Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revised Syllabus - XII 2021-22
Revised Syllabus - XII 2021-22
Uploaded by
lucifer aviCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Jo Khola Uski Ma Ki ChutDocument92 pagesJo Khola Uski Ma Ki ChutTech SupportNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - XII 2022-23-2Document92 pagesSyllabus - XII 2022-23-2Alex SmithNo ratings yet
- Booklist - XII 2020Document4 pagesBooklist - XII 2020Kratika VarshneyNo ratings yet
- XI - Main Syllabus (For March+April+May) - 2023-24Document17 pagesXI - Main Syllabus (For March+April+May) - 2023-24roshani yadavNo ratings yet
- Xi 2021-22Document4 pagesXi 2021-22vinayraj 9a2020No ratings yet
- Booklist - XI 2024-25Document4 pagesBooklist - XI 2024-25rajinderkaur115599No ratings yet
- Note - : Subjects Name of The Books PublishersDocument6 pagesNote - : Subjects Name of The Books Publishersa k singhNo ratings yet
- BOOK LIST For Class - X (2020-21) : Ubjects Ame of The Ooks UblishersDocument2 pagesBOOK LIST For Class - X (2020-21) : Ubjects Ame of The Ooks UblishersRudra Narayn PandaNo ratings yet
- Class Xii PMC & PBCDocument50 pagesClass Xii PMC & PBCIhaNo ratings yet
- Book List12 SciDocument1 pageBook List12 SciJoyjeet Mitra XI-ANo ratings yet
- Revized Booklist-IX 2020Document4 pagesRevized Booklist-IX 2020yashitasehgal1111No ratings yet
- Sfws Xii BooklistDocument2 pagesSfws Xii Booklistofficialfarmaan1009No ratings yet
- Sfws Xii BooklistDocument2 pagesSfws Xii Booklistofficialfarmaan1009No ratings yet
- Book ListDocument4 pagesBook ListShahAzeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Book List of Class XiiDocument4 pagesBook List of Class XiiAshish ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- TitleDocument2 pagesTitleSampanna DhakalNo ratings yet
- Prescribed Textbooks 2023 24Document4 pagesPrescribed Textbooks 2023 24muskanm8888No ratings yet
- Class 11Document2 pagesClass 11shashanksurada05No ratings yet
- Book List Class XI ScienceDocument1 pageBook List Class XI ScienceSwayamNo ratings yet
- 3) Grade 11 - Book ListDocument4 pages3) Grade 11 - Book ListxyzNo ratings yet
- WCP 2404051633 2093238092 13Document1 pageWCP 2404051633 2093238092 13Sumit ShekherNo ratings yet
- Pwqsi XiDocument2 pagesPwqsi XiAhana PoddarNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Final Booklist (Session 2020-21) Class Name of The Book Name OF THE Author/Publishers Book Type EnglishDocument1 pageClass Ix Final Booklist (Session 2020-21) Class Name of The Book Name OF THE Author/Publishers Book Type EnglishMohd. QadriNo ratings yet
- Jawahar Vidya Mandir, Shyamali, Ranchi - 834002 BOOK - LIST - Class XI (2019-20)Document1 pageJawahar Vidya Mandir, Shyamali, Ranchi - 834002 BOOK - LIST - Class XI (2019-20)Varun Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- XI HumanitiesDocument2 pagesXI HumanitiesArchana SinghNo ratings yet
- Xii Book ListDocument4 pagesXii Book ListSamriddhi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Class XIDocument2 pagesClass XIAushnik RoyNo ratings yet
- Std. Xii (Text Book List) 24 - 25Document1 pageStd. Xii (Text Book List) 24 - 25devadarshan.viiieNo ratings yet
- Book List Xi Xii 2022 23Document4 pagesBook List Xi Xii 2022 23Shalini JhaNo ratings yet
- Science XiDocument2 pagesScience Xiparthamohanta447No ratings yet
- Booklist 2023 24Document9 pagesBooklist 2023 24Purnima TiwariNo ratings yet
- List of Books For Class IX Session (2020-2021)Document2 pagesList of Books For Class IX Session (2020-2021)Nandan KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Acadmic Syllabus 2022 23Document13 pagesClass 12 Acadmic Syllabus 2022 23Guru Gulab KkhatriNo ratings yet
- CLASS X - List of Books For The Session 2022Document2 pagesCLASS X - List of Books For The Session 2022Ni shNo ratings yet
- 12 Class Book ListDocument1 page12 Class Book ListLallan SinghNo ratings yet
- Book List 2024 - 25, XIDocument2 pagesBook List 2024 - 25, XIneeraj6968eNo ratings yet
- TEXT BOOK DETAILS (2020 - 2021) : Class Subject PublisherDocument3 pagesTEXT BOOK DETAILS (2020 - 2021) : Class Subject PublisherGopi BabuNo ratings yet
- HHDocument10 pagesHHRaj MishraNo ratings yet
- DLL-2nd-week 7-12Document6 pagesDLL-2nd-week 7-12Brannon EludoNo ratings yet
- Book List Class XII 2024-25Document2 pagesBook List Class XII 2024-25ajaymishra26087No ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Kalinga: Book List For The Year: 2023-24Document3 pagesDelhi Public School Kalinga: Book List For The Year: 2023-24saquibasif98270No ratings yet
- Book List Class XiiDocument3 pagesBook List Class XiiRg RrgNo ratings yet
- S.N Subjects Name of The Book Name of The Publishers 1Document1 pageS.N Subjects Name of The Book Name of The Publishers 1Jocy9No ratings yet
- (Syllabus For Class-Xii) 2015-2016Document4 pages(Syllabus For Class-Xii) 2015-2016Daniel KhanNo ratings yet
- Book List: Class Xi - Humanities FOR THE SESSION: 2019 - 2020Document1 pageBook List: Class Xi - Humanities FOR THE SESSION: 2019 - 2020GT ANUPNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Cyclic Test - 1 Syllbaus Sheets 2022-2023Document3 pagesClass Xii Cyclic Test - 1 Syllbaus Sheets 2022-2023PranavNo ratings yet
- U.T. Syllabus Class 10thDocument2 pagesU.T. Syllabus Class 10thwardhanyashmishraNo ratings yet
- Notes Physics ImportantDocument11 pagesNotes Physics Importantcustompros420No ratings yet
- STD IxDocument1 pageSTD Ixkumarharsh7425No ratings yet
- Sample Paper Syllabus 2021-22: ClassDocument2 pagesSample Paper Syllabus 2021-22: ClassPranav S Nair67% (3)
- Class 12-UpdatedDocument9 pagesClass 12-UpdatedVaibhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bcom - Sem1 - Iks - Unit 2Document20 pagesBcom - Sem1 - Iks - Unit 2nandinisonar05No ratings yet
- XII ScienceDocument2 pagesXII ScienceMokshita JainNo ratings yet
- Prescribed Textbooks 2023 24Document10 pagesPrescribed Textbooks 2023 24ravibhaknpNo ratings yet
- GS NCERT LIST (2 Yr Foundation Batch) 20221121060632Document1 pageGS NCERT LIST (2 Yr Foundation Batch) 20221121060632enchantress soulsingerNo ratings yet
- Nust Chemistry 1550Document136 pagesNust Chemistry 1550Meer UmarNo ratings yet
- 10sm Science 2021 22Document344 pages10sm Science 2021 22Impulse Academy NoidaNo ratings yet
- Class XII PT1 Syllabus and HHWDocument3 pagesClass XII PT1 Syllabus and HHWbitthariashivangiNo ratings yet
- Booklist XII-2024Document1 pageBooklist XII-2024stiphenmarandiNo ratings yet
- 17 Aldovino V Pujalte, Jr.Document8 pages17 Aldovino V Pujalte, Jr.Princess Samantha SarcedaNo ratings yet
- IBC CodeDocument1 pageIBC CodeEezmaira S ShaharuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12Document2 pagesLesson 12Kimberly Lunar AlaskaNo ratings yet
- Disciplines and Ideas in The Applied Social SciencesDocument5 pagesDisciplines and Ideas in The Applied Social SciencesJonalyn Banez0% (1)
- Mephi Guide PDFDocument30 pagesMephi Guide PDFMuhammad FaizNo ratings yet
- Readings On Participatory Planning: Available OnlineDocument21 pagesReadings On Participatory Planning: Available Onlinepallavidelite22No ratings yet
- Direct Selling Report PDFDocument3 pagesDirect Selling Report PDFJigar PatelNo ratings yet
- Japanese Immigration To Mexico PDFDocument19 pagesJapanese Immigration To Mexico PDFCarlos MorenoNo ratings yet
- Lembar Kerja 1Document14 pagesLembar Kerja 1niaNo ratings yet
- The Differentiated University: Recognizing The Diverse Needs of Today'S StudentsDocument10 pagesThe Differentiated University: Recognizing The Diverse Needs of Today'S StudentspedropauloNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Connections: A Study of Effective Calculator Use in Secondary Mathematics ClassroomsDocument22 pagesMathematical Connections: A Study of Effective Calculator Use in Secondary Mathematics ClassroomsChess NutsNo ratings yet
- Security Officer Part Time in Orange County CA Resume Robert TalleyDocument2 pagesSecurity Officer Part Time in Orange County CA Resume Robert TalleyRobertTalleyNo ratings yet
- Suffolk Family Carers ' Caring Touch November 2010Document24 pagesSuffolk Family Carers ' Caring Touch November 2010Suffolk Family CarersNo ratings yet
- Skim Boarding: Carlyn PolisticoDocument13 pagesSkim Boarding: Carlyn PolisticoDonn NeriNo ratings yet
- Mary Kay Inc., Company AnalysisDocument7 pagesMary Kay Inc., Company Analysisrio boseNo ratings yet
- Apo Fruits Corporation v. Land Bank of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesApo Fruits Corporation v. Land Bank of The PhilippinesJoshua TanNo ratings yet
- Political MarketingDocument10 pagesPolitical MarketingNigora_AdizovaNo ratings yet
- Exam Policies and ProceduresDocument6 pagesExam Policies and ProceduresFirstnameNo ratings yet
- Starhub Case Study Ipc v4Document4 pagesStarhub Case Study Ipc v4Sean NgNo ratings yet
- Trends Nov25 29Document6 pagesTrends Nov25 29Rudnickz MagbujosNo ratings yet
- Rescind DMV Contract PDFDocument1 pageRescind DMV Contract PDFKevin YohburtNo ratings yet
- RS 4Document25 pagesRS 4Lata JagwaniNo ratings yet
- Challenges in Accessing Sexual and Reproductive Health Services by People With Physical Disabilities in Kampala, UgandaDocument9 pagesChallenges in Accessing Sexual and Reproductive Health Services by People With Physical Disabilities in Kampala, UgandaFlorence Kyoheirwe MuhanguziNo ratings yet
- DLL Chinese Peking OperaDocument3 pagesDLL Chinese Peking OperaCiarah Leynes Mangcoy100% (1)
- En10Lc-Iib-15.1: En10Rc-Iia-11: Transcode En10Wc-Iia-13.1: Identify PartsDocument4 pagesEn10Lc-Iib-15.1: En10Rc-Iia-11: Transcode En10Wc-Iia-13.1: Identify Partsjoel bagalanonNo ratings yet
- Kendalls and Marzanos New TaxonomyDocument22 pagesKendalls and Marzanos New TaxonomyRUTHY ANN BALBIN BEEd 2-1100% (1)
- Full Sail Housing Guide PDFDocument64 pagesFull Sail Housing Guide PDFRoshinNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Visual Arts Course OutlineDocument5 pages7th Grade Visual Arts Course OutlineMaureen Cusenza100% (1)
- Linguistics, Second Edition - David CrystalDocument292 pagesLinguistics, Second Edition - David CrystalYozamy Triana100% (3)
- LESSON PLANNING - Quadratic Inequality WatermarkDocument10 pagesLESSON PLANNING - Quadratic Inequality WatermarkAzizi. Ah SuhupiNo ratings yet
Revised Syllabus - XII 2021-22
Revised Syllabus - XII 2021-22
Uploaded by
lucifer aviOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Revised Syllabus - XII 2021-22
Revised Syllabus - XII 2021-22
Uploaded by
lucifer aviCopyright:
Available Formats
R
Estd. 1972
Sunbeam School
Bhagwanpur, Lahartara, Suncity, Varuna & Knowledge Partners
BOOK LIST for Class – XII (2021-22)
(Please ensure that you buy the New Editions only)
Subjects Name of the Books Publishers
a) Flamingo (Bgn & Sct) NCERT
b) Vistas (Bgn & Sct) NCERT
English Core c) Collins Cobuild Learner's Illustrated Dictionary Collins
Ref. Book– High School English Grammar & Composition (Wren S. Chand
& Martin)
a) Physics Part I & II Text Book for class-XII NCERT
b) Together with Physics (Laboratory Manual Rachna Sagar
(with Lab Register - 1 complete set) – XII
c) Physics Exemplar Problems-XII (for Lht, Vrn & Knowledge
NCERT
Partners)
Physics Reference Book -
Dhanpat Rai & Co.
a) New Simplified Physics-XII (S. L. Arora)
b) Foundation Physics-XII (H.C. Verma) Vol.-2 Bharti Bhawan
c) Comprehensive Physics – XII Laxmi Publication
d) Nootan Physics – XII Nageen Publication
e) New Era Physics GRB Publication
a) Chemistry Part I & II Text Book for class-XII NCERT
b) Together with Chemistry - Laboratory Manual Rachna Sagar
(with Lab Register - 1 complete set) - XII
c) Chemistry Exemplar Problems-XII (for Lht, Vrn & Knowledge NCERT
Partners)
Chemistry Reference Book -
Laxmi
a) Comprehensive Chemistry - XII
b) New Course Chemistry – XII Pradeep
c) New Millennium Chemistry - XII Vol.- I & II Dinesh Pub.
d) New Era Chemistry part I & II GRB Publications
e) All in One Chemistry - XII Arihant
a) Biology Text Book for class - XII NCERT
b) Together with Biology - Laboratory Manual- XII
Rachna Sagar
(with Lab Register - 1 complete set) - XII
Biology c) Biology Exemplar Problems-XII (for Lht, Vrn & Knowledge Partners) NCERT
Reference Books -
GRB Publishers
a) New Era of Biology –XII
b) Elementary Biology Class - XII Trueman Publication
Class XII (Pg. 01)
a) Mathematics Text Book for class - XII part I & II NCERT
b) Mathematics - XII (R.D. Sharma) Dhanpat Rai
c) Mathematics Exemplar Problems-XII NCERT
d) New Millennium Lab Manual Mathematics Dinesh Pub.
Mathematics
(with Lab Register - 1 complete set) – XII
Reference Books- Arya Publications
a) Mathematics- Class XII (M.L.Aggarwal)
b) Senior Secondary School Mathematics- XII (R.S. Agarwal) Bharti Bhawan
c) All in One – Mathematics – XII Arihant
a) Introductory Macro Economics - XII NCERT
b) Indian Economic Development - Text Book for class-XII NCERT
Economics Reference Books-
a) Indian Economic Development (Sandeep Garg) Dhanpat Rai
b) Introductory Macro Economics – XII (Sandeep Garg) Dhanpat Rai
a) Business Studies Part I Principles and Functions of Management NCERT
NCERT
Business Studies b) Business Studies Part II Business Finance & Marketing
c) Case Studies Mentor in Business Studies (Class XII) – Alka Arya Pub. Co.
Dhawan
a) Accountancy Partnership NCERT
b) Company Accounts & Analysis of Financial Statements NCERT
Reference Book – a) Accountancy - XII (Partnership & Company
Arya Publications
Accounts) (D.K. Goel & Rajesh Goel)
b) Accountancy - XII (Analysis of Financial Statements) Arya Publications
Accountancy
(D.K. Goel & Rajesh Goel)
c) Accountancy - XII (T.S. Grewal) part-A (I & II) & part-B Sultan Chand
d) Accountancy - XII (P.C. Tulsian) part-A Srijan Publishers
e) Accountancy Part-II (P.C. Tulsian) part-B Srijan Publishers
f) Accountancy – XII (H.C. Sharma) part-A & part-B Arya Book Depot
a) Themes in Indian History Part - I NCERT
History b) Themes in Indian History Part – II NCERT
c) Themes in Indian History Part - III NCERT
a) Structure of Indian Society NCERT
Sociology NCERT
b) Social Change in India
a) Fundamentals of Human Geography NCERT
b) India – People & Economy NCERT
Geography NCERT
c) Practical Work in Geography Part-II class XII
Ref. Book- Geography Class XII – R.D. Khullar Saraswati
a) Contemporary World Politics – XII NCERT
Political Science
b) Politics in India since Independence – XII NCERT
Class XII (Pg. 02)
Ref. Book – Political Science – XII V.K. Global Publication
a) Aaroh – II (For BGN, SCT) NCERT
b) Vitaan – II (For BGN, SCT) NCERT
Hindi Core Saraswati
c) Hindi Vyakran Aur Vyavhar - XI - XII
d) Abhivyakti Aur Madhyam NCERT
a) HkkLorh Hkkx & 2 CBSE
b) O;kdj.k lkSjHke~ NCERT
Sanskrit NCERT
c) laLd`r lkfgR; ifjp;
d) jpukuqokn dkSeqnh & ¼dfiynso f}osnh½ V.V. Prakashan
Entreprenuership-XII CBSE
Entreprenuership
Entreprenuership-XII (Reference Book) Full Marks
Computer Science with Python - A Text Book for class XII (Sumita Arora) Dhanpat Rai
Computer
Science Ref. book – Computer Science with Python: Text book for CBSE Sultan Chand
Class XII (2020 Edition) by Preeti Arora
Informatics Informatics Practices - A Text Book for class XII (Sumita Arora) Dhanpat Rai
Sultan Chand
Practices Ref. Book-Informatics Practices with Python Class XII (Preeti Arora)
Information a) Database Management Applications (e-book Class XII) CBSE site
CBSE site
Technology b) Employability Skills (e-book Class XII)
Physical a) CBSE Text Book of Physical Education – XII (Sanjay Kundra) Evergreen
Education b) 1 Practical File Evergreen
Arya Book Depot
Music/ Vocal/ a) Loj fuf/k (only for vocal and sitar students)
Tabla / Sitar/ b) JhokLro½ (only for tabla students) Ruby Pub.
Sunbeam Pub.
Kathak c) laxhr fl)kar (Dr. Jayshree Rai)
Psychology – Text Book for Class XII NCERT
Psychology
Reference Book –Move fast with Psychology Dhanpat Rai
Panoramic Indian Painting XI & XII Vishal Pub. Co.
c) History of Indian Art Fullmarks
Applied Arts d) Contemporary Indian Artists (Geeta Kapoor) Vikas
e) Indian Painting (Percy Brown) YMCA
f) Drawing & Sketching (Sunil Vishwakarma) Lalit Kala Aashram
Legal Studies Legal Studies – XII NCERT
Bharatnatyam (Laxmi Narayan) Vishwavidyalaya
Bharatnatyam Prakashan
Hkkjrh; ukV~; ijEijk vkSj vfHku; niZ.k Vachaspati Garola
Mass Communication Mass Media Studies - XII CBSE
French Coursole langue et de Civilsation Francaises – II by G. Mauger (for Goyal Publications
Class XII (Pg. 03)
Lht, Vrn)
Song Book Swaranjali – Songs for Sunbeams Eternal Pub.
