Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Hiv?: Aids and Hivs
What Is Hiv?: Aids and Hivs
Uploaded by
carlous brathwate0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views8 pagesHIV originated in primates and was clinically diagnosed in humans in the 1980s. It has since spread worldwide, killing over 25 million people. HIV infects and destroys immune cells, progressively destroying the body's ability to fight infections and disease. Within 10 years HIV develops into AIDS if not treated. There is no cure for AIDS, so prevention through safe sexual practices, sterile needle use, screening blood and pregnancy are critical ways to stop transmission of the virus.
Original Description:
hj
Original Title
essa
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHIV originated in primates and was clinically diagnosed in humans in the 1980s. It has since spread worldwide, killing over 25 million people. HIV infects and destroys immune cells, progressively destroying the body's ability to fight infections and disease. Within 10 years HIV develops into AIDS if not treated. There is no cure for AIDS, so prevention through safe sexual practices, sterile needle use, screening blood and pregnancy are critical ways to stop transmission of the virus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views8 pagesWhat Is Hiv?: Aids and Hivs
What Is Hiv?: Aids and Hivs
Uploaded by
carlous brathwateHIV originated in primates and was clinically diagnosed in humans in the 1980s. It has since spread worldwide, killing over 25 million people. HIV infects and destroys immune cells, progressively destroying the body's ability to fight infections and disease. Within 10 years HIV develops into AIDS if not treated. There is no cure for AIDS, so prevention through safe sexual practices, sterile needle use, screening blood and pregnancy are critical ways to stop transmission of the virus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
WHAT IS HIV?
HIV originated in non-human primates and eventually
spread to humans over the eons. Even though the disease
had been around for a long time, it was clinically
diagnosed in the 1980s. Ever since then, it has spread all
over the world, killing over 25 million people till date. AIDS
and HIV are terms that are used interchangeably even
though they are not quite related. So what exactly is the
difference between AIDS and HIVs? Essentially, HIV is the
virus that causes AIDS. It wreaks havoc on the body’s
immunity system until it is incapable of fending off
infections on its own. It is a retrovirus and has RNA as the
genetic material. The HIV infection spreads through the
following ways
Unprotected sexual interaction with an already
infected person.
Reusing needles used by an infected person.
From an infected mother to the baby through the
placenta.
Blood transfusion from an infected person.
This virus has a long incubation period before it starts to
attack the immune system (10 years). The immune system
is the human body’s natural defense mechanism; hence
HIV can make it harder for the patient to fight off infections
and diseases.HIV demolishes a particular type of WBC
(White Blood Cells) and the T-helper cells. This virus also
makes copies of itself inside these cells. T-helper cells are
also known as CD4 cells.
CAUSES OF MODES OF INFECTION:
The HIV infects the macrophages in the blood. Once they
infect, the viral RNA enters the host cell and produces
DNA with the help of reverse transcription.
This viral DNA then integrates into the host
genome and produces multiple RNA copies
by the process of transcription. These RNAs
then form multiple copies of the virus and
continue the infection in the same way.
At the same time, HIV also enters
the T lymphocytes and continues the
same set of events as it does in macrophages.
This leads to a decrease in the number of helper
T lymphocytes. Thus, the immunity of the
body is considerably
Compromised. The immunity is lowered
to such an extent that the infected person
Suffers from even minor infections, which
Is one of AIDS’ characteristic symptoms?
Other symptoms include bouts of fever,
Diarrhea and significant weight loss.
Symptoms of AIDS:
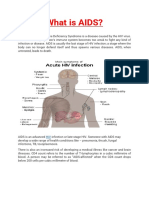
The symptoms of HIV usually differ from person to
person and in some cases, a patient infected with the
HIV infection may not experience any symptoms at
all. The common signs and symptoms of HIV include:
Fever
Chills
Headache
Joint pains
Sore throat
Muscle aches
Upset stomach
Red rashes on the skin
Tiredness and weakness
Sweating during the night
Swollen or enlarged Glands
The above symptoms can last from a few days to
several weeks. A person with HIV often experiences
no symptoms, feels healthy, and appears healthy.
Tests for HIV and AIDS:
Blood tests are the most common way to diagnose the
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that
causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
These tests look for antibodies to the virus that are
present in the blood of infected individuals. People
exposed to the virus should get tested immediately.
Early testing is crucial with HIV.
If you test positive for the virus,
You and your doctor can develop
a treatment plan to help fight HIV
and ward off complications.
Early testing also can alert you to avoid high-risk
behavior that could spread the virus to others.
