impact your life?
- All of the Earth’s systems create a big impact in our lives. They enable us
to survive in this planet we are in. We can get the essential elements of
life, we have buildings like our home to live, water to drink, and shield
against environmental problems.
After seeing many examples, what conclusions about Earth’s systems can you
make?
- I will conclude that the four Earth’s systems are consist of the land, oceans, and
atmosphere. They include the planet’s natural cycles- the carbon, water, nitrogen,
phosphorous, sulfur, and deep Earth processes. When human population in your
study site increases, how would this affect the rest of the system?
When human population in your study site increases, how would this affect the
rest of the system?
- For me, global warming will take place due to the overpopulation. And
when it comes to overpopulation, carbon dioxide will also increase in
many ways.
WHAT I CAN DO
Evaluate
Match these words inside the box that correspond to the system below.
water, earth materials, air, living things
Hydrosphere = Water
Biosphere = Living things
Atmosphere = Air
Lithosphere = Earth material
ASSESSMENT
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
1) A
2) D
3) C
4) B
5) B
6) D
7) C
8) B
9) A
10) D
11) B
12) D
13) D
14) C
15) A
16) C
17) A
18) C
19) A
20) C
PERFORMANCE TASK
Create a poster/illustration that represents your environment showing the
interactions among the four spheres.
QUARTER 1 – MODULE 3: Minerals and Rocks
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
WHAT I KNOW/Pre-Assessment
1) B
2) C
3) D
4) C
5) A
6) A
7) D
8) B
9) D
10) B
11) C
WHAT’S NEW
a) Observe the crystals that had form. Draw how it looks like and write a brief
description of it.
- The crystal is shiny.
b) How would you know that the crystals are already forming? How do crystals
form?
- Crystals often form in nature when liquids cool and start to harden. Certain
molecules in the liquid gather together as they attempt to become stable.
c) Why do more crystals dissolve when the water is heated?
- When the temperature of the solution is increased, hot water can dissolve more solid
substance than cold water. This is because heated water molecules move farther
apart, making room for more solid substance to dissolve. Crystals begin to form and
build on one another as the water lets go of the excess solute.
d) Do you think that the identifying properties of the crystal or water change
when they are mixed?
- Yes, because crystal will be dissolved and become part of the water.
WHAT’S MORE
In what ways do you think the minerals are helpful to your life?
- They help us to develop new technologies and are used
in our everyday lives. Our use of rocks and minerals includes as building
material, cosmetics, cars, roads, and appliances.
WHAT HAVE I LEARNED?
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
I.
1) √
2)
3)
4) √
5)
6)
7) √
8)
II. What other minerals are known to have important uses like silicates?
- These include minerals such as quartz, feldspar, mica, amphibole,
pyroxene, olivine, and a great variety of clay minerals.
WHAT I CAN DO
1) HARDNESS
2) HARDNESS
3) LUSTER
4) CLEAVAGE
5) DENSITY
6) CRYSTAL HABIT
7) SOLUBILITY
8) SPECIFIC GRAVITY
9) MELTING POINT
10) FRACTURE
ASSESSMENT
1) A
2) A
3) D
4) B
5) D
6) B
7) D
8) A
9) C
10) B
11) C
ADDITIONAL ACTIVITIES
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
Choose one task to do:
Poem
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
QUARTER 1 – MODULE 4: Rocks: Its Three Main Categories
WHAT I NEED TO KNOW
1) B
2) D
3) A
4) D
5) C
6) A
7) C
8) B
9) A
10) B
ACTIVITY 1. Reaping Rocks
Rock Chart
Rock Sketch
Shape CIRCULAR CIRCULAR
Size SMALL SMALL
Observation Colors BROWNISH BEIGE WITH DARK
SPOTS
Texture ROUGH ROUGH
Collection Site NEAR A RIVER BACKYARD
Classification SEDIMENTARY SEDIMENTARY
Origin SEDIMENTS SEDIMENTS
Interpretation
COMPACTED COMPACTED
TOGETHER TOGETHER
WHAT I HAVE LEARNED
- Rocks are mostly found in oceanic crust and on continental crust in
which humans can directly access. There are three main types of rocks:
sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic. Each of these rocks are formed
by physical changes—such as melting, cooling, eroding, compacting, or
deforming—that are part of the rock cycle. Sedimentary rocks are formed
from pieces of other existing rock or organic material. Metamorphic rocks
are rocks that have been changed from their original form by immense
heat or pressure. Igneous rocks (derived from the Latin word for fire) are
formed when molten hot material cools and solidifies.