Learner’s PBC+PMC; Commerce; Humanities Eternal Pub.
Comate
STATIONERY LIST CLASS – XII
1. Register of 140 pages (PBC/PMC/COMM/HUM) 08
2. Graph 100 pages (big size) (PMC) 01
3. Geometry box (PMC) 01
4. Gel Pens (Blue,) 01
5. a) Camel Poster Colour - (12 shades of 10 ml)
b) Camel Artists' Photo Colour (12 shades) Only for Applied
c) Ivory Sheets (6 pcs.) Arts Students
d) Round Brushes no. (2, 4, 6, 8) Flat brushes 1 set
6. Business Studies / Economics 2 Files + 50 blank A4 sheets
7. Psychology / Sociology 2 Files + 30 interleaf sheets
8. Accounts / Entrepreneureship / History 1 File + 100 interleaf sheets
9. Vocal / Sitar / Tabla / Bharatnatyam / Violin / Kathak / Phy. Edu. 1 file + 30 interleaf sheets
(each) (Lht, Vrn, Sct)
1 notebook (120 pgs) (Bgn)
10. Computer Science / Informatics Practices / Information Technology 1 file + 30 interleaf sheets (each)
11. File (for filing Unit Test Papers) 01
Please Note :
1. Stainless Steel Rulers are not allowed in school. Only Plastic Rulers are to be used.
2. We discourage covering notebooks to save paper. If needed, all notebooks should be covered
only with used paper as we are an eco-conscious school and realize the importance of
recycling. Plastic covers are strictly prohibited.
3. The text books should be covered only with used paper or bound so that they don’t tear during
the session.
4. All text books and notebooks should be properly labelled with name, class and section.
5. All notebooks should be of big size. Small notebooks will not be accepted in school for
correction.
6. Parents are requested to buy the books at the earliest before the stock is sold.
7. Reference books mentioned (if any) are optional to buy.
8. Since we believe that the child should carry a few books to school so as to avoid burden on the
young shoulders, please see that the child brings books according to the time table.
Class XII (Pg. 04)
Class XII (Pg. 05)
Class XII (Pg. 06)
Class XII (Pg. 07)
Information for internet usage
Dear Parents
Please do take note that we will continue to use blended form of
learning so all links, updates, texts, research materials will be
provided by the school in the G Suite (Google Classroom). It will
take between 30-40 minutes of internet time for your ward to go
through and benefit.
Please be conscious about the net usage beyond the mentioned
allotted time since beyond that your ward may be using the internet
for non-productive/addictive things, not in the best of his/her interest,
intelligently/emotionally.
Class XII (Pg. 08)
Art Integrated Learning (AIL)
Art integrated Learning (AIL) has become an
integral part of the learning process. Hence Art
Integrated Learning (AIL) is being introduced in
all the subjects to give students an opportunity to
study deeply about the ‘Uniqueness in Indian
work culture and present it through different art
forms like dance, music, skit, role play, theatre
etc. It also helps to imbibe the Indian ethos
through integration of Indian art and culture in
the teaching and learning process at every level.
This art integrated approach will strengthen the
linkages between education and culture.
Class XII (Pg. 09)
INDEX
Name of the Subject Page Nos.
English Core 27
Physics 30
Chemistry 37
Biology 44
Mathematics 49
Accountancy 55
Business Studies 59
Economics 63
History 68
Political Science 75
Psychology 78
Career Information Centre 81
Drill 82
Song on the Band 83
Music 84
Time Management 85
Class XII (Pg. 010)
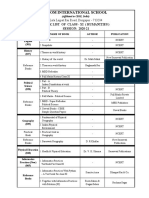
1ST UNIT TEST SCHEDULE (1st Term)-SCIENCE
SUBJECT DATE SYLLABUS
English Core 15.04.21 Comprehension Passage (Prose)
17.04.21 Comprehension Passage (Prose), An Elementary School
English Core
Classroom in a Slum, Notice Writing.
24.04.21 Relation and functions, Inverse trigonometric functions
Maths
Reproduction in organisms, Sexual reproduction in flowering
Biology 24.04.21
plants, Human reproduction, Reproductive health
Chemistry 01.05.21 Solutions, Electrochemistry
Physics 08.05.21 Electric Charges & Fields, Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance
5th Subjects
Hindi Core 24.06.21 vifBr x|ka'k
Computer 26.06.21 Python Revision Tour – I ,Python Revision Tour - II
Science
Informatics 26.06.21 Data Handlings-2 (Numpy, Python Pandas)
Practices
Information 26.06.21 Employment Skills, Vocational Skills, Unit-1—Basics of RDBMS
Technology (SQL)
Physical 26.06.21 Planning in Sports, Sports and Nutrition, Yoga & Lifestyle
Education
The Deccan School, The Indian National Flag, The
Rajasthani Schools of Miniature Paintings, Bengal School of
Applied Arts & 26.06.21 Paintings, Contribution of Indian artists in the struggle for
Painting National Freedom Movement, The Pahari School of
Miniature Paintings, Six Limbs of Indian Painting and
fundamentals of Visual Arts (Elements & Principles)
Definition of the following terms :-
Peshkar, Uthan, Fard, Chakkradar, Baont, Jhaptaal, Rupak Tala,
Chautaal, Ektaal, Dhamar
26.06.21
Tabla Definition of the following terms :-History of Tabla and Pakhawaj
Brief Description of Gharanas--Tabla and Pakhawaj
1. Comparative study of some antartals
a) Chautal - Ektal
Class XII (Pg. 011)
b) Jhaptal – Sool Tala
c) Tilwara - Teentala
2. Description of Talas prescribed for class XII practical.
3. Writing notation of the prescribed tals and composition.
4. Recognition of talas from given portion of the thekas and
composition.
Description of Raag Bhairav with the composition (gat) notation, One
Masitkhani and one Razakhani Gat in Raag Bhairav. Knowledge of
26.06.21
Sitar structure of tuning of Sitar. Life sketch of Abdul Halim Zafer,
Description of Raag Shuddha Sarang and its notations, one Masitkhani
and one Razakhani, Gat in Teental. Detail study of Sangeet Ratnakar.
Definition of following – Varna, Alankar, Khatka Kan, Meend,
26.06.21
Vocal Description of Raag Bhairav.Biography of Ustad Faiyaz
Khan.Contribution and short life sketch of Ustad Abdul Karim Khan.
A brief history and acquaintance with other classical styles or folk form
prevalent in the region, other than the one offered for study.
Acquaintance with the life history of the chief exponents and
contributors of the past of the dance form (Rukmini Devi Arundel,
Bharatnatya 26.06.21 Balasraswati, Meenakshi Sundaram Pillai, Tanjore quartette)
m Acquaintance with the contents of the Abhinaya Darpana. (the chapters
as the aspects of dance dealts within them.)
Nritta, Nritya, Natya, (Sanskrit slokas from the Abhinaya Darpana and
basic definition) Tandava (7 tandavas with detailed stories), Lasya,
Lokadharmi, Natyadharmi (definitions with examples)
26.06.21 Topics in Law
Legal Studies
26.06.21 igyoku dh <ksyd, dSejs esa can vikfgt, lg"kZ Lohdkjk gS, ued, m"kk, vrhr esa ncs
Hindi Core ik¡o, jpukRed ys[ku, i= ys[ku
26.06.21
Maths Relation and functions, Inverse trigonometric functions, Matrices
Macro Economics- Unit I- National Income and Related Aggregate, Unit
26.06.21
Economics II- Money and banking, Indian Economic Development- Chapter 1-
Indian Economy on the eve of Independence
26.06.21 Reproduction in organisms, Sexual reproduction in flowering
Biology
plants, Human reproduction, Reproductive health
26.06.21 Variations in psychological attributes, Self & Personality
Psychology
Lesson 18 to 22; informal letter; unseen passage and grammar
26.06.21 (Interrogative adjective and pronoun; simple and compose
French
relative pronouns; preposition and indefinitive adjectives and
pronouns)
Class XII (Pg. 012)
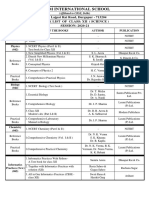
2ND UNIT TEST SCHEDULE (1st Term)-SCIENCE
SUBJECT DATE SYLLABUS
English Core 04.08.21 Comprehension Passage (Poem)
07.08.21 A Thing of Beauty, The Rattrap, Invitations and Replies (Formal &
English Core
Informal)
14.08.21 Matrices, Determinants, Continuity and Differentiability
Maths
14.08.21 Heredity and variation, Molecular basis of inheritance, Evolution,
Biology
Human health and diseases
21.08.21 Chemical Kinetics, Solid State, Surface Chemistry, General Principles
Chemistry
and Processes of isolation of elements
28.08.21 Current Electricity, Moving Charges & Magnetism, Magnetism and
Physics
Matter
5th Subjects
Hindi Core 01.09.21 vifBr dkO;ka'k
Computer 03.09.21 Ch-3 Functions, Ch-4 Python Libraries, Ch-5 File Handling, Ch-6
Science Recursion
Informatics 03.09.21 Data Handling-2 (Plotting with Pyplot), Introduction to Software
Practices Engineering.
Information 03.09.21 Unit-3—Fundamentals of JAVA Programming (Introduction, OOPs,
Technology JAVA Language Elements, Operators, Control Flow, Array)
Physical 03.09.21 Physical Education & Sports for Differently-Abled, Children and
Education Sports, Women & Sports, Test and Measurement in Sports
03.09.21 The Modern Trends in Indian Art, Paintings, Sculpture, The
Applied Arts
Mughal Schools of Miniature Paintings
Brief History of Medieval and Modern period of Hindustani Music
03.09.21 especially in the field of Percussion instruments. Biographies of
Tabla Musicians – Pandit Kishan Maharaj, Raja Chattrapati Singh, Ustad
Karmatullah Khan. Dhamar & Teevra Tala
‘Sangeet Ratnakar’. Definition of Gamak, Murchhana, Murki, Grama, Alaap, Tana.
Biography of Pandit Krishna Rao Shankar Pandit.. Description of Raag Bageshri.
03.09.21 Jhaptaal & Tilwada in dugun and Rupak Taal. Classification of Ragas. Detail
Sitar study of Sangeet Parijat, Description of Kan, Meend, Murki, Gamak, Gram,
Murchchana. Description of Raag Bagheshwari, Biography of Ustad
Mushtaq Ali Khan
Class XII (Pg. 013)
‘Sangeet Ratnakar’. Definition of Gamak, Murchhana, Murki, Grama,
03.09.21 Alaap, Tana. Biography of Pandit Krishna Rao Shankar Pandit..
Vocal Description of Raag Bageshri. Jhaptaal & Tilwada in dugun and Rupak
Taal.
Anga, Upanga, Pratyanga (slokas and meaning from Abhinaya
Darpana), Sthana, Chari, Mandala, bharmari, Utplavana (slokas and
Bharatnat 03.09.21 meaning from Abinaya Darpana, Definitions of the following :
yam araimandi, muzhumandi, khuttanam, korvai, karvai, adavu, shollu,
aradhi, theerumana, jati, jaati, gati, avartana, yati, taalanga,
thattukazhi, nattuvangam, arangetram
Legal 03.09.21 Arbitration, Tribunal, Adjudication and Alternate Dispute Resolution
Studies Tribunal, Human Rights in India
f'kjh"k ds Qwy, dforkoyh, y{e.k&ewPNkZ vkSj jke dk foyki,
Hindi 03.09.21
Core Mk;jh ds iUus, tulapkj ek/;e, pkyhZ pSfIyu ;kuh ge lc
ckny jkx
03.09.21 Determinants, Continuity and Differentiability
Maths
03.09.21 National income and related aggregates
Economics
03.09.21 Heredity and variation, Molecular basis of inheritance, Evolution,
Biology
Human health and diseases
03.09.21 Meetings life challenges, Psychological disorders, Therapeutic
Psychology
approaches
Lesson 23 to 26; Composition on open ended topics with clues;
03.09.21 Unseen Passage & grammar (Personal Pronouns, infinitive and
French
sentence re-ordering)
Class XII (Pg. 014)
6TH SUBJECTS
The Deccan School, The Indian National Flag, The Rajasthani
Schools of Miniature Paintings, Bengal School of Paintings,
Contribution of Indian artists in the struggle for National
Applied Arts 11.09.21 Freedom Movement, The Pahari School of Miniature
& Painting Paintings, The Modern Trends in Indian Art, Paintings,
Sculpture, The Mughal Schools of Miniature Paintings
Six Limbs of Indian Painting and fundamentals of Visual Arts
(Elements & Principles)
Definition of the following terms :-
Peshkar, Uthan, Fard, Chakkradar, Baont.
Definition of the following terms :-History of Tabla and Pakhawaj
Brief Description of Gharanas--Tabla and Pakhawaj
1. Comparative study of some antartals
a) Chautal - Ektal
b) Jhaptal – Sool Tala
c) Tilwara - Teentala
Tabla 11.09.21
2. Description of Talas prescribed for class XII practical.
3. Writing notation of the prescribed tals and composition.
4. Recognition of talas from given portion of the thekas and
composition.
Brief History of Medival and Modern period of Hindustani Music
specially in the field of Percussion instruments. Biographies of
Musicians – Pandit Kishan Maharaj, Raja Chattrapati Singh, Ustad
Karmatullah Khan
Description of Ragas and ability to recognize Ragas from given passages of
swaras. Description of Raag Bhairav, Write the composition (gat) notation,
One Masitkhani and one Razakhani Gat in Raag Bhairav. Knowledge of
structure of tuning of instrument opted for. Life sketch of Abdul Halim
Zafer, Description of Raag Shuddha Sarang and its notations, one
11.09.21 Masitkhani and one Razakhani, Gat in Teental. Detail study of Sangeet
Sitar Ratnakar. Definition of Varna, Alankar, Krintan, Zamzama, Any two raag
masit khani gat, few todas, Ability to recognize raag from passage of Swar
song or played by the examiner. Classification of Ragas. Detail study of
Sangeet Parijat, Description of Kan, Meend, Murki, Gamak, Gram,
Murchchana. Description of Raag Bagheshwari, Biography of Ustad
Mushtaq Ali Khan
Definition of following – Varna, Alankar, Khatka, Kan, Meend, Description of
11.09.21 Raag Bhairav.Biography of Ustad Faiyaz Khan.Contribution and short life sketch of
Vocal Ustad Abdul Karim Khan. ‘Sangeet Ratnakar’. Definition of Gamak, Murchhana,
Murki, Grama, Alaap, Tana. Biography of Pandit Krishna Rao Shankar Pandit..
Class XII (Pg. 015)
Description of Raag Bageshri. Classification of Ragas. ‘Sangeet Parijat’.
Biography of Ustad Bade Ghulam Ali Khan.
A brief history and Acquaintance with other classical styles or folk
form prevalent in the region, other than the one offered for study.
Acquaintance with the life history of the chief exponents and
contributors of the past of the dance form (Rukmini Devi Arundale,
Balasraswati, Meenakshi Sundaram Pillai, Tanjore quartette)
Acquaintance with the contents of the Abhinaya Darpana. (the
chapters as the aspects of dance dealts within them.)
Bharatnat 11.09.21 Nritta, Nritya, Natya, (Sanskrit slokas from the Abhinaya Darpana
and basic definition) Tandava (7 tandavas with detailed stories),
yam
Lasya, Lokadharmi, Natyadhovumi (definitions with examples)
Anga, Upanga, Pratyanga (slokas and meaning from Abhinaya
Darpana), Sthana, Chari, Mandala, bharmari, Utplavana (slokas and
meaning from Abinaya Darpana, Definitions of the following :
araimandi, muzhumandi, khuttanam, korvai, karvai, adavu, shollu,
aradhi, theerumana, jati, jaati, gati, avartana, yati, taalanga,
thattukazhi, nattuvangam, arangetram
1ST UNIT TEST SCHEDULE (1st Term)-COMMERCE & HUMANITIES
SUBJECT DATE SYLLABUS
English Core 15.04.21 Comprehension Passage (Prose)
Comprehension Passage (Prose), An Elementary School Classroom
English Core 17.04.21 in a Slum, Notice Writing.
24.04.21 Accounting for partnership firms: Fundamentals, Reconstitution:
Accountancy
Change in Profit Sharing ratio
Pol. Science 24.04.21 The End of bipolarity, New entries of power
Macro Economics- Unit I- National Income and Related Aggregate,
Economics 01.05.21 Unit II- Money and banking, Indian Economic Development - Chapter
1- Indian Economy on the eve of Independence.
Psychology 01.05.21 Variations in psychological attributes
Class XII (Pg. 016)
05.05.21 Case Studies (Ch- Nature and significance of management,
Busi. Studies
Principles of management, Business environment)
08.05.21 Nature and significance of management, Principles of management,
Busi. Studies
Business environment
08.05.21 Kinship, Caste & Class, Thinkers, Beliefs & Buildings, Map work
History
related to the chapters
5th Subjects
Hindi Core 24.06.21 vifBr x|ka'k
Computer 26.06.21 Python Revision Tour – I ,Python Revision Tour - II
Science
Informatics 26.06.21 Data Handlings-2 (Numpy, Python Pandas)
Practices
Information 26.06.21 Employment Skills, Vocational Skills, Unit-1—Basics of RDBMS (SQL)
Technology
Physical 26.06.21 Planning in Sports, Sports and Nutrition, Yoga & Lifestyle
Education
The Deccan School, The Indian National Flag, The Rajasthani
Applied Arts 26.06.21 Schools of Miniature Paintings, Bengal School of Paintings,
& Painting Contribution of Indian artists in the struggle for National
Freedom Movement, The Pahari School of Miniature Paintings
Definition of the following terms :-
Peshkar, Uthan, Fard, Chakkradar, Baont, Jhaptaal, Rupak Tala, Chautaal,
Ektaal, Dhamar
Definition of the following terms :-History of Tabla and Pakhawaj
Brief Description of Gharanas--Tabla and Pakhawaj
1. Comparative study of some antartals
26.06.21
Tabla a) Chautal - Ektal
b) Jhaptal – Sool Tala
c) Tilwara - Teentala
2. Description of Talas prescribed for class XII practical.
3. Writing notation of the prescribed tals and composition.
4. Recognition of talas from given portion of the thekas and
composition.
Description of Raag Bhairav with the composition (gat) notation, One
Masitkhani and one Razakhani Gat in Raag Bhairav. Knowledge of
26.06.21
Sitar structure of tuning of Sitar. Life sketch of Abdul Halim Zafer, Description
of Raag Shuddha Sarang and its notations, one Masitkhani and one
Razakhani, Gat in Teental. Detail study of Sangeet Ratnakar.
26.06.21 Definition of following – Varna, Alankar, Khatka, Kan, Meend,
Vocal Description of Raag Bhairav.Biography of Ustad Faiyaz Khan.Contribution
Class XII (Pg. 017)
and short life sketch of Ustad Abdul Karim Khan.
A brief history and acquaintance with other classical styles or folk
form prevalent in the region, other than the one offered for study.
