Professional Documents
Culture Documents
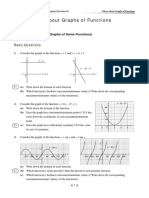
Section # 4 A (RELATIONS, FUNCTIONS, GRAPHS I)
Section # 4 A (RELATIONS, FUNCTIONS, GRAPHS I)
Uploaded by
Anthony BensonCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Perlman - Indian-Concertino - Piano AccompanimentDocument15 pagesPerlman - Indian-Concertino - Piano Accompanimentkos ana50% (2)
- You've Lost That Lovin' Feeling - Righteous BrothersDocument4 pagesYou've Lost That Lovin' Feeling - Righteous BrothersAulas De Violino Londrina100% (7)
- CSEC® Mathematics Past Papers (Paper 2)Document20 pagesCSEC® Mathematics Past Papers (Paper 2)Anthony Benson100% (1)
- Relations, Functions and Graphs - WorksheetDocument5 pagesRelations, Functions and Graphs - WorksheetAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Relations Functions and GraphDocument8 pagesRelations Functions and GraphCarl ThomasNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics - Graphs - (2015-2010)Document12 pagesCSEC Mathematics - Graphs - (2015-2010)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Paper 1 June 2017Document6 pagesGR 11 Paper 1 June 2017rivondlovu07No ratings yet
- Advanced Math 1 - 2001Document4 pagesAdvanced Math 1 - 2001rahim najimNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Section 1Document3 pagesAdditional Mathematics Section 1FidelNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2007 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument9 pagesJames Ruse 2007 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsYe ZhangNo ratings yet
- Canadian School of Arts and Science Easter Term Exam - March 2020 Mathematics - Paper 2 (Total 100 Marks) Grade 11 2 Hours 30 MinutesDocument20 pagesCanadian School of Arts and Science Easter Term Exam - March 2020 Mathematics - Paper 2 (Total 100 Marks) Grade 11 2 Hours 30 MinutesTrevor G. SamarooNo ratings yet
- Das 10203 Finals em 21415Document9 pagesDas 10203 Finals em 21415Fatin NurNo ratings yet
- 2018 Maths Methods Midyear ExamDocument17 pages2018 Maths Methods Midyear ExamvgNo ratings yet
- MS2B Conex08 eDocument29 pagesMS2B Conex08 eYan WongNo ratings yet
- ESS 1001 E Tutorial #5Document3 pagesESS 1001 E Tutorial #5a21217No ratings yet
- Circles and Relations Exam Style QuestionsDocument6 pagesCircles and Relations Exam Style Questionszack.wallNo ratings yet
- Revision - Paper 1 - Math SL: (Total 6 Marks)Document7 pagesRevision - Paper 1 - Math SL: (Total 6 Marks)RudyWahyudiNo ratings yet
- Mid-Year Examination 2007/08 Mathematics and Statistics Form Six Time Allowed: 2 Hours InstructionsDocument4 pagesMid-Year Examination 2007/08 Mathematics and Statistics Form Six Time Allowed: 2 Hours InstructionsSeefood YoNo ratings yet
- Aqa MPC1 W QP Jan05Document4 pagesAqa MPC1 W QP Jan05Stuart GregoryNo ratings yet
- Jan 2005 Core 1 PaperDocument4 pagesJan 2005 Core 1 PaperNisanthJoelNo ratings yet
- c1 Test Paper 2Document2 pagesc1 Test Paper 2Hesham MohamedNo ratings yet
- Cubic SketchingDocument1 pageCubic Sketchingrz15945No ratings yet
- Add Maths Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1 p2Document12 pagesAdd Maths Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1 p2Yeow Pow Choo100% (1)
- WS FunctionsDocument8 pagesWS FunctionsasmaNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Math Practice PDFDocument4 pagesForm 4 Math Practice PDFAliyah wrightNo ratings yet
- Aqa MBP1 W QP Nov04Document4 pagesAqa MBP1 W QP Nov04yanghaoyi1985No ratings yet
- Solomon H QP - C1 EdexcelDocument4 pagesSolomon H QP - C1 Edexcelkhalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- RVHS 9758 H2 Promo 2022Document5 pagesRVHS 9758 H2 Promo 2022txjun41No ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics (IE 1010) 2019 JuneDocument5 pagesEngineering Mathematics (IE 1010) 2019 JunevihinsabNo ratings yet
- 6A CH 3 More About Graphs of Functions QuestionsDocument18 pages6A CH 3 More About Graphs of Functions Questions[4P08] 曹詠嘉 CHO WING KANo ratings yet
- Grade 9 1 SaDocument20 pagesGrade 9 1 SaMaths Facilitator iALNo ratings yet
- Exam MATH 201 2021Document4 pagesExam MATH 201 2021Gloria Moraa OKARINo ratings yet
- Ol Mock 2019 575 Add Math p2 2019Document5 pagesOl Mock 2019 575 Add Math p2 2019Alphonsius WongNo ratings yet
- G11 Add Maths P2Document18 pagesG11 Add Maths P2Trevor G. SamarooNo ratings yet
- Feb 2015Document3 pagesFeb 2015kipkoecharonz korirNo ratings yet
- REVIEW TEST Unfamiliar Functions Calculus Mar 2014 PDFDocument3 pagesREVIEW TEST Unfamiliar Functions Calculus Mar 2014 PDFNick MNo ratings yet
- IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Document32 pagesIB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1ibrahim fadelNo ratings yet
- School Holiday ModuleDocument3 pagesSchool Holiday ModuleBye Zuera OthmanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics IIDocument5 pagesMathematics IIitsmeshimrithNo ratings yet
- 06 Due 13th JanDocument9 pages06 Due 13th JanWinson LauNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2006 3U Prelim YearlyDocument3 pagesJames Ruse 2006 3U Prelim YearlyParpatiVasuNo ratings yet
- SPH 205 Mathematical PhysicsDocument3 pagesSPH 205 Mathematical Physicsodib478No ratings yet
- CP2 - Paper 2Document3 pagesCP2 - Paper 2prashasti0410No ratings yet
- 2000 P1u1 Pure MathsDocument7 pages2000 P1u1 Pure MathsTariq RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Practice 2 - SAT 1Document8 pagesPractice 2 - SAT 1RobertNo ratings yet