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
WHAT I CAN DO
1) IGNEOUS
2) SEDIMENTARY
3) METAMORPHIC
4) SEDIMENTARY
5) SEDIMENTARY
6) IGNEOUS
7) SEDIMENTARY
8) METAMORPHIC
9) SEDIMENTARY
10) IGNEOUS
ASSESSMENT
1) B
2) D
3) A
4) D
5) C
6) A
7) C
8) B
9) A
10) B
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
QUARTER 1 – MODULE 5: Rocks: Magma Formation
WHAT I KNOW
1. B
2. F
3. J
4. D
5. A
6. G
7. H
8. I
9. C
10. K
WHAT’S NEW
ACTIVITY 2: MAGMA VISCOUS
1. What is the representation of flour in this experiment?
- This experiment shows the varying viscosity of magma upon cooling.
2. Why does the flour become polymerized after cooling the mixture?
- Polymerization occurs due to sudden change of temperature as well as
the increase in amount of flour in the mixture.
3. How do this experiment related to magma formation?
- This experiment is related to magma formation. Magmas have variable
contents of silica (flour) and therefore have widely varying viscosities
(“thicknesses”) during cooling. This formation usually happens when the
hot molten magma from the mantle is slowly moving upward to crust
which has a lower temperature.
WHAT I HAVE LEARNED
A.
First, I know that magma is composed of mixture of molten or semi molten rock
that is found beneath the surface of the Earth.
Second, there are four types of magma, these are primary magma, primitive
magma, parental magma, and derivative magma.
Third, the overall composition of magma is changed as crystallization happens.
Fourth, Silicate is mostly composed of silicon, oxygen, aluminum, alkalis (sodium,
potassium, calcium), magnesium and iron.
Finally, there ate two processes which the magma ceases to exist, these are
through volcanic eruption or crystallization.
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
WHAT I CAN DO
1. A
2. C
3. C
4. B
5. C
6. D
7. A
8. D
9. A
10. B
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
QUARTER 1 – MODULE 6: Earth Materials and Resources- Energy Resources
LESSON 1
WHAT I KNOW
1.B
2.B
3.B
4.C
5.C
6.B
7.A
8.B
9.B
10.A
11.D
12.C
13.C
14.A
15.D
16.C
17.A
18.B
19.D
20.C
WHAT’S MORE
ACTIVITY 1.2
1. Arrange these words below in proper sequence based on geothermal energy
diagram.
(cooling water, hot water, generator, turbine, injection well, steam)
Rewrite: hot water, steam, turbine, generator, cooling water, injection well
2. Enumerate the types of Geothermal power plant
a. low power geothermal
b. medium power geothermal
c. high power geothermal
3. Differentiate geothermal power plant from geothermal heat pump.
- The difference between Geothermal power plants and Geothermal heat pump is that
geothermal power plant generates electricity by forcing hot steam or hot steam from
the earth's interior through a turbine. This electricity can be used to power, heat,
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
and cool homes, among other uses. While, geothermal heat pumps circulate fluid
through underground pipes, where they absorb heat.
4. List down at least 5 geothermal power plants in the Philippines.
a. Nasulo Geothermal Power Plant
b. Tiwi Geothermal Power Plant
c. Maibarara Geothermal Power Plant
d. Makiling-Banahaw (Mak-Ban) Geothermal Power Plant
e. Montelago Power Plant
WHAT I CAN DO
3) Make a brochure highlighting the different geothermal power plants in the
Philippines.
