Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(R2) Prenatal Detection of Birth Defects
(R2) Prenatal Detection of Birth Defects
Uploaded by
Nicole HonradoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(R2) Prenatal Detection of Birth Defects
(R2) Prenatal Detection of Birth Defects
Uploaded by
Nicole HonradoCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Prenatal Detection of Birth defects NCM 109
NURSING CARE OF THE PREGNANT CLIENT O.B. LEC.
I. PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS smaller abnormalities, and abnormalities can be seen
earlier, more accurately, or both.
● Prenatal diagnosis determine whether the fetus has certain
abnormalities, including certain hereditary or spontaneous
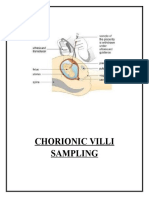
genetic disorders. Some of these tests, such as ultrasonography Chorionic Villus Sampling
and certain blood tests, are often part of routine prenatal care. ● In here, a doctor removes a small sample of the chorionic
Usually, these more invasive tests done when couples have an villi, which are tiny projections that make up part of the
increased risk of having a baby with a genetic abnormality (such placenta.
as a neural tube defect) or a chromosomal abnormality ● The main advantage of chorionic villus sampling is that its
(particularly when the woman is 35 or older). These tests have results are available much earlier in the pregnancy than
risks, although very small, particularly for the fetus. those of amniocentesis. Thus, if no abnormality is detected,
● If in vitro fertilization is done, genetic disorders can sometimes the couple's anxiety can be relieved earlier.
be diagnosed before the fertilized egg is transferred from the ● Before the chorionic villus sampling, ultrasonography is
culture dish to the uterus. These tests are available only in done to determine whether the fetus is alive, to confirm the
specialized centers and are used primarily for couples with a high length of the pregnancy, to check for obvious abnormalities,
risk of certain genetic disorders (such as cystic fibrosis) or and to locate the placenta.
chromosomal abnormalities. ● A sample of the chorionic villi can be removed through the
● Couples should discuss the risks with their health care cervix(transcervically) or the abdominal wall
practitioner and weigh the risks against their need to know. (transabdominally). With both methods, ultrasonography is
used for guidance and the tissue sample is suctioned
through a needle or catheter with a syringe and then sent for
laboratory analysis. Many women have light spotting for a
day or two afterward.
● Methods used to acquire a sample of the chorionic villi :
� Through the cervix: The woman lies on her back
with her hips and knees bent, usually supported
by heel or knee stirrups, as for a pelvic
examination. The doctor inserts a thin, flexible
tube (catheter) through the vagina and cervix into
the placenta. For most women, the procedure
feels very similar to a Papanicolaou (Pap) test, but
a few women find it more uncomfortable. This
method cannot be used in women who have an
active genital infection (such as genital herpes or
gonorrhea), chronic inflammation of the cervix, or
a placenta that covers the passage between the
cervix and uterus.
II. METHODS � Through the abdominal wall: The doctor
anesthetizes an area of skin over the abdomen and
Ultrasonography inserts a needle through the abdominal wall into
● It has no known risks for the woman or fetus. the placenta. Most women do not find this
● Ultrasonography can do the following: procedure painful. But for some women, the area
� confirm the length of the pregnancy over the abdomen feels slightly sore for an hour
� locate the placenta or two afterward.
� indicate whether the fetus is alive ● After chorionic villus sampling, most women who have Rh-
� After the third month, detect certain obvious structural negative blood and who do not have antibodies to Rh factor
birth defects, including those of the brain, spinal cord, are given an injection of Rh0 (D) immune globulin to
heart, kidneys, stomach, abdominal wall, and bones prevent them from producing antibodies to Rh factor A
� in the 2nd trimester, detect findings that tend to woman with Rh-negative blood may produce these
indicate a higher-than-normal chance of a antibodies if the fetus has Rh- positive blood and it comes
chromosomal abnormality in the fetus into contact with her blood, as it may during chorionic
● Ultrasonography is done before chorionic villus sampling and villus sampling. These antibodies can cause problems in the
amniocentesis to confirm the length of the pregnancy so that fetus. The injection is not needed if the father also has Rh-
these procedures can be done at the appropriate time during the negative blood because in such cases, the fetus always has
pregnancy. During these procedures, ultrasonography is used to Rh-negative blood.
monitor the fetus and to guide placement of instruments.
