Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Budget Process: Learning Objectives
The Budget Process: Learning Objectives
Uploaded by
MarkOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Budget Process: Learning Objectives
The Budget Process: Learning Objectives
Uploaded by
MarkCopyright:
Available Formats
24
ha p r •
I r
Chapter 2
The Budget Process
Learning Objectives
1. Enumerate the steps in the budget process.
2. Describe briefly the principles of responsibility accounting.
The National Budget
Government accounting is primarily budgetary accounting.
Government accounting does not only aim to provide information
on past events and transactions but also budget information in
accordance with PPSAS 24.
The Philippine Constitution and other laws require
government funds to be utilized in accordance with a national
budget that is duly approved by · legislation. Government
accounting, therefore, is concerned with providing information
useful in assessing the conf ormance of utilization of government
funds with the approved budget.
The national budget (government budget) is government
estimate of the sources and uses of government fund ·within
fiscal year . ·This forms the basis for expenditure s and is
the government's key instrument for promoting its socio-
economics objectives.
The formulation and eventual utilization of the national
budget are summarized in the budget cycle.
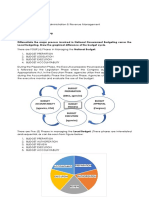
The Budget Cycle
The budget cycle has four phases namely
1. Budget Preparation
2. Budget Legislation
3. Budget Execution
4. Budget Accountability
Tire B11rfgct Process
Budget Prepa ration
The budget preparation in the Phi l ippi n , . . ,,
8 u s s
approach. Under "bottom-up" budgc • bottom-u
c:i
Un , ?,,
. . . . g, sev ra 1 pa rb'·',
participa te m the budget prepa ra tion sta rHng firom th L •
. ' e owest fo the
highest levels of the govern ment Governmen t ag"nc'
. · "' ics a re a1 s<>
tasked to increase the participation of citizen-stakeholder s in th
budget preparation. The opposite of "bottom-up' ' b udgeting is
"top-down" budgeting - wherein the budget prepa ration starts
from the agency heads.
In 2011, the Philippine Government attempted to a start
Junting. a new tradition by shif ting from the old "incrmental" system of
'lllation budgeting to. the nzero-based budgeting" approach . (The Philippine
Public Transparency Reporting Project, January 11, 2011)
ttion in
require vs.
);;> The current year's budget is > The current year's budget is
zational formulated based on the formulated without regard
nrnent previous year's budget, to the previous year's
iJ1ation which is just adjusted for budget. Government
tunent any variances experienced agencies are required to
in the past. Presumably, the justify their current year's
en rs proposed programs and proposed programs and
thin a expenditures m the expenditures, irrespective
i's the previous year are of whether these are new or
automatically approved in carried over from the
the current year. previous year.
> Uses a "roll-over" approach. );:> Uses a "back-to-zero" or
> Prone to abuse. "clean late" approach.
);:> Promotes efficient and
effective utilization of
funds.
1. Budget call _ The budget preparation starts when the
Department of Budget and Management (DBM) issues a
Budget Call to all government agencies. The budget call
You might also like
- Budgeting The Educational PlanDocument5 pagesBudgeting The Educational Plancameracafe90% (21)
- Barangay Budget ProcessDocument188 pagesBarangay Budget ProcessRaquel dg.Bulaong100% (8)
- Roche Genentech Investor PresentationDocument18 pagesRoche Genentech Investor PresentationRiccardo Andreola0% (1)
- Unit-12 (Budgting)Document12 pagesUnit-12 (Budgting)Harsh AroraNo ratings yet
- Budgeting in EducationDocument4 pagesBudgeting in Educationvanessa adriano100% (2)
- Reaction Paper Public AdDocument4 pagesReaction Paper Public AdAshley Ann Carable100% (1)
- Alfred-Marshall UpdatedDocument7 pagesAlfred-Marshall UpdatedChristina AureNo ratings yet
- Outlook Business e Magazine PDFDocument60 pagesOutlook Business e Magazine PDFMadhura ChafleNo ratings yet
- The Budget Process: (The Philippine Public Transparency Reporting Project, January 11, 2011)Document8 pagesThe Budget Process: (The Philippine Public Transparency Reporting Project, January 11, 2011)rochNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Budget ProcessJ EDITED TO MORE READABLEDocument69 pagesThe Philippine Budget ProcessJ EDITED TO MORE READABLEFav TangonanNo ratings yet
- Week 1 .04 - Philippine Budgetary ProcessDocument70 pagesWeek 1 .04 - Philippine Budgetary ProcessElaineJrV-Igot100% (1)