- EB Calc 1 Test Prep 206 Mins With Mark SchemeDocument23 pagesEB Calc 1 Test Prep 206 Mins With Mark SchemeZhang JingkangNo ratings yet
- Test On GeometryDocument10 pagesTest On GeometryKarthik NNo ratings yet
- 2023 Mathematics II MCB MCE MEG MPC MPG PCMDocument4 pages2023 Mathematics II MCB MCE MEG MPC MPG PCMlorrainemu012No ratings yet
- Advanced Mathematics 1Document4 pagesAdvanced Mathematics 1james paul100% (1)
- Aqa MBP2 W QP Nov04Document4 pagesAqa MBP2 W QP Nov04yanghaoyi1985No ratings yet
- Holiday Work Set 1 (CALCULUS)Document6 pagesHoliday Work Set 1 (CALCULUS)PGM140009 StudentNo ratings yet
- GraphingDocument2 pagesGraphingChiam Jia HaoNo ratings yet
- Corozal Community College Third Form Mathematics RemedialDocument4 pagesCorozal Community College Third Form Mathematics RemedialAngel ZetinaNo ratings yet
- Cssa 1995 Ext 2 THSCDocument4 pagesCssa 1995 Ext 2 THSCsherinNo ratings yet
- c1 A PDFDocument6 pagesc1 A PDFSayantan MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- C1 07-Jun PDFDocument4 pagesC1 07-Jun PDFAnderson AlfredNo ratings yet
- Httpsinst Fs Sin Prod - Inscloudgate.netfilescdb03c95 E4d7 4456 94d1 04da285b2d51C3A20Tutorial - Pdfdownload 1&token EyJ0eXADocument4 pagesHttpsinst Fs Sin Prod - Inscloudgate.netfilescdb03c95 E4d7 4456 94d1 04da285b2d51C3A20Tutorial - Pdfdownload 1&token EyJ0eXAwatertempsp01No ratings yet
- 1) GivenDocument11 pages1) Givenibrahim fadelNo ratings yet
- HKCEE AMath 1999 Paper 2 deDocument21 pagesHKCEE AMath 1999 Paper 2 deLin Wing HoNo ratings yet
- April 2013Document3 pagesApril 2013kipkoecharonz korirNo ratings yet
- AL Maths Pure Unit 3 TestDocument2 pagesAL Maths Pure Unit 3 TestTitus Anagho100% (1)
- Cape Physics OTHER ISLANDS June Paper 2 (2008)Document12 pagesCape Physics OTHER ISLANDS June Paper 2 (2008)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Social Studies SbaDocument10 pagesSocial Studies SbaAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics - Graphs - (2015-2010)Document12 pagesCSEC Mathematics - Graphs - (2015-2010)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Plan of Work - Grade 11 2017-2018Document12 pagesPlan of Work - Grade 11 2017-2018Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Construction: Geometric Construction Involves Drawing Shapes That Satisfy Certain RequirementsDocument30 pagesConstruction: Geometric Construction Involves Drawing Shapes That Satisfy Certain RequirementsAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Grade 10 2017-2018Document21 pagesLesson Plan Grade 10 2017-2018Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CSECMath (Notes)Document44 pagesCSECMath (Notes)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Decimals, Fractions, Consum ArithmDocument6 pagesDecimals, Fractions, Consum ArithmAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics - EvaluationDocument5 pagesCSEC Mathematics - EvaluationAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Sets - SPQDocument10 pagesSets - SPQAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Trigonometry and Geometry IIDocument12 pagesChapter 10: Trigonometry and Geometry IIAnthony Benson100% (1)
- Transformations - SPQDocument10 pagesTransformations - SPQAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CSEC® Mathematics Past Papers (Paper 2)Document4 pagesCSEC® Mathematics Past Papers (Paper 2)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Relations, Functions and Graphs - WorksheetDocument5 pagesRelations, Functions and Graphs - WorksheetAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Past Papers - P2 - Sequence, Patterns and TrendsDocument10 pagesPast Papers - P2 - Sequence, Patterns and TrendsAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Graphs and Variations IDocument16 pagesGraphs and Variations IAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics - Algebra - P2 - (2015-2010)Document15 pagesCSEC Mathematics - Algebra - P2 - (2015-2010)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Lessons - Part 4Document6 pagesMatrices - Lessons - Part 4Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CSEC® Mathematics Past Papers (Statistics)Document10 pagesCSEC® Mathematics Past Papers (Statistics)Anthony Benson100% (1)
- Coordinate Geometry, Relations, Functions, Graphs and VariationsDocument30 pagesCoordinate Geometry, Relations, Functions, Graphs and VariationsAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Vectors - Lessons - Part ADocument14 pagesVectors - Lessons - Part AAnthony Benson100% (1)
- Wetlands: 11 Science 1Document18 pagesWetlands: 11 Science 1Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Lessons - Part 5Document7 pagesMatrices - Lessons - Part 5Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Lessons - Part 3Document6 pagesMatrices - Lessons - Part 3Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Lessons - Part 2Document22 pagesMatrices - Lessons - Part 2Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Geometry - Angle PropertiesDocument14 pagesGeometry - Angle PropertiesAnthony Benson100% (1)
- Information ProcessingDocument10 pagesInformation ProcessingAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry II and Circle TheoremDocument27 pagesTrigonometry II and Circle TheoremAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- 3.b MeasurementsDocument23 pages3.b MeasurementsAnthony Benson100% (1)
- The History of JazzDocument4 pagesThe History of JazzRomina Neagu100% (2)
- Ang Panginoon Ang Aking PastolDocument3 pagesAng Panginoon Ang Aking PastolServi Dei ChoraleNo ratings yet