Acquaintance with the life history of the chief exponents and
contributors of the past of the dance form (Rukmini Devi Arundel,
Bharatnat 26.06.21 Balasraswati, Meenakshi Sundaram Pillai, Tanjore quartette)
yam Acquaintance with the contents of the Abhinaya Darpana. (the
chapters as the aspects of dance dealts within them.)
Nritta, Nritya, Natya, (Sanskrit slokas from the Abhinaya Darpana
and basic definition) Tandava (7 tandavas with detailed stories),
Lasya, Lokadharmi, Natyadharmi (definitions with examples)
Legal 26.06.21 Topics in Law
Studies
Hindi 26.06.21 igyoku dh <ksyd, dSejs esa can vikfgt, lg"kZ Lohdkjk gS,
Core ued, m"kk, vrhr esa ncs ik¡o, jpukRed ys[ku, i= ys[ku
26.06.21
Maths Relation and functions, Inverse trigonometric functions, Matrices
Macro Economics- Unit I- National Income and Related Aggregate,
26.06.21
Economics Unit II- Money and banking, Indian Economic Development - Chapter
1- Indian Economy on the eve of Independence
26.06.21 Reproduction in organisms, Sexual reproduction in flowering plants,
Biology
Human reproduction, Reproductive health, Heredity and variation
26.06.21 Variations in psychological attributes, Self and personality
Psychology
Lesson 18 to 22; informal letter; unseen passage and grammar
26.06.21
French (Interrogative adjective and pronoun; simple and compose relative
pronouns; preposition and indefinitive adjectives and pronouns)
Class XII (Pg. 018)
2ND UNIT TEST SCHEDULE (1st Term)- COMMERCE & HUMANITIES
SUBJECT DATE SYLLABUS
English Core 05.08.21 Comprehension Passage (Poem)
07.08.21 A Thing of Beauty, The Rattrap, Invitations and Replies (Formal &
English Core
Informal)
14.08.21 Admission of partner, Reconstitution of partnership: Retirement
Accountancy
and death of a partner, Dissolution of a partnership firm
South Asia and Contemporary World, United Nations and its
14.08.21
Pol. Science organizations, Security in contemporary world, Environment and
Naturl resources, Globalisation.
Macro Economics- Unit III Determination of Income and
21.08.21 Employment, Indian Economic Development - Indian Economy 1947-
Economics
1990, Economic Reforms since 1991, Poverty, Human Capital
Formation
21.08.21 Self & Personality, Meetings life challenges, Psychological disorders
Psychology
25.08.21 Case studies (Ch-Planning, Organizing, Staffing)
Busi. Studies
Busi. Studies 28.08.21 Planning, Organizing, Staffing
28.08.21 Through the Eyes of Travellers, Bhakti-Sufi Traditions, An Imperial
History
Capital: Vijayanagara, Map work related to the chapters
5th Subjects
Hindi Core 01.09.21 vifBr dkO;ka'k
Computer 03.09.21 Data File Handling, Pointers
Science
Computer 03.09.21 Ch-3 Functions, Ch-4 Python Libraries, Ch-5 File Handling, Ch-6
Science Recursion
Informatics 03.09.21 Data Handling-2 (Plotting with Pyplot), Introduction to Software
Practices Engineering.
Information 03.09.21 Unit-3—Fundamentals of JAVA Programming (Introduction, OOPs,
Technology JAVA Language Elements, Operators, Control Flow, Array)
Physical 03.09.21 Physical Education & Sports for Differently-Abled, Children and
Education Sports, Women & Sports, Test and Measurement in Sports
03.09.21 The Modern Trends in Indian Art, Paintings, Sculpture, The
Applied Arts
Mughal Schools of Miniature Paintings
Class XII (Pg. 019)
Brief History of Medieval and Modern period of Hindustani Music
03.09.21 especially in the field of Percussion instruments. Biographies of Musicians
Tabla – Pandit Kishan Maharaj, Raja Chattrapati Singh, Ustad Karamatullah
Kha,. Dhamar & Khemta
Classification of Ragas. Detail study of Sangeet Parijat, Description of Kan,
03.09.21 Meend, Murki, Gamak, Gram, Murchchana. Description of Raag
Sitar
Bagheshwari, Biography of Ustad Mushtaq Ali Khan
‘Sangeet Ratnakar’. Definition of Gamak, Murchhana, Murki, Grama,
03.09.21 Alaap, Tana. Biography of Pandit Krishna Rao Shankar Pandit..
Vocal Description of Raag Bageshri. Jhaptaal & Tilwada in dugun and Rupak
Taal.
Anga, Upanga, Pratyanga (slokas and meaning from Abhinaya
Darpana), Sthana, Chari, Mandala, bharmari, Utplavana (slokas and
Bharatnat 03.09.21 meaning from Abinaya Darpana, Definitions of the following :
yam araimandi, muzhumandi, khuttanam, korvai, karvai, adavu, shollu,
aradhi, theerumana, jati, jaati, gati, avartana, yati, taalanga,
thattukazhi, nattuvangam, arangetram
Legal 03.09.21 Tribunal, Adjudication and Alternate Dispute Resolution Human
Studies Rights in India
f'kjh"k ds Qwy, dforkoyh, y{e.k&ewPNkZ vkSj jke dk foyki,
Hindi 03.09.21
Core Mk;jh ds iUus, tulapkj ek/;e, pkyhZ pSfIyu ;kuh ge lc
ckny jkx
03.09.21 Determinants, Continuity and Differentiability
Maths
Macro Economics- Unit III Determination of Income and
03.09.21 Employment, Indian Economic Development - Indian Economy 1947-
Economics
1990, Economic Reforms since 1991, Poverty, Human Capital
Formation
03.09.21 Molecular basis of inheritance, Evolution, Human health and
Biology
diseases, Strategies for improvement in food production
03.09.21 Meetings life challenges, Psychological disorders, Therapeutic
Psychology
approaches
Lesson 23 to 26; Composition on open ended topics with clues;
03.09.21 Unseen Passage & grammar (Personal Pronouns, infinitive and
French
sentence re-ordering)
Class XII (Pg. 020)
6TH SUBJECTS
The Deccan School, The Indian National Flag, The Rajasthani
Schools of Miniature Paintings, Bengal School of Paintings,
Applied Arts 11.09.21 Contribution of Indian artists in the struggle for National
& Painting Freedom Movement, The Pahari School of Miniature Paintings,
The Modern Trends in Indian Art, Paintings, Sculpture, The
Mughal Schools of Miniature Paintings
Definition of the following terms :-
Peshkar, Uthan, Fard, Chakkradar, Baont.
Definition of the following terms :-History of Tabla and Pakhawaj
Brief Description of Gharanas—Tabla and Pakhawaj
1. Comparative study of some antartals
a) Chautal — Ektal
b) Jhaptal – Sool Tala
11.09.21 c) Tilwara — Teentala
Tabla 2. Description of Talas prescribed for class XII practical.
3. Writing notation of the prescribed tals and composition.
4. Recognition of talas from given portion of the thekas and
composition.
Brief History of Medival and Modern period of Hindustani Music
specially in the field of Percussion instruments. Biographies of
Musicians – Pandit Kishan Maharaj, Raja Chattrapati Singh, Ustad
Karamatullah Khan
Description of Ragas and ability to recognize Ragas from given passages of
swaras. Description of Raag Bhairav, Write the composition (gat) notation,
One Masitkhani and one Razakhani Gat in Raag Bhairav. Knowledge of
structure of tuning of instrument opted for. Life sketch of Abdul Halim
Zafer, Description of Raag Shuddha Sarang and its notations, one Masitkhani
11.09.21
Sitar and one Razakhani, Gat in Teental. Detail study of Sangeet Ratnakar.
Definition of Varna, Alankar, Krintan, Zamzama, Any two raag masit khani
gat, few todas, Ability to recognize raag from passage of Swar song or
played by the examiner. Classification of Ragas. Detail study of Sangeet
Parijat, Description of Kan, Meend, Murki, Gamak, Gram, Murchchana.
Description of Raag Bagheshwari, Biography of Ustad Mushtaq Ali Khan
Definition of following – Varna, Alankar, Khatka, Kan, Meend, Description
of Raag Bhairav.Biography of Ustad Faiyaz Khan.Contribution and short life
sketch of Ustad Abdul Karim Khan. ‘Sangeet Ratnakar’. Definition of
11.09.21 Gamak, Murchhana, Murki, Grama, Alaap, Tana. Biography of Pandit
Vocal
Krishna Rao Shankar Pandit.. Description of Raag Bageshri. Classification of
Ragas. ‘Sangeet Parijat’.
Biography of Ustad Bade Ghulam Ali Khan.
Class XII (Pg. 021)
A brief history and Acquaintance with other classical styles or folk
form prevalent in the region, other than the one offered for study.
Acquaintance with the life history of the chief exponents and
contributors of the past of the dance form (Rukmini Devi Arundale,
Balasraswati, Meenakshi Sundaram Pillai, Tanjore quartette)
Acquaintance with the contents of the Abhinaya Darpana. (the
chapters as the aspects of dance dealts within them.)
Bharatnat 11.09.21 Nritta, Nritya, Natya, (Sanskrit slokas from the Abhinaya Darpana
and basic definition) Tandava (7 tandavas with detailed stories),
yam
Lasya, Lokadharmi, Natyadhovumi (definitions with examples)
Anga, Upanga, Pratyanga (slokas and meaning from Abhinaya
Darpana), Sthana, Chari, Mandala, bharmari, Utplavana (slokas and
meaning from Abinaya Darpana, Definitions of the following :
araimandi, muzhumandi, khuttanam, korvai, karvai, adavu, shollu,
aradhi, theerumana, jati, jaati, gati, avartana, yati, taalanga,
thattukazhi, nattuvangam, arangetram
UNIT TEST SCHEDULE (2ND TERM)-SCIENCE
SUBJECT DATE SYLLABUS
English Core 15.09.21 Comprehension Passage (Prose)
18.09.21 Comprehension Passage (Prose), Aunt Jennifer’s Tigers, The Enemy,
English Core
Article writing, Formal Letters
Maths 25.09.21 Application of Derivative, Integrals
Strategies for improvement in food production, Microbes in human
Biology 25.09.21 welfare, Biotechnology-Principles and Processes, Biotechnology and
its application
5TH SUBJECTS
Hindi Core 29.09.21 vifBr x|ka’k
Computer 04.10.21 Ch-7 Idea of efficiency, Ch 8 & 9 Data Structure, Ch 10 Networking
Science Concepts
Informatics 04.10.21 Data Management -2 (Web Development with Django)
Practices
Information 04.10.21
Unit-3- JAVA Programming (Class Design, Exception Handling,
Technology
Class XII (Pg. 022)
Assertions, Threads, Wrapers Class, String Manipulations)
Physical 04.10.21 Physiology and Injuries in sports, Biomechanics & Sports,
Education Psychology & Sports
Applied Arts 04.10.21 Contemporary (Modern) Indian Art, Graphic-prints, Sculptures
& Painting
04.10.21 Classification of Jatis of different patterns. Classification of
Tabla Layakari
Time theory of Ragas, Meend in Raag Bhairav
04.10.21 Biography of Ustad Alauddin Khan, Ustad Inayat Khan . Ability to recite
Sitar Thekas of Tilwar, Dhamar and Rupak taal with thah and dugun, keeping
tala with hand beats.Description of Raag Malkauns.
04.10.21
Vocal Time theory of Raga. Description of Raag Shuddh Sarang.
Ability to write a korvai of two avartanams in Adi taalam with Adavu
Bharatnat 04.10.21 syllable. Abhinaya (Angika, Vachika, Satvika, Aharya-slokas from the
yam Abhinaya Darpan along with the meaning) with special reference to hasta-
Abhinaya, Mukhaja Abhinaya and Netra Abhinaya (basic definition only)
Legal 04.10.21
Legal Profession in India, Legal Services
Studies
Je foHkktu vkSj tkfr&izFkk, esjh dYiuk dk vkn’kZ lekt, NksVk
Hindi 04.10.21
Core esjk [ksr, cxqyksa ds ia[k, dfork] dgkuh] ukVd vkSj vkys[k ys[ku]
fizUV ek/;e ¼lekpkj½
04.10.21
Maths Application of Derivative, Integrals
04.10.21
Economics Money and banking, Determination of income and employment
Strategies for improvement in food production, Microbes in human
04.10.21
Biology welfare, Biotechnology-Principles and Processes, Biotechnology and
its application
04.10.21
Psychology Attitude and Social cognition, Social influence and Group processes
Lesson 27 to 30; writing a story based on outlines provided, Unseen
04.10.21
French passage & grammar (direct + indirect speech, reflexive pronoun,
sentence correction & tenses)
09.10.21 Electromagnetic Induction, Alternating Currents, Electromagnetic
Physics
Waves, Ray Optics
Class XII (Pg. 023)
p, d & f block elements, co-ordination compounds, Halo alkanes
Chemistry 20.10.21
and Halo arenes.
6th Subjects
Applied Arts
& Painting
22.10.21 Contemporary (Modern) Indian Art, Graphic-prints, Sculptures
Classification of Layakari, Teentaal, Jhaptaal, Ektaal, Kaharwa,
22.10.21
Tabla Dadra, Rela, Ckahradhar paran, Farmaisi in Sool Tal, Chautala,
Dhamar
Time theory of Ragas, Meend in Raag Bhairav
22.10.21 Biography of Ustad Alauddin Khan, Ustad Inayat Khan . Ability to
Sitar recite Thekas of Tilwada, Dhamar and Rupak taal with thah and
dugun, keeping tala with hand beats.Description of Raag Malkauns.
22.10.21 Time theory of Raga. Description of Raag Shuddha Sarang,
Vocal Biography of Ustad Bade ghulam Ali Khan, Taal Dhamar
Ability to write a korvai of two avartanams in Adi taalam with
Adavu syllable. Abhinaya (Angika, Vachika, Satvika, Aharya-slokas
Bharatnat 22.10.21 from the Abhinaya Darpan along with the meaning) with special
yam reference to hasta-Abhinaya, Mukhaja Abhinaya and Netra
Abhinaya (basic definition only)
UNIT TEST SCHEDULE (2ND TERM)-COMMERCE & HUMANITIES
SUBJECT DATE SYLLABUS
English Core 15.09.21 Comprehension Passage (Prose)
18.09.21 Comprehension Passage (Prose), Aunt Jennifer’s Tigers, The Enemy,
English Core
Article writing, Formal Letters
25.09.21 Accounting for Share Capital and Accounting for debentures: Issue
Accountancy
of debentures & N.P.O.
25.09.21 Challenges of Nation-Building, Planning and Development, India’s
Pol. Science
foreign policy, Parties and the party systems in India
5TH SUBJECTS
Hindi Core 29.09.21 vifBr x|ka'k
Computer 04.10.21 Ch-7 Idea of efficiency, Ch 8 & 9 Data Structure, Ch 10 Networking
Science Concepts
Informatics 04.10.21 Data Management -2 (Web Development with Django)
Practices
Class XII (Pg. 024)
Unit-3- JAVA Programming (Class Design, Exception Handling,
Information 04.10.21
Technology Assertions, Threads, Wrapers Class, String Manipulations)
04.10.21 Physiology and Injuries in sports, Biomechanics & Sports,
Phy. Edu.
Psychology & Sports
Applied Arts 04.10.21 Contemporary (Modern) Indian Art, Graphic-prints, Sculptures
& Painting
04.10.21 Dhamari Adadartala, Adi Tala, Stuti Param, Farmaisi Chakradar
Tabla
Time theory of Ragas, Meend in Raag Bhairav
04.10.21 Biography of Ustad Alauddin Khan, Ustad Inayat Khan . Ability to recite
Sitar Thekas of Tilwada, Dhamar and Rupak taal with thah and dugun, keeping
tala with hand beats.Description of Raag Malkauns.
04.10.21 Time theory of Raga. Description of Raag Shuddh Sarang.
Vocal
Ability to write a korvai of two avartanams in Adi taalam with
Adavu syllable. Abhinaya (Angika, Vachika, Satvika, Aharya-slokas
04.10.21
Bharatnatyam from the Abhinaya Darpan along with the meaning) with special
reference to hasta-Abhinaya, Mukhaja Abhinaya and Netra
Abhinaya (basic definition only)
04.10.21 Legal Profession in India, Legal Services
Legal Studies
Je foHkktu vkSj tkfr&izFkk, esjh dYiuk dk vkn’kZ lekt, NksVk
Hindi 04.10.21
Core esjk [ksr, cxqyksa ds ia[k, dfork] dgkuh] ukVd vkSj vkys[k ys[ku]
fizUV ek/;e ¼lekpkj½
04.10.21 Application of Derivative, Integrals
Maths
Macro Economics- Unit IV- Balance of Payment, Indian Economic
04.10.21 Development- Chapter 6- Rural Development, Chapter 7-
Economics
Employment- Growth, Informalisation and other issues, Chapter 8-
Infrastructure.
04.10.21 Microbes in human welfare, Biotechnology-Principles and
Biology
Processes, Biotechnology and its application
04.10.21 Attitude and Social cognition, Social influence and Group processes
Psychology
04.10.21 Lesson 27 to 30; writing a story based on outlines provided, Unseen
French
passage & grammar (direct + indirect speech, reflexive pronoun,
Class XII (Pg. 025)
sentence correction & tenses)
Busi. Studies 06.10.21 Case Studies (Ch- Directing, Controlling, Financial Management)
Busi. Studies 09.10.21 Directing, Controlling, Financial Management
Peasants, Zamindars & the State, Kings & Chronicles, Colonialism
History 09.10.21
and Country side, Map work related to the chapters
Macro Economics- Unit IV- Balance of Payment, Indian Economic
20.10.21 Development- Chapter 6- Rural Development, Chapter 7-
Economics
Employment- Growth, Informalisation and other issues, Chapter 8-
Infrastructure.
Therapeutic Approaches, Attitude and Social cognition, Social
20.10.21
Psychology influence and Group processes
6th Subjects
Applied Arts Contemporary (Modern) Indian Art, Graphic-prints, Sculptures
22.10.21
& Painting
Dadra, Kaharwa with Mihhda Tihai. Classification of Layakari,
22.10.21
Tabla Teentaal, Jhaptaal, Ektaal, Kaharwa, Dadra, Rela, Ckahradhar paran,
Farichi in Sool Tal, Chautala, Dhamar
Time theory of Ragas, Meend in Raag Bhairav
22.10.21 Biography of Ustad Alauddin Khan, Ustad Inayat Khan . Ability to
Sitar recite Thekas of Tilwada, Dhamar and Rupak taal with thah and
dugun, keeping tala with hand beats.Description of Raag Malkauns.
22.10.21 Time theory of Raga. Description of Raag Shuddha Sarang,
Vocal Biography of Ustad Bade ghulam Ali Khan, Taal Dhamar
Ability to write a korvai of two avartanams in Adi taalam with
Adavu syllable. Abhinaya (Angika, Vachika, Satvika, Aharya-slokas
22.10.21
Bharatnatyam from the Abhinaya Darpan along with the meaning) with special
reference to hasta-Abhinaya, Mukhaja Abhinaya and Netra
Abhinaya (basic definition only)
Busi. Studies 27.10.21 Case Studies (Ch- Directing, Controlling, Financial Management)
Class XII (Pg. 026)
ENGLISH CORE (Code No. 301)
Number of Registers - 1 (combined) for Literature & Language.
