Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Expresscare 410-328-4111: Maryland Critical Care Network
Expresscare 410-328-4111: Maryland Critical Care Network
Uploaded by
friyoga syahrilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Expresscare 410-328-4111: Maryland Critical Care Network
Expresscare 410-328-4111: Maryland Critical Care Network
Uploaded by
friyoga syahrilCopyright:
Available Formats
Maryland Critical Care Network
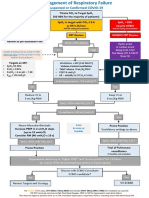
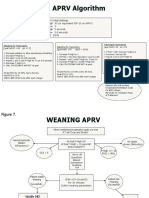
Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Syndrome consistent with ARDS?
- Acute onset (< 1 week)
- No evidence of isolated left heart failure (ECHO)
Berlin Criteria for ARDS Diagnosis and Staging
- Bilateral opacities on chest radiograph
YES
Gas exchange goals met?
PaO2/FiO2 > 200
SpO2/FiO2 > 235
pH > 7.25
YES NO
ARDS Definition Task Force. JAMA 2012.
- Diagnose and treat underlying cause for ARDS
- Consider non-invasive positive pressure - Avoid volutrauma (tidal volume 6 mc/kg/PBW)
ventilation - Avoid barotrauma (goal PPlt < 30 cm H2O)
- Consider high flow nasal cannula - Avoid atelectais Moderate -
- Treat the underlying condition (titrate PEEP according to ARDSnet tables) Severe ARDS
Mild - Optimize oxygenation
ARDS (PaO2 goal: 55- 80 mm Hg or SpO2 > 88-96 %)
- Optimize ventilation (pH > 7.25)
Improved respiratory dynamics? Continue
Clinically stable? Achieving goals?
NO PaO2/FiO2 > 150 YES Current
PaO2/FiO2 > 200 or SpO2 / FiO2 > 235? Therapy
pH > 7.25
- Start deep sedation AND
Severe
YES NO - Prone positioning (refer to institutional protocol)
ARDS
- Consider neuromuscular blockade (max 48 hrs)
Continue
Current Achieving goals? Continue
NO PaO2/FiO2 > 80 YES Current
Therapy
pH > 7.25 Therapy
UMMC/STC consultation for transfer
- Extracoropreal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
- Advanced lung rescue techniques
Consider consultation for transfer to UMMC if unable to implement proning,
neuromuscular blockade, etc. or if the patient continues to deteriorate
17 January 2019
J. Lantry / S. Galvagno
Adapted from Fan EF et al.
JAMA 2018; 319 (7).
EXPRESSCARE
410-328-4111
You might also like
- BiPAP Full FlowchartDocument1 pageBiPAP Full FlowchartArjun KumarNo ratings yet
- NCP Acl TearDocument2 pagesNCP Acl TearEd Pascasio100% (2)
- ABG Interpretation 3.0Document73 pagesABG Interpretation 3.0Jesus Mario Lopez100% (1)
- Pance Review Q&ADocument40 pagesPance Review Q&ABetsy Issac Pidugu100% (2)
- Psychotherapy Notes Sample GeriatricDocument2 pagesPsychotherapy Notes Sample GeriatricKadek Mardika0% (3)
- A Beautiful MindDocument7 pagesA Beautiful Mindapi-308731198No ratings yet
- Suspected or Confirmed Covid-19: Spo 92% Despite NRBM Urgent CRT Review WardDocument1 pageSuspected or Confirmed Covid-19: Spo 92% Despite NRBM Urgent CRT Review WardHAMMYER ALROKHAMINo ratings yet
- Ards Pocket Card 4.7 QRDocument1 pageArds Pocket Card 4.7 QRGenghis SupnetNo ratings yet
- Clinical Cheat Sheet: Radiographic AssessmentDocument1 pageClinical Cheat Sheet: Radiographic AssessmentTracy PopeNo ratings yet
- Takikardia Acls SayaDocument16 pagesTakikardia Acls Sayaolga adhityaNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Initial ManagmentDocument1 pageCovid-19 Initial ManagmentCelia Seneh GwandiNo ratings yet
