Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp-3 Aim-To Study Telemetry, Tracking and Command Subsystem Theory
Exp-3 Aim-To Study Telemetry, Tracking and Command Subsystem Theory
Uploaded by
Mansi Kolwankar Kokate0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesThe telemetry, tracking, and command subsystem monitors parameters from the satellite and transmits the data to ground stations. It tracks the satellite's position and sends correction signals to account for disturbing forces. The command subsystem receives commands from ground stations, verifies their reception, and executes the commands. Examples of commands include switching transmitters and antennas or controlling the solar arrays and thrusters.
Original Description:
Original Title
Exp3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe telemetry, tracking, and command subsystem monitors parameters from the satellite and transmits the data to ground stations. It tracks the satellite's position and sends correction signals to account for disturbing forces. The command subsystem receives commands from ground stations, verifies their reception, and executes the commands. Examples of commands include switching transmitters and antennas or controlling the solar arrays and thrusters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesExp-3 Aim-To Study Telemetry, Tracking and Command Subsystem Theory
Exp-3 Aim-To Study Telemetry, Tracking and Command Subsystem Theory
Uploaded by
Mansi Kolwankar KokateThe telemetry, tracking, and command subsystem monitors parameters from the satellite and transmits the data to ground stations. It tracks the satellite's position and sends correction signals to account for disturbing forces. The command subsystem receives commands from ground stations, verifies their reception, and executes the commands. Examples of commands include switching transmitters and antennas or controlling the solar arrays and thrusters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
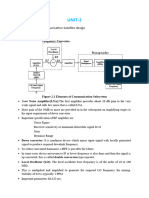
Exp-3
Aim-To Study Telemetry,Tracking and Command Subsystem
Theory-
Telemetry
1. The function of Telemetry sub system is to monitor various aircraft
parameters and to transmit the measured values to the satellite control
centre.
2. It refers to the overall operation of generating an electrical signal
proportional to the quantity being measured and encoding and
transmitting this to a distant station, which for the satellite is one of the
earth stations.
3. The telemetry data are analyzed at the control centre is used for routine
operation and failure diagnostic purposes.
4. The parameters most commonly monitored are:
1) Voltage, current and Temperatures of all major systems
2) Switch status of communications transponders.
3) Pressure of propulsion tanks
4) Output from attitude sensors
5) Reaction wheel speed
6) Environmental information such as the magnetic field intensity and
direction, the frequency of meteorite impact.
5. Several sensors provide analog signals whereas some others provide
digital signals.
6. Analog signals are digitally encoded and multiplexed with other signals,
forming a continuous digital stream. Typical telemetry data rates are in
the range of 150 to 100 bps.
7. The telemetry data are transmitted as FSK, PSK via telemetry antenna.
The telemetry signal is commonly used as a beacon by ground stations for
tracking purpose
Tracking
1. In this the satellite movement is tracked and correction signals are
sending to satellite because various disturbing forces are acting on the
satellite.
2. This system is located at the earth station providing information on
elevation and azimuth angles of the satellite.
3. Tracking is obviously important during the transfer and drift orbital
phases of the satellite launch. Once it is on station, the position of a
geostationary satellite will tend to be shifted as a result of the various
disturbing forces. Therefore, it is necessary to be able to track the
satellite’s movement and send correction signals as required.
4. Tracking beacons may be transmitted in the telemetry channel or by pilot
carriers at frequencies in one of the main communications channels, or by
special tracking antennas. Satellite range from the ground station is also
required from time to time. This can be determined by measurement of
the propagation delay of signals especially transmitted for ranging
purposes. Command
5. The command subsystem receives commands from the satellite control
centre, verifies this reception and executes received commands.
6. Telemetry and command may be thought of as complementary functions.
The telemetry subsystem transmits information about the satellite, while
the command subsystem receives command signals from the earth station,
often in response to telemetered information.
7. It is clearly important to prevent unauthorized commands from being
received and decoded, and for this reason, the command signals are often
encrypted.
Examples of common commands are:
1) Transponder switching
2) Switch matrix reconfiguration.
3) Antenna pointing control.
4) Controlling direction and speed of solar drive array.