Month & Content
No. of Days
March+ April a. An Elementary School Class Room in a Slum
12+21 = 33 days (Poetry) - Flamingo
Learner’s Comate
I. Reading Comprehension
a. Passage – 1
II. Advanced Writing Skills
a. Notice
AIL
Draw sketches of the elementary school classroom in slum as
depicted in the chapter (poem).
a. Lost Spring (Prose) – Flamingo
b. A Roadside Stand- Flamingo
Learner’s Comate
I. Reading Comprehension
a. Passage 2
II. Advanced Writing Skills
a. Advertisements
May + June+July
b. Report Writing
7 + 15 + 26 =
48 days a. A Thing of Beauty (Poetry) - Flamingo
b. The Rattrap (Prose) - Flamingo
Learner’s Comate
I. Reading Comprehension
a. Passage 3
II. Advanced Writing Skills
a. Invitations & Replies (Formal & Informal)
Class XII (Pg. 027)
August a. Aunt Jennifer's Tigers (Poetry) - Flamingo
24 days b. The Enemy (Prose) – Vistas
Learner’s Comate
I. Reading Comprehension
a. Passage 4
II. Advanced Writing Skills
a. Articles
Sept. a. On the Face of It (Prose) - Vistas
25 days Learner’s Comate
I. Reading Cmprehension
a. Passage 5
II. Advanced Writing Skills
a. Formal Letters –
Oct.
19 days Learner’s Comate
I. Reading Comprehension
a. Passage 6
III. Advanced Writing Skills
REVISION: The Last Lesson, Deep Water, Indigo, Should
Wizard Hit Mommy, Evans Tries an O Level,My Mother At 66, Keeping
Quiet, The Third Level
Nov. Revision+ Pre Board I
20 days
Dec+Jan+Feb Preboard-II
25 +21 +22= 68 days Board Examination
Class XII (Pg. 028)
UNIT WISE DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
Class XII (Pg. 029)
XII - PHYSICS (Code No. - 042)
(2021-22)
Together with Physics (Rachna Sagar)—Lab Manual (with Lab
Register - 1 complete set) - XII
1 Single Lined Register.
Month & Content
No. of Days
Unit I: Electrostatics
March + Ch-1- Electric Charges and Fields.
April+May Electric Charges; Conservation of charge, Coulomb's law-
12+21+ 07 force between two point charges, forces between multiple
= 40 days charges; superposition principle and continuous charge
distribution. Electric field, electric field due to a point charge,
electric field lines, electric dipole, electric field due to a dipole,
torque on a dipole in uniform electric fleld. Electric flux,
statement of Gauss's theorem and its applications to find field
due to infinitely long straight wire, uniformly charged infinite
plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell (field
inside and outside).
Ch-2- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Electric potential, potential difference, electric potential due to
a point charge, a dipole and system of charges; equipotential
surfaces, electrical potential energy of a system of two point
charges and of electric dipole in an electrostatic field.
Conductors and insulators, free charges and bound charges
inside a conductor. Dielectrics and electric polarisation,
capacitors and capacitance, combination of capacitors in series
and in parallel, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with
and without dielectric medium between the plates, energy
stored in a capacitor.
Unit II: Current Electricity
Ch-3- Current Electricity
Electric current, flow of electric charges in a metallic
conductor, drift velocity, mobility and their relation with
electric current; Ohm's law, electrical resistance, V-I
characteristics (linear and non-linear), electrical energy and
power, electrical resistivity and conductivity, Carbon resistors,
colour code for carbon resistors; series and parallel
Class XII (Pg. 030)
combinations of resistors; temperature dependence of
resistance. Internal resistance of a cell, potential difference and
emf of a cell, combination of cells in series and in parallel,
Kirchhoff's laws and simple applications, Wheatstone bridge,
metre bridge. Potentiometer - principle and its applications to
measure potential difference and for comparing EMF of two
cells; measurement of internal resistance of a cell.
(LC to be discussed)
1 project to be allotted for summer vacation. (this project will
be evaluated for CBSE board practical exam.)
June + July Unit III: Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
15 + 26 = 41 days Ch-4- Moving Charges and Magnetism
Concept of magnetic field, Oersted's experiment. Biot - Savart law
and its application to current carrying circular loop. Ampere's law
and its applications to infinitely long straight wire. Straight and
toroidal solenoids (only qualitative treatment), force on a moving
charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields, Cyclotron. Force on
a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field, force
between two parallel current-carrying conductors-definition of
ampere, torque experienced by a current loop in uniform magnetic
field; moving coil galvanometer-its current sensitivity and
conversion to ammeter and voltmeter.
Ch-5- Magnetism and Matter
Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment,
magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron, magnetic field
intensity due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) along its axis and
perpendicular to its axis, torque on a magnetic dipole (bar magnet)
in a uniform magnetic field; bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid,
magnetic field lines; earth's magnetic field and magnetic elements.
Para-, dia- and ferro - magnetic substances, with examples.
Electromagnets and factors affecting their strengths, permanent
magnets.
Unit IV : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
Ch-6- Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic induction; Faraday's laws, induced EMF and
current; Lenz's Law, Eddy currents. Self and mutual induction.
(LC to be discussed)
Class XII (Pg. 031)
August Ch- 7- Alternating Currents
24 days Alternating currents, peak and RMS value of alternating
current/voltage; reactance and impedance; LC oscillations
(qualitative treatment only), LCR series circuit, resonance;
power in AC circuits, power factor, wattless current. AC
generator and transformer.
Unit V : Electromagnetic Waves
Ch-8- Electromagnetic Waves
Basic idea of displacement current, Electromagnetic waves,
their characteristics, their Transverse nature (qualitative ideas
only).
Electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves, microwaves, infrared,
visible, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays) including elementary
facts about their uses.
AIL
Making cartoons on ‘e.m.w.’ for dealing the E.M. spectra, their
sequence according to wavelength or frequency. (using proverbs as
analogy with cartoon presentations)
A skit to be presented to show behavior of conductors and
insulators in external electric field.
Unit VI: Optics
Ch-9- Ray Optics and Optical instruments
Ray Optics: Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, mirror
formula, refraction of light, total internal reflection and its
applications, optical fibres, refraction at spherical surfaces,
lenses, thin lens formula, lensmaker's formula, magnification,
power of a lens, combination of thin lenses in contact,
refraction and dispersion of light through a prism.
Scattering of light - blue colour of sky and reddish
apprearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset.
Optical instruments: Microscopes and astronomical
telescopes (reflecting and refracting) and their magnifying
powers.
(LC to be discussed)
Class XII (Pg. 032)
Sept. Ch-10- Wave Optics
25 days Wave Optics: Wave front and Huygen's principle, reflection
and refraction of plane wave at a plane surface using wave
fronts. Proof of laws of reflection and refraction using
Huygen's principle. Interference, Young's double slit
experiment and expression for fringe width, coherent sources
and sustained interference of light, diffraction due to a single
slit, width of central maximum, resolving power of microscope
and astronomical telescope, polarisation, plane polarised light,
Brewster's law, uses of plane polarised light and Polaroids.
Unit VII: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Ch-11- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Dual nature of radiation, Photoelectric effect, Hertz and
Lenard's observations; Einstein's photoelectric equation-
particle nature of light. Experimental study of Photo electric
effect. Matter waves-wave nature of particles, de-Broglie
relation, Davisson-Germer experiment (experimental details
should be omitted; only conclusion should be explained).
Unit VIII: Atoms & Nuclei
Ch-12- Atoms
Alpha-particle scattering experiment; Rutherford's model of
atom; Bohr model, energy levels, hydrogen spectrum.
Ch-13- Nuclei
Composition and size of nucleus, Radioactivity, alpha, beta
and gamma particles/rays and their properties; radioactive
decay law. Half Life and Mean Life. Mass-energy relation,
mass defect; binding energy per nucleon and its variation with
mass number; nuclear fission, nuclear fusion.
(LC to be discussed)
Oct. Unit IX: Electronic Devices
19 days Ch-14- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and
Simple Circuits.
Energy bands in conductors, semiconductors and insulators
(qualitative ideas only) Semiconductor diode - I-V
characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as a rectifier;
Special purpose p-n junction diodes: LED, photodiode, solar
cell and Zener diode and their characteristics, zener diode as a
voltage regulator. (LC to be discussed)
Class XII (Pg. 033)
Nov. Revision + Preboard-I
20 days
Dec+ Jan+Feb Preboard-II
25 +21 +22=68 Board Examination
days
PRACTICALS
Note - The record to be submitted by the students at the time of their annual examination has to
include -
Record of at least 12 Experiments [with 6 from each section], to be performed by the students
Record of at least 6 Activities [with 3 each from section A and section B], to be performed by the
students
The Report of the project to be carried out by the students.
SECTION - A
Experiments
1. To determine Resistivity of two/three wires by plotting a graph of potential difference versus current.
2. To find resistance of a given wire using metre bridge.
3. To verify the laws of combination (series) of resistances using a metre bridge.
4. To compare the EMF of two given primary cells using potentiometer.
5. To determine resistance of a galvanometer by half-deflection method and to find its figure of merit.
6. To convert the given galvanometer (of known resistance and figure of merit) into a voltmeter of desired
range and to verify the same.
Activities (for the purpose of demonstration only)
1. To measure resistance, voltage (AC/DC), current (AC) and check continuity of a given circuit using
multimeter.
2. To assemble a household circuit comprising three bulbs, three (on/off) switches, a fuse and a power
source.
3. To study the variation in potential drop with length of a wire for a steady current.
SECTION B
Experiments
1. To find the value of v for different values of u in case of a concave mirror and to find the focal length.
2. To find the focal length of a convex lens by plotting graphs between u and v or between 1/u and 1/v.
3. To determine angle of minimum deviation for a given prism by plotting a graph between the angle of
incidence and angle of deviation.
4. To find the refractive index of a liquid by using convex lens and plane mirror.
5. To draw the I-V characteristic curve of a p-n junction in forward bias and reverse bias.
6. To draw the characteristic curve of a zener diode and to determine its reverse breakdown voltage.
Activities (For the purpose of demonstration only)
1. To identify a diode, an LED, a resistor and a capacitor from mixed collection of such items.
2. To study effect of intensity of light (by varying distance of the source) on an L.D.R.
3. To obtain a lens combination with the specified focal length by using two lenses from the given set of
lenses.
Class XII (Pg. 034)
STUDENTS WILL BE ALLOTTED ONE PROJECT DURING THE SUMMER VACATION
CLASS XII
1. To study various factors on which the internal resistance/EMF of a cell depends.
2. To study the variations in current flowing in a circuit containing an LDR because
of a variation in (a) the power of the incandescent lamp, used to 'illuminate' the
LDR (keeping all the lamps at a fixed distance). (b) the distance of a incandescent
lamp (of fixed power) used to 'illuminate' the LDR.
3. To find the refractive indices of (a) water (b) oil (transparent) using a plane
mirror, an equi convex lens (made from a glass of known refractive index) and an
adjustable object needle.
4. To investigate the relation between the ratio of (i) output and input voltage and
(ii) number of turns in the secondary coil and primary coil of a self-designed
transformer.
5. To investigate the dependence of the angle of deviation on the angle of incidence
using a hollow prism filled one by one, with different transparent fluids.
6. To estimate the charge induced on each one of the two identical styrofoam (or
pith) balls suspended in a vertical plane by making use of Coulomb's law.
7. To study the factor on which the self-inductance of a coil depends by observing
the effect of this coil, when put in series with a resistor/(bulb) in a circuit fed up by
an A.C. source of adjustable frequency.
8. To study the earth's magnetic field using a tangent galvanometer.
Class XII (Pg. 035)
UNIT WISE DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
THEORY
UNIT MARKS
Unit I Electrostatics
16
Unit II Current Electricity
Unit III Magnetic effect of current & Magnetism
17
Unit IV Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating current
Unit V Electromagnetic Waves
18
Unit VI Optics
Unit VII Dual Nature of Radiation & Matter
12
Unit VIII Atoms and Nuclei
Unit IX Electronic Devices 07
TOTAL 70
PRACTICAL
i) Two experiments one from each section 07 + 07
ii) Practical record [Experiments + Activities] 05
iii) One activity from any section 03
iv) Investigatory Project 03
v) Viva on experiments, activities and project 05
TOTAL 30
Class XII (Pg. 036)
XII - CHEMISTRY (Code No. - 043)
(2021-22)
Together with Chemistry Laboratory Manual - (with Lab Register - 1 complete set) – XII Rachna Sagar
1 Single Lined Register.
Month & Content
No. of Days
Unit I :--Solid State
March+April Classification of solids based on different binding forces: molecular, ionic,
12+21=33 days covalent and metallic solids, amorphous and crystalline solids (elementary
idea). Unit cell in two dimensional and three dimensional lattices, calculation
of density of unit cell, packing in solids, packing efficiency, voids, number of
atoms per unit cell in a cubic unit cell, point defects, electrical and magnetic
properties. Band theory of metals, conductors, semiconductors and insulators
and n and p type semiconductors.
Unit II: Solutions
Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in
liquids, solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, colligative properties -
relative lowering of vapour pressure, Raoult's law, elevation of boiling point,
depression of freezing point, osmotic pressure, determination of molecular
masses using colligative properties, abnormal molecular mass, Van't Hoff
factor.
(LC to be discussed)
1 project to be allotted to the students for the summer vacation. (this project
will be evaluated for CBSE board practical exam.)
Unit III: Electrochemistry
Redox reactions, EMF of a cell, standard electrode potential, Nernst equation
and its application to chemical cells, Relation between Gibbs energy change
and EMF of a cell, conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific and molar
conductivity, variations of conductivity with concentration, Kohlrausch's
Law, electrolysis and law of electrolysis (elementary idea), dry cell-
electrolytic cells and Galvanic cells, lead accumulator, fuel cells, corrosion.
May + June+July (LC to be discussed)
7 + 15 + 26 = Unit IV :--Chemical Kinetics
Rate of a reaction (Average and instantaneous), factors affecting rate of
48 days reaction: concentration, temperature, catalyst; order and molecularity of a
reaction, rate law and specific rate constant,integrated rate equations and half
life (only for zero and first order reactions), concept of collision theory
(elementary idea, no mathematical treatment). Activation energy, Arrhenious
equation.
Unit V: Surface Chemistry
Adsorption - physisorption and chemisorption, factors affecting adsorption of
gases on solids, catalysis: homogenous and heterogenous, activity and
selectivity of solid catalysts; enzyme catalysis, colloidal state: distinction
between true solutions, colloids and suspension; lyophilic, lyophobic, multi-
Class XII (Pg. 037)
molecular and macromolecular colloids; properties of colloids; Tyndall effect,
Brownian movement, electrophoresis, coagulation, emulsion - types of
emulsions.
Unit VI: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Principles and methods of extraction - concentration, oxidation, reduction -
electrolytic method and refining; occurrence and principles of extraction of
aluminium, copper, zinc and iron.
(LC to be discussed)
August Unit VII:p-Block Elements
24 days Group -15 Elements: General introduction, electronic configuration,
occurrence, oxidation states, trends in physical and chemical properties;
Nitrogen preparation properties and uses; compounds of Nitrogen:
preparation and properties of Ammonia and Nitric Acid, Oxides of Nitrogen
(Structure only); Phosphorus - allotropic forms, compounds of Phosphorus:
Preparation and properties of Phosphine, Halides and Oxoacids (elementary
idea only).
Group 16 Elements: General introduction, electronic configuration,
oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties,
dioxygen: preparation, properties and uses, classification of Oxides, Ozone,
Sulphur -allotropic forms; compounds of Sulphur: preparation properties and
uses of Sulphur-dioxide, Sulphuric Acid: industrial process of manufacture,
properties and uses; Oxoacids of Sulphur (Structures only).
Group 17 Elements: General introduction, electronic configuration,
oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties;
compounds of halogens, Preparation, properties and uses of Chlorine and
Hydrochloric acid, interhalogen compounds, Oxoacids of halogens (structures
only).
Group 18 Elements: General introduction, electronic configuration,
occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties, uses.
Unit VIII: d and f Block Elements
General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics
of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first row transition
metals – metallic character, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, ionic radii,
colour, catalytic property, magnetic properties, interstitial compounds, alloy
formation, preparation and properties of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4.
Lanthanoids - Electronic configuration, oxidation states, chemical reactivity
and lanthanoid contraction and its consequences.
Actinoids - Electronic configuration, oxidation states and comparison with
lanthanoids.
Unit IX: Coordination Compounds
Coordination compounds - Introduction, ligands, coordination number,
colour, magnetic properties and shapes, IUPAC nomenclature of
mononuclear coordination compounds. Bonding, Werner's theory, VBT, and
CFT; structure and stereoisomerism, importance of coordination compounds
(in qualitative analysis, extraction of metals and biological system).
Class XII (Pg. 038)
AIL
Presentation through slideshow/PPT. The students will present the
core principles of the chapter through the slides and make concept
maps.
Sept. Unit X: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes.
25 days Haloalkanes: Nomenclature, nature of C–X bond, physical and chemical
properties, optical rotation mechanism of substitution reactions.
Haloarenes: Nature of C–X bond, substitution reactions (Directive influence
of halogen in monosubstituted compounds only). Uses and environmental
effects of - dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane,
iodoform, freons, DDT.
Unit XI: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Alcohols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical
properties (of primary alcohols only), identification of primary, secondary
and tertiary alcohols, mechanism of dehydration, uses with special reference
to methanol and ethanol.
Phenols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical
properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophillic substitution reactions, uses
of phenols.
Ethers: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical
properties, uses.
Unit XII: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes and Ketones: Nomenclature, nature of carbonyl group, methods
of preparation, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of nucleophilic
addition, reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes, uses.
Carboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of preparation,
physical and chemical properties; uses.
Oct. Unit XIII: Amines
19 days Amines: Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of
preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses, identification of
primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Diazonium salts: Preparation,
chemical reactions and importance in synthetic organic chemistry.
Unit XIV: Biomolecules
Carbohydrates - Classification (aldoses and ketoses),
monosaccahrides (glucose and fructose), D-L configuration
oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), polysaccharides (starch,
cellulose, glycogen); Importance of carbohydrates.
Proteins -Elementary idea of - amino acids, peptide bond,
polypeptides, proteins, structure of proteins - primary, secondary,
tertiary structure and quaternary structures (qualitative idea only),
denaturation of proteins; enzymes. Hormones - Elementary idea
excluding structure.
Vitamins - Classification and functions.
Class XII (Pg. 039)
Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA.
Unit XV: Polymers
Classification - natural and synthetic, methods of polymerization
(addition and condensation), copolymerization, some important
polymers: natural and synthetic like polythene, nylon polyesters,
bakelite, rubber. Biodegradable and non-biodegradable polymers.
Unit XVI: Chemistry in Everyday life
Chemicals in medicines - analgesics, tranquilizers antiseptics,
disinfectants, antimicrobials, antifertility drugs, antibiotics, antacids,
antihistamines. Chemicals in food - preservatives, artificial
sweetening agents, elementary idea of antioxidants. Cleansing
agents- soaps and detergents, cleansing action. Nucleic Acids: DNA
and RNA.
