Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Other Members of The Solar System
Other Members of The Solar System
Uploaded by
arlene aliporoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Other Members of The Solar System
Other Members of The Solar System
Uploaded by
arlene aliporoCopyright:
Available Formats
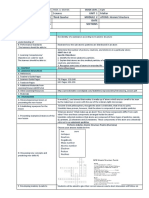
Grade
School DASNHS Level 8
Learning
Teacher ARLENE M. ALIPORO Area SCIENCE
Teaching February 9, 2021
DAILY Dates and (Burgos, Del Pilar,
LESSON Quarter SECOND
Time Agoncillo, Dagohoy,
LOG Luna)
I. OBJECTIVES
The learners demonstrate understanding of the characteristics of comets, meteors, and
A. Content Standard
asteroids.
B. Performance Standard Discuss whether beliefs and practices about comets and meteors have scientific belief.
C. Learning Competency Compare and contrast comets, meteors and asteroids. S8ES-IIg-22
1. Compare and contrast comets, meteors, and asteroids.
D. Specific Learning 2. identify the characteristics of a comet, a meteor, and an asteroid.
Objectives 3. see their value in providing scientists with information about the origin of the solar
system.
II. CONTENT Asteroids, Comets, and Meteors
III. LEARNING
RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide
pages
2. Learner’s Materials Self-Learning Modules of students Week 6
pages
3. Textbook pages Science Learners Module pp. 153-159
4. Additional Materials
from Learning
Resource (LR) portal
B. Other Learning Internet Sources
Resource
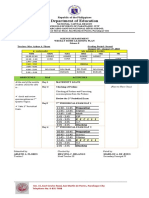
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing Unscramble Me
previous lesson or
presenting the new S D O I T A E S R – ASTEROIDS
lesson E M I D O T O E R – METEOROID
(ELICIT) R E M E T S O – METEORS
I T E ME T I O E R – METEORITE
S T C M O E – COMETS
*Ask the students about their knowledge on those objects. Ask them to describe each.
They can refer in their module Let’s Recall.
ASTEROIDS – known as planetoids or minor planets
METEOROID – “space rocks”
METEORS – “shooting stars”
METEORITE – meteoroid survived from a trip through the Earth’s atmosphere
and hits the Earth’s surface.
COMETS – large “dirty snowball”
B. Establishing a Describing distinct features of comets, asteroids, and meteors
purpose for the
lesson The students will watch a video presentation about comets, asteroids, and meteors. They
(ENGAGE) will take some important notes in their notebook.
C. Presenting GUIDE QUESTIONS:
examples/Instances 1. What are near-earth objects?
of the new lesson 2. Why are comets and asteroids called NEO by astronomers?
(ENGAGE) 3. How do you distinguish comets from asteroids and meteors?
D. Discussing new Venn Diagram
concepts and Come, Come, Come…COMETS- Go, Go, Go Astray ASTEROID
practicing new skills ACTIVITY 1: Venn Diagram – Characteristics of
#1 comets and asteroids
(EXPLORE) Directions: Complete the Venn diagram below to
compare comets and asteroids. Write
their differences in the outer circle and their
E. Discussing new similarities in the center (where the circles
concepts and overlap). Choose your answer from the given
practicing new skills items in the table.
#2
F. (EXPLORE)
GUIDE QUESTION: How are comets, meteors, and asteroids alike?
You Can Do This...Space ROCKeteers!
Activity 2: COMET vs. METEOR vs. ASTEROID
Directions: Write down the differences among the three based on description, location and
movement. Do this on your answer sheet.
G. Developing mastery
(EXPLAIN)
GUIDE QUESTION: Why do scientists on earth need to know the description, location
and movement of comets, meteors, and asteroids?
H. Finding practical Activity 3: Hit Me With Your Best Shot!
application of Objective: Simulate the impacts of comets or asteroids on Earth.
concepts and skills Materials:
in daily living Tray (any size available at home), Sand (can try also flour or starch; gaw-gaw), 3
(ELABORATE) different-sized
I. Making (Small, medium, and large) rocks, 30 cm Rule, Pencil with eraser and Paper
generalizations and Procedure:
abstractions about 1. Fill in the try with sand, flour, or starch.
the lesson 2. Place the try with sand on the floor.
3. Measure a 1-meter height from the tray and mark it the highest point.
4. Drop each rock one at a time from the same height.
Make each three trials for each rock.
5. Draw your observations on a separate sheet of paper following the format below.
GUIDE QUESTIONS:
1. What was formed when you dropped the rock to the sand?
2. How will you compare your observation to the crater found on earth and moon?
3. Was there a difference on the impact made by each rock? How will you relate this to
the actual impact of space rock?