- Summary of Ofsted's Music Research ReviewDocument2 pagesSummary of Ofsted's Music Research ReviewMolly NewtonNo ratings yet
- Brain and Cognition: Marie-Claude Ménard, Sylvie BellevilleDocument8 pagesBrain and Cognition: Marie-Claude Ménard, Sylvie Bellevilleapi-538965270No ratings yet
- GRE Test GuideDocument220 pagesGRE Test GuideSherry ShenNo ratings yet
- Lyrics - Many English SongsDocument449 pagesLyrics - Many English Songsral paguerganNo ratings yet
- 6MUSIC Gr10 TG - QTR 3 (10 April 2015)Document25 pages6MUSIC Gr10 TG - QTR 3 (10 April 2015)June Emerson ManalangNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year B ES 25Document29 pages2nd Year B ES 25Yesica BasualdoNo ratings yet
- Us3873779 PDFDocument12 pagesUs3873779 PDFAlex PerezNo ratings yet
- I. Objective: at The End of The Lesson, The Students Are Expected ToDocument2 pagesI. Objective: at The End of The Lesson, The Students Are Expected ToGerome LopezNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Final DLL Mapeh 9Document105 pages3rd Quarter Final DLL Mapeh 9KILVEN MASION100% (1)
- Sapta Swaras - The Seven Musical Notes of Carnatic MusicDocument2 pagesSapta Swaras - The Seven Musical Notes of Carnatic MusicprashanthNo ratings yet
- Max Weber and The Sociology of MusicDocument22 pagesMax Weber and The Sociology of MusicjesusrrebolledoNo ratings yet
- Senior Project PaperDocument13 pagesSenior Project Paperapi-406062042No ratings yet
- North Jersey Jewish Standard, May 8, 2015Document60 pagesNorth Jersey Jewish Standard, May 8, 2015New Jersey Jewish StandardNo ratings yet
- Musical Pitch Relation ChartDocument2 pagesMusical Pitch Relation ChartDanielNo ratings yet
- 2022 MusiCaviteño Precribed Line Up For Lenten Season Easter Triduum and Easter SeasonDocument40 pages2022 MusiCaviteño Precribed Line Up For Lenten Season Easter Triduum and Easter SeasonSJP2 PMMNo ratings yet
- Dragonfly - Dana and Alden Themes From Dragonfly in BB - Dana and Alden Sheet Music For Saxophone Tenor (Solo)Document1 pageDragonfly - Dana and Alden Themes From Dragonfly in BB - Dana and Alden Sheet Music For Saxophone Tenor (Solo)rockivy666No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument55 pagesUntitledThu TrangNo ratings yet
- Outline For Informative SpeechDocument62 pagesOutline For Informative SpeechJames G. Villaflor IINo ratings yet
- Loadbang: Programming Electronic Music in PDDocument12 pagesLoadbang: Programming Electronic Music in PDTom HirstNo ratings yet
- Susan Fast RockDocument6 pagesSusan Fast Rockpablo palaciosNo ratings yet
- Brett Vachon: About The ArtistDocument5 pagesBrett Vachon: About The ArtistFrancesco BaigueraNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 9 1ST Periodical ExaminationDocument4 pagesMapeh 9 1ST Periodical ExaminationGiezelle LeopandoNo ratings yet
- For No OneDocument1 pageFor No OneEduardo AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Alamo Music Center BuyBoard CatalogDocument362 pagesAlamo Music Center BuyBoard CatalogAlamo Music CenterNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document109 pagesCase Study 1Zee ZaaNo ratings yet
- 4 Simple Bass Fills For BeginnersDocument2 pages4 Simple Bass Fills For BeginnersLeo AlarcónNo ratings yet
Section # 4 A (RELATIONS, FUNCTIONS, GRAPHS I)
Section # 4 A (RELATIONS, FUNCTIONS, GRAPHS I)
Uploaded by
Anthony BensonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Section # 4 A (RELATIONS, FUNCTIONS, GRAPHS I)
Section # 4 A (RELATIONS, FUNCTIONS, GRAPHS I)
Uploaded by
Anthony BensonCopyright:
Available Formats
Relations, Functions and Graphs
May 2014
2
6. The graph of the quadratic function y = x for 4 < x < 4 is shown below.
(a) The coordinates of the points M and N are (- l, y) and (x, 9) respectively.
Determine the value of
(i) x (1 mark)
(ii) y. (1 mark)
(b) Determine
(i) the gradient of the line MN (1 mark)
(ii) the equation of the line MN (2 marks)
(iii) the equation of the line parallel to MN, and passing through the origin.
(2 marks)
2
(c) Carefully draw the tangent line to the graph y = x at the point (2, 4). (2 marks)
(d) Estimate the gradient of the tangent to the curve at (2, 4). (2 marks)
Total 11 marks
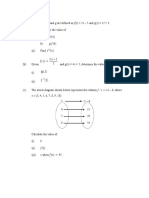
9. (a) Two functions are defined as follows:
g( x ) = 4 x + 3
2x + 7
f (x ) =
x+1
(i) State the value of x for which f(x) is undefined. (1 mark)
Relations, Functions, Graphs
(ii) Calculate the value of gf (5). (3 marks)
−1
Find f ( x) (3 marks)
(iii)
(b) A ball is thrown vertically upwards. Its height, h metres, above the ground after t
seconds is shown in the table below.
t
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
(s)
h
0 50 80 90 80 50 0
(m)
(i) Using 2 cm to represent 1 second on the x-axis and 1 cm to represent 10
metres on the y-axis, plot a graph to show the height of the ball during the first
6 seconds. (4 marks)
(ii) Using your graph, determine
a) the average speed of the ball during the first 2 seconds (2 marks)
b) the speed of the ball when t = 3 seconds. (2 marks)
Total 15 marks
Jan 2014
4. The diagram below shows the graphs of three straight lines:
y = 2, y=x and y = x + 2.
(a) State the correct equation for EACH of the following:
(i) Line 1 (1 mark)
(ii) Line 2 (1 mark)
(iii) Line 3 (1 mark)
(b) Show that the gradient of Line 2 is 1. (1 mark)
(c) Shade the region which is described as y > x + 2. (2 marks)
(d) Write THREE inequalities that define the shaded region, S, shown in the diagram.
