Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IST CH - 1
IST CH - 1
Uploaded by
Emad yassinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IST CH - 1
IST CH - 1
Uploaded by
Emad yassinCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch_1
Information Technology (IT):
Computer technology (hardware and software) for processing and storing information
Communications technology (voice and data networks) for transmitting information.
IT has become more pervasive
IT is not used only by back-office workers, but also front-line workers
More and more employees are reliant to IT for complete their work activities
Business managers, not just IT managers, are responsible for IT investments and effective system utilization
By the Year 2000, the total yearly cost of IT purchases was more than half of the yearly capital expenditures
of businesses in developed countries
IT is linking emerging, developing and developed economies, which can help “level” the economic playing
field
Computer Hardware: Faster, Cheaper, Mobile
- Computers have become smaller and faster
- Hardware prices have dropped
- High growth in small, mobile devices for communications and access to the Internet
Computer Software: Integrated, Downloadable, Social
Integrated
- Standardization has enabled more integration
- Many “standards” are just de facto standards (Microsoft Windows, Office, Internet Explorer)
- Many companies have benefitted from “Enterprise Systems” investments (e.g., electronic health records in
hospitals)
Enterprise Systems:
Software packages with integrated modules that pass common business transactions across groups, divisions, and
geographic locations in “real time”
Downloadable
- Bit-size software programs for smart phones downloadable from App stores
- Download speeds have increased so that even large files can be downloaded by users
Social
- Growth of Web 2.0 (social media) applications (such as Facebook, LinkedIn)
- Used by companies for marketing and branding activities
- Collaboration tools connect employees across distance
Computer Networks: High Bandwidth, Wireless and Cloudy
- High demand for high speed Internet access
- Wireless technologies to replace hardwired lines; support for mobile devices anytime/anywhere
- Use of Internet to access remote hosts, data storage, and other IT capabilities from the “Cloud”
New ways for businesses to use IT to compete on:
Low Cost – Competing with other businesses by being a low-cost producer for a good or a service
- Automating transaction time
- Shortening order cycle time
- Providing operational information for decision making
Differentiation – Competing with other businesses by offering products or services that customers prefer due
to superiority in
- product innovativeness, quality or customer service
- Giving sales personnel information to better serve customers
- Providing just-in-time supplies for customers
- Creating new information-based products
- Allowing product customization by the consumer
OR Both Low Cost and Differentiation, enabled by IT
New ways for people to work using IT:
1- Telecommuters: Individuals who use mobile technology and/or network connections to work remotely
Pros
- Flexibility
- Work-life balance
Cons
- Feelings of being isolated
- Concerns about job promotion opportunities
2- Virtual Teams: Geographically separated work teams whose members communicate through the use of IT
Pros
- Workers can be located anywhere
- Teams can be composed of members with specialized skills from different business units or companies
Cons
- Coordination across team members more difficult
3- Free Agents: Individuals who choose to contract out their services and are not tied to an organization
Pros
- Work may change more than when an employee of a single organization
Cons
- Lack of benefits
- Unpredictability in scheduling and work
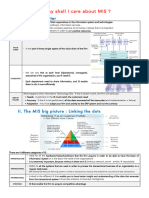
Information Systems (IS) Department:
The organizational unit or department that has the primary responsibility for managing IT
Information Systems departments can vary greatly across businesses, depending on the organization’s dependency
on IT for:
- reliable & secure business operations and
- competitive advantage based on new technologies
Example: IS Organization in Support Mode
- Low Need for New Information Technology for competing
- Low Need for Reliable & Secure Information Technology for business operations
- IT used mostly to support back-office support functions
Example: IS Organization in Strategic Mode
- High Need for New Information Technology for competitive advantage
- High Need for Reliable & Secure Information Technology for business operations
- Strategically dependent on IT to enable new business strategies
Three Types of IT Resources
1- Technology Infrastructure: Computers, software and networks that enable an organization to conduct business
and share information across organizational units as well as business partners
2- Human Resources: IT professionals and managers who have the needed mix of technology, business and
interpersonal skills to plan for, design and manage the other IT resources
3- Business/IT Relationships: Established relationships between business and IT workers to ensure that the other
IT resources are aligned with the business needs
In many organizations, the senior IT leader is a CIO.