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
LESSON 2
WHAT’S MORE
Activity 2.2. It’s time to be Refresh with Hydropower.
1) Name 3 types of hydropower plant.
a) Run-of-river plants
b) Off-stream plants
c) Pumped storage power plants
2) Enumerate the 3 main components of hydroelectric power plant.
a) dam
b) penstock
c) powerhouse
3) Describe Maria Cristina Falls.
- The waterfall is located about 9.3 km Southwest of Illigan City and is ringed by
Ditucalan, Buru-an and Barangay Maria Cristina. It’s fed by the River Agus and the
water falls 98 meters before supplying the Agus VI hydroelectric plant. Besides
supplying power in Illigan City, it helps in the production of 70 % of Mindanao’s
electricity.
4) Give at least two (2) advantages of hydropower plant.
It is extremely efficient, and operation and maintenance costs are low.
WHAT I CAN DO
3) Make a brochure highlighting the different hydroelectric power plants in the
Philippines.
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
ASSESSMENT
1.A
2.D
3.C
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
4.C
5.A
6.D
7.C
8.A
9.B
10.D
11.B
12.B
13.B
14.C
15.C
16.B
17.A
18.B
19.B
20.A
QUARTER 1 – MODULE 7: History of the Earth: Relative vs. Absolute Dating
WHAT I KNOW
1. D
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
2. D
3. C
4. D
5. D
6. D
7. D
8. A
9. A
10. C
WHAT’S NEW
Activity 1: Dating a rock!
Set Up A.
What material is at the bottom? What material is on
topmost layer?
- The material at the bottom is the sand and the material at the topmost is
the stone.
Imagine the bottle as an ocean basin, and the materials
became the rocks after millions of years. Which do you
think is the oldest? youngest? Why?
- The oldest is the sand and the youngest is the rock that is on top. There
are two methods of telling how old rock is. When one sample is compared
by simply describing as older or younger than the other, it is called as
relative dating. The bottom part is older than the one above it, it is called
as Law of Superposition.
Set Up B
How old is the oldest layer? youngest layer?
- The oldest layer is 30 years old while the youngest layer is 10 years old.
Compare the two set ups. Which set up describes the age
relative to its position? Which tells the exact or absolute
age?
- The Setup B tells the exact or absolute age.
What do shells represent in set up B?
- Pebbles represent shells.
WHAT I CAN DO
Activity 1: Back in Time!
LOCATION: ISULAN, SULTAN KUDARAT
1. FORMS OF LIFE
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
RELATIVE: Iguanas and different fishes on our river such as hito and tilapia.
ABSOLUTE:
1997: Clean water
2000: Different species dominated the area.
2011: Decrease of fish and animal species in river because of the garbage.
2020: Total decrease of land and marine life near the river.
2. TOPOGRAPHY
RELATIVE: Mountains and unoccupied space of plains.
ABSOLUTE:
1988- Peaceful mountain and unoccupied space of plains.
1997- People start to build resort near the mountain.
2011- Almost all of the plains are occupied.
2020- Unpeaceful Mountain but helpful occupied space of plains because of grains.
3. BODIES OF WATER
RELATIVE: River
ABSOLUTE:
1988-2002- Clean and clear river
2006- Little garbage have been spotted
2014- Many garbage such as diapers and plastics found in the river.
2020- Uncontrolled throwing of garbage causing Marine and Land life decrease.
4. BARANGAYS AND/OR NATIONAL ROAD
RELATIVE: Almost all road or district in our barangay has not been done cemented.
ABSOLUTE:
1999- Non-cemented road on all district on our barangay
2016- Government started to notice it.
2019-2020- Almost all of the road on all district on our barangay has been done
cemented.
5. HUMAN INHABITANTS
RELATIVE: Unoccupied space of land on our district.
ABSOLUTE:
1999- Unoccupied spaces around the district has been spotted.
2007- People start to build house on the unoccupied spaces of lane in our district.
2018- All spaces of land had been occupied causing rapid increase on human
inhabitant.
6. FOUNDATION OF THE AREA
RELATIVE: Court, covered court and Road cementing has not been done.