Because it can take from six weeks to six months to
develop antibodies to the virus, follow-up tests may be
needed. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms,
medical history and risk factors and perform a physical
examination.
The primary tests for diagnosing HIV and AIDs include:
ELISA Test ELISA, which stands for enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay, is used to detect HIV infection. If
an ELISA test is positive, the Western blot test is usually
administered to confirm the diagnosis.
If an ELISA test is negative, but you think you may have
HIV, you should be tested again in one to three months.
ELISA is quite sensitive in chronic HIV infection, but
because antibodies aren't produced immediately upon
infection, you may test negative during a window of a few
weeks to a few months after being infected. Even though
your test result may be negative during this window, you
may have a high level of the virus and be at risk of
transmitting infection.
Home Tests The only home test approved by the U.S.
Food and Drug Administration is called the Home Access
Express Test, which is sold in pharmacies.
Saliva Tests A cotton pad is used to obtain saliva from
the inside of your cheek. The pad is placed in a vial and
submitted to a laboratory for testing. Results are
available in three days. Positive results should be
confirmed with a blood test.
Viral Load Test This test measures the amount of HIV in
your blood. Generally, it's used to monitor treatment
progress or detect early HIV infection. Three
technologies measure HIV viral load in the blood —
reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-
PCR), branched DNA (bDNA) and nucleic acid
sequence-based amplification assay (NASBA). The basic
principles of these tests are similar. HIV is detected using
DNA sequences that bind specifically to those in the
virus. It is important to note that results may vary
between tests.
Western Blot This is a very sensitive blood test used to
confirm a positive ELISA test result.
Prevention of AIDS:
HIV’s infection can be detected with the help of a test
called ELISA which stands for ‘Enzyme Linked Immuno
Sorbent Assay’. AIDS is incurable, so far; thus, HIV
prevention is the wisest option. As we have already
discussed the causes of AIDS, the prevention can be
deduced from them.
For example – Using disposable needles, practising safe
sex, i.e., use of protection like condoms, regular health
check-ups and monitoring blood transfusion and
pregnancy.
Another important factor is the awareness of AIDS. As it
does not spread by mere physical contact, the infected
persons should not be discriminated and must be treated
in a friendly manner.
You might also like
- BIO CBSE 12 PROJECT On HIV/AISDocument15 pagesBIO CBSE 12 PROJECT On HIV/AISAnonymous KdUrkMIyJQ72% (58)
- Prevalence of Residual Limb Pain and Symptomatic.3Document8 pagesPrevalence of Residual Limb Pain and Symptomatic.3Deng PanNo ratings yet
- Parenteral NutritionDocument6 pagesParenteral NutritionAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Gastric Outlet ObstructionDocument9 pagesGastric Outlet ObstructionVivek AhanthemNo ratings yet
- Antiretroviral Therapy Guidelines For HIV-Infected Adults and AdolescentsDocument122 pagesAntiretroviral Therapy Guidelines For HIV-Infected Adults and AdolescentsManoj Kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- ROHITDocument17 pagesROHITDivyansh kNo ratings yet
- Bio BirjuDocument17 pagesBio BirjuDivyansh kNo ratings yet
- Sameer BeelwalDocument13 pagesSameer Beelwalsameerbeelwal42No ratings yet
- Hiv Aids The BasicsDocument3 pagesHiv Aids The BasicsHyrum KamandeNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument9 pagesIntroductionSiti Zamilatul AzkiyahNo ratings yet
- ColouredDocument11 pagesColouredsharad chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Hivuni 181108082940 DikonversiDocument66 pagesHivuni 181108082940 DikonversiBiben FikrianaNo ratings yet
- Types of HIV and HIV Testing (2) .PPT.XDocument19 pagesTypes of HIV and HIV Testing (2) .PPT.XronojerutomNo ratings yet
- Aids FileDocument13 pagesAids Fileayansiddiqui0422No ratings yet
- Lecture VI DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF HIVDocument6 pagesLecture VI DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF HIVreginaamondi133No ratings yet