Chief information officer (CIO): A firm’s high-level general IT manager with both technology and business leadership
experience
Two primary responsibilities:
1- Computer and communication operation
2- Acquiring and maintaining application software
You might also like
- Strategic ManagementDocument15 pagesStrategic ManagementRamisa TasfiahNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Quality Assurance InsulationDocument15 pages6.0 Quality Assurance InsulationMukiara LuffyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Managing IT in A Digital WorldDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Managing IT in A Digital WorldliamdrlnNo ratings yet
- AIS 3 Chapter 1 Managing IT in A Digital WorldDocument5 pagesAIS 3 Chapter 1 Managing IT in A Digital WorldJames David Torres MateoNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document32 pagesWeek 1meghnadangiNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document44 pagesWeek 1meghnadangiNo ratings yet
- Information System:-: IT in IndustryDocument7 pagesInformation System:-: IT in Industryalok006No ratings yet
- Final Mis 2024Document33 pagesFinal Mis 2024abdelrahmanmhmdkamalNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security I unitDocument21 pagesCyber Security I unitPrince SinghNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument4 pagesMidtermFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- MISS MidDocument27 pagesMISS MidLinh HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Managing It in A Digital WorldDocument20 pagesManaging It in A Digital WorldbhavyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Activity Module For MIS Chapter 1Document12 pagesAssignment Activity Module For MIS Chapter 1Yanna MendozaNo ratings yet
- HelenDocument6 pagesHelenTamiru BeyeneNo ratings yet
- ABI Summary LUsDocument35 pagesABI Summary LUsh9rkbdhx57No ratings yet
- Ais ReviewerDocument9 pagesAis Reviewer21-67400No ratings yet
- Definition: Information System (IS) : Organisation, and Technology DimensionsDocument18 pagesDefinition: Information System (IS) : Organisation, and Technology DimensionsNguyên PhanNo ratings yet
- It NotesDocument4 pagesIt Noteskt. rznNo ratings yet
- Answers of QuizDocument5 pagesAnswers of QuizAmr GamalNo ratings yet
- Notes OF MISDocument51 pagesNotes OF MISGulEFarisFarisNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument14 pagesManagement Information SystemJhonnelyn AlvesorNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Management Information SystemDocument41 pagesChapter One: Management Information Systemobsinan dejeneNo ratings yet
- Advantages Disadvantages Information System MISDocument2 pagesAdvantages Disadvantages Information System MISNurul HawaNo ratings yet
- Advantages Disadvantages Information System MISDocument2 pagesAdvantages Disadvantages Information System MISNurul Hawa100% (3)
- Chapter 1 ITMDocument4 pagesChapter 1 ITMrsNo ratings yet
- PrE4 Module 1Document8 pagesPrE4 Module 1Galang, Princess T.No ratings yet
- Introduction To System Analysis and Design MethodsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To System Analysis and Design Methodsarchanashri2748No ratings yet
- Written Report in Management Information System (Chapter 11)Document4 pagesWritten Report in Management Information System (Chapter 11)Jason VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Mlo5s Is Elmnhg KoloDocument30 pagesMlo5s Is Elmnhg KoloRafeek makramNo ratings yet
- MIS Assignment 2Document6 pagesMIS Assignment 2khalidsana603No ratings yet
- INFO3 Revision NotesDocument31 pagesINFO3 Revision Notespenji_manNo ratings yet
- Information System For ManagerDocument8 pagesInformation System For ManagerDeepanshu SinghalNo ratings yet
- MIS Full CourseDocument56 pagesMIS Full Courseadrien.graffNo ratings yet
- PCA20S01L - IT Infrastructure ManagementDocument25 pagesPCA20S01L - IT Infrastructure ManagementMOHAMED FIRNAS (RA1931005020191)No ratings yet
- ICT Lesson 1 - Introduction To ICTDocument72 pagesICT Lesson 1 - Introduction To ICTOTIENO ELIJAHNo ratings yet
- DSS 200 SG1-3Document9 pagesDSS 200 SG1-3Kevin SchusterNo ratings yet
- Week OneDocument8 pagesWeek OneAzin RostamiNo ratings yet
- BBM 7TH Note (E-Commerce)Document14 pagesBBM 7TH Note (E-Commerce)shree ram prasad sahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Business Driven Information TechnologyDocument77 pagesChapter 1 - Business Driven Information TechnologyJessica LimaNo ratings yet
- Group-2, MIS in The 21st CenturyDocument9 pagesGroup-2, MIS in The 21st CenturyNazmus Sakib100% (2)
- EFINITIONDocument7 pagesEFINITIONSanduni kaushalyaNo ratings yet
- Lessons 4.1 and 4.2Document38 pagesLessons 4.1 and 4.2Shiela Mae SagaNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument14 pagesClass NotesPema Sonam YangchenNo ratings yet
- And Services, Maintain Customer Loyalty and Make Sound DecisionsDocument7 pagesAnd Services, Maintain Customer Loyalty and Make Sound DecisionsVienna Corrine Q. AbucejoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Modern Organization: Functioning in A Global EnvironmentDocument16 pagesLesson 1: The Modern Organization: Functioning in A Global EnvironmentJonathan BausingNo ratings yet
- Busi 2400 Test One NotesDocument15 pagesBusi 2400 Test One NotesBrian Elliott TateNo ratings yet