ABSOLUTE:
1956- No road has been cemented yet.
1989- Almost all of the road has been cemented and created gyms has been done.
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
2001- Created gyms brought smile to people as also the cemented road for smooth
ride.
2014- Gyms and cemented roads are found on all areas.
GUIDE QUESTIONS
1. What caused the changes in;
a. Forms of life- Garbage
b. Topography- Building, resorts, and grains
c. Bodies of water- Garbage
d. Roads- Non-cemented roads
e. Human inhabitants- Increase on human inhabitant
f. Foundation- Covered courts and cemented roads
2. How do you see your local area twenty years from now? Support your answer
based on the changes it underwent.
- Human population will increase, and that will cause pollution in all forms, as well as
traffic.
3. Which information was more difficult to get, relative or absolute dating?
Why?
- The absolute dating since it already happened years ago and it is really hard to
remember.
4. How does a record of events help in gathering information?
- It helps in a way that it gives accurate information.
ASSESSMENT
1. C
2. C
3. A
4. A
5. D
6. A
7. B
8. B
9. B
10. D
11. D
12. A
13. C
14. D
15. B
QUARTER 1 – MODULE 8: Mitigation of the Impacts of Land Development,
Waste Disposal and Construction on Coast
WHAT I KNOW
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
1. C
2. B
3. B
4. B
5. D
WHAT’S NEW
ACTIVITY 1
WHAT’S MORE
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
2
ASSESSMENT
1. TRUE
2. FALSE, reduce
3. FALSE, Lousy
4. TRUE
5. FALSE, beneficial
EARTH SCIENCE SLM ACTIVITY SHEET | BY: MARYLOU J. MALUYO
You might also like
- A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers 13Th Edition Full ChapterDocument42 pagesA Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers 13Th Edition Full Chapterchristopher.hess142100% (23)
- Earth and Life Science Reviewer PDFDocument16 pagesEarth and Life Science Reviewer PDFAndrea Detera83% (12)
- Hino E13c Engine Workshop Manual PDFDocument413 pagesHino E13c Engine Workshop Manual PDFmahadeo ramphal100% (15)
- Solution Manual For Introduction To Probability Models 7thDocument62 pagesSolution Manual For Introduction To Probability Models 7thJosé Carlos100% (3)
- Physics of The Solid Earth (Phy 202)Document11 pagesPhysics of The Solid Earth (Phy 202)Gaaga British0% (2)
- GRADE 11 EARTH AND LIFE Quarter 1Document3 pagesGRADE 11 EARTH AND LIFE Quarter 1Chantal Althea100% (6)
- Grade-11 W1-Earth and Life Science-ModuleDocument5 pagesGrade-11 W1-Earth and Life Science-ModuleLeslie Mermelo100% (1)
- Module Quarter 1 Earth and Life ScienceDocument18 pagesModule Quarter 1 Earth and Life ScienceEmmanuel Ronquillo100% (1)
- Case Study-Pert MustangDocument4 pagesCase Study-Pert Mustangvipul tuteja100% (1)
- Apple: Corporate Governance and Stock Buyback: Company OverviewDocument11 pagesApple: Corporate Governance and Stock Buyback: Company OverviewKania BilaNo ratings yet
- Airtel - A Case StudyDocument30 pagesAirtel - A Case StudyTanya Dutta57% (7)
- ELS Q1 M1 2 3 Activity SheetDocument25 pagesELS Q1 M1 2 3 Activity SheetLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science: This Hypothesis Suggest That A Cloud of Gas and Dust, 10 Million KM in Diameter Rotated SlowlyDocument26 pagesEarth & Life Science: This Hypothesis Suggest That A Cloud of Gas and Dust, 10 Million KM in Diameter Rotated SlowlyLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- AaaaDocument32 pagesAaaaSakuta AzusagawaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sciences 2 Weeks Lessons PDFDocument11 pagesEarth and Life Sciences 2 Weeks Lessons PDFDanabelle PasionNo ratings yet
- q1m1 Earth Structure and SpheresDocument17 pagesq1m1 Earth Structure and Spheressiarah0777No ratings yet