Let’s Evaluate
DIRECTION: Choose the letter that corresponds to the correct answer. Write your answer
on your answer sheet.
1. How can you differentiate a comet from an asteroid?
A. Comets orbit planets and most asteroids orbit the Sun.
B. Comets are hot ball of gas and asteroids are made mostly of ice.
C. Comets are made mostly of ice and asteroids are made mostly of rocks.
D. Comets form constellations in the sky and asteroids form fireballs in the sky.
2. What do we call these objects from space that enter Earth’s atmosphere and commonly
called “shooting stars”?
A. Comets C. Meteors
J. Evaluating learning B. Asteroids D. Meteorite
(EVALUATE) 3. What do we call when an object strikes the surface of a planet or moon, and they leave
a deep impression on its surface?
A. Canyon C. Pothole
B. Crater D. Sinkhole
4. Which of the two properties of an impacting object have the greatest effect on the
amount of energy released by the impact?
A. Mass and Diameter C. Impact angle and Density
B. Diameter and Density D. Mass and Impact Velocity
5. What are the two most abundant elements in the Earth’s crust and are also the main
composition of Asteroids?
A. Oxygen and Silicon C. Iron and Nickel
B. Hydrogen and Nitrogen D. Helium and Silver
K. Additional activities Let’s Create
for application or Designing an Earth Protector
remediation
Goal: Generate ideas on how to prevent a catastrophe that would result if a large
(EXTEND)
meteor hit the Earth.
Role: You are an artist, engineer and scientist
Audience: Physics teacher, Earth Science teacher and students
Situation: Reflect on your experimental results and consider what your new
understanding of impact tells about an actual meteor hitting the Earth. Write down ways
in which this knowledge could be applied to the design of an Earth Protector, a device
that would prevent a meteor from damaging the Earth. You can review the concepts
from your previous learning.
Draw a diagram of your Earth Protector to help explain your ideas and label the
various components.
Draw your idea on the separate worksheet.
Performance
You will be graded according to the rubrics below.
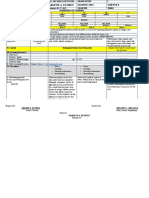
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation
A. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80%
B. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson
C. No. of learners who continue to require remediation
D. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these works?
E. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve?
F. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers?
Prepared by: ARLENE M. ALIPORO Checked by: MELVINA C. BELANGO
Science Teacher Head Teacher, Science Department
You might also like
- Philippine Area of ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesPhilippine Area of ResponsibilityANGELIQUE DIAMALON86% (7)
- Eq Test Questionnaire PDFDocument5 pagesEq Test Questionnaire PDFAnna May Daray0% (1)
- Lesson Plan (Understanding Typhoon)Document6 pagesLesson Plan (Understanding Typhoon)jelena jorgeoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Teaching Meteors, Meteorites and MeteoroidsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Teaching Meteors, Meteorites and MeteoroidsKaren Polinar75% (8)
- Daily Lesson Log Science Grade 8Document3 pagesDaily Lesson Log Science Grade 8Michael Ervin Guerzon100% (2)
- Demo Lesson Plan in Science 8 Cot 1Document9 pagesDemo Lesson Plan in Science 8 Cot 1Cristina Noble100% (3)
- Lesson Plan Using Inquiry - Based Teaching: Show An Image of A Comet, Meteor and AsteroidDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Using Inquiry - Based Teaching: Show An Image of A Comet, Meteor and AsteroidPrincess Mortega100% (5)
- Lesson Exemplar On Comets and MeteorsDocument4 pagesLesson Exemplar On Comets and MeteorsJimielle Shane Simon75% (4)
- DLL sCIENCE gRADE 8 Quarter 2 Week 13Document7 pagesDLL sCIENCE gRADE 8 Quarter 2 Week 13Gerald E Baculna100% (11)
- Meteors Meteoroids and MeteoriteDocument6 pagesMeteors Meteoroids and Meteoriteapi-313517608100% (5)
- DLP August 19,2019Document2 pagesDLP August 19,2019Shane Catherine Besares100% (1)
- Interdisciplinary Contextualization (Icon) and Inquiry-Based Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument3 pagesInterdisciplinary Contextualization (Icon) and Inquiry-Based Lesson Plan in ScienceMarie Saren100% (1)
