Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ether
Ether
Uploaded by
Jenny YaoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- SchleunigerDocument74 pagesSchleunigerSakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- ETHERSDocument2 pagesETHERSApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Ethers, Epoxide, ThiolsDocument12 pagesEthers, Epoxide, Thiolsmanlangit.francislyn09No ratings yet
- Siml Geometric Presentation by SlidesgoDocument62 pagesSiml Geometric Presentation by SlidesgobltrnNo ratings yet
- Are A Class of Organic Compounds That Have An OxygenDocument6 pagesAre A Class of Organic Compounds That Have An OxygenArianne MontañoNo ratings yet
- 18章 PDFDocument41 pages18章 PDF台師大蔡銘揚No ratings yet
- Naming EthersDocument11 pagesNaming EthersPedro SuyuNo ratings yet
- Ethers PDFDocument2 pagesEthers PDFDanielNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesPage 1 of 5Cheriza BeteNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledsam cuadraNo ratings yet
- Running Head: ISOMERS 1Document4 pagesRunning Head: ISOMERS 1AssignmentLab.comNo ratings yet
- PONTERAS (Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers)Document3 pagesPONTERAS (Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers)KARYLLE JUNE PONTERASNo ratings yet
- Ethers 22Document22 pagesEthers 22waleed734445No ratings yet
- Alkohol...Document47 pagesAlkohol...R.Afr26 0403No ratings yet
- Chem 102. EthersDocument24 pagesChem 102. Etherskeanna.samaniegoNo ratings yet
- Alcoholes 2Document9 pagesAlcoholes 2Дана ЧилибаеваNo ratings yet
- Ethers and Epoxides PDFDocument2 pagesEthers and Epoxides PDFMelissaNo ratings yet
- Ethers: Dr. Naureen ShehzadiDocument28 pagesEthers: Dr. Naureen ShehzadiBismah SaeedNo ratings yet
- Loaded1-Prof - DO.Moronkola-CHE-176-2023-Course Content1Document58 pagesLoaded1-Prof - DO.Moronkola-CHE-176-2023-Course Content1taiwodamola789No ratings yet
- EthersDocument9 pagesEthersSameep KalraNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Alcohol, Ether and AldehydeDocument62 pagesModule 4 - Alcohol, Ether and AldehydePrincess NavarroNo ratings yet
- 4-Chem 109 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers 0 0Document17 pages4-Chem 109 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers 0 0Black CatNo ratings yet
- Ether IntroDocument3 pagesEther IntroCheriza BeteNo ratings yet
- Warna-Warni Ilustratif Lucu Presentasi SainsDocument11 pagesWarna-Warni Ilustratif Lucu Presentasi Sains18. MUHAMMAD ATSIIL DHAIFULLAHNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ethers James Richard FrommDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Ethers James Richard FrommFrician Bernadette MuycoNo ratings yet
- EtherDocument23 pagesEtherOng Kok Leong100% (1)
- Chemistry Module 9Document4 pagesChemistry Module 9angelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- Final ScriptDocument6 pagesFinal ScriptKresley GamayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Functional GroupsDocument81 pagesChapter 23 Functional GroupsYudi PermanaNo ratings yet
- Ether: Navigation Search AetherDocument7 pagesEther: Navigation Search AetherMuhammad Wahyu Nugraha0% (1)
- Diethyl EtherDocument13 pagesDiethyl EtherPreyansh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & EthersDocument27 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & Ethershgp9ms5gjcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Alcohols, Phenols, and EthersDocument37 pagesChapter 3 Alcohols, Phenols, and EthersGreedy FoodieNo ratings yet
- EthersDocument16 pagesEthersPriskoNo ratings yet
- Ether and AldehydesDocument11 pagesEther and Aldehydes18. MUHAMMAD ATSIIL DHAIFULLAHNo ratings yet
- EtherDocument23 pagesEtherTitin Evania ManaluNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Derivatives Notes 2013 Chemistry 2202Document43 pagesHydrocarbon Derivatives Notes 2013 Chemistry 2202ShainaNo ratings yet
- 8.4 Solvents in Organic Chemistry: A. Classification of SolventsDocument8 pages8.4 Solvents in Organic Chemistry: A. Classification of SolventsjacNo ratings yet