Amniocentesis
● often offered to women over 35 to estimate their risk of
having a baby with Down syndrome
● In this procedure, a sample of the fluid that surrounds the
fetus (amniotic fluid) is removed and analyzed.
Amniocentesis is usually done at 15 weeks of pregnancy or
● At some specialized medical centers, targeted ultrasonography later. The fluid contains cells that have been shed by the
can be done. For this test, experts carefully assess the fetus to fetus. These cells are grown in a laboratory so that the
check for structural defects that indicate an increased risk of a chromosomes in them can be analyzed.
chromosomal abnormality. This test can provide greater detail ● Amniocentesis enables doctors to measure the alpha-
than conventional ultrasonography. Thus, this test may detect fetoprotein level in the amniotic fluid. This measurement
Page 1 of 2
[OB LEC.] 1. Prenatal detection of birth defects
more reliably indicates whether the fetus has a brain or spinal ● Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling is an invasive
cord defect than does measurement of this level in the woman's procedure and has risks for the woman and fetus. Loss of
blood. the pregnancy as a result of this test occurs in about 1 in
● Procedure: 100 procedures.
� Before the procedure, ultrasonography is done to
evaluate the heart of the fetus, to confirm the length of
the pregnancy, to locate the placenta and amniotic
fluid, and to determine how many fetuses are present.
� A doctor inserts a needle through the abdominal wall
into the amniotic fluid. Sometimes a local anesthetic is
first used to numb the site. During the procedure,
ultrasonography is done so that the fetus can be
monitored and the needle can be guided into place.
Fluid is withdrawn, and the needle is removed. Results
are usually available in about 1 to 2 weeks.
● Occasionally, the amniotic fluid contains blood from the fetus.
Such blood may increase the alpha-fetoprotein level, making the
results hard to interpret.
● Amniocentesis rarely causes any problems for the woman or the
fetus. The following may occur:
� Soreness: Some women feel slightly sore for an hour
or two afterward.
� Spotting of blood or leakage of amniotic fluid from
the vagina: About 1 to 2% of the women have these
problems, but the problems do not last long and usually
stop without treatment.
� Miscarriage: The chance of miscarriage due to
amniocentesis is about 1 in 500 to 1,000.
� Needle injuries to the fetus: These injuries are very
rare.
Percutaneous Umbilical Sampling
● used when rapid chromosome analysis is needed, particularly
toward the end of pregnancy when ultrasonography has detected
abnormalities in the fetus.
● Often, results can be available within 48 hours. It is occasionally
done for other reasons—for example, when doctors suspect that a
fetus has anemia. If the fetus has severe anemia, blood can be
transfused to the fetus during percutaneous umbilical blood
sampling.
● Procedure:
� The doctor first anesthetizes an area of skin over the
abdomen. Guided by ultrasonography, the doctor then
inserts a needle through the abdominal wall into the
umbilical cord. A sample of the fetus's blood is
withdrawn and analyzed, and the needle is removed.