Unit XV: Polymers
Classification - natural and synthetic, methods of polymerization
(addition and condensation), copolymerization, some important
polymers: natural and synthetic like polythene, nylon polyesters,
bakelite, rubber. Biodegradable and non-biodegradable polymers.
Unit XVI: Chemistry in Everyday life
Chemicals in medicines - analgesics, tranquilizers antiseptics,
disinfectants, antimicrobials, antifertility drugs, antibiotics, antacids,
antihistamines.
Chemicals in food - preservatives, artificial sweetening agents,
elementary idea of antioxidants.
Cleansing agents- soaps and detergents, cleansing action.
Nov. Revision + Pre Board I
20 days
Dec+ Jan+Feb Preboard-II
25 +21 +22=68 days Board Examination
Class XII (Pg. 040)
PRACTICALS
A. Surface Chemistry
(a) Preparation of one lyophilic and one lyophobic sol Lyophilic sol - starch, egg albumin and
gum
Lyophobic sol - aluminium hydroxide, ferric hydroxide, arsenous sulphide.
(b) Study of the role of emulsifying agents in stabilizing the emulsion of different oils.
B. Chemical Kinetics
(a) Effect of concentration and temperature on the rate of reaction between sodium thiosulphate
and hydrochloric acid.
C. Chromatography
i) Separation of pigments from extracts of leaves and flowers by paper chromatography
and determination of Rf values.
D. Preparation of Inorganic Compounds
i) Preparation of double salt of ferrous ammonium sulphate or potash alum.
E. Preparation of Organic Compounds
Preparation of any one of the following compounds
i) Acetanilide
ii) Di -benzal acetone
F. Test for the functional groups present in organic compounds:
Unsaturation, Alcoholic, phenolic, aldehydic, ketonic, carboxylic and amino (Primary)groups.
G. Determination of concentration/ molarity of KMnO4 solution by titrating it against
a standard solution of:
i) Oxalic acid,
ii) Ferrous ammonium sulphate
(Students will be required to prepare standard solutions by weighing themselves).
H. Qualitative analysis
Determination of one cation and one anion in a given salt.
Cations - Pb2+,Cu2+, As3+, Al3+, Fe3+, Mn2+, Zn+2 , Co2+, Ni2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, Ca2+, NH4+,
Mg2+
-
Anions - CO3 2-, S2-, SO32-, NO2–, Cl–, Br–, I–, NO3 , C2O4 2-, CH3COO–, SO42-, PO4 3-
(Note: Insoluble salts excluded)
Class XII (Pg. 041)
INVESTIGATORY PROJECT (One project to be allotted for summer vacation)
Study of presence of oxalate ions in guava fruit at different stages of
ripening.
Study of quantity of casein present in different samples of milk.
Preparation of soybean milk and its comparison with the natural milk with
respect to curd formation, effect of temperature, etc.
Study of the effect of potassium bisulphate as food preservative under
various conditions (temperature, concentration, time etc.) :
Study of digestion of starch by salivary amylase and, effect of pH and
temperature on it.
Comparative study of the rate of fermentation of following materials: wheat
flour, gram flour, potato juice, carrot juice etc.
Extraction of essential oils present in Saunf (aniseed), Ajwain (carum),
Illaichi (cardamom).
Study of common food adulterants in fat, oil, butter, sugar, turmeric powder,
chilli powder
and pepper.
Class XII (Pg. 042)
UNIT WISE DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
THEORY
UNIT MARKS
Unit I Solid State
Unit II Solutions
Unit III Electrochemistry 23
Unit IV Chemical kinetics
Unit V Surface chemistry
Unit VI General principles and processes of Isolation of Elements
Unit VII p-Block Elements
Unit VIII d- and f- Block Elements 19
Unit IX Coordination Compounds
Unit X Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Unit XI Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Unit XII Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids
Unit XIII Amines 28
Unit XIV Biomolecules
Unit XV Polymers
Unit XVI Chemistry in Everyday life
TOTAL 70
PRACTICAL
i) Volumetric Analysis 08
ii) Salt Analysis 08
iii) Content Based Experiment 06
iv) Project Work 04
v) Class Record + Viva 04
TOTAL 30
Class XII (Pg. 043)
XII - BIOLOGY (Code No. - 044)
Together with Biology Laboratory Manual - (with Lab Register - 1 complete set) – XII Rachna Sagar
1 Single Lined Register.
Month & Content
No. of Days
March+April Unit -I - REPRODUCTION
12+21=33 days Ch-1 Reproduction in organisms: Reproduction, a
characteristic feature of all organisms for continuation of
species; modes of reproduction - asexual and sexual
reproduction; asexual reproduction - binary fission,
sporulation, budding, gemmule formation, fragmentation;
vegetative propagation in plants; events in sexual reproduction
Ch-2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants: Flower
structure; development of male and female gametophytes;
pollination - types, agencies and examples; outbreeding
devices; pollen-pistil interaction; double fertilization; post
fertilization events - development of endosperm and embryo,
development of seed and formation of fruit; special modes-
apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed
dispersal and fruit formation
Ch-3 Human Reproduction: Male and female reproductive
systems; microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary;
gametogenesis - spermatogenesis and oogenesis; menstrual
cycle; fertilisation, embryo development upto blastocyst
formation, implantation; pregnancy and placenta formation
(elementary idea); parturition (elementary idea); lactation
(elementary idea).
Ch-4 Reproductive health: Need for reproductive health and
prevention of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs); birth
control - need and methods; medical termination of pregnancy
(MTP); amniocentesis; infertility and assisted reproductive
technologies - IVF, ZIFT, GIFT, AI (brief overview).
Practicals -
1. Study pollen germination on slide.
2. Study of flowers adapted to pollination by different agencies
(wind, insect, bird)
3. Study of pollen germination on stigma through a permanent slide.
4. Study and identify stages of gamete development i.e. T.S. testis
Class XII (Pg. 044)
and T.S. ovary through permanent slides. (from grass hopper/mice)
5. Study of T.S. of blastula through permanent slides. (mammalian)
6. Exercise on controlled pollination-Emasculation, tagging and
bagging.
(LC to be discussed)
Unit - II GENETICS AND EVOLUTION
Ch-5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Heredity and variation, Mendelian inheritance; deviations from
Mendelism – incomplete dominance, co-dominance, multiple alleles
and inheritance of blood groups, pleiotropy; elementary idea of
polygenic inheritance; chromosome theory of inheritance;
chromosomes and genes; linkage and crossing over; Sex
determination - in human being, birds, grasshopper and honey bee;
Mutation, Pedigree analysis, sex linked inheritance - haemophilia,
colour blindness; Mendelian disorders in humans –sickle cell
anaemia, Phenylketonuria, thalassemia; chromosomal disorders in
humans; Down's syndrome, Turner's and Klinefelter's syndromes.
AIL
Presentation of the results of hybridization experiment by Mendel in
front of those scientists who have verified it later. Students will
enact the roles of those scientists.
May + June+July Practicals--
7 + 15 + 26 = 7. Study Mendelian inheritance using seeds of different colour/size
48 days of any plant.
8. Study prepared pedigree charts of any one of genetic traits such as
rolling of tongue, blood groups, ear lobes, widow’s peak, colour
blindness.
9. Prepare a temporary mount of onion root tip to study mitosis.
(LC to be discussed)
Ch-6 Molecular basis of inheritance: Structure of DNA and
RNA; DNA packaging; Search for genetic material and DNA
as genetic material; DNA replication; Central Dogma;
transcription, genetic code, translation; gene expression and
regulation - lac operon; Human genome project; DNA
fingerprinting.
Ch-7 Evolution: Origin of life; biological evolution and
evidences for biological evolution (paleontology, comparative
anatomy, embryology and molecular evidences); adaptive
radiation; Biological evolution: Lamarck’s theory of use and
disuse of organs, Darwin's theory of evolution; mechanism of
Class XII (Pg. 045)
evolution - variation (mutation and recombination) and natural
selection with examples, types of natural selection; Gene flow
and genetic drift; Hardy - Weinberg's principle; brief account
of evolution; human evolution.
UNIT - III BIOLOGY AND HUMAN WELFARE
Ch 8 Human Health and Diseases:
Pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (malaria, dengue,
chikungunya, filariasis, ascariasis, typhoid, pneumonia,
common cold, amoebiasis, ring worm) and their control; Basic
concepts of immunology - vaccines; cancer, HIV and AIDS;
Adolescence - drug and alcohol abuse.
Ch 9 Strategies for Enhancement in food production:
Animal husbandry, Plant breeding, tissue culture, single cell
protein.
Practicals--
10-Study meiosis in onion bud cell or grass hopper testis through
permanent slide.
11. To study the effect of the different temperatures and three
different pH on the activity of salivary amylase on starch.
12. To identify common disease causing organisms like Ascaris,
Entamoeba, Plasmodium, Ringworm through permanent slides or
specimens. Comment on symptoms of diseases that they cause.
(LC to be discussed)
August Ch 10 Microbes in human welfare: Microbes in food
24 days processing, industrial production, Antibiotics; production and
judicious use, sewage treatment, energy generation and microbes as
bio-control agents and bio-fertilizers.
UNIT -IV -BIOTECHNOLOGY AND ITS APPLICATION
Ch 11 Biotechnology-Principles and processes: Genetic
Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology).
Ch 12 Biotechnology and its applications:
Application of biotechnology in health and agriculture: genetically
modified organisms - Bt crops; RNA interference, Human insulin,
gene therapy; molecular diagnosis; transgenic animals; biosafety
issues, biopiracy and patents.
Practical -
13. Isolation of DNA from available plant material such as spinach,
green pea seeds, papaya, etc.
(LC to be discussed)
Class XII (Pg. 046)
UNIT -V- ECOLOGY and ENVIRONMENT
Sept. Ch 13 Organisms and population:
25 days Organisms and environment: Habitat and niche, abiotic factors, ecological
adaptations; population interactions - mutualism, competition, predation,
parasitism, commensalism; population attributes - growth, birth rate and
death rate, age distribution.
Ch 14 Ecosystems:
Ecosystem: structure and function; productivity and decomposition; energy
flow; pyramids of number, biomass, energy; nutrient cycles (carbon and
phosphorous); ecological succession; ecological services - carbon fixation,
pollination, seed dispersal, oxygen release (in brief).
Practicals -
14. Collect and study soil from at least two different sites and study these
for texture, moisture content, pH and water holding capacity of soil.
Correlate with the kinds of plants found in them.
15. Collect water from two different water bodies around you and study
them for pH, clarity and presence of any living organisms.
16. Study the presence of suspended particulate matter in air at the two
widely different sites.
17. Study of plant population density by quadrate method.
18. Study of plant population frequency by quadrate method.
19. Study two plants and two animals (models/virtual images) found in
xeric condition. Comment upon their morphological adaptations.
20. Study two plants and two animals (models/virtual images) found in
aquatic conditions. Comment upon their morphological adaptations.
(LC to be discussed)
Oct. Ch 15 Biodiversity and its conservation:
19 days Biodiversity - Concept, levels, patterns, importance; loss of biodiversity;
biodiversity conservation; hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction, Red
Data Book, Sacred Groves, biosphere reserves, national parks, wildlife,
sanctuaries and Ramsar sites.
Ch 16 Environmental issues:
Air pollution and its control; water pollution and its control; agrochemicals
and their effects; solid waste management; radioactive waste management;
greenhouse effect and climate change impact and mitigation; ozone layer
depletion; deforestation; case study exemplifying success story addressing
environmental issue(s).
(LC to be discussed)
Nov. Revision + Pre Board I
21 days
Dec+ Jan+Feb Preboard-II
25 +21 +22=68 days Board Examination
Class XII (Pg. 047)
UNIT WISE DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
THEORY
UNIT MARKS
Reproduction 14
Genetics and Evolution 18
Biology and Human Welfare 14
Biotechnology and its Applications 10
Ecology and Environment 14
TOTAL 70
PRACTICALS
EVALUATION SCHEME MARKS
One Major Experiment 5
One Minor Experiment 4
Slide Preparation 5
Spotting 7
Practical Record + Viva 4
Project Record + Viva 5
TOTAL 30
Note--Project should be made on any topic after proper literature survey and
discussion with the teacher.
Class XII (Pg. 048)
XII -MATHEMATICS (Code No. - 041)
(for Science & Commerce Streams)
1 Single Lined Register.
Month Content
No. of Days
UNIT I. RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
March+April 1. Relations and Functions :
12+21=33 days Types of relations: reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence
relations. One to one and onto functions, composite functions,
inverse of a function.
2. Inverse Trigonometric Functions:
Definition, range, domain, principal value branch. Graphs of inverse
trigonometric functions. Elementary properties of inverse
trigonometric functions.
UNIT-II: ALGEBRA
3. Matrices:
Concept, notation, order, equality, types of matrices, zero and
identity matrix, transpose of a matrix, symmetric and skew
symmetric matrices. Operation on matrices: Addition and
multiplication and multiplication with a scalar. Simple properties of
addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication. Non-
commutativity of multiplication of matrices and existence of non-
zero matrices whose product is the zero matrix (restrict to square
matrices of order 2). Concept of elementary row and column
operations. Invertible matrices and proof of the uniqueness of
inverse, if it exists; (Here all matrices will have real entries).
AIL
Formation of different types of matrices by arranging students (in
the place of elements) and making them stand row and column wise.
Application : Symmetric matrix, Transpose of a matrix, Skew
symmetric matrix
Practical-1
To demonstrate function which is one-one not onto.
Practical-2
To draw the graph of Sin-1 x using the graph of sin x and
demonstrate the concept of mirror reflection (about the line y=x)
(LC to be discussed)
Class XII (Pg. 049)
4. Determinants:
Determinant of a square matrix (up to 3 x 3 matrices), properties of
determinants, minors, co-factors and applications of determinants in
finding the area of a triangle. Adjoint and inverse of a square matrix.
Consistency, inconsistency and number of solutions of system of linear
equations by examples, solving system of linear equations in two or three
variables (having unique solution) using inverse of a matrix.
UNIT-III: CALCULUS
5. Continuity and Differentiability:
Continuity and differentiability, derivative of composite functions, chain
rule, derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions, derivative of implicit
functions.Concept of exponential and logarithmic functions. Derivatives of
logarithmic and exponential functions. Logarithmic differentiation,
derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms. Second order
derivatives. Rolle's and Lagrange's Mean Value Theorems (without proof)
and their geometric interpretation.
Practical-3
To sketch the graph of a” and log, a>0, a 1 and to examine that they are
May + mirror images of each other.
June+July Practical-4
7 + 15 + 26 = To veryify Rolle’s theorem.
48 days (LC to be discussed)
6. Applications of Derivatives:
Applications of derivatives: rate of change of bodies, increasing/
decreasing functions, tangents and normals, use of derivatives in
approximation, maxima and minima (first derivative test motivated
geometrically and second derivative test given as a provable tool).
Simple problems (that illustrate basic principles and understanding
of the subject as well as real-life situations).
7. Integrals:
Integration as inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a
variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts.
Evaluation of simple intergrals of the following type and problems
based on them:
Class XII (Pg. 050)
Definite integrals as a limit of a sum, Fundamental Theorem of
Calculus (without proof). Basic properties of definite integrals and
evaluation of definite integrals.
8. Applications of the Integrals:
Applications in finding the area under simple curves, especially
lines, circles/parabolas/ellipses (in standard form only), Area
between any of the two above said curves (the region should be
clearly identifiable).
Practical-5
To understand the concepts of decreasing and increasing functions.
Practical-6
To understand the concepts of local maxima, local minima and point
of inflexion.
Practical-7
To evaluate the definite integral ……as the limit of a sum and
verify it by actual integration.
(LC to be discussed)
August 9. Differential Equations:
24 days Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential
equation, formation of differential equation whose general solution is given.
Solution of differential equations by method of separation of variables, solutions
of homogeneous differential equations of first order and first degree. Solutions of
linear differential equation of the type:
(dy/dx) + py = q, where p and q are functions of x or constants
(dx/dy) + px = q, where p and q are functions of y or constants
UNIT-IV: VECTORS AND THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
10. Vectors:
Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines and
direction ratios of a vector. Types of vectors (equal, unit, zero, parallel and
collinear vectors), position vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a
vector, addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector
of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Definition, Geomertrical
Interpretation, properties and applications of scalar (dot) product of vectors.
Vector (cross) product of vectors. Scalar triple product of vectors.
Practical- 8
To verify that angle in a semi-circle is a right angle, using vector method.
(LC to be discussed)
Sept. 11. Three - Dimensional Geometry:
25 days Direction cosines and direction ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian
equations and vector equation of a line, coplanar and skew lines, shortest distance
between two lines. Cartesian and vector equation of a plane. Angle between (i)
Class XII (Pg. 051)
two lines, (ii) two planes, (iii) a line and a plane. Distance of a point from a plane.
UNIT-V: LINEAR PROGRAMMING
12. Linear Programming:
Introduction, related terminology such as constraints, objective function,
optimization. Different types of linear programming (L.P.) problems,
mathematical formulation of L.P. problems, graphical method of solution for
problems in two variables, feasible and infeasible regions (bounded or
unbounded), feasible and infeasible solutions, optimal feasible solutions (up to
three non-trivial constraints).
Practical- 9
To measure the shortest distance between two skew lines and verify it
analytically.
(LC to be discussed)
Oct. UNIT-VI: PROBABILITY
19 days 13. Probability:
Conditional probability, multiplication theorem on probability,
independent events, total probability, Baye's theorem, Random
variable and its probability distribution, mean and variance of a
random variable. Binomial probability distribution.
Practical-10
To explain the computation of conditional probability of given event
A, when event B has already occurred, through an example of
throwing a pair of a dice.
(LC to be discussed)
Nov. Revision + Preboard-I
20 days
Dec+ Jan+Feb Preboard-II
25 +21 +22=68 Board Examination
days
Class XII (Pg. 052)
UNIT WISE DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
UNIT MARKS
RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS 08
ALGEBRA 10
CALCULUS 35
VECTORS AND THREE - DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY 14
LINEAR PROGRAMMING 05
PROBABILITY 08
INTERNAL ASSESSMENT 20
TOTAL 100
Class XII (Pg. 053)
PROFESSIONAL SECTION (LHT)
The following topics will be given special emphasis in class—
Physics—
1. Magnetic effect of current and magnetism
2. Electromagnetic waves
3. Optics
4. Electronics
Chemistry—
1. Electrochemistry
2. p-block elements
3. d & f block elements
4. Co-ordination Compounds
5. Biomolecules
Maths—
1. Calculus
2. Vectors & 3-dimensional geometry
Biology—
1. Genetics & Evolution
2. Biotechnology
PROFESSIONAL SECTION (VRN)
The following topics will be given special emphasis in class—
Physics—
1. Electromagnetic waves
2. Electronics
Chemistry—
1. Electrochemistry
2. p-block elements
3. Co-ordination Compounds
4. Conversion of Organic Chemistry
Maths—
1. Calculus
2. Vectors & 3-dimensional geometry
Biology—
1. Genetics & Evolution
2. Biotechnology
Class XII (Pg. 054)
XII - ACCOUNTANCY (Code No - 055)
1 Single Lined Register.
Month & Content
No. of Days
PART A: Accounting for Partnership Firms and Companies
March+April Unit 1 : Accounting for Partnership Firms (Revision)
12+21=33 days • Partnership: Features, Partnership deed.