5) Battery reconditioning
6) Beacon switching
7) Thrusters firing
8) Switching heaters of various subsystem
1. The receiving antennas used are omnidirectional antennas to maintain
contact for all orientation of the satellite, so that the satellite can receive
the signals during launch, orbit transfer and other periods prior to attitude
stabilization.
2. The receiver then converts RF signal to base band signal and command
decoder decodes the command.
3. Then verification is done in which involves transmitting decoded
commands to satellite control centre via telemetry carrier and the
command is stored in the satellite till verification is done.
4. The command receiver also provides baseband ranging tone which is
modulated on beacon telemetry and sent to satellite control centre.
5. The antennas used for telemetry and command signals are parabolic
reflectors.
Conclusion-
You might also like
- Bernanos, Georges - MouchetteDocument156 pagesBernanos, Georges - MouchetteJaCoby HutchinsonNo ratings yet
- PictureOfDorianGray TM 956Document16 pagesPictureOfDorianGray TM 956pequen30No ratings yet
- Hip-Hop - Subculture or Super BrandDocument33 pagesHip-Hop - Subculture or Super Brandart2sinNo ratings yet
- ONS Unit-5Document19 pagesONS Unit-5Alia JavedNo ratings yet
- Satellite Subsystems: Telemetry, Tracking and Command SystemDocument2 pagesSatellite Subsystems: Telemetry, Tracking and Command SystemEllandula kumaraswamyNo ratings yet
- Satellite TechnologyDocument10 pagesSatellite TechnologyDHARANI PNo ratings yet
- Satellite TTC Module 4Document21 pagesSatellite TTC Module 4AmitNo ratings yet
- Satellite SubsystemsDocument4 pagesSatellite SubsystemsJenkin WInstonNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 TelemetryDocument48 pagesUnit 4 TelemetryHaresh SivaNo ratings yet
- Satellite NavigationDocument30 pagesSatellite Navigationzakiannuar100% (1)
- Telemetry Tracking 0 Commanding Subsystems PDFDocument15 pagesTelemetry Tracking 0 Commanding Subsystems PDFshruti soniNo ratings yet
- Satellite-Based PositioningDocument11 pagesSatellite-Based Positioningarchana palNo ratings yet
- 37 Research PaperDocument5 pages37 Research PaperAbhishek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 SatellitesDocument16 pagesUnit 5 SatellitesPrema ElizabethNo ratings yet
- SBM1401Document130 pagesSBM1401raj251003No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (Satellite Communication)Document3 pagesAssignment 2 (Satellite Communication)The JamesNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Engineering and Science Invention (IJESI)Document9 pagesInternational Journal of Engineering and Science Invention (IJESI)inventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Fruits Satrack DocumentationDocument22 pagesFruits Satrack Documentationmar 931996No ratings yet
- Bme 518Document18 pagesBme 518Emmanuel NwankwoNo ratings yet
- FRD MTTSDocument20 pagesFRD MTTSpranavNo ratings yet
- Telemetry Encoder PDFDocument5 pagesTelemetry Encoder PDFAleem AzharNo ratings yet
- GPS SystemDocument2 pagesGPS Systemapi-26088064No ratings yet
- Earth Station DesignDocument27 pagesEarth Station DesignKushal ParmarNo ratings yet
- Omega HandoutDocument10 pagesOmega HandoutVey Alvezo IwaratNo ratings yet
- Early Developments in Satellite NavigationDocument10 pagesEarly Developments in Satellite NavigationAnkur AroraNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 Satellite Communications IIIDocument27 pagesCh-4 Satellite Communications IIIXalu XalManNo ratings yet
- SatracDocument16 pagesSatracvenkat_raj_38No ratings yet
- Satellite Communication Solutions (EC414)Document26 pagesSatellite Communication Solutions (EC414)Shaivi DewanganNo ratings yet