- LESSON-PLAN - in Earth Space Grade 8Document8 pagesLESSON-PLAN - in Earth Space Grade 8ritchel comoderoNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8: Poypoy National High SchoolDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8: Poypoy National High SchoolAika Unica GabrielNo ratings yet
- Cot1 Sy 2021-2022 (2nd Quarter)Document11 pagesCot1 Sy 2021-2022 (2nd Quarter)Annzki GenonNo ratings yet
- Asteroids and Meteors LPDocument2 pagesAsteroids and Meteors LPBuzz manzhjanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Grade 8 DemoDocument6 pagesLesson Plan - Grade 8 DemoMialyn S. Cañete0% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanClenchtone Celiz100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 8Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 8Vincent AbapialNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Lesson Plan (Meteroids)Document8 pagesScience 8 Lesson Plan (Meteroids)Jaztine C MagnoNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Q2-Comets Meteors AsteroidsDocument14 pagesScience 8 Q2-Comets Meteors AsteroidsMelerose Dela Serna100% (1)
- Cot-Asteroids and CometsDocument4 pagesCot-Asteroids and Cometslyka laoNo ratings yet
- COT 1 - Lesson Plan in Science 8Document3 pagesCOT 1 - Lesson Plan in Science 8Janecil A. BonzaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Guide G8 Q2 Part3Document12 pagesLesson Guide G8 Q2 Part3Lauro Albano Jr.100% (1)
- Determine The Number of Proton (Observation)Document12 pagesDetermine The Number of Proton (Observation)Doreen Graziel Abadia Sabulao100% (2)
- Science - 8 - q2 - wk6 - Compare and Contrast Comets, Meteors and Asteroids 1Document12 pagesScience - 8 - q2 - wk6 - Compare and Contrast Comets, Meteors and Asteroids 1Aileen Ocampo100% (1)
- S8ES-IIe-20 Dissecting Tropical CycloneDocument4 pagesS8ES-IIe-20 Dissecting Tropical CycloneAsniah Takiri McrndsNo ratings yet
- Learning Area UNIT 1 Matter QUARTER Third Quarter MODULE 2 ATOMS: Atomic Structure Date Date Sections SectionsDocument37 pagesLearning Area UNIT 1 Matter QUARTER Third Quarter MODULE 2 ATOMS: Atomic Structure Date Date Sections SectionsAdrian Suladay100% (1)
- Ii. Content Iii. Learning Resources: Pencil/ Pen Crayon or Colored PencilsDocument2 pagesIi. Content Iii. Learning Resources: Pencil/ Pen Crayon or Colored Pencilsjanice alquizarNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: Grade 8 Daily Lesson LOG Region Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument3 pagesI. Objectives: Grade 8 Daily Lesson LOG Region Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterBongskie escalonaNo ratings yet
- Typhoon PARDocument5 pagesTyphoon PARreynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of Elements in The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesArrangement of Elements in The Periodic TableBerna TenioNo ratings yet
- DLL For Cot 1Document9 pagesDLL For Cot 1AVEGAY CELISNo ratings yet
- Sci8 Q3 Mod4 PeriodicTableofElements v3Document41 pagesSci8 Q3 Mod4 PeriodicTableofElements v3Cirille AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 5 ChemistryDocument9 pagesLesson Plan 5 ChemistryLeslayy CelizNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science (Grade 8 - 3 Quarter) Time Frame: 60 MinutesDocument7 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science (Grade 8 - 3 Quarter) Time Frame: 60 MinutesWayne David C. PadullonNo ratings yet
- DLP - G8 Science Indicator 4th GradingDocument8 pagesDLP - G8 Science Indicator 4th GradingMontealegre NhetNo ratings yet
- Tracing The Location of A Typhon Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesTracing The Location of A Typhon Lesson PlanJoh A Nna100% (2)
- Lesson Plan in Science 8: Second QuarterDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in Science 8: Second QuarterApple Grace Marie Sebastian100% (3)
- DLP 3Document2 pagesDLP 3ANGELIQUE DIAMALON100% (3)
- Science 8 3rd April 5-9, 2021: Learning Area Grade Level Quarter DateDocument2 pagesScience 8 3rd April 5-9, 2021: Learning Area Grade Level Quarter DateCriselAlamag100% (2)
- DLL Periodic TableDocument4 pagesDLL Periodic TableJonna Mae Llameg Hubac100% (1)
- DLL-Science 8Document2 pagesDLL-Science 8GERRY CHEL LAURENTE100% (2)
- 3rd Quarter DLP 20 MODULE 2Document4 pages3rd Quarter DLP 20 MODULE 2Jim Alesther LapinaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatJim Alesther LapinaNo ratings yet
- S8Mt-Iiia-B-8 S8Mt-Iiic-D-9Document3 pagesS8Mt-Iiia-B-8 S8Mt-Iiic-D-9LENETTE ALAGON100% (1)
- Lesson Plan - Plotting The ParDocument5 pagesLesson Plan - Plotting The ParCrisanto Llorente100% (2)
- DLP Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesDLP Atomic StructureEdmar AustriaNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science (Grade 8 - 3 Quarter) Time Frame: 60 MinutesDocument7 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science (Grade 8 - 3 Quarter) Time Frame: 60 MinutesEllaine0% (1)
- Tracking A Tropical CycloneDocument8 pagesTracking A Tropical CycloneRonadel Mecayer Magcalas CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Lesson ExemplarDocument4 pagesLesson ExemplarCielo Tobias JacintoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan PeriodictableDocument17 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan PeriodictableMary Rose RamosNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ChemistryDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ChemistryDivine Grace ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON PLAN 4a's (THE PARTICLE NATURE OF MATTER)Document4 pagesDAILY LESSON PLAN 4a's (THE PARTICLE NATURE OF MATTER)Janice PranadaNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science 8 Module 5Document15 pagesQ3 Science 8 Module 5Aiza Dagandan BangaNo ratings yet
- DLP IsotopesDocument10 pagesDLP IsotopesChristine Espinoza100% (2)
- Grade 8 Quarter 3 - DLLDocument39 pagesGrade 8 Quarter 3 - DLLDhangManongas-LlaboreVete100% (2)
- DLL Sci 8 12-13-2022Document3 pagesDLL Sci 8 12-13-2022Lovely Shiena C. AragoncilloNo ratings yet
- DLP FormatDocument6 pagesDLP FormatJay Vien Mark DulosaNo ratings yet
- G 8 2nd Quarter Module 3 Lesson 1920Document5 pagesG 8 2nd Quarter Module 3 Lesson 1920John Patrick IbonNo ratings yet
- DLL Sci 8 12-12-2022Document4 pagesDLL Sci 8 12-12-2022Lovely Shiena C. AragoncilloNo ratings yet
- Lac Session Ibona and LongakitDocument1 pageLac Session Ibona and Longakitarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Flores - WHLP - Aug 29-Sept 2Document2 pagesFlores - WHLP - Aug 29-Sept 2arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Graduation and Moving Up MessageDocument2 pagesGraduation and Moving Up Messagearlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Dll-Jan.30-Feb 3Document2 pagesDll-Jan.30-Feb 3arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- What's in The BucketDocument21 pagesWhat's in The Bucketarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- 3rd PTC - Minutes of The Meeting - 8 BURGOSDocument2 pages3rd PTC - Minutes of The Meeting - 8 BURGOSarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Pretest2023 24Document4 pagesPretest2023 24arlene aliporo100% (1)
- 2nd Periodical Test Schedule SY 2022 2023 DASNHSDocument5 pages2nd Periodical Test Schedule SY 2022 2023 DASNHSarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- 4th PTC MINUTES DEL PILARDocument2 pages4th PTC MINUTES DEL PILARarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- DLL Jan.23 27Document2 pagesDLL Jan.23 27arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Unit3matter 171128220356Document56 pagesUnit3matter 171128220356arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Flores WHLP Jan.23-27Document1 pageFlores WHLP Jan.23-27arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- DLL 1 Nov 2 4Document4 pagesDLL 1 Nov 2 4arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Q3W1 Properties of MatterDocument13 pagesQ3W1 Properties of Matterarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Flores - WHLP - Jan.30 - Feb 3Document1 pageFlores - WHLP - Jan.30 - Feb 3arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document1 pageActivity 1arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- FLORES COT1 T I III For SY 2021 2022 FEBRUARY 17 2022Document2 pagesFLORES COT1 T I III For SY 2021 2022 FEBRUARY 17 2022arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Smashed Phils. Narrative ReportDocument3 pagesSmashed Phils. Narrative Reportarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- DLL Q3W1Document2 pagesDLL Q3W1arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Pandemic in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 Pandemic in The Philippinesarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Region