- Budget ProcessDocument7 pagesBudget Processmaefgr1012No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Budget ProcessDocument5 pagesChapter 2 The Budget ProcessEthel Joy Tolentino GamboaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Agency FOCUS: Department of Budget and Management: Usec. Ryan L. Estevez, Mare, MPPDocument79 pagesUnit 3: Agency FOCUS: Department of Budget and Management: Usec. Ryan L. Estevez, Mare, MPPArnel Chavez SalazarNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Budget Process: Local Government Management GuideDocument32 pagesUnderstanding The Budget Process: Local Government Management GuideAigene PinedaNo ratings yet
- 6-Budget ProcessDocument4 pages6-Budget ProcessMs. ANo ratings yet
- Principles of Public BudgetingDocument56 pagesPrinciples of Public BudgetingDM SilonganNo ratings yet
- Aragones AccntgGovt&NonProfitOrgs Ass1Document6 pagesAragones AccntgGovt&NonProfitOrgs Ass1Jamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Eg CachaperoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Budget Process CompressDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Budget Process CompressK cNo ratings yet
- Instructional Supervisory Plan For ED 22Document8 pagesInstructional Supervisory Plan For ED 22RonaldDechosArnocoGomezNo ratings yet
- Government Accounting Chapter 2Document5 pagesGovernment Accounting Chapter 2Jeca RomeroNo ratings yet
- Budget PreparationDocument8 pagesBudget PreparationViolet EvergardenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Budget ProcessDocument9 pagesChapter 2 The Budget Processdomingoramos685No ratings yet
- GovAcc HO No. 2 - The Philippine Budget CycleDocument9 pagesGovAcc HO No. 2 - The Philippine Budget Cyclebobo kaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2Adan EveNo ratings yet
- The Role of BudgetaryDocument8 pagesThe Role of BudgetaryadegloryNo ratings yet
- Government BudgetingDocument15 pagesGovernment BudgetingPaul100% (1)
- Budgetary System: Phlippine GovernmentDocument20 pagesBudgetary System: Phlippine GovernmentMark Vincent Z. PadillaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Assignment 2 Public FinanceDocument4 pagesMidterm Assignment 2 Public FinanceCHARRYSAH TABAOSARESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Budget Cycle (Notes)Document7 pagesChapter 2 - The Budget Cycle (Notes)Angela Denisse FranciscoNo ratings yet
- The Budget Process: Group 1 LeaderDocument16 pagesThe Budget Process: Group 1 LeaderJabbaNo ratings yet
- Public Ad (Lecture 19) Budgeting and Financial AdministrationDocument23 pagesPublic Ad (Lecture 19) Budgeting and Financial AdministrationHafiz Farrukh Ishaq IshaqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document16 pagesChapter 2Aldrin John TungolNo ratings yet
- Prelims 2017: in DaysDocument40 pagesPrelims 2017: in Daysჯონ ფრაატეეკNo ratings yet
- MPA Quiz No. 3Document3 pagesMPA Quiz No. 3Fykies:No ratings yet
- What Is Government BudgetingDocument13 pagesWhat Is Government BudgetingVienna Mei Romero100% (7)
- Executive Summary: (Type Text)Document11 pagesExecutive Summary: (Type Text)Mahera NazninNo ratings yet
- Government BudgetingDocument6 pagesGovernment BudgetingMariaCarlaMañago100% (1)
- The BudgetDocument4 pagesThe BudgetrodyaromanoNo ratings yet
- Aspire March 2023 Psaf Intervention - 04-03-2023Document46 pagesAspire March 2023 Psaf Intervention - 04-03-2023Desmond Grasie ZumankyereNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 BudgetProcess. Gr.3Document20 pagesCh.2 BudgetProcess. Gr.3Jhonrey BragaisNo ratings yet
- Financial Administration - Special TopicsDocument19 pagesFinancial Administration - Special TopicsNAYOMI LOIS CISNEROSNo ratings yet
- Public Sector Accounting CHAPTER TWODocument9 pagesPublic Sector Accounting CHAPTER TWOPhil SatiaNo ratings yet
- Distribution and Expenditures of Philippine National BudgetDocument92 pagesDistribution and Expenditures of Philippine National Budgetdarlyn avanceNo ratings yet
- PSA Assgn 1Document12 pagesPSA Assgn 1Mathews SakalaNo ratings yet
- Budget ProcessDocument35 pagesBudget ProcesstjasonkiddNo ratings yet
- Budgetary System Budget Process of The Philippine GovernmentDocument48 pagesBudgetary System Budget Process of The Philippine GovernmentCarlo Ray Diase100% (3)
- Chapter Three FundDocument9 pagesChapter Three FundnaodbrtiNo ratings yet
- Text Book: Chapter 5 & 6: Farah Binti AzizDocument31 pagesText Book: Chapter 5 & 6: Farah Binti AzizAsheequin ZainolNo ratings yet
- Public Finance GROUP 4Document18 pagesPublic Finance GROUP 4Roby IbeNo ratings yet