• Provisions of the Indian Partnership Act 1932 in the absence of partnership
deed.
• Fixed v/s fluctuating capital accounts.Preparation of Profit & Loss
Appropriation account- division of profit among partners, guarantee of
profits.
• Past adjustments (relating to interest on capital, interest on drawing, salary
and profit sharing ratio).
• Goodwill: nature, factors affecting and methods of valuation - average
profit, super profit and capitalization.
Goodwill to be adjusted through partners capital/current account or by raising
and writing off goodwill (AS 26)
Note:
Interest on partner’s loan is to be treated as a charge against profits.
Raising and writing off good will is exluded.
Accounting for Partnership firms - Reconstitution and Dissolution.
• Change in the Profit Sharing Ratio among the existing partners - sacrificing
ratio, gaining ratio. Accounting for revaluation of assets and re-assessment of
liabilities and treatment of reserves and
accumulated profits. Preparation of revaluation account and balance sheet.
• Admission of a partner - effect of admission of a partner on change in the
profit sharing ratio, treatment of goodwill (as per AS 26), treatment for
revaluation of assets and re - assessment of liabilities, treatment of reserves
and accumulated profits, adjustment of capital accounts and preparation of
balance sheet. (LC to be discussed)
May + June Accounting for Partnership firms - Reconstitution and Dissolution.
07 +15 • Retirement and death of a partner: effect of retirement /death of a
=22 days partner on change in profit sharing ratio, treatment of goodwill (as per AS
26), treatment for revaluation of assets and re - assessment of liabilities,
adjustment of accumulated profits and reserves, adjustment of capital
accounts and preparation of balance sheet.
Preparation of loan account of the retiring partner.
Calculation of deceased partner's share of profit till the date of death.
Preparation of deceased partner's capital account and his executor's account.
Class XII (Pg. 055)
July Dissolution of a partnership firm: meaning of dissolution of
26 days partnership and partnership firm, types of dissolution of a firm.
Settlement of accounts - preparation of realization account, and other
related accounts: capital accounts of partners and cash/bank a/c
(excluding piecemeal distribution, sale to a company and insolvency
of partner(s)).
Note:
(i) The realized value of each asset must be given at the time of
dissolution.
(ii) In case, the realisation expenses are borne by/paid by a partner,
clear indication should be given regarding the payment thereof.
Financial statement of not for profit organisation
Not-for-profit organizations: concept.
Receipts and Payments Account: features and preparation.
Income and Expenditure Account: features, preparation of
income and expenditure account and balance sheet from the
given receipts and payments account with additional
information.
Scope: (i) Adjustments in a question should not exceed 3 or 4 in
number and restricted to subscriptions, consumption of consumables
and sale of assets/ old material. (ii) Entrance/admission fees and
general donations are to be treated as revenue receipts. (iii) Trading
Account of incidental activities is not to be prepared.
(LC to be discussed)
August Unit 2 : Accounting for Companies
24 days Accounting for Share Capital
Share and share capital: nature and types.
Accounting for share capital: issue and allotment of equity and preference
shares, Public subscription of shares - over subscription and under
subscription of shares; Issue at par and at premium, calls in advance and
arrears (excluding interest), issue of shares for consideration other than cash.
• Concept of Private Placement & Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP).
• Accounting treatment of forfeiture and re-issue of shares.
• Disclosure of share capital in company's Balance Sheet.
Accounting for Debentures
• Debentures: Issue of debentures at par, at a premium and at a
discount. Issue of debentures for consideration other than cash; Issue
of debentures with terms of redemption; debentures as collateral
Class XII (Pg. 056)
security-concept, interest on debentures. Writting off discount/loss on
issue of debentures.
Note: Discount or loss on issue of debentures to be written off in the year
debentures are allotted from Security Premium Reserve (if it exists) and
then from Statement of Profit and Loss as Financial Cost (AS 16)
(LC to be discussed)
Sept. • Redemption of debentures methods:
25 days Lump sum, draw of lots, Creation of Debenture Redemption Reserve.
Note-
Related sections of the Indian Companies Act 2013 will apply.
Concept of TDS is excluded.
PART B: Financial Statement Analysis
Unit3 : Analysis of Financial Statements
• Financial statements of a company: Statement of Profit and Loss
and Balance Sheet in the prescribed form with major headings and sub
headings (as per Schedule III to the Companies Act, 2013).
Scope: Exceptional Items, Extraordinary Items and Profit (loss) from
Discontinued Operations are excluded.
• Financial Statement Analysis: Objectives, Importance and limitations.
• Tools for Financial Statement Analysis: Comparative statements,
common size statements, cash flow analysis, ratio analysis.
• Accounting Ratios: Meaning, Objectives, classification and
computation.
Liquidity Ratios: Current ratio and Quick ratio.
Solvency Ratios: Debt to Equity Ratio, Total Asset to Debt Ratio,
Proprietary Ratio and Interest Coverage Ratio.
Activity Ratios: Inventory Turnover Ratio, Trade Receivables
Turnover Ratio, Trade Payables Turnover Ratio and Working Capital
Turnover Ratio.
Profitability Ratios: Gross Profit Ratio, Operating Ratio, Operating
Profit Ratio, Net Profit Ratio and Return on Investment.
Note- Net Profit ratio is to be calculated on before and after tax.
(LC to be discussed)
Oct. Unit 4. Cash Flow Statement
19 days • Meaning, objectives and preparation (as per AS 3 (Revised) (Indirect Method only)
Scope:
(i) Adjustments relating to depreciation and amortisation, profit or loss on sale of
assets including investments, dividend (both final and interim) and tax.
Class XII (Pg. 057)
(ii) Bank overdraft and cash credit to be treated as short term borrowings.
(iii) Current Investments to be taken as Marketable securities unless otherwise
specified.
AIL
Nearpod presentation or any other medium and group discussion on main
features and some special features of N.P.O. and Income and Expenditure
A/c. How can we make N.P.O. accounting more feasible?
Note:- Previous years’ Proposed Dividend to be given effect, as prescribed in AS-
4, Events occurring after the Balance Sheet date. Current years’ Proposed
Dividend will be accounted for in the next year after it is declared by the
sharholders
Project Work:
Kindly refer to the Guidelines published by the CBSE.
The comprehensive project may contain simple GST calculations.
(this project will be avaluated for CBSE board practical exam.).
(LC to be discussed)
Nov. 20 days Revision + Preboard-I
Dec+ Jan+Feb Preboard-II
25 +21 +22=6 Board Examination
days
UNIT WISE DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
Theory - 80 marks Practical - 20 marks
UNIT MARKS
Part A : Accounting for Not-For-Profit Organisations Partnership 60
Firms and Companies
1. Financial statements of Not-For-Profit Organisations 10
2. Accounting for Partnership Firms 30
3. Accounting for Companies 20
Part B: Financial Statement Analysis 20
4. Analysis of Financial Statements 12
5. Cash Flow Statement 08
Part C: Project Work 20
Unit 1 : Project File 04
Unit 2 : Written Test 12
04
Unit 3 : Viva Voce
TOTAL 100
Class XII (Pg. 058)
XII - BUSINESS STUDIES (Code No.- 054)
1 Single Lined Register.
Month & Content
No. of Days
Part A: Principles and Functions of Management
March+April Concept includes meaning and features
12+21=33 days Unit I: Nature and Significance of Management
Management-concept, objectives, and importance
Concept includes meaning and features
Management as Science, Art and Profession
Levels of Management
Management functions-planning, organizing, staffing
directing and controlling
Coordination- concept and importance, characteristics.
Unit 2: Principles of Management
Principles of Management - concept and significance
Fayol’s principles of management
Taylor’s Scientific Management - principles and techniques
(LC to be discussed)
Unit 3: Managment and Business Environment
Business Environment - concept and importance
Dimensions of Business Environment - Economic, Social,
Technological, Political and Legal
Demonetization- concept and features
Impact of Government policy changes on business with
special reference to liberalization, privatization and
May + June+ July
07 + 15 + 26 globalisation in India.
= 48 days AIL
Pear Deck presentation or any other medium on the external factors
affecting a running business. Virtual tour of a manufacturing
company as automobile or any FMCG product.
(LC to be discussed)
Unit 4: Planning
Concept, importance and limitation
Planning process
Class XII (Pg. 059)
Single use and Standing Plans - Objectives, Strategy,
Policy, Procedure, Method, Rule, Budget and Programme.
Unit 5:
Organising
Concept and importance.
Organizing Process
Structure of organization - functional and divisional concept
Formal and informal organization-concept
Delegation: concept, elements and importance.
Decentralization: concept and importance.
Unit 6: Staffing
Concept and importance of staffing
Staffing as a part of Human Resource Management-concept
Staffing process :
Recruitment – process
Selection – process
Training and Development - Concept and importance.
Methods of training- on the job and off the job- vestibule
training, apprenticeship training and internship training.
(LC to be discussed)
August Unit 7: Directing
24 days Concept and importance
Elements of Directing
Supervision - concept, functions of a supervisor.
Motivation - concept, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs;
Financial and non-financial incentives.
Leadership - concept, styles - authoritative, democratic and
laissez faire.
Communication - concept, formal and informal
communication; barriers to effective communication, how
to overcome the barriers.
Unit 8: Controlling
Concept and importance
Relationship between planning and controlling
Steps in the process of controlling
(LC to be discussed)
Class XII (Pg. 060)
Sept. Part B : Business Finance and Marketing (Revision)
25 days Unit 9: Financial Management
Concept, role and objectives of financial management.
Financial decisions: investment, financing and dividend –
meaning and factors affecting.
Financial planning - concept and importance.
Capital Structure - concept and factors affecting Capital
Structure.
Fixed and Working Capital - concept and factors affecting
their requirements
Project to be allotted to the students. (this project will be evaluated for
CBSE board practical exam.)
Unit 10: Financial Markets
Financial Markets: Concept, Function and types.
Money market and its instruments.
Capital market and its types (primary and secondary)
Methods of floatation in the primary market.
Stock Exchange- Functions and trading procedure.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)- objectives and
functions.
(LC to be discussed)
Oct. Unit 11: Marketing Management (Revision)
19 days Marketing Concept, Functions & Philosophies.
Marketing Mix - Concept & elements
- Product-Concept, branding, labelling and packaging.
- Price- Concept, Factors determining price.
- Physical Distribution – concept and components,
channels of distribution: types, choice of channels.
- Promotion- Concept and elements; advertising-
concept, role, objections against advertising, personal selling-
concept and qualities of a good salesman, sales promotion- concept
and techniques, public relations- concept and role.
Unit 12: Consumer Protection
Concept and importance of consumer protection.
Consumer Protection Act 1986
- Meaning of consumer
Class XII (Pg. 061)
- Rights and responsibilities of consumers
- Who can file a complaint against whom?
- Redressal machinery.
- Remedies available.
Consumer awareness-Role of consumer organizations and
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)
(LC to be discussed)
Nov. 20 days Revision + Preboard-I
Dec+ Jan+Feb Preboard-II
25 +21 +22=68 days Board Examination
UNIT WISE DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
UNIT MARKS
Part A : Principles and Functions of Management 50
1. Nature and Significance of Management
2. Principles of Management 16
3. Business Environment
4. Planning
14
5. Organising
6. Staffing
7. Directing 20
8. Controlling
Part B : Business Finance Marketing 30
9. Financial Management
15
10. Financial Markets
11. Marketing Management
15
12. Consumer Protection
Part C : Project Work 20
TOTAL 100
Class XII (Pg. 062)
XII - ECONOMICS (Code No. - 030)
1 Single Lined Register.
Month & Content
No. of Days
March+April Introductory Macroeconomics
12+21=33 days Unit 1: National Income and Related Aggregates
Some basic concepts: consumption goods, capital goods, final goods,
intermediate goods; stocks and flows; gross investment and depreciation.
Circular flow of income (two sector model); Methods of calculating
National Income - Value Added or Product method, Expenditure
method, Income method. Aggregates related to National Income: Gross
National Product (GNP), Net National Product (NNP), Gross and Net
Domestic Product (GDP and NDP) - at market price, at factor cost; Real
and Nominal GDP. GDP and Welfare
Unit 2: Money
Money - meaning and supply of money - Currency held by the public
and net demand deposits held by commercial banks. Money creation by
the commercial banking system.
Indian Economic Development
Chapter 1-- Indian economy on the eve of Independence-
A brief introduction of the state of Indian economy on the eve of
independence.
(LC to be discussed)
May + June Unit 2: Banking
07 + 15 Central bank and its functions (example of the Reserve Bank of India):
=22 days Bank of issue, Govt. Bank, Banker's Bank, Control of Credit through
Bank Rate, CRR, SLR, Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate, Open Market
Operations, Margin requirement.
Indian Economic Development
Chapter 2:- Indian Economy 1947-1990
Common goals of Five Year Plans. Main features, problems and policies
of agriculture (institutional aspects and new agricultural strategy, etc.),
industry (IPR 1956, SSI-role and importance etc.) and foreign trade.
Chapter 3:- Economic Reforms since 1991:- An Appraisal. -- Need
and main features - liberalisation, globalisation and privatisation; An
appraisal of LPG policies. Concepts of demonetization and GST.
Class XII (Pg. 063)
Project : Analyse any concept from the syllabus
The purpose of this project is to –
Develop interest of the students in the concepts of Economic theory
and application of the concept
to the real life situations.
Provide opportunity to the Learner’s to develop economic reasoning
vis-a-vis to the given concept
from the syllabus.
Enable the students to understand abstract ideas, exercise the power of
thinking and to develop
his/her own perception
To develop the understanding that there can be more than one view on
any economic issue and to
develop the skill to argue logically with reasoning
Compare the efficacy of economic policies in real world situations
To expose the student to the rigour of the discipline of economics in a
systematic way
Impact of Economic Theory/ Principles and concepts on the lives of
common people
Scope of the project:
Following essentials are required to be fulfilled in the project.
Explanation of the concept:
- Meaning and Definition
- Application of the concept
- Diagrammatic Explanation (if any)
- Numerical Explanation related to the concept etc. (if any)
- Students’ own views/perception/ opinion and learning from the topic..
Mode of presentation and submission of the Project:
At the end of the stipulated term, each student(s) will present their work
in the Project File (with viva voce)
to the external examiner
(LC to be discussed)
Class XII (Pg. 064)
July Macro Economics--
26 days Unit III- Determination of Income and Employment:-
Aggregate demand and aggregate supply--
Aggregate demand and its components. Propensity to consume
and propensity to save (average and marginal). Short-run
equilibrium output, investment multiplier and its mechanism.
Meaning of full employment and involuntary unemployment.
Indian Economic Development-
Chapter 4--Poverty
absolute and relative; Main programmes for poverty alleviation: A
critical assessment;
Chapter 5-- Human Capital Formation
How people become resource; Role of human capital in economic
development; Growth of Education Sector in India
(LC to be discussed)
August Macro Economics--
24 days Unit III- Determination of Income and Employment:-
Problems of excess demand and deficient demand:- measures to
correct them - changes in government spending, taxes and money
supply
Indian Economy--
Chapter 6 - Rural Development:-
Key issues - credit and marketing - role of cooperatives;
agricultural diversification; alternative farming - organic farming
Chapter 7 - Employment:-
Growth and changes in workforce participation rate in formal and
informal sectors, Problems and policies.
(LC to be discussed)
Sept. Macro Economics--
25 days Government Budget & Economy:- Government budget - meaning,
objectives and components. Classification of receipts - revenue
receipts and capital receipts; classification of expenditure –
revenue expenditure and capital expenditure. Measures of
government deficit - revenue deficit, fiscal deficit, primary deficit
their meaning.
Indian Economic Development--
Chapter 8 - Infrastructure-
Meaning and Types: Case Studies: Energy and Health: Problems
Class XII (Pg. 065)
and Policies- A critical assessment;
Chapter 9 - Environment and Sustainable Development--
Meaning, Effects of Economic Development on Resources
and Environment, including global warming.
AIL
(a) Students will present nukkad natak on various topics given in the
chapter such as global warming and its impact, strategies for
sustainable development etc.
(b) Students will present a nukkad natak on the traditional methods
taken up by the ‘Tribes of Arunachal Pradesh’ for water conservation.
(LC to be discussed)
Oct. Macro Economics--
19 days Unit IV: Balance of Payments
Balance of payments account - meaning and components; balance
of payments deficit-meaning. Foreign exchange rate - meaning of
fixed and flexible rates and managed floating. Determination of
exchange rate in a free market.
Indian Economic Development--
Chapter 10- Comparative Development Experience of Indian
Economy and its neighbours.
A comparison with neghbours- India and Pakistan, India and
China Issues: Economic growth, population, sectoral development
and other Human Development Indicators.
(LC to be discussed)
Nov. Revision + Preboard-I
21 days
Dec+ Jan+Feb Preboard-II
25 +21 +22=68 Board Examination
days
Class XII (Pg. 066)
UNIT WISE DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
UNIT MARKS
Part A : Introductory Macroeconomics 40
1. National Income and Related Aggregates 10
2. Money and Banking 06
3. Determination of Income and Employment 12
4. Government Budget and the Economy 06
5. Balance of Payments 06
Part B : Indian Economic Development 40
Development Experience (1947-90) and Economic Reforms since 1991 12
Current Challenges facing Indian Economy 22
Development Experience of India-A Comparison with Neighbours 06
Part C : PROJECT WORK 20
TOTAL 100
Class XII (Pg. 067)
XII - HISTORY (Code No - 027 )
1 Single Lined Register.
Month & Content
No. of Days
PART 1
March+April 3. KINSHIP, CASTE & CLASS--SOCIAL HISTORIES : Early
12+21 =33 days Societies.
Broad overview: Issues in social history, including caste, class, kinship
and gender.
Story of discovery: Transmission and publications of the Mahabharata.
Excerpt: from the Mahabharata, illustrating how it has been used by
historians.
Discussion: Other sources for reconstructing social history.
Map Work
4. THINKERS, BELIEFS & BUILDINGS—CULTURAL
DEVELOPMENTS.
Broad overview:
(a) A brief review of religious histories of Vedic religion, Jainism,
Vaishnavism, Shaivism.(Puranic Hindiusm)
(b) Focus on Buddhism.
Story of discovery: Sanchi stupa
Excerpt: Reproduction of sculptures from Sanchi.
Discussion: Ways in which sculpture has been interpreted by historians,
other sources for reconstructing the history of Buddhism.
Map Work
(LC to be discussed)
Project Work (this project will be evaluated for CBSE board practical exam.)
The theme of the topics for the project are as follows:--
1. Help, Humanity and Sacrifices during Partition.
2. Glimpses inside Mughals Imperial Household.
3. The process behind the framing of the Indian Constitution.
4. The Emerald city of Colonial Era-BOMBAY
5. “Mahatma Gandhi”-A legendary soul
6. Buddha’s Path to Enlightenment
7. The Zamindars and land revenue system of Mughal India.
8. INDIA-Through the traveller’s eye.
9. Comparison of administration of Government of the present day
and that in the Mughal Court.