- Sedation Pain AlgorithmDocument1 pageSedation Pain Algorithmdamondouglas100% (2)
- Covid-19 Respiratory Failure Guide 112020.1Document2 pagesCovid-19 Respiratory Failure Guide 112020.1Anna JuniedNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Basics - Conventional, Graphics, SBTDocument97 pagesVentilation Basics - Conventional, Graphics, SBTsumantamohammedNo ratings yet
- Analisis Gas DarahDocument33 pagesAnalisis Gas DarahMerryNo ratings yet
- 03 RSV Adults Friedland 508Document23 pages03 RSV Adults Friedland 508incinerate81No ratings yet
- Acid and Base Imbalance 1Document18 pagesAcid and Base Imbalance 1Keziah TampusNo ratings yet
- ARDS Management Protocol: February 2018Document6 pagesARDS Management Protocol: February 2018soulstakers100% (1)
- Lobal Initiative For Chronic Bstructive Ung Isease: G O L DDocument14 pagesLobal Initiative For Chronic Bstructive Ung Isease: G O L DNATTAPAT SANGKAKULNo ratings yet
- Call For Help: © 2020 American Heart Association KJ-1425Document3 pagesCall For Help: © 2020 American Heart Association KJ-1425kamila auliyaNo ratings yet
- Newly Proposed Diagnostic Criteria For Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - Does Inclusion of High Flow Nasal Cannula Solve The Problem? - PMCDocument13 pagesNewly Proposed Diagnostic Criteria For Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - Does Inclusion of High Flow Nasal Cannula Solve The Problem? - PMCThiago Antonio FontouraNo ratings yet
- Appendix 4b - NIV Algorithm (ICHT)Document1 pageAppendix 4b - NIV Algorithm (ICHT)Josi JeremiaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Antidysrhythmics IIDocument1 page1.2 Antidysrhythmics IIwallahussainNo ratings yet
- How To Deal Acute Pulmonary OedemDocument23 pagesHow To Deal Acute Pulmonary Oedemdhika2496No ratings yet
- Guidelines For PT in The ICUDocument1 pageGuidelines For PT in The ICUPhitsanu SuntornpiyapanNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Blood Gases in The Neonatal Unit Blood Gas ValuesDocument2 pagesInterpretation of Blood Gases in The Neonatal Unit Blood Gas ValuespacsolanoNo ratings yet
- 76 AcutePB840PAVPlusMgmtProtocolSS10VE5543 1316719265 PDFDocument2 pages76 AcutePB840PAVPlusMgmtProtocolSS10VE5543 1316719265 PDFNATHALIA MORENO PERILLANo ratings yet
- Neonate / Infant Child / AdultDocument1 pageNeonate / Infant Child / AdultRizky Ayu RNo ratings yet
- Algorithm For Management of Acute Pulmonary Oedema PDFDocument1 pageAlgorithm For Management of Acute Pulmonary Oedema PDFDewi Rabiatul AkhzamiNo ratings yet
- Algorithm For Management of Acute Pulmonary OedemaDocument1 pageAlgorithm For Management of Acute Pulmonary OedemayayaNo ratings yet
- Algorithm For Management of Acute Pulmonary OedemaDocument1 pageAlgorithm For Management of Acute Pulmonary OedemaEndar SulistyoNo ratings yet
- Algorithm For Management of Acute Pulmonary Oedema PDFDocument1 pageAlgorithm For Management of Acute Pulmonary Oedema PDFErnest ReddcliffvcksuNo ratings yet
- Peri-OP ICU AlgorithmsDocument46 pagesPeri-OP ICU AlgorithmsCiria Coromoto Rondon RojasNo ratings yet
- ARDSDocument82 pagesARDSfeniNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Protocol For Non-Invasive Ventilation Using The GO2Vent®Document4 pagesCOVID-19 Protocol For Non-Invasive Ventilation Using The GO2Vent®Diego VenegasNo ratings yet