- EthersDocument27 pagesEtherssafiabarkat5No ratings yet
- G6 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument64 pagesG6 Alcohols Phenols and EthersHarijaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and EtherDocument29 pagesAlcohol and Etherapi-276904981No ratings yet
- Publication - Aston - Personal Care Mag Esters Article Nov 17Document4 pagesPublication - Aston - Personal Care Mag Esters Article Nov 17Mayra PeñaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 1668930466231767088Document33 pagesInbound 1668930466231767088urprettygirl14No ratings yet
- Applied Chem Week 4Document8 pagesApplied Chem Week 4Loraine May R. AcopNo ratings yet
- Yow BroDocument20 pagesYow BroPatricia Mae RegalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Ethers and Epoxides: Ether Functional GroupDocument12 pagesChapter 8: Ethers and Epoxides: Ether Functional Grouphussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Ethers Ethers: Inhalation Apparatus Inhalation ApparatusDocument21 pagesEthers Ethers: Inhalation Apparatus Inhalation ApparatusMalar Mathi MannanNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Alcohols, Ethers, ThiolsDocument17 pages1.4 Alcohols, Ethers, ThiolsMia PereiraNo ratings yet
- Ethers Ethers: Dr. Mohamed El-NewehyDocument9 pagesEthers Ethers: Dr. Mohamed El-NewehysarahNo ratings yet
- P11-13 Isomerisms Functional Groups and ReactionDocument62 pagesP11-13 Isomerisms Functional Groups and ReactionNing CahNo ratings yet
- Ethers: By: DR Saima NajmDocument10 pagesEthers: By: DR Saima NajmSaima NajmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 2SPPDocument37 pagesChapter 03 2SPPnuhaanwar26No ratings yet
- Name: Andi Ria Indahsari Asik ID: 1913442004: AldehydeDocument6 pagesName: Andi Ria Indahsari Asik ID: 1913442004: AldehydeAndi RiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form-Four (Chapters Summery of Questions With Answers)Document13 pagesChemistry Form-Four (Chapters Summery of Questions With Answers)Mohamed Abuukar AbdukadirNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones KODocument2 pagesAldehydes and Ketones KOabhishektheoneNo ratings yet
- Bautista, John Mhar M. (Experiment 7)Document4 pagesBautista, John Mhar M. (Experiment 7)2g8vdspqm5No ratings yet
- Biochem Prelim NotesDocument14 pagesBiochem Prelim NotesPretty Grace101No ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument35 pagesChapter FourAsad MohNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Macsteel VRN VRN 200 DatasheetDocument1 pageMacsteel VRN VRN 200 DatasheetIgor NhamanoNo ratings yet
- LSU Digital Commons LSU Digital Commons: Louisiana State University Louisiana State UniversityDocument284 pagesLSU Digital Commons LSU Digital Commons: Louisiana State University Louisiana State UniversityPhil DinningNo ratings yet
- Secondary 1 & 2 Science-Chemical Composition of MatterDocument15 pagesSecondary 1 & 2 Science-Chemical Composition of MatterKoh Kai XuanNo ratings yet
- Formulasi Krim Ekstrak Etanol Herba Krokot (Portulacca Oleracea L.) Sebagai Tabir SuryaDocument5 pagesFormulasi Krim Ekstrak Etanol Herba Krokot (Portulacca Oleracea L.) Sebagai Tabir SuryaTeguh Hidayat PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Nitofi LL UR63: Solvent Free, Two Part Polyurethane Resin For Sealing CracksDocument3 pagesNitofi LL UR63: Solvent Free, Two Part Polyurethane Resin For Sealing CracksFaisal FaizNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Chamois Leather Tanning ProcessDocument11 pagesAccelerated Chamois Leather Tanning ProcessAlejandro MirandaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Rice Husk Ash (Rha) Brick As Partial Replacement of ClayDocument9 pagesMechanical Properties of Rice Husk Ash (Rha) Brick As Partial Replacement of ClayMauricio David Ruiz OdarNo ratings yet
- LAB QO 1 - P-MethoxyacetanilideDocument17 pagesLAB QO 1 - P-MethoxyacetanilidemarioNo ratings yet
- Amity International School Class: XIDocument10 pagesAmity International School Class: XIksjinnieNo ratings yet