- Government Budgeting: Principle and The Budget CycleDocument46 pagesGovernment Budgeting: Principle and The Budget CycleHadji Mohammad Ajul MunicipalityNo ratings yet
- Budget LegislationDocument3 pagesBudget LegislationMitch Flores AlbisoNo ratings yet
- Budget & PPPDocument39 pagesBudget & PPPaleenam.shaheerNo ratings yet
- Theory of State BudgetsDocument15 pagesTheory of State BudgetsWyrlo Binamira Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Budgeting and Financial Management-1Document27 pagesChapter 5 Budgeting and Financial Management-1Syed Zohaib KazmiNo ratings yet
- Baps 09 Block 03 IDocument63 pagesBaps 09 Block 03 IMd ShamiNo ratings yet
- Report Budget Preparation and DeliberationDocument27 pagesReport Budget Preparation and DeliberationChristine CerdaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Accounting For Budgetary AccountsDocument8 pagesChapter 4 - Accounting For Budgetary AccountsAdan EveNo ratings yet
- Aspire April 2022 Psaf Intervention Final 26 03 22-FinalDocument40 pagesAspire April 2022 Psaf Intervention Final 26 03 22-FinalDesmond Grasie ZumankyereNo ratings yet
- Local Public Finance Management in the People's Republic of China: Challenges and OpportunitiesFrom EverandLocal Public Finance Management in the People's Republic of China: Challenges and OpportunitiesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Encouraging Entrepreneurship in The Philippines: Name: Renelle Habac SECTION: CBET-01-401PDocument4 pagesChapter 9: Encouraging Entrepreneurship in The Philippines: Name: Renelle Habac SECTION: CBET-01-401PRenelle HabacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Set 1 Dividend Discount ModelsDocument14 pagesChapter 6 Set 1 Dividend Discount ModelsNick HaldenNo ratings yet
- 13 Corporate FinancingDocument25 pages13 Corporate FinancingKanika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Tally Erp 9 It AssignmentDocument8 pagesTally Erp 9 It Assignmenta0mittal7No ratings yet
- Assignment Chapter 4/6Document4 pagesAssignment Chapter 4/6Muhammad Tahir NawazNo ratings yet
- Nestle McsDocument14 pagesNestle Mcsprasanna_lad11100% (1)
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty ThesisDocument6 pagesCustomer Satisfaction and Loyalty Thesisanaespinalpaterson100% (2)
- Philip KotlerDocument3 pagesPhilip Kotlernantha74No ratings yet
- Part 1Document7 pagesPart 1Mir AnikNo ratings yet
- What Is Business FailureDocument3 pagesWhat Is Business Failurecosmas crymore MugwandaNo ratings yet
- Blue and White Finance PresentationDocument18 pagesBlue and White Finance PresentationluisjmvNo ratings yet
- CBDCs Beyond Borders - Results From A Survey of Central Banks (Jun 2021)Document22 pagesCBDCs Beyond Borders - Results From A Survey of Central Banks (Jun 2021)Fernando HernandezNo ratings yet
- FEIA Mid-Term Assignment - FNPV: Year T 0 1 2 3 4 5 OutflowsDocument16 pagesFEIA Mid-Term Assignment - FNPV: Year T 0 1 2 3 4 5 OutflowsMaurice ScholtesNo ratings yet
- Mau Bao Cao Tai Chinh Bang Tieng Anh 131104211352 Phpapp02Document4 pagesMau Bao Cao Tai Chinh Bang Tieng Anh 131104211352 Phpapp02Vy Nguyen0% (1)
- Accelerating The Transition To The Circular EconomyDocument62 pagesAccelerating The Transition To The Circular EconomyarifkoseogluNo ratings yet
- Revised Pharmaceutical Supply Transformation Plan 2018-2020Document76 pagesRevised Pharmaceutical Supply Transformation Plan 2018-2020Demis TeshomeNo ratings yet
- How COVID-19-is-changing-consumer-behaviornow-and-foreverDocument6 pagesHow COVID-19-is-changing-consumer-behaviornow-and-forevermesay83No ratings yet
- Marketing Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesMarketing Plan TemplatesuderNo ratings yet
- Group 9 - Montreaux ChocolateDocument10 pagesGroup 9 - Montreaux ChocolateNikhil PathakNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 3.1 Balance Sheet of Horizon Limited As at March 31, 20x1Document121 pagesExhibit 3.1 Balance Sheet of Horizon Limited As at March 31, 20x1DrSwati BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Strategy Planning MatrixDocument2 pagesQuantitative Strategy Planning MatrixKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Poly Peck Case Question 1Document6 pagesPoly Peck Case Question 1sdfdsf100% (1)
- ITC Sustainability Integrated Report 2023Document212 pagesITC Sustainability Integrated Report 2023Sanchit ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Steph Business PlanDocument17 pagesSteph Business PlanVictor ImehNo ratings yet
- Islamic Finance Project-MutualFundsDocument42 pagesIslamic Finance Project-MutualFundsMuhammad Mamoon Iqbal0% (1)
- GardenDocument30 pagesGardenNilay JogadiaNo ratings yet
- Research in MathDocument6 pagesResearch in MathMika Dato ValdezNo ratings yet