- Pews Sample Paediatric Observation Chart Type B Without Paed Med Team 24 7Document10 pagesPews Sample Paediatric Observation Chart Type B Without Paed Med Team 24 7Aniruddha ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Crashing PTDocument1 pageCrashing PTansylaeNo ratings yet
- Basic Pediatric Ventilation: A 10 Slide Production by James Rubino USAF RTDocument10 pagesBasic Pediatric Ventilation: A 10 Slide Production by James Rubino USAF RTjcrubinoNo ratings yet
- Algorithm Tatalaksana Kelainan KongenitalDocument32 pagesAlgorithm Tatalaksana Kelainan KongenitalLa Ode Muhammadin MatahanaNo ratings yet
- Lung Recruitment in General AnesthesiaDocument2 pagesLung Recruitment in General AnesthesiaIda SutawanNo ratings yet
- Guidance On Oxygen Therapy For Patients With COVID-19: General Principles of Assessing Respiratory StatusDocument1 pageGuidance On Oxygen Therapy For Patients With COVID-19: General Principles of Assessing Respiratory StatusAsh mohamedNo ratings yet
- Pitavastatin 4mgDocument48 pagesPitavastatin 4mg松山內科部No ratings yet
- NIV Algorithm Final Version Jan 2020Document3 pagesNIV Algorithm Final Version Jan 2020AmalNo ratings yet
- ICU Management of Respiratory Failure in Suspected or Confirmed COVID-19Document2 pagesICU Management of Respiratory Failure in Suspected or Confirmed COVID-19Quique GarciaNo ratings yet
- Why LAMA Is Fundamental Treatment For COPD: Rudi DermawanDocument29 pagesWhy LAMA Is Fundamental Treatment For COPD: Rudi DermawanwitwiiwNo ratings yet
- Ponda Leiomyosarcoma 7-9-2018Document12 pagesPonda Leiomyosarcoma 7-9-2018DoctoRides 46No ratings yet
- Foti G. - NIV Casco Maschera e Alti Flussi Come ScegliereDocument45 pagesFoti G. - NIV Casco Maschera e Alti Flussi Come ScegliereAssessoria da Gerência Geral HEHANo ratings yet
- Aprv ManagementDocument2 pagesAprv ManagementSamNo ratings yet
- Abg InterpretationDocument5 pagesAbg InterpretationGeoffrey Panjeton100% (1)
- High Yield Surgery Compatible Version-2Document20 pagesHigh Yield Surgery Compatible Version-2zoozsuhai2No ratings yet
- Smart Independent Dependent Collaborative: General Malvar ST., Davao CityDocument2 pagesSmart Independent Dependent Collaborative: General Malvar ST., Davao CityKhim BalcitaNo ratings yet
- ECRI COVID Comparison Chart Intensive Care VentilatorsDocument336 pagesECRI COVID Comparison Chart Intensive Care VentilatorsdawadhaliNo ratings yet
- 1.acid Base & Blood Analysis InterpretationDocument37 pages1.acid Base & Blood Analysis Interpretationsh4ntydjajakusliNo ratings yet
- Precipitants of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Pulseless or Breathless ?Document4 pagesPrecipitants of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Pulseless or Breathless ?giessyNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base HaberDocument11 pagesAcid-Base HaberChago MencosNo ratings yet
- High Yield Surgery Compatible Version PDFDocument20 pagesHigh Yield Surgery Compatible Version PDFSurgery CSC1No ratings yet
- Aprv DiagramDocument2 pagesAprv DiagramMaine AsuncionNo ratings yet
- LRP CriticalCare Sample2Document46 pagesLRP CriticalCare Sample2Aniket ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- RRT Care Plan Protocol GuideDocument4 pagesRRT Care Plan Protocol GuideTahani KhalilNo ratings yet
