Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circuit Diagram With A Resistive Load: Multistage Sequence Control of AC Converter
Circuit Diagram With A Resistive Load: Multistage Sequence Control of AC Converter
Uploaded by
L KOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circuit Diagram With A Resistive Load: Multistage Sequence Control of AC Converter
Circuit Diagram With A Resistive Load: Multistage Sequence Control of AC Converter
Uploaded by
L KCopyright:
Available Formats
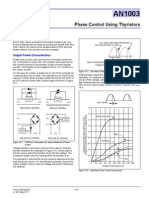
A single-phase AC controller voltagecontrollervoltagecontroller is used to vary the
value of the alternating voltage after it has been applied to a load circuit. A thyristor is
also placed between the load and the constant source of AC voltage.
The root mean square alternating voltage is regulated by changing the thyristor triggering
angle. In the case of phase control, the thyristors are employed as switches to establish
a connection from the AC input supply to the load circuit during each input cycle. For
every positive input voltage, chopping occurs and voltage is reduced.
Circuit Diagram with a Resistive Load
During half part of the cycle, the thyristor switch is turned ON to enable the voltage input
to appear across the load. This is followed by the OFF state during the last half cycle so
as to disconnect the load from the source voltage.
When the triggering angle α is controlled, the RMS value of the voltage on the load is
also controlled. The triggering angle α is therefore, defined as the value of ωt at which
the thyristor switches ON.
Multistage Sequence Control of AC Converter
When two or more sequence control stages are connected, it is possible to have an
improvement in power factor and further reduction in
THD totalharmonicdistortiontotalharmonicdistortion. An n-stage sequence control
converter has n windings in the transformer secondary part with each rated
e /n thesourcevoltagethesourcevoltage.
s
When two AC converters are placed parallel to each other, the zero sequence way is
created. A little difference between the two converters causes a great zero sequence in
circulating current. The diagram below shows the parallel system of a converter. The
direction of the current is anti-clockwise with respect to that of the voltage system.
You might also like
- 3 Eee Pe PDFDocument107 pages3 Eee Pe PDFjose19313922No ratings yet
- Ac Voltage Controllers: V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FDocument6 pagesAc Voltage Controllers: V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FRoss ShawNo ratings yet
- 02 Power ElectronicsDocument211 pages02 Power Electronicsకృష్ణ మురళి100% (2)
- Single Phase AC Voltage ControllerDocument6 pagesSingle Phase AC Voltage Controllermozaher1No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 AC ConverterDocument27 pagesChapter 5 AC ConverterArjun KumarNo ratings yet
- AC-AC ControllerDocument16 pagesAC-AC ControllerLokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ac Voltage Controller PDFDocument36 pagesAc Voltage Controller PDFsolo4000100% (3)
- Ac Voltage ControllersDocument11 pagesAc Voltage ControllersHemlata RaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter (6) AC Voltage ControllerDocument5 pagesChapter (6) AC Voltage ControllerGgfgsgege GegsgsNo ratings yet
- AC Voltage Controller CircuitsDocument211 pagesAC Voltage Controller CircuitsTran Binh DuongNo ratings yet
- AC-DC Converter - Single PhaseDocument16 pagesAC-DC Converter - Single Phasebishnu prasad muniNo ratings yet
- Controlled RectifiersDocument78 pagesControlled RectifiersAnonymous TJRX7CNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document22 pagesModule 2canusha820No ratings yet
- Edusat Programme Lecture Notes ON Power Electronics BY Prof. M. Madhusudhan RaoDocument213 pagesEdusat Programme Lecture Notes ON Power Electronics BY Prof. M. Madhusudhan RaoSana BanuNo ratings yet
- 3 Line ConverterDocument10 pages3 Line ConverterJay Romar PabianiaNo ratings yet
- Punith 2Document50 pagesPunith 2Punith Kumar YanagandulaNo ratings yet
- Ac Voltage Controller Circuits (Rms Voltage Controllers) : V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FDocument22 pagesAc Voltage Controller Circuits (Rms Voltage Controllers) : V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FDasari SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Phase-Shifting Transformer Modeling in PSSEDocument7 pagesPhase-Shifting Transformer Modeling in PSSEuser260709No ratings yet