- DP Operator Manual: Section 12 Satellite Positioning Systems, and Differential Systems SystemsDocument5 pagesDP Operator Manual: Section 12 Satellite Positioning Systems, and Differential Systems SystemsKunal SinghNo ratings yet
- Bio TelemetryDocument25 pagesBio TelemetryPramanik Sayan100% (2)
- Sat. Com (R20) Unit-2Document9 pagesSat. Com (R20) Unit-2kavuri indulakshmiNo ratings yet
- Outline: Combining GPS & Cellular Network Measurements For PositioningDocument9 pagesOutline: Combining GPS & Cellular Network Measurements For PositioningMuhammad Niyas N SNo ratings yet
- Aircraft NavigationDocument28 pagesAircraft NavigationVinay Sriramoju100% (1)
- Navigation Lecture 5thDocument7 pagesNavigation Lecture 5thali aliNo ratings yet
- Course Material (Question Bank)Document5 pagesCourse Material (Question Bank)Saravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Telemetry Basics (9 Pages)Document9 pagesChapter-1 Telemetry Basics (9 Pages)Alberto OlivosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Telemetry Basics (9 Pages)Document9 pagesChapter-1 Telemetry Basics (9 Pages)Nadia FarheenNo ratings yet
- Global Positioning System: Introduction ToDocument58 pagesGlobal Positioning System: Introduction ToYasir Malik0% (1)
- Report-Major Satellite Communications SystemDocument36 pagesReport-Major Satellite Communications SystemMohammad Mostofa Kamal KowshikNo ratings yet
- Chapter-XXII Satellite Communication SystemDocument13 pagesChapter-XXII Satellite Communication SystemFirdous AhmedNo ratings yet
- Space Craft SubsytemsDocument12 pagesSpace Craft SubsytemsneerajaNo ratings yet
- How GPS Works: Karan Barua (2K8/EC/644) Kavita Kajla (2K8/EC/646) Kritika Nimesh (2K8/EC/648)Document35 pagesHow GPS Works: Karan Barua (2K8/EC/644) Kavita Kajla (2K8/EC/646) Kritika Nimesh (2K8/EC/648)Kritika NimeshNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument19 pagesReportKuldeep TeekasNo ratings yet
- SatracDocument18 pagesSatracvenkat_raj_38No ratings yet
- GPS 1Document4 pagesGPS 1Aman AroraNo ratings yet
- TelemetryDocument16 pagesTelemetryBalagovind BaluNo ratings yet
- Satellite SubsystemsDocument19 pagesSatellite SubsystemssanthoshkumardonthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1မိုး မိုးNo ratings yet
- Global Positioning System & Geographical Information System: BY: Dr. Thomas MathewDocument42 pagesGlobal Positioning System & Geographical Information System: BY: Dr. Thomas MathewSHIVAM BHATTACHARYANo ratings yet
- What Is GPS?Document40 pagesWhat Is GPS?vigneshNo ratings yet
- GPS ArchitectureDocument13 pagesGPS ArchitectureMohamed ArifNo ratings yet
- Part I Working of GPS/DGPS Part II Programming of GPSDocument28 pagesPart I Working of GPS/DGPS Part II Programming of GPSSnehashish PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication Elective - IV: Dr. Mahadev S. PatilDocument76 pagesSatellite Communication Elective - IV: Dr. Mahadev S. Patilprasad babarNo ratings yet
- SatelliteDocument8 pagesSatelliteRifat ahmmedNo ratings yet
- Target Tracking RadaDocument6 pagesTarget Tracking RadaShoyeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication Link Design and TTMCDocument24 pagesSatellite Communication Link Design and TTMCpriyanshi mehtaNo ratings yet
- Accuracy Assestment of Dgps in Control Survey Work in MinesDocument28 pagesAccuracy Assestment of Dgps in Control Survey Work in MinessumitmatheNo ratings yet
- Class 8Document22 pagesClass 8K R BiradarNo ratings yet
- SubsystemsDocument6 pagesSubsystemsSai Prasad Iyer JNo ratings yet
- 13 - Electronic NavigationDocument19 pages13 - Electronic NavigationAKANKSHA PANDEYNo ratings yet