10. Vision of unity behind the first war of Independence.
Please note that:
Project will be of 20 marks which includes research/file
Class XII (Pg. 068)
work and viva.
Project will be done in a group assigned by the teacher.
Each group will choose any one of the topics mentioned
above.
One project will be done per session & will be subjected for
evaluation & the marks obtained will be reflected in the
student’s report card.
The teacher will facilitate and guide the students in drafting,
reviewing and finalizing the project.
PART – II
5. Through the Eyes of Travellers
Broad overview:
Outline of social and cultural life as they appear in travellers'
accounts.
Story of their writings: A discussion of where they travelled, what
they wrote, and for whom they wrote.
Excerpts: from Al-Biruni, Ibn Battuta, Franed’s Bernier.
Discussion: What these travel accounts can tell us and how they
have been interpreted by historians.
Map Work
(LC to be discussed)
May + June + July 6. The Bhakti-Sufi traditions: Changes In Religious Beliefs And
07 +15 + 26 Devotional Texts.
=48 days Broad overview:
(a) Outline of religious developments during this period saints.
(b) Ideas and practices of the Bhakti-Sufi.
Story of Transmission: How Bhakti-Sufi compositions have been
preserved.
Excerpt: Extracts from selected Bhakti-Sufi works.
Discussion: Ways in which these have been interpreted by
historians.
Map Work
ART INTEGRATED LEARNING
After completion of the chapter a short video on the life history of
Mirabai, Kabirdas and Gurunanak will be shown in 3 periods. Class will
be divided into groups. (3-4 students in a group) Each group will choose
any of the topics given below and prepare a presentation on the
Class XII (Pg. 069)
compositions and achievements of the bhakti saint/sufi groups. The class
will be taken on a virtual trip to the important places related to saint’s
life and also explain its practice in present day by the followers. Any
form of art can be taken up by the child as per his/her own interest i.e.
singing, recitation, instrumental, painting etc.
Topics
ALWARS
NAYANARS
VIRASHAIVAS
MIRABAI
GURUNANAK DEV
KABIR DAS
ANY SUFI SAINTS HOSPICE IN INDIA
7. AN IMPERIAL CAPITAL: VIJAYANAGAR
Broad overview:
(a) Outline of new buildings during Vijayanagar period-temples,
forts, irrigation facilities.
(b) Relationship between architecture and the political system.
Story of Discovery: Account of how Hampi was found.
Excerpt: Visuals of buildings at Hampi
Discussion: Ways in which historians have analyzed and
interpreted these structures.
Map Work
8. PEASANTS, ZAMINDARS & THE STATE--AGRARIAN
SOCIETY AND THE MUGHAL EMPIRE
Broad overview:
(a) Structure of agrarian relations in the 16th and 17th centuries.
(b) Patterns of change over the period.
Story of Discovery: Account of the compilation and translation of
Ain-i-Akbari.
Excerpt: from the Ain-i-Akbari
Discussion: Ways in which historians have used the text to
reconstruct history.
Map Work (LC to be discussed)
Class XII (Pg. 070)
August 9. KINGS AND CHRONICLES : THE MUGHAL COURT :
24 days Broad overview : (a) Outline of political history 15th – 17th centuries. (b)
Discussion of the Mughal court and politics.
Story of discovery : Acount of the production of court chronicles, and
‘their subsequent, translation and transmission.
Excerpts: from the Akbarnama and Badshahnama.
Discussion: Ways in which historians have used the texts to reconstruct
political histories.
Map Work
PART – III
10. COLONIALISM AND THE COUNTRYSIDE:
EXPLORING OFFICIAL ARCHIVES.
Evidence from Official Reports
Broad overview:
(a) Life of zamindars, peasants and artisans in the late 18th century
(b) East India Company, revenue settlements in various regions of
India and surveys.
(c) Changes over the nineteenth century.
Story of official records: An account of why official
investigations into rural societies were undertaken and the types of
records and reports produced.
Excerpts: From Firminger's Fifth Report, Accounts of Francis
Buchanan-Hamilton, and Deccan Riots Report.
Discussion: What the official records tell and do not tell, and how
they have been used by historians.
Map Work
11. REBELS AND THE RAJ: THE REVOLT OF 1857 AND
ITS REPRESENTATIONS
Broad overview:
(a) The events of 1857-58.
(b) Vision of Unity
(c) How these events were recorded and narrated.
Focus: Lucknow.
Excerpts: Pictures of 1857. Extracts from contemporary accounts.
Discussion: How the pictures of 1857 shaped British opinion of
what had happened.
Map Work
(LC to be discussed)
Class XII (Pg. 071)
Sept. 12. COLONIAL CITIES: URBANISATION, PLANNING AND
25 days ARCHITECTURE
Town Plans and Municipal Reports.
Broad overview: History of Towns in India, Colonization and
cities, hill stations, town planning of Madras, Calcutta and
Bombay.
Excerpts: Photographs and paintings. Plans of cities. Extract from
town plan reports. Focus on Calcutta town planning.
Discussion: How the above sources can be used to reconstruct the
history of towns. What these sources do not reveal.
Map Work
13. MAHATMA GANDHI AND THE NATIONALIST
MOVEMENT: CIVIL DISOBEDIENCE AND BEYOND
(a) The Nationalist Movement 1918 - 48.
(b) The nature of Gandhian politics and leadership.
Focus: Mahatma Gandhi and the three movements & his last days
as ‘Finest Hours’.
Excerpts: Reports from English and Indian language newspapers
and other contemporary writings.
Discussion: How newspapers can be a source of history.
Map Work
14. UNDERSTANDING PARTITION : POLITICS,
MEMORIES, EXPERIENCES
Broad overview:
(a) The history of the 1940s.
(b) Nationalism, Communalism and Partition. Focus: Punjab and
Bengal.
Excerpts: Oral testimonies of those who experienced partition.
Discussion: Ways in which these have been analyzed to reconstruct
the history of the event.
Map Work (LC to be discussed)
Oct. 15. FRAMING THE CONSTITUTION: THE BEGINNING OF A NEW
19 days ERA
Broad overview:
(a) Independence and the new nation state.
(b) The making of the Constitution.
Focus: The Constitutional Assembly debates.
Class XII (Pg. 072)
Excerpts: from the debates.
Discussion: What such debates reveal and how they can be analyzed.
PART-1
1. BRICKS, BEADS AND BONES: THE HARAPPAN CIVILIZATION
(REVISION)
Harappan Archaeology.
Broad overview: Early urban centres.
Story of discovery: Harappan civilization
Excerpt: Archaeological report on a major site.
Discussion: How it has been utilized by archaeologists/historians.
Map Work
2. KINGS, FARMERS AND TOWNS: EARLY STATES AND
ECONOMIES (REVISION)
How Inscriptions tell a story.
Broad overview: Political and economic history from the Mauryan to the Gupta
period.
Story of discovery: Inscriptions and the decipherment of the script. Shifts in the
understanding of political and economic history.
Excerpt: Asokan inscription and Gupta period land grant.
Discussion: Interpretation of inscriptions by historians.
Map Work
(LC to be discussed)
Nov. Revision + Preboard-I
20 days
Dec+ Jan+Feb Preboard-II
25 +21 +22=68 Board Examination
days
LIST OF MAPS
Book 1
1. P-2. Mature Harappan Sites: Harappa, Banawali, Kalibangan, Balakot, Rakhigarhi,
Dholavira, Nageshwar, Lothal, Mohenjodaro, Chanhudaro, Kot Diji.
2. P-30. Mahajanapada And Cities :Vajji, Magadha, Kosala, Kuru, Panchala, Gandhara,
Avanti, Rajgir, Ujjain, Taxila,Varanasi.
3. P-33. Distribution Of Ashokan Inscriptions:
(I) Kushanas, Shakas, Satavahanas, Vakatakas, Guptas
(Ii) Cities/Towns: Mathura, Kannauj, Bharukachchha
(Iii) Pillar Inscriptions - Sanchi, Topra, Meerut pillar and Kaushambi.
(Iv) Kingdom Of Cholas, Cheras And Pandyas.
4. P-43. Important Kingdoms And Towns:
Class XII (Pg. 073)
(I) Kushanas, Shakas, Satavahanas, Vakatakas, Guptas
(II) Cities/Towns: Mathura, Kanauj, Puhar, Rajgir,Vaishali, Varanasi, Vidisha
5. P-95. Major Buddhist Sites:
Nagarjunakonda, Sanchi, Amaravati, Lumbini, Nasik, Bharhut, Bodhgaya, Shravasti,
Ajanta.
Book 2
1. P-174. Bidar, Golconda, Bijapur, Vijayanagar, Chandragiri, Kanchipuram, Mysore,
Thanjavur, Kolar, Tirunelveli, Quilon
2. P-214. Territories Under Babur, Akbar And Aurangzeb: Delhi, Agra, Panipat, Amber,
Ajmer, Lahore, Goa.
Book 3
1. P-297. Territories/Cities Under British Control In 1857:Punjab, Sindh, Bombay,
Madras Fort St. David, Masulipatam, Berar, Bengal, Bihar,Orissa, Avadh, Surat, Calcutta,
Dacca/Dhaka, Patna, Benaras, Allahabad and Lucknow.
2. P-305. Main Centres Of The Revolt Of 1857:Delhi, Meerut, Jhansi, Lucknow, Kanpur,
Azamgarh, Calcutta, Benaras, Gwalior,Jabalpur, Agra, Avadh.
3. P-305. Important Centres Of The National Movement:Champaran, Kheda, Ahmedabad,
Benaras, Amritsar, Chauri Chaura, Lahore, Bardoli,Dandi, Bombay (Quit India
Resolution), Karachi.
UNIT WISE DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
Theory - 80 marks Project - 20 marks
UNIT MARKS
Themes in Indian History Part-I--Units 1 – 4 24
Themes in Indian History Part-II--Units 5 - 9 25
Themes in Indian History Part-III--Units 10 - 15 25
Unit 16: Map Work 06
Project Work 20
Total 100
Class XII (Pg. 074)
XII – POLITICAL SCIENCE (Code No - 028 )
1 Single Lined Register.
Month & Content
No. of Days
2. The End of Bipolarity
March+April Unipolar World, Middle East Crisis – Afghanistan, Gulf War
12+21=33 days 3 New Centres of Power
Organizations: European Union, ASEAN, SAARC, BRICS. Nations: Russia,
China, Israel, India.
(LC to be discussed)
4 South Asia and the Contemporary World
Conflicts and efforts for Peace and Democratization in South Asia:
Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Maldives.
5 United Nations and its Organizations
Principle Organs, Key Agencies: UNESCO, UNICEF, WHO, ILO, Security
Council and the Need for its Expansion.
(LC to be discussed)
6 Security in Contemporary World
Security: Meaning and Types; Terrorism
May + June + July 7 Environment and Natural Resources
Environmental Movements, Global Warming and Climate Change,
07 +15+26 Conservation of Natural Resources.
=48 days 8 Globalisation
Globalization: Meaning, Manifestations and Debates.
AIL
Group presentation through Pear Deck or any other medium and role
play. The following topics will be taken up.
(a) Flows of globalization
(b) Cultural homogenization
(c) Cultural heterogenization
(d) Spread of education and awareness in ‘Arunachal Pradesh’ as an
impact of globalization.
(LC to be discussed)
August PART B: POLITICS IN INDIA SINCE INDEPENDENCE
24 days 9 Challenges of Nation- Building
Nation and Nation Building, Sardar Vallabh Bhai Patel and Integration of
States, Legacy of Partition: Challenge of Refugee, Resettlement, Kashmir
Issue, Nehru’sApproach to Nation – Building, Political Conflicts over
Class XII (Pg. 075)
Language and Linguistic Organization of States.
10 Planning and Development
Changing nature of India’s Economic Development, Planning Commission
and Fiveyear Plans, National Development Council, NITI Aayog
11 India's Foreign Policy
Principles of Foreign Policy; India’s Changing Relations with Other
Nations: US, Russia, China, Israel; India’s Relations with its Neighbours:
Pakistan, Bangladesh,Nepal, Sri Lanka and Myanmar; India’s Nuclear
Programme.
(LC to be discussed)
Sept. 12 Parties and the Party Systems in India
25 days Congress System, Bi-party System, Multi-party Coalition System.
13 Democratic Resurgence
Jaya Prakash Narayan and Total Revolution, Ram Manohar Lohia and
Socialism,Pandit Deendayal Upadhyaya and Integral Humanism, National
Emergency, Democratic Upsurges – Participation of the Adults,
Backwards and Youth.
14 Social and New Social Movements in India
Social vs. New Social Movements, Farmer’s movements, Worker’s
Movements, Women’s Movements, Ecological Movements.
(LC to be discussed)
Oct. 15 Regional Aspirations
19 days Rise of Regional Parties, Punjab Crisis, The Kashmir issue, Movements
forAutonomy.
16 Indian Politics: Trends and Developments
Era of Coalitions: National Front, United Front, United Progressive
Alliance [UPA] – I & II, National Democratic Alliance [NDA] – I, II, III & IV,
Issues of Development and Governance
PART A: CONTEMPORARY WORLD POLITICS
1. Cold War and Non-aligned Movement (REVISION)
Emergence of two power blocs/Bipolarity, Non-aligned Movement
(NAM).
2. The End of Bipolarity (REVISION)
Disintegration of Soviet Union, Democratic Politics and Democratization – CIS
st
and 21 Century (Arab Spring)
(LC to be discussed)
Nov. 20 days Revision + Preboard-I
Dec+ Jan+Feb Preboard-II
25 +21 +22=68 days Board Examination
Class XII (Pg. 076)
UNIT WISE DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
Class XII (Pg. 077)
XII - PSYCHOLOGY (Code No – 037)
1 Single Lined Register
Month & Content
No. of Days
Unit I : Variations in Psychological Attributes
March+April 1. Introduction, 2. Individual Differences in Human Functioning, 3. Assessment
12+21=33 days of Psychological Attributes 4. Intelligence, 5. Theories of Intelligence:- a)
Theory of Multiple Intelligence, b)Triarchic Theory of Intelligence, c)Planning,
Attention-Arousal, and Simultaneous- Successive Model of Intelligence. 6.
Individual Differences in Intelligence- Variations of Intelligence, 7. Culture and
Intelligence, 8. Emotional intelligence, 9. Speacial Abilities- a) Aptitude: Nature
and Measurement, 10. Creativity.
(LC to be discussed)
Unit II : Self and Personality
1. Introduction, 2. Self and Personality, 3. Concept of Self, 4. Cognitive and
Behavioural aspect of self- Self-esteem, Self-regulation and Self efficacy.
5. Culture and self; 6. Concept of Personality 7. Major approaches to the study of
personality: a) Type Approaches, b) Trait Approaches.
Practical – 1
Unit II : Self and Personality (cont…..)
c) Psychodynomic Approach, d) Behavioural Approach e) Cultural Approach f)
Humanistic Approach, 8) Assessment of Personality: a) Self-report Measures, b)
Projective Techniques c) Behavioural Analysis.
Practical - 2
Project and Case Study
(LC to be discussed)
Unit III : Meeting Life Challenges
1. Introduction 2. Nature, Types and Sources of Stress, 3. Effects of a stress on
Psychological Functioning and Health- a) Stress and Health b) General Adaption
Syndrome c) Stress and Immune System d) Life Style 4. Coping with stress- a)
May + June + July Stress Management technique 5. Promoting positive Health and well being-a )
07+15+26 Life Skills, Stress Resistant Personality, Positive Health.
= 48 days Unit IV: Psychological Disorders
1. Introduction, 2. Concepts of abnormality and psychological disorders,
Historical Background 3. Classification of psychological disorders, 4. Factors
underlying abnormal behaviour, 5.Major psychological disorders: Anxiety
Disorders, Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders, Trauma and Stressor-
Related Disorders, Somatic Symptom and Related Disorders, Dissociative
Disorder, Depressive Disorder, Biploar and Related Disorders, Schizophrenia
Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorders, Neurodevelopment Disorders,
Disruptive, Impulse-Control and Conduct Disorders. Feeding and Eating
Disorders, Substance Related and Addictive Disorders
AIL
Individual/group presentation through posters and role play on the
following topics. (a) Student will be presenting any one psychological
Class XII (Pg. 078)
disorder or therapy through the poster from the prescribed syllabus. (b)
Students will be presenting role play based on any one disorder or
therapy.
Practical – 3
(LC to be discussed)
August Unit V : Therapeutic Approaches
24 days 1. Nature and process of Psychotherapy-a) Therapeutic relationship 2. Types of
therapies: a) Psychodynamic Therapy, b) Behaviour Therapy c) Cognitive
Therapy d) Humanistic Existential Theraphy, e) Bio-Medical Therapy, f)
Alternative therapies: 3. Rehabilitation of the Mentally ill.
Practical - 4
Unit VI : Attitude and Social Cognition
1. Introduction, 2. Explaining Social Behaviour, 3. Nature and Components of
Attitudes, 4. Attitude Formation and change- a) attitude formation b) attitude
change c) attitude behaviour relationship 5. Prejudice and discrimination, 6
Strategies for handling prejudice 7. Social Cognition 8. Schemas and Sterotypes
9. Impression formation and explaining 10. Behaviour of others through
attributions-a) impression formation b) attribution of causality 11. Behaviour in
the presence of others 12. Pro-Social behaviour a) Factors affecting pro-social
behaviour.
(LC to be discussed)
Sept. Unit VII : Social Influence and Group Processes
25 days 1. Introduction 2. Nature and formation of groups 3. Types of groups 4. Influence
of group on individual behaviour- a) social loafing b) group polarization 5.
Conformity, Compliance and Obedience 6. Cooperation and Competition-a)
Determinants of Cooperation and Competition 7. Social Indentity 8. Inter group
conflict: Nature and Causes. 9. Conflict resolution strategies
Practical - 5
Unt VIII: Psychology & Life
1. Introduction 2. Human- environment relationship- a) Different views of the
human Environment Relationship 3. Environmental effects on Human behaviour
a) human influence on environment b) Noise c) Pollution d) Crowding e) Natural
disaster 4. Promoting Pro-environmenal behaviour 5. Psychology and Social
Concerns- a) Poverty and Discrimination b) Aggretions, Violences and Peace, c)
Mahatma Gandhi on Non-Violence, d) Health, e) Impact of television on
behaviour.
(LC to be discussed)
Oct. Unit IX: Developing Psychological Skills
19 days 1. Introduction 2. Developing as an effective psychologist 3) General Skills 4.
Observational Skills 5. Specific Skills –a) Communication Skills b)
Psychological Testing Skills 6. Interviewing Skills 7. Counselling Skills
(LC to be discussed)
Class XII (Pg. 079)
Nov. Revision + Preboard-I
20 days
Dec+ Jan+Feb Preboard-II
25 +21 +23=68 Board Examination
days
UNIT WISE DISTRIBUTION OF MARKS
UNIT MARKS
Psychology, Self and Society
09
I. Variations in Psychological Attributes
II. Self and Personality 10
III. Meeting Life Challenges 07
IV. Psychological Disorders 10
V. Therapeutic Approaches 07
VI. Attitude and Social Cognition 08
VII. Social Influence and Group Processes 07
VIII. Psychology & Life 06
IX. Developing Psychological Skills 06
70
Practicals
Development of case profile: Using appropriate methods like, interview, observation
and pyschological tests.