Relations, Functions and Graphs
(3 marks)
(e) Write the equation of the straight line which is perpendicular to Line 1 and passes
through the origin. (2 marks)
Total 11 marks
9. (a) The functions h (x) and g (x) are defined as:
10
h( x) = −3
x g( x ) = 3 x − 2
(i) Evaluate
a) g (4) (1 mark)
b) hg (4) (2 marks)
(ii) Write expressions in x for:
a) h–1 (x)
b) g g (x) (4 marks)
2
(b) The diagram below shows a sketch of the quadratic function y = x +bx + c ,
2 ≤x ≤ 6 , where b and c are constants.
2
(i) State the roots of the equation x +bx + c = 0. (2 marks)
2
(ii) For the function y = x +bx + c
a) determine the value of c (2 marks)
b) show that b = - 4. (2 marks)
(iii) State the coordinates of the MINIMUM point on the graph of the function
2
y = x +bx + c . (2 marks)
Total 15 marks
May 2013
4. (b) A (‒1, 4) and B (3, 2) are the end points of a line segment AB. Determine
(i) the gradient of AB (2 marks)
(ii) the coordinates of the midpoint of AB (2 marks)
Relations, Functions, Graphs
(iii) the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB. (3 marks)
5. (a) The incomplete table below shows one pair of values for A and R where A is directly
proportional to the square of R.
A 36 196
R 3 5
(i) Express A in terms of R and a constant k. (1 mark)
(ii) Calculate the value of the constant k. (2 marks)
(iii) Copy and complete the table. (2 marks)
2x + 1
f (x ) =
(b) Given 3 and g(x) = 4x + 5, determine the values of:
(i) fg(2 ) (3 marks)
−1
(ii) f (3) (3 marks)
Total 11 marks
9. (a) Trish wishes to buy x oranges and y mangoes which she intends to carry in her bag. Her
bag has space for only 6 fruits.
(i) Write an inequality to represent this information. (1 mark)
To get a good bargain, she must buy AT LEAST 2 mangoes.
(ii) Write an inequality to represent this information. (1 mark)
More information about the number of oranges and mangoes associated with the
good bargain is represented by
y 2x.
(iii) Write the information represented by this inequality as a sentence in your own
words. (2 marks)
(iv) Draw the lines associated with the inequalities obtained in (i), (ii) and (iii)
above. (3 marks)
(v) Shade on your graph the region which represents the solution set for the three
inequalities. (1 mark)
2 2
(b) (i) Write 3 x − 12 x + 8 in the form a ( x + h ) + k where a, h and k are constants.
(3 marks)
2
(ii) Sketch the graph of y = 3 x − 12 x + 8 , showing on your sketch
a) the intercept on the y-axis
b) the coordinates of the minimum point.
(4 marks)
Total 15 marks
Relations, Functions and Graphs
Jan 2013
4. (b) The functions f and g are defined as follows:
x−3
g( x) =
f (x ) = 2 x + 5 and 2
Evaluate:
−1
(i) f (19) (2 marks)
(ii) gf (3) (2 marks)
(c) A line segment GH has equation 3 x + 2 y = 15.
(i) Determine the gradient of GH. (1 mark)
(ii) Another line segment, JK, is perpendicular to GH and passes through the point
(4, 1). Determine the equation of the line JK. (3 marks)
9. (a) The table below shows corresponding values of x and y for the function.
3
y =
x , x≠0
where y represents the velocity of a particle after x seconds.
x (sec) 0.25 0.5 1 2 3 4 5 6
y (m/s) 12 3 1.5 0.75 0.5
(i) Copy and complete the table for the function. (2 marks)
(ii) Using a scale of 2 cm to represent 1 unit on the xaxis and 1 cm to represent
1 unit on the y axis, plot the points from your table, drawing a smooth curve
through all points. (5 marks)
2 2
(b) (i) Write 3 x − 5 x + 1 in the form a ( x + h ) + k where a, h and k are constants to
be determined. (2 marks)
(ii) Hence, or otherwise, determine the minimum value of f(x) and the value of x for
which f(x) is a minimum. (2 marks)
(iii) Solve the equation
2
3 x − 5 x + 1 = 0, expressing your answer correct to two decimal places.
(4 marks)
Total 15 marks
Relations, Functions, Graphs
May 2012
5. (a) (i) Using a ruler, a pencil and a pair of compasses, construct triangle PQR with
PQ = 8 cm, PQR = 60° and QPR = 45°. (4 marks)
(ii) Measure and state the length of RQ. (1 mark)
(b) The line l passes through the points S (6, 6) and T (0, - 2).
Determine
(i) the gradient of the line, l (2 marks)
(ii) the equation of the line, l (2 marks)
(iii) the midpoint of the line segment, TS (1 mark )
(iv) the length of the line segment, TS. (2 marks)
Total 12 marks
Jan 2012
3. (a) A universal set, U, is defined as:
U = { 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59 }
A and B are subsets of U, such that:
A = { odd numbers }
B = { prime numbers }
(i) List the members of the set A. (1 mark)
(ii) List the members of the set B. (1 mark)
(iii) Draw a Venn diagram to represent the sets A, B and U. (3 marks)
May 2011
3. (a) The Venn diagram below shows the number of students who study Music and Art in a
class of 35 students.
U = {students in the class}
M = {students who study Music}
A = {students who study Art}
Relations, Functions and Graphs
(i) How many students study neither Art nor Music? (1 mark)
(ii) Calculate the value of x. (3 marks)
(iii) Hence, state the number of students who study Music only. (1 mark)
Jan 2011
4. (a) The Universal set, U, is given as
U = {Whole numbers from 1 to 12}
H is a subset of U, such that H = {Odd numbers between 4 and 12}.
(i) List the members of the set H. (1 mark)
J is a subset of U, such that J = {Prime numbers}.
(ii) List the members of the set J. (1 mark)
(iii) Draw a Venn diagram to represent the sets U, H and J, showing ALL the
elements in the subsets. (3 marks)
May 2010
3. (a) A survey was conducted among 40 tourists. The results were:
28 visited Antigua (A)
30 visited Barbados (B)
3x visited both Antigua and Barbados
x visited neither Antigua nor Barbados
(i) Copy and complete the Venn diagram below to represent the given information
above.