- SATRACKDocument22 pagesSATRACKapi-19937584100% (6)
- Radio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftFrom EverandRadio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Exp-2 Aim-To Study Antenna Look Angles Using Octave Software-Octave TheoryDocument6 pagesExp-2 Aim-To Study Antenna Look Angles Using Octave Software-Octave TheoryMansi Kolwankar KokateNo ratings yet
- Modes of Operations in Jpeg: Sequential Mode Progressive Mode Lossless Mode Hierarchical ModeDocument6 pagesModes of Operations in Jpeg: Sequential Mode Progressive Mode Lossless Mode Hierarchical ModeMansi Kolwankar KokateNo ratings yet
- Experiment2 PDFDocument62 pagesExperiment2 PDFMansi Kolwankar KokateNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document61 pagesExperiment 1Mansi Kolwankar KokateNo ratings yet
- Major and Minor TriadsDocument16 pagesMajor and Minor TriadsSAYINo ratings yet
- Time Division Multiplexed Audio Interface: A Tutorial: Frame Sync Serial ClockDocument4 pagesTime Division Multiplexed Audio Interface: A Tutorial: Frame Sync Serial ClockJeff PeilNo ratings yet
- Roland TR-08 ManualDocument2 pagesRoland TR-08 Manualutopian_mintrubberNo ratings yet
- Navsure N400iDocument76 pagesNavsure N400iJohn LawsonNo ratings yet
- Philips DTR 230 ManualDocument2 pagesPhilips DTR 230 ManualBaz Ticket-ManNo ratings yet
- SAXOLOGY2Document1 pageSAXOLOGY2Mario BaragioliNo ratings yet
- Workshop Sixth GradeDocument4 pagesWorkshop Sixth GradeDAVID ALEJANDRO ESCOBAR RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Smart Traffic Control and Congestion Management Systems: A ReviewDocument6 pagesSmart Traffic Control and Congestion Management Systems: A ReviewAnonymous izrFWiQNo ratings yet
- Like A Prayer Ledtra Con AcordesDocument3 pagesLike A Prayer Ledtra Con AcordesJavier Edo AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Summary Analog Integrated Circuits ITET Lukas Cavigelli PDFDocument6 pagesSummary Analog Integrated Circuits ITET Lukas Cavigelli PDFLukas CavigelliNo ratings yet
- Acc15 Program WebDocument8 pagesAcc15 Program WebgayhitlerNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 23.003Document71 pages3GPP TS 23.003Gregory CapellaNo ratings yet
- 1.PP Pelan Komunikasi KPMPerkasaKUDocument12 pages1.PP Pelan Komunikasi KPMPerkasaKUZurayushazman IsmailNo ratings yet
- Mapeh HWDocument3 pagesMapeh HWbeelzebubNo ratings yet
- AnimeDocument7 pagesAnimerpaladin1No ratings yet
- One Number Away - Luke CombsDocument2 pagesOne Number Away - Luke CombsYvessaVerheyden0% (1)
- Phenomena User GuideDocument13 pagesPhenomena User Guidevicher2020No ratings yet
- Speaker Crossover LabDocument51 pagesSpeaker Crossover LabRoland HendriksNo ratings yet
- Genitive CaseDocument4 pagesGenitive CaseSlađana ŠepecanovićNo ratings yet
- Bad Moon Rising: Arr. Christoph Görres Creedence Clearwater Revival 180 D A G D D ADocument1 pageBad Moon Rising: Arr. Christoph Görres Creedence Clearwater Revival 180 D A G D D ASteve Clijnhens100% (1)
- Coast GuardDocument127 pagesCoast Guardjohn eric garciaNo ratings yet
- LCD42V68PK Final InspectionDocument19 pagesLCD42V68PK Final InspectionMiloud ChouguiNo ratings yet
- Ket Topic SpeakingDocument46 pagesKet Topic SpeakingDương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Tda 2613 QDocument11 pagesTda 2613 Qpaulmx13No ratings yet
- Redhead 074175aDocument44 pagesRedhead 074175alexNo ratings yet
- Willy Wonka Audition Info Forms CutsDocument14 pagesWilly Wonka Audition Info Forms CutsRab100% (1)
- Mondschein Sonate: Adagio SostenutoDocument5 pagesMondschein Sonate: Adagio SostenutoJose AndrésNo ratings yet