- Answers of Power Electronics NewDocument9 pagesAnswers of Power Electronics NewSyed ZabiullahNo ratings yet
- 15EC73 - PE - Mod 3 - QB - 12102019 PDFDocument35 pages15EC73 - PE - Mod 3 - QB - 12102019 PDFAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Module-5 Extra Material (Power Converters)Document69 pagesModule-5 Extra Material (Power Converters)NamiraNo ratings yet
- Triac Tutorial and Triac Switching CircuitsDocument7 pagesTriac Tutorial and Triac Switching CircuitsBill WhiteNo ratings yet
- Triac Tutorial and Triac Switching CircuitsDocument7 pagesTriac Tutorial and Triac Switching Circuitsmarcoms75No ratings yet
- 02 Power ElectronicsDocument212 pages02 Power Electronicsmarkschurer223453No ratings yet
- Ac Voltage Controller Circuits: Unit-8Document49 pagesAc Voltage Controller Circuits: Unit-8Naeemo IraqiNo ratings yet
- Facts 3Document14 pagesFacts 3gjk1236596100% (1)
- Ee20m084 Report FileDocument12 pagesEe20m084 Report Filepallavharshvardhan27No ratings yet
- Puni 1 Phase Controlled RectifiersDocument58 pagesPuni 1 Phase Controlled RectifiersKomal Praneeth KotaNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Ac Voltage ControllerDocument3 pagesThree Phase Ac Voltage ControllerShubham DixitNo ratings yet
- RTCCDocument9 pagesRTCCer_ashutosh87No ratings yet
- Thyristor Based HVDC SystemDocument5 pagesThyristor Based HVDC SystemAnonymous hzXy93FAE0% (1)
- Voltage Regulation OF Hydro Generator: Presented byDocument22 pagesVoltage Regulation OF Hydro Generator: Presented bySanjay Agrawal100% (1)
- E1 - Controlled Rectifiers PDF NotesDocument84 pagesE1 - Controlled Rectifiers PDF NotesSatyanarayana Gurram100% (1)
- Phase-Controlled Converters: Unit IiDocument29 pagesPhase-Controlled Converters: Unit IiChinnaGurappaNo ratings yet
- Report Converter 3Document7 pagesReport Converter 3عمار الشهاريNo ratings yet
- Review For MidtermDocument44 pagesReview For MidtermMettah Conrad BamehNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit For TransformerDocument8 pagesShort Circuit For TransformerNoli OtebaNo ratings yet
- Phase Control Using SCR SDocument8 pagesPhase Control Using SCR StekellamerZ aka tekellamerNo ratings yet
- Three Phase InvertersDocument36 pagesThree Phase InvertersSrinivasRao100% (3)
- Three Phase ControlledDocument9 pagesThree Phase ControlledSaif HassanNo ratings yet
- What Is Tap ChangerDocument42 pagesWhat Is Tap ChangerThức Võ100% (1)
- Control of HVDCDocument38 pagesControl of HVDCPrasanna Kumar100% (2)
- DR PeDocument211 pagesDR PeNaeemo IraqiNo ratings yet
- IEC Exam 2023Document15 pagesIEC Exam 2023Phyo KoNo ratings yet
- Bs-El-344 - Lecture-05 - P2Document13 pagesBs-El-344 - Lecture-05 - P2Bushra IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Phase Controlled RectifiersDocument59 pagesPhase Controlled RectifiersAravindh EnggNo ratings yet
- High Voltage DC Transmission 2: Inverters. The Term Converter Is Used To GenericallyDocument25 pagesHigh Voltage DC Transmission 2: Inverters. The Term Converter Is Used To GenericallyadnanNo ratings yet
- Ac Voltage Controllers: V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FDocument6 pagesAc Voltage Controllers: V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V Fcr_neethishNo ratings yet
- AC-DC Converter - Multi PhaseDocument39 pagesAC-DC Converter - Multi Phasebishnu prasad muniNo ratings yet
- 13 AC RegulatorsDocument65 pages13 AC RegulatorszapzahtNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-21 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-21 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Module BuckDocument13 pagesModule BuckShankara BNo ratings yet
- Relay Setting (Directional) : Leakage FluxDocument8 pagesRelay Setting (Directional) : Leakage Fluxjyoti kachareNo ratings yet
- AC-DC Converter - DDocument39 pagesAC-DC Converter - DBishnu100% (1)
- Thyristor Application & Photosensitive Control Circuits: Chapter No.5Document28 pagesThyristor Application & Photosensitive Control Circuits: Chapter No.5Kim ManaloNo ratings yet
- Progect 2Document12 pagesProgect 2ali hussainNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 28 (Ch. 11) Ac Voltage Controllers: ECE 452 Power ElectronicsDocument18 pagesLECTURE 28 (Ch. 11) Ac Voltage Controllers: ECE 452 Power ElectronicsNishant ParikhNo ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)