- Key Terms of Unit Two (2) : 2.1.4 Challenges of Big DataDocument6 pagesKey Terms of Unit Two (2) : 2.1.4 Challenges of Big Datahambisatiruneh6No ratings yet
- 5014 Technology Policy and AdministrationDocument7 pages5014 Technology Policy and AdministrationKanwal umerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document50 pagesChapter 2pathan1990No ratings yet
- Jane Ann Austria Pre 4: Information Systems Operations and Maintenance Chapter 1: Information Systems An OverviewDocument20 pagesJane Ann Austria Pre 4: Information Systems Operations and Maintenance Chapter 1: Information Systems An OverviewliamdrlnNo ratings yet
- 1.5performance Management PDFDocument232 pages1.5performance Management PDFsolstice567567No ratings yet
- Introduction To Information TechnologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Information TechnologyMuthoharoh MuthoharohNo ratings yet
- CONCEPTS OF IT and ICTDocument43 pagesCONCEPTS OF IT and ICTMoon IightNo ratings yet
- Business SystemDocument17 pagesBusiness SystemAna Clara MelloNo ratings yet
- Information Technology in BusinessDocument5 pagesInformation Technology in Businesslidia zNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Components: OpeningDocument6 pagesInfrastructure Components: OpeningXanius HallNo ratings yet
- What Is Information SystemDocument2 pagesWhat Is Information SystemGrace FuentesNo ratings yet
- P5 C16 C17 ControllingDocument18 pagesP5 C16 C17 ControllinglimnkNo ratings yet
- Management of DataDocument25 pagesManagement of DataSujal ManandharNo ratings yet
- Summary For Ict 2023 Grade 11Document11 pagesSummary For Ict 2023 Grade 11Petrus NangoloNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing: Securing your workforceFrom EverandMobile Computing: Securing your workforceBCS, The Chartered Institute for ITNo ratings yet
- Satisfaction Is Nice, But Value Drives LoyaltyDocument5 pagesSatisfaction Is Nice, But Value Drives LoyaltyVickram PersadNo ratings yet
- Policy Guidelines For Providing Last Mile Connectivity For Provisioning of Leased Circuits Through FTTH PolicyDocument5 pagesPolicy Guidelines For Providing Last Mile Connectivity For Provisioning of Leased Circuits Through FTTH PolicySDE TRANS BSNLNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Trade Receivables (Accounts Receivable) - Continuation 11Document5 pagesAccounting For Trade Receivables (Accounts Receivable) - Continuation 11rufamaegarcia07No ratings yet
- Modified Schedule For Class Test - II Session 2020-21 ODD SemesterDocument3 pagesModified Schedule For Class Test - II Session 2020-21 ODD SemesterGobhiNo ratings yet
- Perjanjian Rakan Kongsi ExnessDocument3 pagesPerjanjian Rakan Kongsi ExnessmyexnessfxNo ratings yet
- Dell Management Information System PDFDocument22 pagesDell Management Information System PDFMalzy AlzNo ratings yet
- Sr. No Course Outline Topics: Chapter - 7 Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS)Document11 pagesSr. No Course Outline Topics: Chapter - 7 Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS)muhammad zainNo ratings yet
- Jennie Marima Imile Wepener Rox Jaden PalmerDocument18 pagesJennie Marima Imile Wepener Rox Jaden PalmerCarmen Elena IvănușNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Profitability of Small Scale Food InustriesDocument9 pagesFactors Affecting The Profitability of Small Scale Food InustriesDeo N. Sarol0% (1)
- Share Price Movements and Its DeterminantsDocument2 pagesShare Price Movements and Its DeterminantsTalha AquilNo ratings yet
- Appoint HemDocument3 pagesAppoint HemhemNo ratings yet
- Meetings of CompanyDocument2 pagesMeetings of CompanySohaibNo ratings yet
- Repayment of Term/Fixed Deposits in BanksDocument2 pagesRepayment of Term/Fixed Deposits in BanksMohammad Sazid AlamNo ratings yet
- 4 Omnibus InvestmentsDocument36 pages4 Omnibus InvestmentsBret BalbuenaNo ratings yet
- Bus TicketDocument1 pageBus TicketSuman Babu KNo ratings yet
- Bonus Shares, Right Shares PDFDocument30 pagesBonus Shares, Right Shares PDFNaga ChandraNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior - DeshalDocument17 pagesConsumer Behavior - DeshalSayeed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- MBA ReportDocument111 pagesMBA Reportsh_bijuNo ratings yet
- Case Study Tren Engine ComponentsDocument2 pagesCase Study Tren Engine ComponentsUmar KhattakNo ratings yet
- Stevenson 13e Chapter 13Document40 pagesStevenson 13e Chapter 13Jerwin MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Liber8 Your BusinessDocument7 pagesLiber8 Your BusinessLaura HumphreysNo ratings yet
- Brgy GinesDocument3 pagesBrgy GinesPing KyNo ratings yet
- History of NIBDocument11 pagesHistory of NIBArfan MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Price - Inefficiency - 3 (@SmartMoneyCourse)Document4 pagesPrice - Inefficiency - 3 (@SmartMoneyCourse)RayanNo ratings yet
- PSA-706 Emphasis On Matter Paragraphs & Other Matter Paragraphs in The Independent Auditor's ReportDocument14 pagesPSA-706 Emphasis On Matter Paragraphs & Other Matter Paragraphs in The Independent Auditor's ReportcolleenyuNo ratings yet
- C Khushi Agarwal 28Document15 pagesC Khushi Agarwal 28Khushi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument58 pagesFinal ProjectAhmed FayazNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NOTES - Measurement of Business IncomeDocument12 pagesLECTURE NOTES - Measurement of Business Incomehua chen yuNo ratings yet