- Ate KrissiaDocument15 pagesAte Krissiaroan marie isaacNo ratings yet
- End Stage AidsDocument33 pagesEnd Stage AidsMichael T GarciaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesClass 12 Biology Investigatory Projectcomlab223No ratings yet
- Stage 1: Acute HIV InfectionDocument16 pagesStage 1: Acute HIV Infectionsalsa bilaNo ratings yet
- AidsDocument22 pagesAidsVicky Singh100% (2)
- Patient Education PDFDocument12 pagesPatient Education PDFAgustinaNo ratings yet
- HIV-AIDS Ward ClassDocument27 pagesHIV-AIDS Ward ClassChristian Anthony L. GamoloNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument22 pagesBio Projectrakeshkiran2007100% (1)
- Aids and Hiv Power Point PresentationDocument26 pagesAids and Hiv Power Point PresentationJohn Masefield100% (1)
- Aids Type Study Biology Investigatory Project: Submitted byDocument28 pagesAids Type Study Biology Investigatory Project: Submitted byveeraNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project: TopicDocument24 pagesBiology Investigatory Project: Topicattishya1104100% (1)
- HIV Health TalkDocument63 pagesHIV Health TalkLiza GustyaningNo ratings yet
- Symptoms Prevention and TestsDocument9 pagesSymptoms Prevention and TestsAkanksha katkarNo ratings yet
- HIV and Its TreatmentDocument24 pagesHIV and Its Treatmentaathira_kNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Ambernath BiologyDocument39 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Ambernath BiologyROHIT SIHRANo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids: Presented By: Chavez - Galang - Kaur - Noguera 2DcnDocument24 pagesHiv Aids: Presented By: Chavez - Galang - Kaur - Noguera 2DcnKate ChavezNo ratings yet
- Definition of AIDS and HIV InfectionDocument7 pagesDefinition of AIDS and HIV InfectionLily SharmaNo ratings yet
- Health & Diseases: Topic: AIDSDocument19 pagesHealth & Diseases: Topic: AIDSkakaramNo ratings yet
- What Is Hiv?: 3 Yearstrusted Source 1.2 MillionDocument11 pagesWhat Is Hiv?: 3 Yearstrusted Source 1.2 Millionhilja shipenaNo ratings yet
- What Is AIDS?Document7 pagesWhat Is AIDS?Bhavya PNo ratings yet
- S.N0 Topic: IndexDocument9 pagesS.N0 Topic: Indexashishkoshy12No ratings yet
- Immune Deficinecy: By: Kirk Odrey O. Jimenez R.NDocument51 pagesImmune Deficinecy: By: Kirk Odrey O. Jimenez R.NKirk08No ratings yet
- Hiv ElisaDocument3 pagesHiv ElisaRasikNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 25 Oct 2023Document16 pagesAdobe Scan 25 Oct 2023trishikaginodiaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - HivDocument10 pagesCase Study - HivJoycee BurtanogNo ratings yet
- Hiv AidsDocument36 pagesHiv AidsNaman Jain100% (1)
- Estimated HIV/AIDS Prevalence Among Young Adults (15-49) by Country As of 2008. UNAIDS 2008 ReportDocument16 pagesEstimated HIV/AIDS Prevalence Among Young Adults (15-49) by Country As of 2008. UNAIDS 2008 Reportlianghoo94No ratings yet
- What Is HIV? ExpandedDocument4 pagesWhat Is HIV? ExpandedAlyannaBesares100% (1)
- Symptoms of AidsDocument6 pagesSymptoms of AidsSidaya ColeyNo ratings yet
- Cassi SidaDocument6 pagesCassi SidanelnotaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: IntroductionDocument5 pagesMicrobiology: IntroductionNimra AmeenNo ratings yet
- What Is HIVDocument14 pagesWhat Is HIVmariam miladNo ratings yet
- HIV AIDS CausesDocument9 pagesHIV AIDS Causescamelapedro574No ratings yet
- Lab Test HivDocument2 pagesLab Test HivCindy MoraNo ratings yet
- BIO Investigatory PROJECTDocument7 pagesBIO Investigatory PROJECTDaphne SimiNo ratings yet
- Details On HIV/AIDSDocument4 pagesDetails On HIV/AIDSTheSubhas ChandraNo ratings yet
- Artikel B. InggrisDocument9 pagesArtikel B. Inggrisbb dias0% (1)
- HIV AIDS SummaryDocument8 pagesHIV AIDS SummarymugpireNo ratings yet
- HIV Simple Case StudyDocument13 pagesHIV Simple Case StudyJanna Pimentel100% (1)
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Gurujang, KhurdaDocument33 pagesJawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Gurujang, KhurdaOmmNo ratings yet
- Bio Cbse 12 Project On Hiv AisDocument15 pagesBio Cbse 12 Project On Hiv Aishelo helium50% (2)
- HIV Infection !: Dalal AlanaziDocument44 pagesHIV Infection !: Dalal AlanaziKarl Vincent SosoNo ratings yet
