Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name: Year & Section: 12
Name: Year & Section: 12
Uploaded by
hiyam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe document summarizes key concepts about the photoelectric effect from a physics lesson. It includes a description of how changing the wavelength and intensity of light affects electron emission from metals. It also discusses how changing the color (wavelength) of light affects the energy of emitted photons and electrons. Finally, it includes a table comparing the work function and maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted from different metals when illuminated with specific frequencies of light.
Original Description:
Physics IAL edexcel revision on nature of light with answers
Original Title
physics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key concepts about the photoelectric effect from a physics lesson. It includes a description of how changing the wavelength and intensity of light affects electron emission from metals. It also discusses how changing the color (wavelength) of light affects the energy of emitted photons and electrons. Finally, it includes a table comparing the work function and maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted from different metals when illuminated with specific frequencies of light.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesName: Year & Section: 12
Name: Year & Section: 12
Uploaded by
hiyamThe document summarizes key concepts about the photoelectric effect from a physics lesson. It includes a description of how changing the wavelength and intensity of light affects electron emission from metals. It also discusses how changing the color (wavelength) of light affects the energy of emitted photons and electrons. Finally, it includes a table comparing the work function and maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted from different metals when illuminated with specific frequencies of light.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Name: Year & Section: 12
Subject: Physics Topic: Nature of light Date: 3-2-2022
http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/photoelectric
1. Describe the effect of wavelength and intensity on electron emission
10 marks
increasing the light intensity increases the rate at which electrons leave the metal, and the
electrons have more kinetic energy.
So if you wavelength gets shorter , then given constant intensity you will have fewer
electrons
Name of the metal Wavelength required for Maximum current Energy of the
electron emission wavelength
Sodium 4.8*10^-9 0.016 4.06*10^-18
zinc 2.68*10^-7 0.016 7.41*10^-19
Copper 1.41*10^-7 1.244 2.37*10^-19
Platinum 1.68*10^-7 0.108 1.18*10^-18
Calcium 1.68*10^-7 1.482 1.18*10^-18
2. What effect does changing the color have?
As electrons move from higher energy levels to lower energy levels a photon (particle of
light) will be given off. This is the process of emission. The photons will have different
wavelengths and frequencies, this makes photons of different energies produce different
colors of light.
3. What effect does changing the brightness of the light have?
the number of photons hitting the metal, increasing the rate at which electrons are emitted
but not changing the maximum kinetic energy of the electrons.
4. Complete the table.
Maximum KE Maximum KE
Work Function Frequency of of
Metal
/J used /Hz Ejected Ejected
electrons /J electrons /eV
Sodium 3.65 x 10 -19
6 x 10
14
3.28 x10^-20 5.2*10^-39
Potassium 3.68 x 10-19 6^10*-54 0.32 x 10-19 2 x10^-39
Lithium 4.64 x 10-19 1 x 1015 6 x10^-16 3.77 x10^-35
Aluminium 6.56 x 10 -19
1 x 10^-53 0.35 x 10
-19
6.6 x10^-73
Zinc 6.88 x 10-19 1.2 x10^-53 1.12 x 10-19 7.5 x10^-73
Copper 7.36 x 10-19 1 x 1015 6.63 x10^-19 4.14 x10-38
You might also like
- H155XL G006 DiagramsDocument88 pagesH155XL G006 DiagramsWagner Dalla Bernardine100% (5)
- EG383 CeramicsDocument68 pagesEG383 CeramicsTom CurtisNo ratings yet