(2 marks)
(ii) Write an expression, in x, to represent the TOTAL number of tourists in the
survey. (2 marks)
(iii) Calculate the value of x. (2 marks)
Relations, Functions, Graphs
Jan 2010
2
7. The graph shown below represents a function of the form: f (x ) = ax + bx + c .
Using the graph above, determine
(a) the value of f(x) when x = 0 (1 mark)
(b) the values of x when f(x) = 0 (2 marks)
(c) the coordinates of the maximum point (2 marks)
(d) the equation of the axis of symmetry (2 marks)
(e) the values of x when f(x) = 5 (2 marks)
(f) the interval within which x lies when f(x) > 5. Write your answer in the form a < x < b.
(2 marks)
May 09
2
5. (a) Given that f (x ) = 2 x−5 and g( x) = x −31 , calculate the value of
(i) f (−2 ) (1 mark)
(ii) g f (1) (2 marks)
(iii) f − 1 (3) (2 marks)
2
(b) Given that f (x ) = x + 2 x − 3
Relations, Functions and Graphs
(i) Complete the table below.
x -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2
y 5 -3 -4 -3 5
(ii) Using a scale of 2 cm to represent 1 unit on the x-axis and 1 cm to represent 1
2
unit on the y-axis, draw the graph of f (x ) = x + 2 x − 3 for −4 ≤ x ≤ 2 .
(4 marks)
Jan 09
2
10. (a) Two functions are defined as f : x → x − 3 and g:x → x − 1
(i) Calculate f (6) (1 mark)
−1
(ii) Find f ( x) (1 mark)
(iii) Show that f g(2 ) = f g (−2 ) = 0 (3 marks)
May 08
9. (b) If f (x ) = 2 x − 3 , find the value of
(i) f (2 ) (1 mark)
(ii) f − 1 (0) (2 marks)
−1
(iii) f f (2 ) (2 marks)
Jan 08
2
7. (a) Given that y = x − 4 x , complete the table below
x -l 0 1 2 3 4 5
y 5 -3 -4 0
(b) Using a scale of 2 cm to represent 1 unit on both axes, draw the graph of the function
2
y = x − 4 x for −1 ≤ x ≤ 5 . (4 marks)
(c) (i) On the same axes used in (b) above, draw the line y = 2. (1 mark)
(ii) State the x-coordinates of the two points at which the curve meets the line.
(2 marks)
(iii) Hence, write the equation whose roots are the x-coordinates stated in (c) (ii)
(1 mark)
May 07
2x +1
g( x) =
9. (a) Given that 5 and f (x ) = x + 4
(i) Calculate the value of g (-2).
Relations, Functions, Graphs
(ii) Write an expression for g f (x) in its simplest form.
(iii) Find the inverse function g -1(x).
(7 marks)
Jan 07
5. (a) f and g are functions defined as follows:
1
g( x) →
f :x → 7 x + 4 and 2x
Calculate
(i) g (3) (1 mark)
(ii) f (-2) ( 2 marks)
(iii) f -1 (11) (2 marks)
May 06
2
5. The diagram below shows the graph of the function f (x ) = x −2 x−3 for a≤x≤b .
The tangent of the graph at (2, - 3) is also drawn.
Use the graph of determine the
(a) values of a and b which define the domain of the graph.
2
(b) values of x for which x −2 x−3 = 0
(c) coordinates of the minimum point on the graph .
2
(d) whole number values of x for which x −2 x−3 <1
2
(e) gradient of f (x ) = x −2 x−3 at x = 2.
Relations, Functions and Graphs
Jan 06
2
8. The path of a ball thrown in the air is given by the equation h = 20 t − 5t where h is the
vertical distance above the ground (in metres) and t is the time (in seconds) after the ball was
thrown.
The table below shows some values of t and the corresponding values of h , correct to 1
decimal place.
t 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
h 0.0 8.8 15 18.8 18.8 8.8 0.0
(a) Copy and complete the table of values. (2 marks)
2
(b) Draw the graph of h = 20 t − 5t for 0 ≤ t ≤ 4 . You may proceed as follows:
(i) Using a scale of 2'cm to represent 0.5 seconds, draw the horizontal t-axis for
0≤t ≤4. (1 mark)
(ii) Using a scale of 1 cm to represent 1 metre, draw the vertical h-axis for
0 .0 ≤ h ≤ 21.0 . (1 mark)
(iii) Plot the points from your table of values on the axes drawn. (2 marks)
(iv) Join the points with a smooth curve. (1 mark)
(c) Using your graph, calculate estimates of
(i) the GREATEST height above the ground reached by the ball (1 mark)
(ii) the number of seconds for which the ball was MORE than 12 metres above the
ground (2 marks)
(iii) the interval of time during which the ball was moving upwards. (1 mark)
May 05
1
f (x ) = x+ 5 2
6. (b) The functions f and g are defined by 2 and g( x) = x .
Evaluate
(i) g(3 )+g (−3 )
(ii) f -1(6)
(iii) fg(2)
(8 marks)
Jan 05
Relations, Functions, Graphs
2x+5
f (x ) =
5. (a) The functions f and g are such that x − 4 and g( x) = 2 x − 3 , Calculate
the value of
(i) g (4)
(ii) f g (2)
(iii) g -1(7)
May 04
6. The amount a plumber charges for services depends on the time taken to complete the repairs
plus a fixed charge.
The graph below shows the charges in dollars (d) for repairs in terms of the number of minutes
(t) taken to complete the repairs.
(a) What was the charge for a plumbing job which took 20 minutes? (1 mark)
(b) How many minutes were spent completing repairs that cost:
(i) $38.00
(ii) $20.00?
(2 marks)
(c) What is the amount of the fixed charge? (1 mark)
(d) Calculate the gradient of the line. (2 marks)
(e) Write down the equation of the line in terms of d and t. (2 marks)
(f) Determine the length of time taken to complete a job for which the charge was $78.00.