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Arvophillia Case StudyDocument5 pagesArvophillia Case StudyMickelson Joseph Vil0% (1)
- Examples of Vaccine Injury Within The DoDDocument20 pagesExamples of Vaccine Injury Within The DoDJim Hoft80% (5)
- Time To Synergize Mental Health With Brain Health: CommentDocument3 pagesTime To Synergize Mental Health With Brain Health: Commentsoliveira_149796No ratings yet
- 12 Psychology - Meeting Life Challenges - Notes & Video LinkDocument11 pages12 Psychology - Meeting Life Challenges - Notes & Video LinkRamesh TalukdarNo ratings yet
- Central Venous Pressure MeasurementDocument2 pagesCentral Venous Pressure Measurementcayla mae carlos100% (2)
- Chorionic Villi SamplingDocument8 pagesChorionic Villi SamplingDivya sharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit X Prenatal Care: Pelvic ExaminationDocument9 pagesUnit X Prenatal Care: Pelvic ExaminationBinita ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Government College of Nursing Jodhpur (Raj.)Document5 pagesGovernment College of Nursing Jodhpur (Raj.)priyankaNo ratings yet
- Cervical IncompetenceDocument30 pagesCervical IncompetenceSignor ArasNo ratings yet
- Cervical IncompetenceDocument28 pagesCervical IncompetenceHoney May Rollan Vicente100% (1)
- OB B Cervical IncompetenceDocument30 pagesOB B Cervical IncompetencechemniedyavilaNo ratings yet
- HARINIDocument19 pagesHARINISaranya JNo ratings yet
- NCM 102: Gynecology Nursing ManagementDocument7 pagesNCM 102: Gynecology Nursing ManagementdubhieNo ratings yet
- Gynec ExamDocument45 pagesGynec ExamPutri Anggia BungaNo ratings yet
- Ob GynDocument13 pagesOb GynDianne Geremy RojoNo ratings yet
- Agenesis VaginaDocument6 pagesAgenesis Vaginai305No ratings yet
- 1 Mother (High Risk Childbearing-Maternal)Document62 pages1 Mother (High Risk Childbearing-Maternal)Maui TingNo ratings yet
- Term Alive Intra Abdominal Ectopic Pregnancy: Case ReportDocument3 pagesTerm Alive Intra Abdominal Ectopic Pregnancy: Case ReportLeannarys Mendoza DelgadoNo ratings yet
- (L13) - Human Reproduction - Aug 4, 2019 - SundayDocument32 pages(L13) - Human Reproduction - Aug 4, 2019 - Sundayصوفي اشوڪ ڪمارNo ratings yet
- Fertility NotesDocument18 pagesFertility NotesXenita VeraNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy: SynopsisDocument21 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: SynopsisARUSHI ARVINDNo ratings yet
- Chorionic Villi SamplingDocument4 pagesChorionic Villi SamplingSagar HanamasagarNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregancy: Chena B. CurigDocument35 pagesEctopic Pregancy: Chena B. CurigJaicca Faith Tandih AllasNo ratings yet
- Name: Year & Course: Test Type Timing Process ResultsDocument3 pagesName: Year & Course: Test Type Timing Process ResultsAllyah Anthonette Ferwelo100% (1)
- HSGDocument27 pagesHSGNauman JavedNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ahlam Al-Kharabsheh: Assistant Professor, OBS & GYN Department Mu'tah UniversityDocument36 pagesDr. Ahlam Al-Kharabsheh: Assistant Professor, OBS & GYN Department Mu'tah Universityraed faisalNo ratings yet
- Benin LesionDocument14 pagesBenin Lesionsandeepv08No ratings yet
- EP C2 by EliDocument40 pagesEP C2 by EliElsai EsbNo ratings yet
- Cervical Incompetence: Dr. Mohammed Abdalla Domiat General HospitalDocument40 pagesCervical Incompetence: Dr. Mohammed Abdalla Domiat General HospitalCristian AlbuNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Module 1 High Risk PregDocument6 pagesNCM 109 Module 1 High Risk PregJellie An TalattagNo ratings yet
- Prelims109 M1L1Document4 pagesPrelims109 M1L1MARY ROSE DOLOGUINNo ratings yet
- Antinetal ScreaningDocument19 pagesAntinetal Screaningkololll lllknNo ratings yet
- Chorionic Villi Sampling: A Nursing Perspective: Marilyn R. Stringer, RNC, BSNDocument4 pagesChorionic Villi Sampling: A Nursing Perspective: Marilyn R. Stringer, RNC, BSNAkhilaNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy - PowerpointDocument60 pagesEctopic Pregnancy - PowerpointAndrada Doţa100% (1)
- Female ReproductiveDocument13 pagesFemale Reproductiveta CNo ratings yet