- How and When Did The Universe Begin? No One Was Around When The Universe Began, So Who Can Say What Really Happened?Document10 pagesHow and When Did The Universe Begin? No One Was Around When The Universe Began, So Who Can Say What Really Happened?Zoren N. InoweNo ratings yet
- Origin of The Solar SystemDocument24 pagesOrigin of The Solar SystemArjie GabrielNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Earths OriginDocument49 pagesTopic 1 Earths OriginJharen Mae AgyaoNo ratings yet
- Midterm ReviewerDocument13 pagesMidterm ReviewerEmanuelle Mosquera100% (1)
- Week 1Document4 pagesWeek 1Ma Melissa DelavinNo ratings yet
- AgeDocument7 pagesAgeAbdo HusseinNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Notes 1 To 7 (UPDATED)Document9 pagesEarth Science Notes 1 To 7 (UPDATED)Joshua PerlasNo ratings yet
- Unit v. The Earth and MoonDocument21 pagesUnit v. The Earth and MoonSunshine SisonNo ratings yet
- Els ReviewerDocument3 pagesEls ReviewerNicole SandovalNo ratings yet
- Earth Science MIDTERMSDocument7 pagesEarth Science MIDTERMSKate GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Planets Orbiting Other Stars - The Search For Extraterrestrial LifeDocument3 pagesPlanets Orbiting Other Stars - The Search For Extraterrestrial LifeMy BuisnessNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Quarter 1 Learning ModuleDocument41 pagesEarth and Life Science Quarter 1 Learning ModuleMARY GRACE PAQUIBOTNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: Origin of The Solar SystemDocument2 pagesEarth Science: Origin of The Solar SystemJesmark ColumbresNo ratings yet
- Meteorology, Oceanography, and Astronomy.: Earth Science The Big BangDocument4 pagesMeteorology, Oceanography, and Astronomy.: Earth Science The Big BangKaryl AarientosNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS NOTES For BSC StudentsDocument27 pagesPHYSICS NOTES For BSC Studentskcameppadi123100% (1)
- Week 1 Lesson 1Document6 pagesWeek 1 Lesson 1YippeNo ratings yet
- PDF Earth and Life Science Reviewerpdf CompressDocument16 pagesPDF Earth and Life Science Reviewerpdf CompressReysha Mae BagayawaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument12 pagesEarth and Life ScienceRimar Jhon ParasNo ratings yet
- ELSCI NOTES Theories To MineralsDocument19 pagesELSCI NOTES Theories To Mineralsejqc proNo ratings yet
- ElsDocument6 pagesElsCiarangeIicNo ratings yet
- State Civil Services: General StudiesDocument17 pagesState Civil Services: General StudiesYashu AhireNo ratings yet
- Earth Science For Senior High School WorkbookDocument34 pagesEarth Science For Senior High School WorkbookameracasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Earth ScienceLeizel MundoNo ratings yet
- DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDocument29 pagesDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDchinna25689No ratings yet
- The Different Hypotheses Explaining The Origin of The UniverseDocument29 pagesThe Different Hypotheses Explaining The Origin of The Universejerros31yahooNo ratings yet
- Origin of The UniverseDocument50 pagesOrigin of The Universeleomar ignacioNo ratings yet
- Sains Form3 Final ChapterDocument14 pagesSains Form3 Final ChapterNik Dhaniel100% (1)
- Module ELSDocument40 pagesModule ELSnotzi6942018890420No ratings yet
- ES 1st Long Test 22-23Document2 pagesES 1st Long Test 22-23Ana Marie PalerNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Lesson 1Document30 pagesEarth Science Lesson 1Frances Marinnelle EstrellanNo ratings yet
- Earth Science QUARTER 1 PrintDocument126 pagesEarth Science QUARTER 1 PrintLorenz JordanNo ratings yet
- Origin and Branches of Earth ScienceDocument9 pagesOrigin and Branches of Earth ScienceJon Meynard TavernerNo ratings yet
- SGES 1201 To Earth: Lecture PPT Files in Http://adec - Um.edu - MyDocument11 pagesSGES 1201 To Earth: Lecture PPT Files in Http://adec - Um.edu - Mychakk3No ratings yet