- Paramagnetic Lab - Farheen & MowDocument8 pagesParamagnetic Lab - Farheen & MowFarheenNo ratings yet
- A Novel Meta-Heuristic Approach For Load Balancing in Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesA Novel Meta-Heuristic Approach For Load Balancing in Cloud ComputingPraveen Kumar UmmidiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Conductivity in MetalsDocument19 pagesElectrical Conductivity in MetalsNicole Anne BorromeoNo ratings yet
- CHM ART Activity 4 Atoms and Isotopes PDFDocument4 pagesCHM ART Activity 4 Atoms and Isotopes PDFMark Vincent DoriaNo ratings yet
- On My Headway ..: Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesOn My Headway ..: Learning ObjectivesZunaira SafdarNo ratings yet
- Electrical or Thermal CondutivityDocument1 pageElectrical or Thermal CondutivityDan SabadusNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2: ST ND RD THDocument24 pagesChemistry Unit 2: ST ND RD THjontstufNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Work Sheet - 04Document4 pagesAnswer Key: Work Sheet - 04Naunidh Singh MadhokNo ratings yet
- Electrical BehaviorDocument40 pagesElectrical BehaviorJHON ALEX LOPINTA CCANSAYANo ratings yet
- Physics 10262 - Chapter 2 - Homework: Kev HG E Kev PB E Ev Z EDocument5 pagesPhysics 10262 - Chapter 2 - Homework: Kev HG E Kev PB E Ev Z ELalón Gitud De OndaNo ratings yet
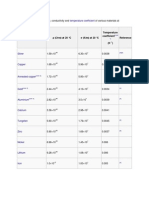
- ρ (Ω - m) at 20 °C σ (S/m) at 20 °C Temperature coefficient ReferenceDocument4 pagesρ (Ω - m) at 20 °C σ (S/m) at 20 °C Temperature coefficient ReferenceNikhil SutharNo ratings yet
- Transition MetalsDocument16 pagesTransition MetalsAditya NandaNo ratings yet
- Presentation - 1 Energy Use in Metal Production: Keywords: Metals, Embodied Energy, Primary Metals, Recycling, GreenhouseDocument3 pagesPresentation - 1 Energy Use in Metal Production: Keywords: Metals, Embodied Energy, Primary Metals, Recycling, GreenhouseNitin RautNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Elements 1Document20 pagesAtoms and Elements 1lucban.136550100297No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Atomic Structure: Test Yourself (Page 3)Document139 pagesChapter 1 - Atomic Structure: Test Yourself (Page 3)Aref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Atomic Structure: Test Yourself (Page 3)Document139 pagesChapter 1 - Atomic Structure: Test Yourself (Page 3)Aref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Atomic Structure: Test Yourself (Page 3)Document139 pagesChapter 1 - Atomic Structure: Test Yourself (Page 3)Aref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Atomic Structure: Test Yourself (Page 3)Document139 pagesChapter 1 - Atomic Structure: Test Yourself (Page 3)Aref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- MTN307 Lecture2 PDFDocument43 pagesMTN307 Lecture2 PDFDevashish MeenaNo ratings yet
- Ass2 ScienceDocument36 pagesAss2 ScienceMostafa ElngarNo ratings yet
- Cap 8Document30 pagesCap 8Ricardo Rincon VegaNo ratings yet
- 1986 Bookmatter HeatTransferDocument69 pages1986 Bookmatter HeatTransferYng Dmb Broke GuyNo ratings yet
- CH 02 DeletedDocument2 pagesCH 02 DeletedKetanRaoNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect WorkshetDocument3 pagesPhotoelectric Effect Workshettuvvac0% (1)
- Unit 4 Basic Electronics: StructureDocument23 pagesUnit 4 Basic Electronics: StructureParminder singh parmarNo ratings yet
- Main Formulas and Ultrasonic Reference Data: 2.1 Physics of Ultrasonics-DefinitionsDocument5 pagesMain Formulas and Ultrasonic Reference Data: 2.1 Physics of Ultrasonics-DefinitionsKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Revision P4 ChemistryDocument3 pagesRevision P4 ChemistryMariana ValoisNo ratings yet
- Electrodeposition and AnodizationDocument3 pagesElectrodeposition and AnodizationMahabub Alam MoonNo ratings yet
- CME 260 2007 Final ExamMay 9 SolutionsDocument5 pagesCME 260 2007 Final ExamMay 9 SolutionsAimi Hazwan AzizanNo ratings yet