(3 marks)
Jan 04
5. (a) Given that, f (x ) = 3 x + 4 and g( x) = √ x , calculate
Relations, Functions and Graphs
(i) g (25)
(ii) g f (15)
(3 marks)
2
(b) (i) Given that y = 3 x − 3 x , copy and complete the table below.
x -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5
y 4 0 -2 0 4 10
(ii) Using a scale of 2 cm to represent 1 unit on the x-axis and 1 cm to represent 1
2
unit on the y-axis, draw the graph of y = 3 x − 3 x for −2 ≤ x ≤ 5
(iii) On the same axes as (ii) above, draw the line y = x for −2 ≤ x ≤ 5
2
(iv) Use your graphs to determine the solution of the equation y = 3 x − 3 x
(10 marks)
May 03
5. The graph below represents the function
Use the graph to determine
(a) the value f (x) when x = 2 (1 mark)
(b) the value of f (x) when x = – 1.5 (1 mark)
Relations, Functions, Graphs
(c) the values of x for which f (x) = 0 (2 marks)
(d) the minimum value of f (x) (1 mark)
(e) the value of x at which f (x) is a minimum. (1 mark)
2
(f) the solution of x − 3 x − 3 = 5 (2 marks)
(g) the interval on the domain for which f (x) is less than – 3. (2 marks)
9. (b) An athlete runs on a track so that his distance, d metres, from the starting point after t
seconds is as shown in the table below.
Time (seconds), t 0 2 4 6 8 10
Distance (metres), d 0 14 40 74 94 100
(i) a) Using a horizontal scale of 1 cm to represent 1 second and a vertical
scale of 1 cm to represent l0 metres, construct a distance-time graph to
show the motion of the athlete.
b) Draw a smooth curve through all the plotted points.
(ii) Use your graph to estimate:
a) the distance travelled by the athlete after 3 seconds
b) the average speed of the athlete during the interval t = 6 seconds to t = 8
seconds
c) the speed of the athlete 6 seconds after leaving the starting point.
(10 marks)
2x +3 1
g: x → h: x →
10. (b) Two functions, g and h, are defined as x − 4 and x
(i) Calculate
a) the value of g(7)
b) the value of x for which g (x) = 6.
(ii) Write expressions for
a) h g (x)
b) g -1(x).
(10 marks)
Relations, Functions and Graphs
Jan 03
3
7. (a) Given that g( x) = 6 − x and h( x) = x
Calculate
(i) h (−3)
(ii) h g (2)
(iii) g h (2).
(5 marks)
2
(b) Given that y = 2 x − x − 6 ,
(i) copy and complete the table below.
x -2 -1 0 1 2 3
y -3 -6 -5 9
(ii) Using a scale of 2 cm to represent 1 unit on the x-axis and 1 cm to represent
2
1 unit on the y-axis, draw the graph of y = 2 x − x − 6 for - 2 < x < 3.
2
(iii) Use your graph to solve the equation 2 x − x − 6 = −3
(7 marks)
Relations, Functions, Graphs
You might also like
- Perlman - Indian-Concertino - Piano AccompanimentDocument15 pagesPerlman - Indian-Concertino - Piano Accompanimentkos ana50% (2)
- You've Lost That Lovin' Feeling - Righteous BrothersDocument4 pagesYou've Lost That Lovin' Feeling - Righteous BrothersAulas De Violino Londrina100% (7)
- CSEC® Mathematics Past Papers (Paper 2)Document20 pagesCSEC® Mathematics Past Papers (Paper 2)Anthony Benson100% (1)
- Relations, Functions and Graphs - WorksheetDocument5 pagesRelations, Functions and Graphs - WorksheetAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Relations Functions and GraphDocument8 pagesRelations Functions and GraphCarl ThomasNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics - Graphs - (2015-2010)Document12 pagesCSEC Mathematics - Graphs - (2015-2010)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Paper 1 June 2017Document6 pagesGR 11 Paper 1 June 2017rivondlovu07No ratings yet
- Advanced Math 1 - 2001Document4 pagesAdvanced Math 1 - 2001rahim najimNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Section 1Document3 pagesAdditional Mathematics Section 1FidelNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2007 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument9 pagesJames Ruse 2007 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsYe ZhangNo ratings yet
- Canadian School of Arts and Science Easter Term Exam - March 2020 Mathematics - Paper 2 (Total 100 Marks) Grade 11 2 Hours 30 MinutesDocument20 pagesCanadian School of Arts and Science Easter Term Exam - March 2020 Mathematics - Paper 2 (Total 100 Marks) Grade 11 2 Hours 30 MinutesTrevor G. SamarooNo ratings yet
- Das 10203 Finals em 21415Document9 pagesDas 10203 Finals em 21415Fatin NurNo ratings yet
- 2018 Maths Methods Midyear ExamDocument17 pages2018 Maths Methods Midyear ExamvgNo ratings yet
- MS2B Conex08 eDocument29 pagesMS2B Conex08 eYan WongNo ratings yet
- ESS 1001 E Tutorial #5Document3 pagesESS 1001 E Tutorial #5a21217No ratings yet
- Circles and Relations Exam Style QuestionsDocument6 pagesCircles and Relations Exam Style Questionszack.wallNo ratings yet
- Revision - Paper 1 - Math SL: (Total 6 Marks)Document7 pagesRevision - Paper 1 - Math SL: (Total 6 Marks)RudyWahyudiNo ratings yet
- Mid-Year Examination 2007/08 Mathematics and Statistics Form Six Time Allowed: 2 Hours InstructionsDocument4 pagesMid-Year Examination 2007/08 Mathematics and Statistics Form Six Time Allowed: 2 Hours InstructionsSeefood YoNo ratings yet
- Aqa MPC1 W QP Jan05Document4 pagesAqa MPC1 W QP Jan05Stuart GregoryNo ratings yet
- Jan 2005 Core 1 PaperDocument4 pagesJan 2005 Core 1 PaperNisanthJoelNo ratings yet
- c1 Test Paper 2Document2 pagesc1 Test Paper 2Hesham MohamedNo ratings yet
- Cubic SketchingDocument1 pageCubic Sketchingrz15945No ratings yet
- Add Maths Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1 p2Document12 pagesAdd Maths Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1 p2Yeow Pow Choo100% (1)