Test administration: Students are required to administer and interpret five tests.
In Practical Examination, the student will be required to administer & interpret two
30
psychological tests.
Distribution of Marks:
(i) Practical file + Project & Case Profile : 10 Marks
(ii) Viva Voice (case profile and practical): 05 Marks
(iv) Two practicals (5 for accurrate conduct and 10 for reporting) 15 marks
Total 100
Class XII (Pg. 080)
Career Information Centre
Class XII
CIC curriculum has been designed by Dr. Amrita Dass, Director, Institute of Career Studies,
Lucknow, a leading Career Counselling Institution of India.
Month & Content
No. of Days
Finalize
March+April +
May -Choice of country as a Study destination
12+21 + 07 = 40
days -3Cs: Course, College, Career
June + July University Application Process Knowhow: India and Abroad
15 + 26 = 41 days
Enhancing skills: Interview and Communication
August
24 days Profile Strengthening and Getting Documents Ready
September Individual queries and University workshops
25 days
October Session on Handling examination pressure
19 days
November
Revision
20 days
December
Revision
25 days
January
Revision
21 days
February
Revision
22 days
Class XII (Pg. 081)
Drill Syllabus 2021-22
Lht/
Anp Knowledge Vrn Bgn Snt Sct Ing
Partners
Karate Karate Karate
Karate Karate Karate Karate
KG & & &
& Ball & PEC & Sticks & PEC
POMPOM Tambourine Tambourine
Stick
Dandia
I-V Stick Pompom with Umbrella Ball Ball
Sticks
ribbons
Hoola Half
VI-VIII Stick Lazium Maypole Lazium Lazium
Hoop Ring
Support Simple
Lazium Simple P.T. Ring Basketball Dumbbell Dumbbell
Staff P.T.
Note: These drill must be performed on 26th January and have to be practiced in the mass
drill period.
* Karate classes to be conducted throughout the session and it is a must for students to
perform on Republic Day.
* Both male and female support staff must be part of the support staff drill on 26th January.
Quality Circle Time (QCT)
Quality Circle Time (QCT) is a creative way of allowing students to talk on a wide range of issues
in a safe inclusive environment. It helps them to develop self esteem and ultimately improve
academics. In this way in the school, we create non-threatening, collaborative and participatory
learning environment.
Four QCT sessions are held in a term in all Sunbeam Schools.
Class XII (Pg. 082)
Song on the Band 2021-22
Branch 15th Aug 26th Jan
Annapurna Sare jahan se achcha Aye mere watan ke logon
Lahartara &
Knowledge Nanha munha rahi hoon Kadam kadam badhaye ja
Partners
Varuna Chhodo kal ki baatein Hum sab bhartiya hain
Sarnath Sare jahan se achcha Aye mere watan ke logon
Suncity Mera mulk mera desh Yeh desh hai veer jawano
mera yeh watan ka
Bhagwanpur Watan ki raah pe watan ke
Taqat watan ki humse hai
naujawan shahid ho
Class XII (Pg. 083)
Class XII (Pg. 084)
TIME MANAGEMENT
NOTE-
1. Time management PPT’s to be shown before 1st PTM in April.
2. A recap session to be done in the last week of October so that
students make optimum use of the time management tips & do well in
their Board Examination.
Important Tips To Crack The Exams With Flying Colours
Recipe for success- Study while others are sleeping, work while others
are loafing, Prepare while others are playing and dream while others
are wishing.
Always feel positive - Positive attitude will make you through the
door of success and make you feel full of self confidence.
Plan Ahead—Make a schedule for your study—Scheduled study is
always better than last minute study. You get more time to
understand the fundamentals and also can study without any
pressure.
Make a long term calendar—Read the syllabus carefully and list out
all the due dates, important activities, projects & UT, exam, pre-
board and stick it in front of your study table or almirah from where
you can see it. Try to complete all your task accordingly on time.
Be organized—Have all your required material, books, ref-books,
notes, stationery, water & snacks on your study table.
Take short breaks—First read for an hour then go for a short break.
Make this break time as your "Me Time". Do whatever you like most
to refresh your mind. It will give a new power and freshness in your
Class XII (Pg. 085)
mind. A couple of hours each day helps you to remember more than
eight hours at once.
Peak concentration time -Varies from person to person, find out
your high concentration time and take up the most difficult topic
during that time. Try to study in the morning at least on
holidays/Sundays as morning is the best time to study as
environment is calm and mind is fresh and you can grasp easily.
Regularity— Attend class regularly & attentively. Write down the
important points as these notes are helpful to get good marks. Keep
in touch with your teachers to discuss your problem areas or any
other problem you come across during preparation.
Read NCERT text books thoroughly and then move on to other
reference books. NCERT books are simple and an absolute must to
clear concepts.
Always refer to tests which have been taken in your school and do
remedial work.
Prepare seriously for preboard.
Diagrams and derivations are challenging, Practice them as much as
you can.
Make notes—Always prepare good notes in your own language.
Notes are your best friend during exams. Books have tons of
information which may confuse you one day before exams.
Revise regularly—There is no point of studying if you don’t
remember it. Our memory fades away gradually. Revision plays a
cardinal role in getting good marks. Keep writing whatever you
revise.
Class XII (Pg. 086)
Improve handwriting—It really helps to get good marks especially
subjective long answers. Better handwriting ensures your teacher is
impressed with the answer.
English—Good Language—Always use simple words, to express
yourself. Make sure that you are grammatically, sound & write
simple grammatically correct English. Having a good vocabulary is of
course an advantage.
CBSE Sample paper—Solve all the questions of last year CBSE
sample paper in given time as it is good way to know the pattern of
questions. Attempt CBSE sample papers, treat them as real papers
and try to finish them in 2 hours 50 minutes and keep 10 minutes to
revise.
Date sheet-When you get the date sheet, note down the gaps
between two papers and date of last paper. Make the schedule for
revision accordingly i.e finish first the revision of last paper and then
according to the number of days (gaps) given in papers.
Don’t neglect your health—Have fruits & vegetable everyday, drink
lots of water & avoid junk food.
Play at least half an hour ever day and sleep well
Tips for the Exam day-
Make sure that you can scan through your notes a day before exam.
Never read a new topic on exam day.
Be confident and relaxed.
Sleep well the night before the exam.
Arrive early at the test center with laminated admit card. (Admit
card should be laminated)
Make sure that you have pen, pencil, eraser and other stationary
required.
Class XII (Pg. 087)
Trust your preparation and give your best.
During Exam time –
Read all the instructions carefully before giving exams.
Time management is very important for solving the answer sheet
.Read out all the questions carefully and allot time according to
the number of questions and questions carries maximum marks.
Be systematic and don’t mix sections while attempting the
questions. It may confuse or irritate the checker and you loose the
marks in confusion.
Don’t get stuck on a question. If you have a difficulty don’t waste
much time and move on to the next question and try doing that
question after you finish your exams and still left with time.
Set aside 15 minutes to revise the answer sheet. It is important to
make sure that you haven’t made any mistakes at least on those
questions which you have attempted confidently.
Answer sheets should be neat and clean. Underline the line you
feel important and want to attract the examiner towards that.
Be specific in your answers, examiners expects you to write
answers to the point.
“NO ONE and NOTHING will help you unless you are willing to
help YOURSELF.”
GOOD LUCK!
Class XII (Pg. 088)
You might also like
- Jo Khola Uski Ma Ki ChutDocument92 pagesJo Khola Uski Ma Ki ChutTech SupportNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - XII 2022-23-2Document92 pagesSyllabus - XII 2022-23-2Alex SmithNo ratings yet
- Booklist - XII 2020Document4 pagesBooklist - XII 2020Kratika VarshneyNo ratings yet
- XI - Main Syllabus (For March+April+May) - 2023-24Document17 pagesXI - Main Syllabus (For March+April+May) - 2023-24roshani yadavNo ratings yet
- Xi 2021-22Document4 pagesXi 2021-22vinayraj 9a2020No ratings yet
- Booklist - XI 2024-25Document4 pagesBooklist - XI 2024-25rajinderkaur115599No ratings yet
- Note - : Subjects Name of The Books PublishersDocument6 pagesNote - : Subjects Name of The Books Publishersa k singhNo ratings yet
- BOOK LIST For Class - X (2020-21) : Ubjects Ame of The Ooks UblishersDocument2 pagesBOOK LIST For Class - X (2020-21) : Ubjects Ame of The Ooks UblishersRudra Narayn PandaNo ratings yet
- Class Xii PMC & PBCDocument50 pagesClass Xii PMC & PBCIhaNo ratings yet
- Book List12 SciDocument1 pageBook List12 SciJoyjeet Mitra XI-ANo ratings yet
- Revized Booklist-IX 2020Document4 pagesRevized Booklist-IX 2020yashitasehgal1111No ratings yet
- Sfws Xii BooklistDocument2 pagesSfws Xii Booklistofficialfarmaan1009No ratings yet
- Sfws Xii BooklistDocument2 pagesSfws Xii Booklistofficialfarmaan1009No ratings yet
- Book ListDocument4 pagesBook ListShahAzeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Book List of Class XiiDocument4 pagesBook List of Class XiiAshish ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- TitleDocument2 pagesTitleSampanna DhakalNo ratings yet
- Prescribed Textbooks 2023 24Document4 pagesPrescribed Textbooks 2023 24muskanm8888No ratings yet
- Class 11Document2 pagesClass 11shashanksurada05No ratings yet
- Book List Class XI ScienceDocument1 pageBook List Class XI ScienceSwayamNo ratings yet
- 3) Grade 11 - Book ListDocument4 pages3) Grade 11 - Book ListxyzNo ratings yet
- WCP 2404051633 2093238092 13Document1 pageWCP 2404051633 2093238092 13Sumit ShekherNo ratings yet
- Pwqsi XiDocument2 pagesPwqsi XiAhana PoddarNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Final Booklist (Session 2020-21) Class Name of The Book Name OF THE Author/Publishers Book Type EnglishDocument1 pageClass Ix Final Booklist (Session 2020-21) Class Name of The Book Name OF THE Author/Publishers Book Type EnglishMohd. QadriNo ratings yet
- Jawahar Vidya Mandir, Shyamali, Ranchi - 834002 BOOK - LIST - Class XI (2019-20)Document1 pageJawahar Vidya Mandir, Shyamali, Ranchi - 834002 BOOK - LIST - Class XI (2019-20)Varun Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- XI HumanitiesDocument2 pagesXI HumanitiesArchana SinghNo ratings yet
- Xii Book ListDocument4 pagesXii Book ListSamriddhi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Class XIDocument2 pagesClass XIAushnik RoyNo ratings yet
- Std. Xii (Text Book List) 24 - 25Document1 pageStd. Xii (Text Book List) 24 - 25devadarshan.viiieNo ratings yet
- Book List Xi Xii 2022 23Document4 pagesBook List Xi Xii 2022 23Shalini JhaNo ratings yet
- Science XiDocument2 pagesScience Xiparthamohanta447No ratings yet
- Booklist 2023 24Document9 pagesBooklist 2023 24Purnima TiwariNo ratings yet
- List of Books For Class IX Session (2020-2021)Document2 pagesList of Books For Class IX Session (2020-2021)Nandan KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Acadmic Syllabus 2022 23Document13 pagesClass 12 Acadmic Syllabus 2022 23Guru Gulab KkhatriNo ratings yet
- CLASS X - List of Books For The Session 2022Document2 pagesCLASS X - List of Books For The Session 2022Ni shNo ratings yet
- 12 Class Book ListDocument1 page12 Class Book ListLallan SinghNo ratings yet
- Book List 2024 - 25, XIDocument2 pagesBook List 2024 - 25, XIneeraj6968eNo ratings yet
- TEXT BOOK DETAILS (2020 - 2021) : Class Subject PublisherDocument3 pagesTEXT BOOK DETAILS (2020 - 2021) : Class Subject PublisherGopi BabuNo ratings yet
- HHDocument10 pagesHHRaj MishraNo ratings yet
- DLL-2nd-week 7-12Document6 pagesDLL-2nd-week 7-12Brannon EludoNo ratings yet
- Book List Class XII 2024-25Document2 pagesBook List Class XII 2024-25ajaymishra26087No ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Kalinga: Book List For The Year: 2023-24Document3 pagesDelhi Public School Kalinga: Book List For The Year: 2023-24saquibasif98270No ratings yet
- Book List Class XiiDocument3 pagesBook List Class XiiRg RrgNo ratings yet
- S.N Subjects Name of The Book Name of The Publishers 1Document1 pageS.N Subjects Name of The Book Name of The Publishers 1Jocy9No ratings yet
- (Syllabus For Class-Xii) 2015-2016Document4 pages(Syllabus For Class-Xii) 2015-2016Daniel KhanNo ratings yet
- Book List: Class Xi - Humanities FOR THE SESSION: 2019 - 2020Document1 pageBook List: Class Xi - Humanities FOR THE SESSION: 2019 - 2020GT ANUPNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Cyclic Test - 1 Syllbaus Sheets 2022-2023Document3 pagesClass Xii Cyclic Test - 1 Syllbaus Sheets 2022-2023PranavNo ratings yet
- U.T. Syllabus Class 10thDocument2 pagesU.T. Syllabus Class 10thwardhanyashmishraNo ratings yet
- Notes Physics ImportantDocument11 pagesNotes Physics Importantcustompros420No ratings yet
- STD IxDocument1 pageSTD Ixkumarharsh7425No ratings yet
- Sample Paper Syllabus 2021-22: ClassDocument2 pagesSample Paper Syllabus 2021-22: ClassPranav S Nair67% (3)
- Class 12-UpdatedDocument9 pagesClass 12-UpdatedVaibhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bcom - Sem1 - Iks - Unit 2Document20 pagesBcom - Sem1 - Iks - Unit 2nandinisonar05No ratings yet
- XII ScienceDocument2 pagesXII ScienceMokshita JainNo ratings yet
- Prescribed Textbooks 2023 24Document10 pagesPrescribed Textbooks 2023 24ravibhaknpNo ratings yet
- GS NCERT LIST (2 Yr Foundation Batch) 20221121060632Document1 pageGS NCERT LIST (2 Yr Foundation Batch) 20221121060632enchantress soulsingerNo ratings yet
- Nust Chemistry 1550Document136 pagesNust Chemistry 1550Meer UmarNo ratings yet
- 10sm Science 2021 22Document344 pages10sm Science 2021 22Impulse Academy NoidaNo ratings yet
- Class XII PT1 Syllabus and HHWDocument3 pagesClass XII PT1 Syllabus and HHWbitthariashivangiNo ratings yet
- Booklist XII-2024Document1 pageBooklist XII-2024stiphenmarandiNo ratings yet
- 17 Aldovino V Pujalte, Jr.Document8 pages17 Aldovino V Pujalte, Jr.Princess Samantha SarcedaNo ratings yet
- IBC CodeDocument1 pageIBC CodeEezmaira S ShaharuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12Document2 pagesLesson 12Kimberly Lunar AlaskaNo ratings yet
- Disciplines and Ideas in The Applied Social SciencesDocument5 pagesDisciplines and Ideas in The Applied Social SciencesJonalyn Banez0% (1)
- Mephi Guide PDFDocument30 pagesMephi Guide PDFMuhammad FaizNo ratings yet
- Readings On Participatory Planning: Available OnlineDocument21 pagesReadings On Participatory Planning: Available Onlinepallavidelite22No ratings yet
- Direct Selling Report PDFDocument3 pagesDirect Selling Report PDFJigar PatelNo ratings yet
- Japanese Immigration To Mexico PDFDocument19 pagesJapanese Immigration To Mexico PDFCarlos MorenoNo ratings yet
- Lembar Kerja 1Document14 pagesLembar Kerja 1niaNo ratings yet
- The Differentiated University: Recognizing The Diverse Needs of Today'S StudentsDocument10 pagesThe Differentiated University: Recognizing The Diverse Needs of Today'S StudentspedropauloNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Connections: A Study of Effective Calculator Use in Secondary Mathematics ClassroomsDocument22 pagesMathematical Connections: A Study of Effective Calculator Use in Secondary Mathematics ClassroomsChess NutsNo ratings yet
- Security Officer Part Time in Orange County CA Resume Robert TalleyDocument2 pagesSecurity Officer Part Time in Orange County CA Resume Robert TalleyRobertTalleyNo ratings yet
- Suffolk Family Carers ' Caring Touch November 2010Document24 pagesSuffolk Family Carers ' Caring Touch November 2010Suffolk Family CarersNo ratings yet
- Skim Boarding: Carlyn PolisticoDocument13 pagesSkim Boarding: Carlyn PolisticoDonn NeriNo ratings yet
- Mary Kay Inc., Company AnalysisDocument7 pagesMary Kay Inc., Company Analysisrio boseNo ratings yet
- Apo Fruits Corporation v. Land Bank of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesApo Fruits Corporation v. Land Bank of The PhilippinesJoshua TanNo ratings yet
- Political MarketingDocument10 pagesPolitical MarketingNigora_AdizovaNo ratings yet
- Exam Policies and ProceduresDocument6 pagesExam Policies and ProceduresFirstnameNo ratings yet
- Starhub Case Study Ipc v4Document4 pagesStarhub Case Study Ipc v4Sean NgNo ratings yet
- Trends Nov25 29Document6 pagesTrends Nov25 29Rudnickz MagbujosNo ratings yet
- Rescind DMV Contract PDFDocument1 pageRescind DMV Contract PDFKevin YohburtNo ratings yet
- RS 4Document25 pagesRS 4Lata JagwaniNo ratings yet
- Challenges in Accessing Sexual and Reproductive Health Services by People With Physical Disabilities in Kampala, UgandaDocument9 pagesChallenges in Accessing Sexual and Reproductive Health Services by People With Physical Disabilities in Kampala, UgandaFlorence Kyoheirwe MuhanguziNo ratings yet
- DLL Chinese Peking OperaDocument3 pagesDLL Chinese Peking OperaCiarah Leynes Mangcoy100% (1)
- En10Lc-Iib-15.1: En10Rc-Iia-11: Transcode En10Wc-Iia-13.1: Identify PartsDocument4 pagesEn10Lc-Iib-15.1: En10Rc-Iia-11: Transcode En10Wc-Iia-13.1: Identify Partsjoel bagalanonNo ratings yet
- Kendalls and Marzanos New TaxonomyDocument22 pagesKendalls and Marzanos New TaxonomyRUTHY ANN BALBIN BEEd 2-1100% (1)
- Full Sail Housing Guide PDFDocument64 pagesFull Sail Housing Guide PDFRoshinNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Visual Arts Course OutlineDocument5 pages7th Grade Visual Arts Course OutlineMaureen Cusenza100% (1)
- Linguistics, Second Edition - David CrystalDocument292 pagesLinguistics, Second Edition - David CrystalYozamy Triana100% (3)
- LESSON PLANNING - Quadratic Inequality WatermarkDocument10 pagesLESSON PLANNING - Quadratic Inequality WatermarkAzizi. Ah SuhupiNo ratings yet