- Solution 02 - Atomic StructureDocument3 pagesSolution 02 - Atomic StructuremarkNo ratings yet
- Plating RateDocument20 pagesPlating RateFrancisco BocanegraNo ratings yet
- RF Sheet Resistance Rev 7Document38 pagesRF Sheet Resistance Rev 7nirav.kateshiyaNo ratings yet
- METALOGRAPHYDocument69 pagesMETALOGRAPHYElias KapaNo ratings yet
- Structure NotesDocument5 pagesStructure NotesNeil HandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Structures of Crystalline Solids: Issues To Address..Document56 pagesChapter 4: Structures of Crystalline Solids: Issues To Address..ramanNo ratings yet
- Development of An Electron Impact Ion Source With High Ionization Efficiency For Future Planetary MissionsDocument26 pagesDevelopment of An Electron Impact Ion Source With High Ionization Efficiency For Future Planetary MissionsAbhayOberoiNo ratings yet
- Science Week 2-7Document9 pagesScience Week 2-7Sonnicalhyn GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-SolutionDocument6 pagesChapter 9-Solutionmp6w9qw7t2No ratings yet
- 10.energy Band Gap Behavior of Binary OxidesDocument24 pages10.energy Band Gap Behavior of Binary OxidesWan HafizaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Diffusivity - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesThermal Diffusivity - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaygraoNo ratings yet
- 3 Matter and MineralsDocument22 pages3 Matter and Mineralsshain begumNo ratings yet
- Chem FinalsDocument13 pagesChem Finalshayleychan6202007No ratings yet
- Name: 茱席拉 Student Number: 4090H430 Date: 110/04/07 Engineering Materials Hw2Document2 pagesName: 茱席拉 Student Number: 4090H430 Date: 110/04/07 Engineering Materials Hw2席拉茱No ratings yet
- Powerpoint ElectrodepositionDocument24 pagesPowerpoint ElectrodepositionsobheysaidNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Form 3Document21 pagesAtomic Structure Form 3Kupakwashe KampiniNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry SAC 1 Data Analysis: Ionization Energy: The Energy Required To Remove An Electron From ADocument2 pagesYear 11 Chemistry SAC 1 Data Analysis: Ionization Energy: The Energy Required To Remove An Electron From ADuyenNo ratings yet
- Electroplating Costs CalculationDocument19 pagesElectroplating Costs CalculationmosesNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework AnswersDocument8 pagesCHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework AnswersGrothendieck Langlands ShtukasNo ratings yet
- History and Subatomic Particle Review Take Two KEYDocument5 pagesHistory and Subatomic Particle Review Take Two KEYAlliya DaymonNo ratings yet
- Important Chap3 1 SemiImportant Chap3-1-Semiconductor-1.pdf Conductor 1Document67 pagesImportant Chap3 1 SemiImportant Chap3-1-Semiconductor-1.pdf Conductor 1Muhammad Ali AbroNo ratings yet
- A New Phase in ND, Fe,,B Magnets. Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of ND, Fe,,SiDocument7 pagesA New Phase in ND, Fe,,B Magnets. Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of ND, Fe,,SiAlberto JimenezNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Acoustic Impedance ChartDocument1 pageVelocity and Acoustic Impedance ChartALBERTO MENDIVILNo ratings yet
- Presentacion Cip Funfamentos IcpDocument107 pagesPresentacion Cip Funfamentos IcpQUETVER LEANDRO JARA QUEZADANo ratings yet
- ★03주차 - 재료학 Ch03a - Engineering Materials and Their Properties - PartA - 재료 - 65쪽Document65 pages★03주차 - 재료학 Ch03a - Engineering Materials and Their Properties - PartA - 재료 - 65쪽littleson119119No ratings yet
- Categories or Electric Materials P1 PDFDocument24 pagesCategories or Electric Materials P1 PDFZach VittoriNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements (Table) 5Document3 pagesClassification of Elements (Table) 5Krishiv RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Title: The Corrosion of Different Metals in Salt Water and Tap WaterDocument21 pagesTitle: The Corrosion of Different Metals in Salt Water and Tap WaterYi Ling GohNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Notes 2024 - 04chemical BondingDocument25 pagesLevel 2 Notes 2024 - 04chemical BondingMatthew TanNo ratings yet
- Endohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideFrom EverandEndohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideNo ratings yet
- (Analysis of Variance) : AnovaDocument22 pages(Analysis of Variance) : AnovaJoanne Bernadette IcaroNo ratings yet
- Samaddar 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1716 012005Document10 pagesSamaddar 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1716 012005Mohit DhawanNo ratings yet
- 2020 Keystone Catalog Low 1Document60 pages2020 Keystone Catalog Low 1sddsdNo ratings yet
- Automated Blood Coagulation Analyzer CA-50: Basic Data Sheet - (Intrinsic Factors)Document12 pagesAutomated Blood Coagulation Analyzer CA-50: Basic Data Sheet - (Intrinsic Factors)Aahsan Iqbal احسن اقبالNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Slope Stability-09Document19 pagesChapter 7-Slope Stability-09Alexander AlexanderNo ratings yet
- BS en 1926:2006Document20 pagesBS en 1926:2006lkzasj dksikNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1: BS-Software Engineering Section XDocument34 pagesAssignment # 1: BS-Software Engineering Section XMuhammad Nawaz AshrafNo ratings yet
- IE 337.HW#5.W10.keyDocument4 pagesIE 337.HW#5.W10.keyJae Hacuculaiy SamoreNo ratings yet
- Unit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesUnit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsRengganis Putri ParmudyaNo ratings yet
- Sica 6,5H1,5CP (Z004100)Document1 pageSica 6,5H1,5CP (Z004100)Carlos Perujo FotosNo ratings yet
- Installation GuideDocument24 pagesInstallation GuideAnonymous ugFBbUfqwNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Uso de CRT ConsolaDocument47 pagesTroubleshooting Uso de CRT ConsolaJorge MartinelliNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatement PlantDocument42 pagesSewage Treatement PlantSunil A. Bakoliya100% (2)
- Lieber 1961 Human Values and Science Art and MathematicsDocument74 pagesLieber 1961 Human Values and Science Art and MathematicsaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Worksheet 1Document4 pagesPre-Calculus Worksheet 1Rogelio Jr. TapiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Translational Equilibrium and FrictionDocument15 pagesChapter 4. Translational Equilibrium and FrictionMarites DalinocNo ratings yet
- OneSteel Pipe Fittings Final LoResDocument49 pagesOneSteel Pipe Fittings Final LoResAnonymous P0yIxVQtNo ratings yet
- Ebook Chemistry and Chemical Reactivity 9Th Edition Kotz Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument44 pagesEbook Chemistry and Chemical Reactivity 9Th Edition Kotz Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFMrNicolasGuerraJrnsadz100% (14)
- Increased Margin From Updated Internals and CatalystDocument7 pagesIncreased Margin From Updated Internals and CatalystBamrung SungnoenNo ratings yet
- hw3 SolDocument3 pageshw3 SolDylan LerNo ratings yet
- XLSXDocument40 pagesXLSXLeonardo BritoNo ratings yet
- How To Draw Basic Linear PerspectiveDocument16 pagesHow To Draw Basic Linear PerspectiveYao N'GoranNo ratings yet
- Power Series MathDocument9 pagesPower Series Mathpadam bhandariNo ratings yet
- Btech Me 5 Sem Strength of Materials Kme502 2023Document3 pagesBtech Me 5 Sem Strength of Materials Kme502 2023ykrish276No ratings yet
- Introduction To Programming With Matlab: ExercisesDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Programming With Matlab: ExercisesHương Đặng100% (1)
- Encoding SchemesDocument1 pageEncoding Schemesdksingh369No ratings yet
- Stahl WasmaaticDocument21 pagesStahl WasmaaticrajevskumarNo ratings yet
- Problem On PSA Primary SchoolDocument2 pagesProblem On PSA Primary SchoolMangleswary SalbarajaNo ratings yet