- Cervical ScreeningDocument3 pagesCervical ScreeningShum Wing Hei Joanne100% (1)
- Gynecology and Minimally Invasive TherapyDocument3 pagesGynecology and Minimally Invasive TherapyAnca BiancaNo ratings yet
- Successful Conservative Treatment of Microinvasive Cervical Cancer During PregnancyDocument3 pagesSuccessful Conservative Treatment of Microinvasive Cervical Cancer During PregnancyEres TriasaNo ratings yet
- Gynecologic - Derived From The Greek Words "Gyne" or "Gynaikos" Meaning Woman orDocument12 pagesGynecologic - Derived From The Greek Words "Gyne" or "Gynaikos" Meaning Woman orCecilio Singzon AguirreNo ratings yet
- Early Pregnancy Complications: Ectopic Pregnancy Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Ji Aggasid, JanniecelDocument60 pagesEarly Pregnancy Complications: Ectopic Pregnancy Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Ji Aggasid, JanniecelmedicoNo ratings yet
- Grand Case Pres - Transverse Vaginal Septum..Document32 pagesGrand Case Pres - Transverse Vaginal Septum..Gio LlanosNo ratings yet
- A. Tunica Albuguinea: NCM 102: Assessment ExamDocument9 pagesA. Tunica Albuguinea: NCM 102: Assessment ExamdubhieNo ratings yet
- 2726 UnrecognizedDocument4 pages2726 UnrecognizedXusetaSanzNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Approach To Vesicovaginal FistulaDocument12 pagesAbdominal Approach To Vesicovaginal FistulaPoto SucioNo ratings yet
- Obg Procedures FinalDocument60 pagesObg Procedures FinalVeena DalmeidaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Intramural Ectopic PregnancyDocument4 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Intramural Ectopic PregnancyDinorah MarcelaNo ratings yet
- 3RD TrimesterDocument7 pages3RD TrimesterAmethystNo ratings yet
- Screening of High-Risk Pregnancy, Newer Modalities of DiagnosisDocument12 pagesScreening of High-Risk Pregnancy, Newer Modalities of DiagnosisSanthosh.S.U100% (10)
- Hymen ImperforataDocument16 pagesHymen ImperforataImanuella KairupanNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy: N Engl J Med 2009 361:379-87Document25 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: N Engl J Med 2009 361:379-87Muhammad AbeeshNo ratings yet
- Assisting With Gynecological ProceduresDocument12 pagesAssisting With Gynecological ProceduresVismayamaliekalNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument76 pagesEctopic PregnancyVivian Jean TapayaNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Retained Intrauterine Device (IUD) : Triple Case Report and Review of The LiteratureDocument9 pagesCase Report: Retained Intrauterine Device (IUD) : Triple Case Report and Review of The LiteratureYosie Yulanda PutraNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer ScreeningDocument25 pagesCervical Cancer Screening6ixSideCreate MNo ratings yet
- PromDocument19 pagesPromJanderlie AspaNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument11 pagesEctopic PregnancyPrincess BalloNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument14 pagesEctopic PregnancytaufiqNo ratings yet
- Marie Belen C. Tamayor, RNDocument26 pagesMarie Belen C. Tamayor, RNKaren Joy Jacinto ElloNo ratings yet
- Infertility - Definition, Causes, Diagnostic Procedures AND CouncellingDocument37 pagesInfertility - Definition, Causes, Diagnostic Procedures AND CouncellingvincentsharonNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Emergencies: First - Trimester Pregnancy EmergenciesDocument14 pagesObstetric Emergencies: First - Trimester Pregnancy EmergenciesdianNo ratings yet
- Beyond Cervical Length: Association Between Postcerclage Transvaginal Ultrasound Parameters and Preterm BirthDocument8 pagesBeyond Cervical Length: Association Between Postcerclage Transvaginal Ultrasound Parameters and Preterm BirthMariana HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug Dose CalculationDocument50 pagesDrug Dose CalculationSwaraj SKNo ratings yet