- Formation of The Universe: Big Bang TheoryDocument3 pagesFormation of The Universe: Big Bang TheoryJianna ClementeNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument8 pagesEarth and Life ScienceKathleen Joy PermangilNo ratings yet
- Space ExplorerDocument126 pagesSpace ExplorerJohn Vivian Prashant jp7vivianNo ratings yet
- 2018 Izidoro - Formation of Terrestrial PlanetsDocument59 pages2018 Izidoro - Formation of Terrestrial PlanetsInflatableOkapiNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument290 pagesEarth ScienceJove Kate Sumalpong Magno50% (2)
- Chapter II: Earth: Its Places in The UniverseDocument4 pagesChapter II: Earth: Its Places in The Universekw2533No ratings yet
- مادة التربة الأفريقيةDocument29 pagesمادة التربة الأفريقيةnet secureNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Earth and Life ScienceDocument6 pagesLecture 1-Earth and Life ScienceJunar SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Earth's Structure and System: LessonDocument40 pagesEarth's Structure and System: LessonGlen MillarNo ratings yet
- Dynamical Shakeup of Planetary Systems II - N-Body Simulations of Solar System Terrestrial Planet Formation Induced by Secular Resonance SweepingDocument14 pagesDynamical Shakeup of Planetary Systems II - N-Body Simulations of Solar System Terrestrial Planet Formation Induced by Secular Resonance SweepingardeegeeNo ratings yet
- St. Mary's College of BaliuagDocument8 pagesSt. Mary's College of BaliuagCamille OngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Origin and Structure of The EarthDocument15 pagesChapter 1 Origin and Structure of The EarthCheska Marie B. OlivaNo ratings yet
- It Is All About The Earth! Journey To The Center of The Earth!Document5 pagesIt Is All About The Earth! Journey To The Center of The Earth!KEANNA SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Earth Science Reviewer UniverseDocument8 pagesEarth Science Reviewer UniverseSophia GarciaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Handout ELSDocument7 pages1st Quarter Handout ELSClifford Tubana100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science NotesDocument18 pagesEarth and Life Science NotesMary Antonette VeronaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Results & InterpretationDocument11 pagesLaboratory Results & InterpretationLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Guide QDocument5 pagesGroup 1 Guide QLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Sustenance and StrengtheningDocument1 pageSustenance and StrengtheningLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science: This Hypothesis Suggest That A Cloud of Gas and Dust, 10 Million KM in Diameter Rotated SlowlyDocument26 pagesEarth & Life Science: This Hypothesis Suggest That A Cloud of Gas and Dust, 10 Million KM in Diameter Rotated SlowlyLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Ecart DrugsDocument2 pagesEcart DrugsLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- ELS Q1 M1 2 3 Activity SheetDocument25 pagesELS Q1 M1 2 3 Activity SheetLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Abm Demayo Etech M1-4Document11 pagesAbm Demayo Etech M1-4Ljae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Frances Juris B. Natino 7-STE 1 ICT Quarter 2-Module 1: Activity 1 ADocument3 pagesFrances Juris B. Natino 7-STE 1 ICT Quarter 2-Module 1: Activity 1 ALjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Why Is Jesus The Lion of JudahDocument6 pagesWhy Is Jesus The Lion of JudahLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Frances Juris B. Natino 7-STE 1 ICT Quarter 2-Module 2 Testing Electronic Components (Part 1)Document2 pagesFrances Juris B. Natino 7-STE 1 ICT Quarter 2-Module 2 Testing Electronic Components (Part 1)Ljae NatinoNo ratings yet
- What's More: Art Dyron A. Demayo Grade 12 - ABM Glendel C. Bermudo Q2 - Module 5Document4 pagesWhat's More: Art Dyron A. Demayo Grade 12 - ABM Glendel C. Bermudo Q2 - Module 5Ljae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learning Activity SheetDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Activity SheetLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For Scoring Is Given: Read and Study The Masterpiece of WilfredoDocument4 pagesRubrics For Scoring Is Given: Read and Study The Masterpiece of WilfredoLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- INT 220 Business Brief Course ProjectDocument5 pagesINT 220 Business Brief Course ProjectTeddy jeremyNo ratings yet
- On The Ten-Year Success in The Application of Partial Extraction Therapy: A Systematic ReviewDocument9 pagesOn The Ten-Year Success in The Application of Partial Extraction Therapy: A Systematic ReviewDr Sharique AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Sustainable Marketing: Social Responsibility and EthicsDocument45 pagesChapter 20 Sustainable Marketing: Social Responsibility and EthicsKAIVALYA PAINo ratings yet
- Networks of Touch A Tactile History of Chinese Art 1790 1840 Perspectives On Sensory History 1St Edition Hatch Full ChapterDocument67 pagesNetworks of Touch A Tactile History of Chinese Art 1790 1840 Perspectives On Sensory History 1St Edition Hatch Full Chapterheather.bekis553100% (12)
- Implementation of A Learning Environment For An Industrie 4.0 Assistance System To Improve The Overall Equipment EffectivenessDocument8 pagesImplementation of A Learning Environment For An Industrie 4.0 Assistance System To Improve The Overall Equipment EffectivenessDany MarquesNo ratings yet
- Revised PROOFREAD Thesis DocumentDocument74 pagesRevised PROOFREAD Thesis DocumentJohn Paul MadroñalNo ratings yet
- Teacher Notes Hooke's Law Program Robert Hooke: Quiz Answers No. Answer DescriptionDocument4 pagesTeacher Notes Hooke's Law Program Robert Hooke: Quiz Answers No. Answer DescriptionDaniel IingNo ratings yet
- Final Viva (Iec)Document13 pagesFinal Viva (Iec)Shaian IslamNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology Module 6Document16 pagesAP Psychology Module 6Klein ZhangNo ratings yet
- White Sika Paper Strengthening ConcreteDocument12 pagesWhite Sika Paper Strengthening ConcreteRaed alkronz Raed alkronzNo ratings yet
- CSE Curriculum - Brac UniversityDocument3 pagesCSE Curriculum - Brac UniversityAsdfgh JklbhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Hyperbolic, Inverse Hyperbolic, Inverse TrigonometricDocument10 pagesChapter 1: Hyperbolic, Inverse Hyperbolic, Inverse TrigonometricRodziah NasirNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - PowerPoint PresentationDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - PowerPoint PresentationVicente CarandangNo ratings yet
- PP Accounting System Analysis & DesignDocument13 pagesPP Accounting System Analysis & DesignCik TeaniNo ratings yet
- Workflow and Service-OrientedDocument6 pagesWorkflow and Service-OrientedShimaa IbrahimNo ratings yet
- AquaMist Machinery Space US 1017 LoResDocument8 pagesAquaMist Machinery Space US 1017 LoResSI Comércio e ServiçosNo ratings yet
- Purdue OwlDocument57 pagesPurdue Owlapi-309710992No ratings yet
- 004 - Power Fuse (LS)Document16 pages004 - Power Fuse (LS)HungPhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 - Manual Metal Arc WeldingDocument14 pagesChapter2 - Manual Metal Arc WeldingAkhil VenugopalNo ratings yet
- ACS Publications 2018 UpdateDocument37 pagesACS Publications 2018 UpdateSeptian Perwira YudhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - SolutionsDocument10 pagesChapter 2 - SolutionsShubh MishraNo ratings yet
- Valvula Alarma de 4 PulgadasDocument22 pagesValvula Alarma de 4 PulgadasRobertoNo ratings yet
- M - Procd For MRMDocument2 pagesM - Procd For MRMravikpandeyNo ratings yet
- Audit ManagementDocument66 pagesAudit ManagementMohamed AshrafNo ratings yet