- Denu.2024.51.1.57.pdf Filename UTF-8''denu.2024.51.1.57Document4 pagesDenu.2024.51.1.57.pdf Filename UTF-8''denu.2024.51.1.57Fatima AliNo ratings yet
- ARDSnet Protocols PDFDocument2 pagesARDSnet Protocols PDFvbfisioNo ratings yet
- History of First AidDocument10 pagesHistory of First AidnihalNo ratings yet
- ACLS DrugsDocument16 pagesACLS Drugstostc100% (2)
- Mesenteric TorsionDocument2 pagesMesenteric TorsionEmerson SiqueiraNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine Thesis TopicsDocument6 pagesOral Medicine Thesis Topicsafloblnpeewxby100% (2)
- Lithium: Mimicry, Mania, and Muscle Relaxants: Simon Flood MRCP FRCA Andrew Bodenham FRCADocument4 pagesLithium: Mimicry, Mania, and Muscle Relaxants: Simon Flood MRCP FRCA Andrew Bodenham FRCARizwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Acls Guidelines 2015Document31 pagesAcls Guidelines 2015AgilNoviarAlvirosaNo ratings yet
- Post Cardiac Arrest CareDocument28 pagesPost Cardiac Arrest CareAkib ArmanNo ratings yet
- Rotaru I - PWS Conference ZalauDocument31 pagesRotaru I - PWS Conference ZalauelutafNo ratings yet
- A Field Manual of Camel Diseases Traditional and Modern Health Care For The DromedaryDocument273 pagesA Field Manual of Camel Diseases Traditional and Modern Health Care For The DromedaryHenrique100% (3)
- AHM Black White Boost FlexiDocument10 pagesAHM Black White Boost FlexiDani Kirky Ylagan100% (1)
- CHEMISTRY and PharmacologyDocument577 pagesCHEMISTRY and PharmacologyIurieUngureanu100% (2)
- Orthopaedic Physical AssessmentDocument2 pagesOrthopaedic Physical Assessment呂為蓁No ratings yet
- Drugs Used in AnaesthesiaDocument32 pagesDrugs Used in Anaesthesiav_vijayakanth7656100% (2)
- Neoplastic Proliferation of White Blood CellDocument35 pagesNeoplastic Proliferation of White Blood Cellnighat khanNo ratings yet
- CVS Case SheetDocument11 pagesCVS Case SheetSANA100% (1)
- VACCINESDocument8 pagesVACCINESzilikajainNo ratings yet
- Urgent Request From CCPSL To The MoH SFDocument4 pagesUrgent Request From CCPSL To The MoH SFDoctors NewsNo ratings yet
- Catálogo Accesorios Mindray PDFDocument64 pagesCatálogo Accesorios Mindray PDFFranco BarezziNo ratings yet
- The Real Cost of The US Health Care SystemDocument3 pagesThe Real Cost of The US Health Care SystemanonNo ratings yet
- Hankin - 1998 - Development of Depression From Preadolescence To AdulthoodDocument13 pagesHankin - 1998 - Development of Depression From Preadolescence To AdulthoodHanni JuhaszNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Disorders in Childhood and Adolescence Fourth Edition Mitchell J Prinstein Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesTreatment of Disorders in Childhood and Adolescence Fourth Edition Mitchell J Prinstein Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFanabaldyrstin100% (7)
- MSN Lesson Plan (Diabetes Mellitus)Document16 pagesMSN Lesson Plan (Diabetes Mellitus)SuchitaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Resume 1Document2 pagesNursing Resume 1api-534072530No ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- New Advanced in RadiotherapyDocument49 pagesNew Advanced in RadiotherapyIndonesian Journal of CancerNo ratings yet
- The Prima Dental Implant System: Simplicity Since 2005 Tilobe SolutionDocument4 pagesThe Prima Dental Implant System: Simplicity Since 2005 Tilobe SolutionOscarNo ratings yet