- The 7 Pillars of Health EbookDocument34 pagesThe 7 Pillars of Health EbookbrghtcrystlNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support Chart.: B-BreathingDocument1 pageBasic Life Support Chart.: B-BreathingOlga OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Unraveling The Unprecedented Economic Implications of The COVID-19 Pandemic: Navigating Towards A Resilient and Sustainable FutureDocument4 pagesUnraveling The Unprecedented Economic Implications of The COVID-19 Pandemic: Navigating Towards A Resilient and Sustainable FutureInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- AIMS. Scales-Abnormal-Involuntary-Movement-Scale PDFDocument2 pagesAIMS. Scales-Abnormal-Involuntary-Movement-Scale PDFVictoria RomeroNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet Q1W7Document26 pagesActivity Sheet Q1W7cristineann.arandiaNo ratings yet
- Ajol File Journals - 87 - Articles - 173693 - Submission - Proof - 173693 1033 444977 1 10 20180625Document7 pagesAjol File Journals - 87 - Articles - 173693 - Submission - Proof - 173693 1033 444977 1 10 20180625Grace ArthurNo ratings yet
- Relationships Between Breast-Feeding, Co-Sleeping, and Somatic Complaints in Early ChildhoodDocument10 pagesRelationships Between Breast-Feeding, Co-Sleeping, and Somatic Complaints in Early ChildhoodZachNo ratings yet
- English Book For Posgraduate Students 4 UnitDocument33 pagesEnglish Book For Posgraduate Students 4 UnitClaudia Vanessa VargasNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument27 pagesDermatologydranilshindeNo ratings yet
- 5th Mbbs Med Osce 2014... KeshDocument29 pages5th Mbbs Med Osce 2014... Keshaboje ochekwuNo ratings yet
- Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia, and Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation 2020Document21 pagesThrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia, and Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation 2020Cris TobalNo ratings yet
- THERAP COMM QuizletDocument28 pagesTHERAP COMM QuizletMary Margareth GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Library Dissertation Topics in EndodonticsDocument4 pagesLibrary Dissertation Topics in EndodonticsWhereToBuyPapersCanada100% (1)
- Main - Dshs Form Dshs 13 830 Admissions Review Team Checklist Admission To An Icf Iid or Sonf at A Residential Habilitation Center RHC WashingtonDocument2 pagesMain - Dshs Form Dshs 13 830 Admissions Review Team Checklist Admission To An Icf Iid or Sonf at A Residential Habilitation Center RHC WashingtonIndry LabungasaNo ratings yet
- MS MG GBSDocument1 pageMS MG GBSJhix JadraqueNo ratings yet
- Human Tissue Removed For Medical Tests Is Personal Property' of Institution, Not Person It Came From - Ruling - National PostDocument5 pagesHuman Tissue Removed For Medical Tests Is Personal Property' of Institution, Not Person It Came From - Ruling - National PostExtreme TronersNo ratings yet
- Sarcodina class. Specify these single-: Кrok 1 Stomatology (англомовнi студенти) 2014 рiкDocument24 pagesSarcodina class. Specify these single-: Кrok 1 Stomatology (англомовнi студенти) 2014 рiкbose_lowe11No ratings yet
- Community and Public HealthDocument25 pagesCommunity and Public HealthCharmaine FaderogNo ratings yet
- Daily Safety TalkDocument102 pagesDaily Safety TalkShabin ShabiNo ratings yet
- Gordis EpidemiologyDocument16 pagesGordis EpidemiologyRaywat DeonandanNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation of ISHRAE Indoor Environmental Quality StandardDocument18 pagesDevelopment and Validation of ISHRAE Indoor Environmental Quality StandardJust KiddingNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data SheetDocument8 pagesMaterial Safety Data SheetAmit Kumar JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Neonatal and Childhood Illness Strategy An Approach For Hypothermia in NewbornsDocument5 pagesIntegrated Management of Neonatal and Childhood Illness Strategy An Approach For Hypothermia in NewbornsEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Role of Panchakarma in Management of Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument5 pagesRole of Panchakarma in Management of Rheumatoid ArthritisIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet