Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shoulder Problem Evaluation: 6 Articulations or Joints
Shoulder Problem Evaluation: 6 Articulations or Joints
Uploaded by
MARY GIZETH GACHO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesThe document summarizes the anatomy of the shoulder complex, including its bones, joints, muscles, and key functions. It describes the 6 articulations of the shoulder joint and the static and dynamic stabilizers that support it. The rotator cuff muscles - supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis - are highlighted for their roles in stabilizing the humeral head and allowing full abduction. An overview is also provided of the major muscles that act on the scapula and humerus.
Original Description:
Original Title
Shoulder-Problem-Evaluation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the anatomy of the shoulder complex, including its bones, joints, muscles, and key functions. It describes the 6 articulations of the shoulder joint and the static and dynamic stabilizers that support it. The rotator cuff muscles - supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis - are highlighted for their roles in stabilizing the humeral head and allowing full abduction. An overview is also provided of the major muscles that act on the scapula and humerus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesShoulder Problem Evaluation: 6 Articulations or Joints
Shoulder Problem Evaluation: 6 Articulations or Joints
Uploaded by
MARY GIZETH GACHOThe document summarizes the anatomy of the shoulder complex, including its bones, joints, muscles, and key functions. It describes the 6 articulations of the shoulder joint and the static and dynamic stabilizers that support it. The rotator cuff muscles - supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis - are highlighted for their roles in stabilizing the humeral head and allowing full abduction. An overview is also provided of the major muscles that act on the scapula and humerus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
•
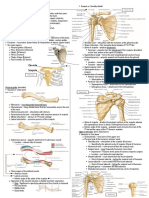
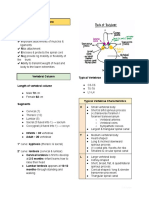
Shoulder Problem Spine of the scapula
Evaluation 6 Articulations or Joints
1. Coraco Clavicular
Shoulder assessment 2. Sterno Clavicular
3. Acromio Clavicular
• Second most common musculoskeletal 4. Gleno Humeral
5. Scapulo Thoracic
complaint 6. Sub Acromial Space
Difficult joint to examine
Separation- sternoclavicular separation/
• Multidirectional range of motion-
dislocation
UNIQUE! a) Sternoclavicular- common anterior
• Shoulder injury can affect nearly every dislocation
b) Acromion – superior dislocation
sport and many daily activities
c) Shoulder – anterior dislocation
Dislocations and separations are protected by
Bony Anatomy both “static” and “dynamic” stabilizers
Anterior a) Static – ligament (not moving)
b) Dynamic – provided by muscles
(moving)
Glenohumeral Joint
• Shallow (“golf ball sitting on a tee”)
Bones Scapula & -Inherently unstable (maximizes ROM)
clavicle
• Static stabilizers
-Move as a unit
-glenohumeral ligaments, glenoid labrum
-Clavicle’s articulation and capsule
with sternum is only
bony link to axial ➢ Dynamic stabilizers
skeleton
-Predominantly rotator cuff muscles
Bones -Also scapular stabilizers (Trapezius,
leavator scapulae, serratus anterior,
Key bony landmarks
rhomboids )
• Manubrium
• Clavicle The Rotator Cuff Muscles: SITS
• Coracoid process ✓ Supraspinatus ABD (rotate externally)
• Acromion process
✓ Infraspinatus ER (rotates externally)
• Glenoid fossa
✓ Teres minor ER ( rotates externally)
• Lateral border
• Inferior angle ✓ Supscapularis IR ( do internal rotation)
• Medial border -Depress humeral head against glenoid to
• Acromion process allow full abduction
• Glenoid fossa
• Lateral border
• Inferior angle
• Medial border
• Superior angle
• Rotation of head to opp. Side
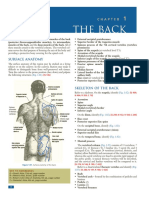
Shoulder Complex Muscles
• Lateral flexion of head to opp. Side
Scapular Muscles Middle Trapezius
Levator Scapulae O-
• Inferior part of ligamentum
O– Transverse processes of C1-C4 nuchea
I – Medial border of scapula between • T1-T5 spinous processes
superior angle and root of spine of I–
scapula
• Medial margin of acromion
N – Nerve root C3-5
process
F- (scapular elevation, retraction)
• Superior lip of spine of scapula
Rhomboid Major (OIN)
N – Spinal accessory
O-
F –Scapular retraction
• Major – T2-T5 spinous processes
Lower Trapezius
• Minor – Ligamentum nuchae, C7- O-T6-T12 spinous processes
T1 spinour processes I –Tubercle at apex of root of spine of
I– scapula
• Major – Medial borde of scapula N – spinal accessory
between spine and inferior angle F –Scapular depression, retraction
• Minor – medial border at root of and upward rotation
spine of scapula Serratus Anterior
N– O-
Dorsal Scapular Outer surfaces and superior border of
Upper Trapezius (OINF) ribs 1-8
O- I–
• Medial 1/3 of nuchal line Ventral scapular surface on medial
• Upper part of ligamentum nuchae border from superior angle to inferior
• C7 spinous process angle
I– N–
• Posterior border of lateral 1/3 of Long Thoracic
clavicle F–
• Acromion process Scapular protraction, upward rotation
N – spinal accessory Scapular depression (lower fibers)
F– Scapular elevation (upper fibers
• Scapular elevation, retraction
Pectoralis Minor Pectoralis Major
O- O-
• Superior margins and outer • Sternal – anterior surface of sternum,
surface ribs 3-5 near cartilages cartilages of ribs 1-6 or7
• Fascia overlying corresponding • Clavicular – anterior surface of sternal
intercostal muscles ½ clavicle
I– I – crest of humerus’s greater tuberosity
Medial border, superior surface of N–
coracoid process • Sternal – medial pectoral
N– • Clavicular – lateral pectora
Medial Pectoral F – GH ADD, H. ADD and IR
F– Anterior Deltoid
Scapular depression, downward O- Anterior border, superior surface of
rotation, protraction lateral third of clavicle
Biceps Brachii I –Deltoid tuberosity
O- N – Axillary
• Short head – coracoid process F–
• Long head – supraglenoid tubercle • GH H. ADD, flexion
of scapula • IR when in supine position
I– Middle Deltoid
• Radial tuberosity O -Lateral margin and superior
• Biceps brachii aponeurosis surface of acromion
N – Musculocutaneous I –Deltoid Tuberosity
F– N –Axillary
• Shoulder – flexion F –GH ABD
• Elbow – flexion, forearm Posterior Deltoid
supination O- Inferior lip of posterior border of
Coracobrachialis spine of scapula
O – Coracoid process I –Deltoid tuberosity
I- Medial surface of mid-humerus, N – Axillary
opposite to deltoid tuberosity F–
N –Musculocutaneous • GH extension, H. ABD,
F – GH flexion, adduction, Hor. • ER when in prone position
Adduction
Triceps Brachii Supraspinatus
O– O -Medial 2/3 supraspinatus fossa
• Long Head – infraglenoid tubercle I–
• Lateral Head – lateral and Superior portion of greater tuberosity
posterior surface of proximal ½ of N – Suprascapular
body of humerus F–
• Medial Head – distal 2/3 of medial • Intiates shoulder ABD
and posterior surfaces of humerus • Humeral head stabilization
below radial groove
I – Posterior surface of olecranon process Infraspinatus
N – Radial O – Medial 2/3 infraspinatus fossa
F– I – Middle portion of greater tuberosity
• Shoulder – long head – Ext and N – Suprascapular
ADD F–
• Elbow -- extension • GH ER
Latissimus Dorsi • Humeral head stabilization
O-
• Posterior layer of lumbodorsal Teres Minor
fascia, then attaching to the T6- O –Upper 2/3 dorsal surface of lateral
T12, lumbar and sacral vertabrae border of scapula
• External lip of iliace creast lateral I -- Lowest portion of greater tuberosity
to erector spinae N –Axillary
• Ribs 9-12 F–
• Slip from inferior angle of scapula • GH ER
I – Intertubercular groove (distal aspect) • Humeral head stabilization
N – Thoracodorsal
F – GH IR, ADD, Ext, Subscapularis
Teres Major (Lat’s Little Helper) O – Subscapular Fossa
O- I-
• Dorsal surface of inferior angle Lesser tuberosity
• Lower 1/3 of scapula lateral border Anterior capsule of GH joint
I –Crest of lesser tuberosity N –Upper and lower subscapular
N – Lower Subscapular F–
F –GH IR, ADD, Ext • GH IR
• Humeral head stabilization
You might also like
- CASE 430 440 ElectricDocument1 pageCASE 430 440 ElectricDian Sikumbang50% (2)
- Handwriting Without TearsDocument63 pagesHandwriting Without TearsEllen Aquino100% (8)
- Miessler-Fischer-Tarr5e SM CH 07 CM FinalDocument10 pagesMiessler-Fischer-Tarr5e SM CH 07 CM FinalgrignardreagnetsNo ratings yet
- 16 Upper Extremity (FINAL)Document30 pages16 Upper Extremity (FINAL)kath-kath100% (1)
- Spine & ThoraxDocument90 pagesSpine & ThoraxSean JosephNo ratings yet
- Shoulder External Impingement HandoutDocument33 pagesShoulder External Impingement HandoutA100% (2)
- Gross HSB A - Gluteal Region, Hip Joint, and Posterior ThighDocument2 pagesGross HSB A - Gluteal Region, Hip Joint, and Posterior ThighGaelle Lisette MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Instrument Installation RequirementsDocument98 pagesInstrument Installation Requirementszelda1022100% (4)
- 2014 09 Rigging Safety QuizDocument1 page2014 09 Rigging Safety Quizporby100% (1)
- BS en 13478 Fire Prevention and ProtectionDocument30 pagesBS en 13478 Fire Prevention and Protectiontoalok4723No ratings yet
- PE067 Handout Shoulder Special Tests and The Rotator Cuff With DR Chris LittlewoodDocument5 pagesPE067 Handout Shoulder Special Tests and The Rotator Cuff With DR Chris LittlewoodTomáš KrajíčekNo ratings yet
- Amputation Lower ExtremityDocument5 pagesAmputation Lower ExtremityJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Protecting Our Seniors: Supporting Efforts To End Elder AbuseDocument85 pagesProtecting Our Seniors: Supporting Efforts To End Elder AbuseScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Acute Anterior Shoulder Dislocation Physical Therapy ProtocolDocument4 pagesAcute Anterior Shoulder Dislocation Physical Therapy Protocolgermano87No ratings yet
- Neuro 1.27.22Document19 pagesNeuro 1.27.22Vhince PiscoNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument2 pagesMyasthenia GravisJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Rotator Cuff TendynopatyDocument10 pagesRotator Cuff TendynopatyDipo SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Phys Ther 2000 Ludewig 276 91Document18 pagesPhys Ther 2000 Ludewig 276 91Diego Díaz SotoNo ratings yet
- Metaphysics PDFDocument6 pagesMetaphysics PDFEli kingNo ratings yet
- Examination of Shoulder Joint-1Document3 pagesExamination of Shoulder Joint-1adiNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - Part 1Document8 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - Part 1karageeNo ratings yet
- 13 - NS6 SC Sensory Pathways All Sites (Handout) F2022 (Exported)Document38 pages13 - NS6 SC Sensory Pathways All Sites (Handout) F2022 (Exported)Lucky NguyenNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYDocument18 pagesANAPHYRaiza Abegail RoxasNo ratings yet
- Gross HSB A - Appendicular Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesGross HSB A - Appendicular Skeletal SystemAngelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of SpineDocument33 pagesAnatomy of SpineMaria RobertaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy RR CerebellumDocument106 pagesAnatomy RR Cerebellumभईया भोसडिकाNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum-Rr - 1 (Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry)Document215 pagesCerebellum-Rr - 1 (Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry)REACT ATTRACTSNo ratings yet
- 5.back and Scapular RegionDocument72 pages5.back and Scapular RegionGish KioiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination of The ShoulderDocument78 pagesClinical Examination of The ShoulderAbcabc34 AbaNo ratings yet
- GA&E 5 - Intro To Arthrology & Osteology IIIDocument51 pagesGA&E 5 - Intro To Arthrology & Osteology IIISu ZikaiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Aspect of Spine Abnormality-Dr - Yoyos.spotDocument37 pagesClinical Aspect of Spine Abnormality-Dr - Yoyos.spotRyan TrianNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Spine: DR Pankaj N Surange MBBS, MD, Fipp Interventional Pain and Spine SpecialistDocument72 pagesAnatomy of Spine: DR Pankaj N Surange MBBS, MD, Fipp Interventional Pain and Spine SpecialistMohammad Riedho Cahya AtazsuNo ratings yet
- Spine: Junior Intern - Csu College of MedicineDocument22 pagesSpine: Junior Intern - Csu College of MedicineCris Soliven DucosNo ratings yet
- 02 IVD Hernia Case Report MedBac&IEDocument18 pages02 IVD Hernia Case Report MedBac&IEClaude ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vertebral Column and ContentsDocument5 pagesVertebral Column and ContentsJewelNo ratings yet
- Thorax 1Document109 pagesThorax 1Insyirah JohariNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of HipDocument6 pagesBiomechanics of HipChristina SuppiahNo ratings yet
- Thorax The Back: Surface AnatomyDocument11 pagesThorax The Back: Surface AnatomyRed DemonNo ratings yet
- Lectured By: Dr. Jesus J. Gracilla Transcribed By: Beverly YuDocument7 pagesLectured By: Dr. Jesus J. Gracilla Transcribed By: Beverly YuFamela Anne GOmez MadambaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Vertebral ColumnDocument60 pagesStructure and Function of The Vertebral ColumnJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Cervical SpineDocument51 pagesCervical SpineEvandiar IzwardyNo ratings yet
- Knee Injury Seminar 2015Document96 pagesKnee Injury Seminar 2015Aqilah Ab RahmanNo ratings yet
- 09:16 - Back & Spinal Cord PDFDocument24 pages09:16 - Back & Spinal Cord PDFVidya BalaNo ratings yet
- Table 2.1 Cervical Vertebrae: LargeDocument14 pagesTable 2.1 Cervical Vertebrae: LargeReham QueNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine Proto GihDocument8 pagesCervical Spine Proto GihAndy Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Spine: Aggasid Azman Corpuz LagundiDocument59 pagesSpine: Aggasid Azman Corpuz LagundiJho AggasidNo ratings yet
- Bones and Joints of TrunkDocument56 pagesBones and Joints of Trunkapi-196413370% (1)
- Materi 4 - Anatomy of Columna Vertebralis Dan VertebraeDocument25 pagesMateri 4 - Anatomy of Columna Vertebralis Dan VertebraeUntuk TugasNo ratings yet
- Workshop 9 - Pre-Workshop and Workshop Slides - Student Version T2Document21 pagesWorkshop 9 - Pre-Workshop and Workshop Slides - Student Version T2Thanh ThảoNo ratings yet
- 2 Cervical SpineDocument23 pages2 Cervical Spinenoor.komalNo ratings yet
- Back Spine AnatomyDocument3 pagesBack Spine AnatomyNinjaNo ratings yet
- Analab Skeletal Reviewer Michie PDFDocument7 pagesAnalab Skeletal Reviewer Michie PDFMichieNo ratings yet
- Back and Spine AnatomyDocument7 pagesBack and Spine AnatomyCarmela Beatriz Suelan100% (1)
- Upper Extremity - Muscle Summary ChartDocument9 pagesUpper Extremity - Muscle Summary ChartpoggerNo ratings yet
- Applied Anatomy of The Vertebral ColumnDocument53 pagesApplied Anatomy of The Vertebral Columnpramodyasithumini202No ratings yet
- L1 Anatomy MSK DR NAbawy 2023Document47 pagesL1 Anatomy MSK DR NAbawy 2023john baptist ngolobeNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Elbow All Joints - OdtDocument4 pagesUnit 3 - Elbow All Joints - OdtAbdulrahman HosnyNo ratings yet
- Back Muscle ChartDocument3 pagesBack Muscle ChartTony Montana100% (1)
- orthoPT-1 - Evaluation For Shoulder - 20230314Document95 pagesorthoPT-1 - Evaluation For Shoulder - 20230314ray RayNo ratings yet
- Appendicular SkeletonDocument10 pagesAppendicular SkeletonJoshua DanielNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The BackDocument33 pagesMuscles of The Backtaha makhloufNo ratings yet
- Orbit - Head & NeckDocument57 pagesOrbit - Head & NeckNandini BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Vertebral ColumnDocument33 pagesIntroduction, Vertebral Columnpokardhruv6997No ratings yet
- ShoulderDocument17 pagesShoulderNehaNo ratings yet
- Vertebra Cervical Part IIDocument9 pagesVertebra Cervical Part IIarungdeyunaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Tulang BelakangDocument30 pagesPemeriksaan Tulang BelakangMatthew LiongNo ratings yet
- Arvind 1819Document256 pagesArvind 1819abhishek100% (1)
- Unit 4 - GeneticsDocument28 pagesUnit 4 - GeneticsRughaya SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- The Rock Cycle and Plate TectonicsDocument27 pagesThe Rock Cycle and Plate TectonicsFakhri HelmiNo ratings yet
- Pas 37Document5 pagesPas 37Angelica100% (2)
- Awwa C 200 Specifications: " Steel Water Pipe - 6 Diameter and More "Document1 pageAwwa C 200 Specifications: " Steel Water Pipe - 6 Diameter and More "joseNo ratings yet
- Non Condensable GasDocument4 pagesNon Condensable GasSherwin AgootNo ratings yet
- Print Ko BukasDocument3 pagesPrint Ko BukasKatrina CaveNo ratings yet
- Proforma Invoice - Simon SafetyDocument1 pageProforma Invoice - Simon SafetyAlex SimonNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric - ATV71 Quick Selection GuideDocument4 pagesSchneider Electric - ATV71 Quick Selection GuideJohn100% (1)
- Yarn Modification: Cotton MercerizationDocument49 pagesYarn Modification: Cotton Mercerizationsolomonsai1No ratings yet
- Soal SMSTR Genap Bahasa InggrisDocument7 pagesSoal SMSTR Genap Bahasa InggrisEric WilkersonNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions As30 Array Sensor en Im0084437Document52 pagesOperating Instructions As30 Array Sensor en Im0084437DeFacto76No ratings yet
- MT36, MT41 Parts BookDocument669 pagesMT36, MT41 Parts Booksergio mata100% (2)
- 046: Unsafe Acts vs. Unsafe Conditions: Background Discussion Leader Duties For This SessionDocument2 pages046: Unsafe Acts vs. Unsafe Conditions: Background Discussion Leader Duties For This SessionVarahi VigneshNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used Drugs in The ERDocument2 pagesCommonly Used Drugs in The ERsberry522No ratings yet
- Valves Quality Control PlanDocument1 pageValves Quality Control Planjok1974No ratings yet
- Space ExplorationDocument11 pagesSpace ExplorationNimisha PandeyNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument5 pagesRRLAyen Alecksandra CadaNo ratings yet
- 10P 2L8M D5 V3 Product SpecificationsDocument6 pages10P 2L8M D5 V3 Product SpecificationsAnkur PrasadNo ratings yet
- Production of Spherical Pellets by A Hot-Melt Extrusion andDocument6 pagesProduction of Spherical Pellets by A Hot-Melt Extrusion andHimanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- Bhopal Gas Tragedy Causes, Effects and Aftermath - GeeksforGeeksDocument1 pageBhopal Gas Tragedy Causes, Effects and Aftermath - GeeksforGeeksmxdczc5yxzNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Mysteries of The Deep SeaDocument2 pagesExploring The Mysteries of The Deep SeaJajon JaesNo ratings yet
- Sensor Geophones BR 091509Document8 pagesSensor Geophones BR 091509Andy KurniyantoNo ratings yet
- SOP02: Standard Operating Procedure For Staff Training & RecordsDocument12 pagesSOP02: Standard Operating Procedure For Staff Training & Recordsnihal mujawarNo ratings yet