- Content Health EdDocument3 pagesContent Health EdAnna FoxNo ratings yet
- Hiv 20infection 20 21 140104152057 Phpapp02Document43 pagesHiv 20infection 20 21 140104152057 Phpapp02Shyden Taghap Billones BordaNo ratings yet
- Infection With Human Immunodeficiency Virus: ELISA/Western Blot Tests For HIVDocument6 pagesInfection With Human Immunodeficiency Virus: ELISA/Western Blot Tests For HIVBianca de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- HIV and AIDS - PDF 2Document26 pagesHIV and AIDS - PDF 2Cheska JunturaNo ratings yet
- HIV and AIDS PDFDocument1 pageHIV and AIDS PDFnatalia gunawanNo ratings yet
- How Can I Tell If I Have HIV?Document61 pagesHow Can I Tell If I Have HIV?April Charose ArongNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportFrom EverandThe Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportNo ratings yet
- Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning: Volume One, Third EditionDocument32 pagesNursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning: Volume One, Third EditionSamip PatelNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure in ChildrenDocument48 pagesCongestive Heart Failure in ChildrenSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- LESSON 5-6: Optimizing One'S Health Through Dance Physical Fitness AssessmentDocument10 pagesLESSON 5-6: Optimizing One'S Health Through Dance Physical Fitness AssessmentVERDADERO LevisthoneNo ratings yet
- Infant and Toddler Concussion Guide: Signs & SymptomsDocument2 pagesInfant and Toddler Concussion Guide: Signs & Symptomspeninah annNo ratings yet
- Impact of Diarrhoea On Nutritional StatusDocument13 pagesImpact of Diarrhoea On Nutritional StatusSAB MICHTITYANo ratings yet
- Ifu Hydrocyn Aqua Advanced Wound Care SolutionDocument1 pageIfu Hydrocyn Aqua Advanced Wound Care SolutionAsNo ratings yet
- Module in Prof Ed 2Document4 pagesModule in Prof Ed 2Abegael PreagolaNo ratings yet
- Hot Stone Massage BenefitsjhxnjDocument2 pagesHot Stone Massage Benefitsjhxnjsecondstove31No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Science Biology Keeping HealthyDocument30 pagesAQA GCSE Science Biology Keeping HealthySteve BishopNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of SalbutamolDocument11 pagesPharmacology of SalbutamolarvinthamelakaNo ratings yet
- Selected Transcriptome Profiles of Oral Cancer Suggestive of Field Cancer Is at Ion Using Second Generation SequencingDocument2 pagesSelected Transcriptome Profiles of Oral Cancer Suggestive of Field Cancer Is at Ion Using Second Generation SequencingRosnah Binti ZainNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY AtorvastatinDocument2 pagesDRUGSTUDY AtorvastatinMicaela Andrea CieloNo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis 2014Document13 pagesAtopic Dermatitis 2014IvanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPLeslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- Tumor Flash Cards - Osteochondroma and Multiple Hereditary ExostosisDocument23 pagesTumor Flash Cards - Osteochondroma and Multiple Hereditary Exostosislaxge54No ratings yet
- Nadi Astrology and DiseasesDocument1 pageNadi Astrology and DiseasesSunil Rupani100% (1)
- Seminar - Heart FailuerDocument19 pagesSeminar - Heart Failuermustafalotfy01No ratings yet
- Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis After Rabies Vaccination: One Case ReportDocument4 pagesAcute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis After Rabies Vaccination: One Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Chalazion PDFDocument3 pagesChalazion PDFPriscillia AlqodryNo ratings yet
- Case Profile PsycologyDocument11 pagesCase Profile Psycologycrazy adwaithNo ratings yet
- The 4 Stages of Habituation (2018)Document1 pageThe 4 Stages of Habituation (2018)Joe BlowNo ratings yet
- Disclosure: Complex Case: Complications After Cardiac Surgery - Glucose, Sedation and ThrombocytopeniaDocument27 pagesDisclosure: Complex Case: Complications After Cardiac Surgery - Glucose, Sedation and ThrombocytopeniaEnrique SánchezNo ratings yet
- EBMT 2021 ProgramDocument288 pagesEBMT 2021 Programtirillas101No ratings yet
- MR-13 LampropoulosBLHealth2003Document19 pagesMR-13 LampropoulosBLHealth2003BillalNo ratings yet
- Surgery 3 White Part 1Document87 pagesSurgery 3 White Part 1Håíthãm KhãtïßNo ratings yet