- WS FunctionsDocument8 pagesWS FunctionsasmaNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Math Practice PDFDocument4 pagesForm 4 Math Practice PDFAliyah wrightNo ratings yet
- Aqa MBP1 W QP Nov04Document4 pagesAqa MBP1 W QP Nov04yanghaoyi1985No ratings yet
- Solomon H QP - C1 EdexcelDocument4 pagesSolomon H QP - C1 Edexcelkhalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- RVHS 9758 H2 Promo 2022Document5 pagesRVHS 9758 H2 Promo 2022txjun41No ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics (IE 1010) 2019 JuneDocument5 pagesEngineering Mathematics (IE 1010) 2019 JunevihinsabNo ratings yet
- 6A CH 3 More About Graphs of Functions QuestionsDocument18 pages6A CH 3 More About Graphs of Functions Questions[4P08] 曹詠嘉 CHO WING KANo ratings yet
- Grade 9 1 SaDocument20 pagesGrade 9 1 SaMaths Facilitator iALNo ratings yet
- Exam MATH 201 2021Document4 pagesExam MATH 201 2021Gloria Moraa OKARINo ratings yet
- Ol Mock 2019 575 Add Math p2 2019Document5 pagesOl Mock 2019 575 Add Math p2 2019Alphonsius WongNo ratings yet
- G11 Add Maths P2Document18 pagesG11 Add Maths P2Trevor G. SamarooNo ratings yet
- Feb 2015Document3 pagesFeb 2015kipkoecharonz korirNo ratings yet
- REVIEW TEST Unfamiliar Functions Calculus Mar 2014 PDFDocument3 pagesREVIEW TEST Unfamiliar Functions Calculus Mar 2014 PDFNick MNo ratings yet
- IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Document32 pagesIB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1ibrahim fadelNo ratings yet
- School Holiday ModuleDocument3 pagesSchool Holiday ModuleBye Zuera OthmanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics IIDocument5 pagesMathematics IIitsmeshimrithNo ratings yet
- 06 Due 13th JanDocument9 pages06 Due 13th JanWinson LauNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2006 3U Prelim YearlyDocument3 pagesJames Ruse 2006 3U Prelim YearlyParpatiVasuNo ratings yet
- SPH 205 Mathematical PhysicsDocument3 pagesSPH 205 Mathematical Physicsodib478No ratings yet
- CP2 - Paper 2Document3 pagesCP2 - Paper 2prashasti0410No ratings yet
- 2000 P1u1 Pure MathsDocument7 pages2000 P1u1 Pure MathsTariq RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Practice 2 - SAT 1Document8 pagesPractice 2 - SAT 1RobertNo ratings yet
- EB Calc 1 Test Prep 206 Mins With Mark SchemeDocument23 pagesEB Calc 1 Test Prep 206 Mins With Mark SchemeZhang JingkangNo ratings yet
- Test On GeometryDocument10 pagesTest On GeometryKarthik NNo ratings yet
- 2023 Mathematics II MCB MCE MEG MPC MPG PCMDocument4 pages2023 Mathematics II MCB MCE MEG MPC MPG PCMlorrainemu012No ratings yet
- Advanced Mathematics 1Document4 pagesAdvanced Mathematics 1james paul100% (1)
- Aqa MBP2 W QP Nov04Document4 pagesAqa MBP2 W QP Nov04yanghaoyi1985No ratings yet
- Holiday Work Set 1 (CALCULUS)Document6 pagesHoliday Work Set 1 (CALCULUS)PGM140009 StudentNo ratings yet
- GraphingDocument2 pagesGraphingChiam Jia HaoNo ratings yet
- Corozal Community College Third Form Mathematics RemedialDocument4 pagesCorozal Community College Third Form Mathematics RemedialAngel ZetinaNo ratings yet
- Cssa 1995 Ext 2 THSCDocument4 pagesCssa 1995 Ext 2 THSCsherinNo ratings yet
- c1 A PDFDocument6 pagesc1 A PDFSayantan MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- C1 07-Jun PDFDocument4 pagesC1 07-Jun PDFAnderson AlfredNo ratings yet
- Httpsinst Fs Sin Prod - Inscloudgate.netfilescdb03c95 E4d7 4456 94d1 04da285b2d51C3A20Tutorial - Pdfdownload 1&token EyJ0eXADocument4 pagesHttpsinst Fs Sin Prod - Inscloudgate.netfilescdb03c95 E4d7 4456 94d1 04da285b2d51C3A20Tutorial - Pdfdownload 1&token EyJ0eXAwatertempsp01No ratings yet
- 1) GivenDocument11 pages1) Givenibrahim fadelNo ratings yet
- HKCEE AMath 1999 Paper 2 deDocument21 pagesHKCEE AMath 1999 Paper 2 deLin Wing HoNo ratings yet
- April 2013Document3 pagesApril 2013kipkoecharonz korirNo ratings yet
- AL Maths Pure Unit 3 TestDocument2 pagesAL Maths Pure Unit 3 TestTitus Anagho100% (1)
- Cape Physics OTHER ISLANDS June Paper 2 (2008)Document12 pagesCape Physics OTHER ISLANDS June Paper 2 (2008)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Social Studies SbaDocument10 pagesSocial Studies SbaAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics - Graphs - (2015-2010)Document12 pagesCSEC Mathematics - Graphs - (2015-2010)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Plan of Work - Grade 11 2017-2018Document12 pagesPlan of Work - Grade 11 2017-2018Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Construction: Geometric Construction Involves Drawing Shapes That Satisfy Certain RequirementsDocument30 pagesConstruction: Geometric Construction Involves Drawing Shapes That Satisfy Certain RequirementsAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Grade 10 2017-2018Document21 pagesLesson Plan Grade 10 2017-2018Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CSECMath (Notes)Document44 pagesCSECMath (Notes)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Decimals, Fractions, Consum ArithmDocument6 pagesDecimals, Fractions, Consum ArithmAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics - EvaluationDocument5 pagesCSEC Mathematics - EvaluationAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Sets - SPQDocument10 pagesSets - SPQAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Trigonometry and Geometry IIDocument12 pagesChapter 10: Trigonometry and Geometry IIAnthony Benson100% (1)