Division School Name School Id: 8 Lapu-Lapu 2021 - 2022 AP8 Mr. E. OlinoDocument1 pageRegion Division School Name School Id: 8 Lapu-Lapu 2021 - 2022 AP8 Mr. E. Olinoarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- An Assessment of The Distance Education in Taguig CityDocument4 pagesAn Assessment of The Distance Education in Taguig Cityarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- (S8Mt-Iiia-B-8) : A. Reviewing Previous Lesson or Presenting The New Lesson (Elicit)Document4 pages(S8Mt-Iiia-B-8) : A. Reviewing Previous Lesson or Presenting The New Lesson (Elicit)arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Internet Sources A. Reviewing Previous Lesson or Presenting The New Lesson (Elicit)Document4 pagesInternet Sources A. Reviewing Previous Lesson or Presenting The New Lesson (Elicit)arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- q3 w1 LessonDocument29 pagesq3 w1 Lessonarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Gear Tooth Contact PatternsDocument3 pagesGear Tooth Contact PatternsToua YajNo ratings yet
- Ancamine Teta UsDocument2 pagesAncamine Teta UssimphiweNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Information and Communication Technology 0417/31Document8 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Information and Communication Technology 0417/31Erdoğan ŞahinNo ratings yet
- Fuel EnergizerDocument29 pagesFuel EnergizeratulsemiloNo ratings yet
- The Roots of Modern Feminism: Mary Wollstonecraft and The French RevolutionDocument16 pagesThe Roots of Modern Feminism: Mary Wollstonecraft and The French RevolutionShirlya LimaNo ratings yet
- Test Architecture For Systolic Array of Edge-Based AI AcceleratorDocument11 pagesTest Architecture For Systolic Array of Edge-Based AI AcceleratorAnkush BLNo ratings yet
- Practical 2 Data TransferDocument3 pagesPractical 2 Data TransferHet PatelNo ratings yet
- 5.5 CBM Waste Skip Open Top - POWER BearDocument1 page5.5 CBM Waste Skip Open Top - POWER Bearqtia71133No ratings yet
- WhypyDocument13 pagesWhypyjhomz_592687235No ratings yet
- PR P3 DirtFish GAMER HandbookDocument9 pagesPR P3 DirtFish GAMER HandbookpeggyNo ratings yet
- Acetone - Deepak PhenolicsDocument1 pageAcetone - Deepak PhenolicsPraful YadavNo ratings yet
- Chem 1-8Document43 pagesChem 1-8Cabacungan, John VinceNo ratings yet
- Emerging 4Document41 pagesEmerging 4ebenezerteshe05No ratings yet
- UNIT 1 - Sequence 1.mdiDocument7 pagesUNIT 1 - Sequence 1.mdi,arcisNo ratings yet
- The Changing Politics of Foreign PolicyDocument3 pagesThe Changing Politics of Foreign PolicyLuís PatriotaNo ratings yet
- How To Choose The Right Cable GlandsDocument3 pagesHow To Choose The Right Cable GlandsRoger JohnNo ratings yet
- UPS KAISE 600-800va - Hoja de DatosDocument2 pagesUPS KAISE 600-800va - Hoja de DatosGermanYPNo ratings yet
- An Intelligent Knowledge Extraction Framework For Recognizing Identification Information From Real-World ID Card ImagesDocument10 pagesAn Intelligent Knowledge Extraction Framework For Recognizing Identification Information From Real-World ID Card ImagesJamesLimNo ratings yet
- Performix™ High Speed Dissolver - Technical DataDocument1 pagePerformix™ High Speed Dissolver - Technical DataNegash JaferNo ratings yet
- 7SG18 - Solkor N Complete Technical Manual PDFDocument154 pages7SG18 - Solkor N Complete Technical Manual PDFmonikaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Elec HD FS CKTruck 100713 ChevroletDocument247 pages2014 Elec HD FS CKTruck 100713 ChevroletREINALDO GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- TDB-E-CM 725-Technisches DatenblattDocument2 pagesTDB-E-CM 725-Technisches DatenblattNarimane Benty100% (1)
- Mixing F Luids: ChapterightDocument49 pagesMixing F Luids: Chapterightvane-16No ratings yet
- Valkokari TIMReview August2015Document8 pagesValkokari TIMReview August2015Héctor BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Devops MCQ PDFDocument6 pagesDevops MCQ PDFSaad Mohamed SaadNo ratings yet
- Limbo PowerpointDocument10 pagesLimbo Powerpointapi-693306390No ratings yet
- OM Chapter-1Document55 pagesOM Chapter-1TIZITAW MASRESHANo ratings yet
- 5th Ed Ch02 QCDocument6 pages5th Ed Ch02 QCmohanNo ratings yet
- Feature: SFP Optical Module 1 .25G Double Optical Fiber 20kmDocument2 pagesFeature: SFP Optical Module 1 .25G Double Optical Fiber 20kmDaniel Eduardo RodriguezNo ratings yet