- Transformations - SPQDocument10 pagesTransformations - SPQAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CSEC® Mathematics Past Papers (Paper 2)Document4 pagesCSEC® Mathematics Past Papers (Paper 2)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Relations, Functions and Graphs - WorksheetDocument5 pagesRelations, Functions and Graphs - WorksheetAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Past Papers - P2 - Sequence, Patterns and TrendsDocument10 pagesPast Papers - P2 - Sequence, Patterns and TrendsAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Graphs and Variations IDocument16 pagesGraphs and Variations IAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics - Algebra - P2 - (2015-2010)Document15 pagesCSEC Mathematics - Algebra - P2 - (2015-2010)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Lessons - Part 4Document6 pagesMatrices - Lessons - Part 4Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CSEC® Mathematics Past Papers (Statistics)Document10 pagesCSEC® Mathematics Past Papers (Statistics)Anthony Benson100% (1)
- Coordinate Geometry, Relations, Functions, Graphs and VariationsDocument30 pagesCoordinate Geometry, Relations, Functions, Graphs and VariationsAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Vectors - Lessons - Part ADocument14 pagesVectors - Lessons - Part AAnthony Benson100% (1)
- Wetlands: 11 Science 1Document18 pagesWetlands: 11 Science 1Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Lessons - Part 5Document7 pagesMatrices - Lessons - Part 5Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Lessons - Part 3Document6 pagesMatrices - Lessons - Part 3Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Lessons - Part 2Document22 pagesMatrices - Lessons - Part 2Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Geometry - Angle PropertiesDocument14 pagesGeometry - Angle PropertiesAnthony Benson100% (1)
- Information ProcessingDocument10 pagesInformation ProcessingAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry II and Circle TheoremDocument27 pagesTrigonometry II and Circle TheoremAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- 3.b MeasurementsDocument23 pages3.b MeasurementsAnthony Benson100% (1)
- The History of JazzDocument4 pagesThe History of JazzRomina Neagu100% (2)
- Ang Panginoon Ang Aking PastolDocument3 pagesAng Panginoon Ang Aking PastolServi Dei ChoraleNo ratings yet
- Summary of Ofsted's Music Research ReviewDocument2 pagesSummary of Ofsted's Music Research ReviewMolly NewtonNo ratings yet
- Brain and Cognition: Marie-Claude Ménard, Sylvie BellevilleDocument8 pagesBrain and Cognition: Marie-Claude Ménard, Sylvie Bellevilleapi-538965270No ratings yet
- GRE Test GuideDocument220 pagesGRE Test GuideSherry ShenNo ratings yet
- Lyrics - Many English SongsDocument449 pagesLyrics - Many English Songsral paguerganNo ratings yet
- 6MUSIC Gr10 TG - QTR 3 (10 April 2015)Document25 pages6MUSIC Gr10 TG - QTR 3 (10 April 2015)June Emerson ManalangNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year B ES 25Document29 pages2nd Year B ES 25Yesica BasualdoNo ratings yet
- Us3873779 PDFDocument12 pagesUs3873779 PDFAlex PerezNo ratings yet
- I. Objective: at The End of The Lesson, The Students Are Expected ToDocument2 pagesI. Objective: at The End of The Lesson, The Students Are Expected ToGerome LopezNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Final DLL Mapeh 9Document105 pages3rd Quarter Final DLL Mapeh 9KILVEN MASION100% (1)
- Sapta Swaras - The Seven Musical Notes of Carnatic MusicDocument2 pagesSapta Swaras - The Seven Musical Notes of Carnatic MusicprashanthNo ratings yet
- Max Weber and The Sociology of MusicDocument22 pagesMax Weber and The Sociology of MusicjesusrrebolledoNo ratings yet
- Senior Project PaperDocument13 pagesSenior Project Paperapi-406062042No ratings yet
- North Jersey Jewish Standard, May 8, 2015Document60 pagesNorth Jersey Jewish Standard, May 8, 2015New Jersey Jewish StandardNo ratings yet
- Musical Pitch Relation ChartDocument2 pagesMusical Pitch Relation ChartDanielNo ratings yet
- 2022 MusiCaviteño Precribed Line Up For Lenten Season Easter Triduum and Easter SeasonDocument40 pages2022 MusiCaviteño Precribed Line Up For Lenten Season Easter Triduum and Easter SeasonSJP2 PMMNo ratings yet
- Dragonfly - Dana and Alden Themes From Dragonfly in BB - Dana and Alden Sheet Music For Saxophone Tenor (Solo)Document1 pageDragonfly - Dana and Alden Themes From Dragonfly in BB - Dana and Alden Sheet Music For Saxophone Tenor (Solo)rockivy666No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument55 pagesUntitledThu TrangNo ratings yet
- Outline For Informative SpeechDocument62 pagesOutline For Informative SpeechJames G. Villaflor IINo ratings yet
- Loadbang: Programming Electronic Music in PDDocument12 pagesLoadbang: Programming Electronic Music in PDTom HirstNo ratings yet
- Susan Fast RockDocument6 pagesSusan Fast Rockpablo palaciosNo ratings yet
- Brett Vachon: About The ArtistDocument5 pagesBrett Vachon: About The ArtistFrancesco BaigueraNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 9 1ST Periodical ExaminationDocument4 pagesMapeh 9 1ST Periodical ExaminationGiezelle LeopandoNo ratings yet
- For No OneDocument1 pageFor No OneEduardo AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Alamo Music Center BuyBoard CatalogDocument362 pagesAlamo Music Center BuyBoard CatalogAlamo Music CenterNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document109 pagesCase Study 1Zee ZaaNo ratings yet
- 4 Simple Bass Fills For BeginnersDocument2 pages4 Simple Bass Fills For BeginnersLeo AlarcónNo ratings yet