- Naming and Formula Practice QuizDocument2 pagesNaming and Formula Practice QuizSharesse Joy GumalalNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan: "Nayi Disha"Document2 pagesLearning Plan: "Nayi Disha"Vikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- High Temperature MaterialsDocument120 pagesHigh Temperature MaterialsMithun Ravichandran80% (5)
- Chemical Analysis of Graphite: Standard Test Methods ForDocument8 pagesChemical Analysis of Graphite: Standard Test Methods For916bushraNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Crosslinked Sodium Alginate/Gelatin Hydrogels For Wound DressingDocument6 pagesA Comparative Study of Crosslinked Sodium Alginate/Gelatin Hydrogels For Wound DressingJake EjaNo ratings yet
- 2.is Matter Around Us PureDocument23 pages2.is Matter Around Us PureGin vhjkk hjkkNo ratings yet
- Zeal Foundation (A Unit of Eduniverse Edusolutions) : Class X - Science Subjective Test - 4 Max - Marks: 80Document5 pagesZeal Foundation (A Unit of Eduniverse Edusolutions) : Class X - Science Subjective Test - 4 Max - Marks: 80Himanshu SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Sans10177 4Document12 pagesSans10177 4engqualsolutionsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry InvestigatoryDocument16 pagesChemistry InvestigatorySai NandhaNo ratings yet
- Week 7-9 Module (Hema 1 Laboratory)Document25 pagesWeek 7-9 Module (Hema 1 Laboratory)Jam RamosNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Green University of BangladeshDocument10 pagesAssignment: Green University of BangladeshNafis HossainNo ratings yet
- Gases: Behavior & PropertiesDocument35 pagesGases: Behavior & PropertiesAdelia SetianingsihNo ratings yet
- Penguard Universal: Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesPenguard Universal: Technical Data Sheetkanogkand kasrirakuptNo ratings yet
- Strengthening Mechanism-30102017Document18 pagesStrengthening Mechanism-30102017Amina MubasharNo ratings yet
- Adjustment of Physical Properties of Viscoelastic Foam (Paper)Document15 pagesAdjustment of Physical Properties of Viscoelastic Foam (Paper)Сергей ДружининNo ratings yet
- Annex Vi List of Preservatives Which Cosmetic Products May ContainDocument11 pagesAnnex Vi List of Preservatives Which Cosmetic Products May ContainNor SurayaNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin DetectionDocument21 pagesHemoglobin Detectionmohannad banatNo ratings yet
- Soil Science Post Test IiiDocument52 pagesSoil Science Post Test IiiTeam Agri CulturaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Summative Test Third Quarter Name: - Year and SectionDocument2 pagesScience 8 Summative Test Third Quarter Name: - Year and SectionJobel Nuestro100% (1)
- BIOL BCHM 111 BiomoleculesDocument49 pagesBIOL BCHM 111 BiomoleculeshavenNo ratings yet
Ether
Ether
Uploaded by
Jenny YaoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ether
Ether
Uploaded by
Jenny YaoCopyright:
Available Formats
Jenny Yao
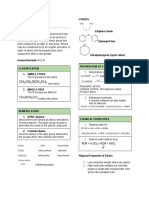
Organic Functional Groups: Ethers
two alcohol molecules react together to form an ether – the general formula is: R-O-R'
the other product of the reaction is water, which is taken up afterwards by a dehydration agent
polyethylene glycol diethyl ether anisole
perfume
pharmaceuticals
insect pheromones
laxative anesthetic
lubricants recreational drug
film coatings diesel fuel
Nomenclature:
Type Instructions Example
simple ether If both groups are simple alkyl compounds, then the ether can be named ethyl methyl ether:
as (alkyl alkyl) ether, with alkyl groups listed in alphabetical order. CH3CH2OCH3
If the two alkyl groups are the same, then it's a di(alkyl) ether.
intermediate ether If one of the groups is more complex, then the ether group is treated as 1-methoxypropane:
an (alkyl)oxy, i.e. R-O-, substituent of the entire chemical. CH3CH2CH2OCH3
The more complex group (e.g. longer chain) defines the root.
complex ether If both groups are complex, then the ether can be named using -oxa. 2-oxapentane2-
2-oxapentane: CH3OCH2CH2CH3
Chemical Properties Physical Properties
Fact: Ethers are slightly polar. Fact: Ethers have relatively low boiling points.
Explanation: The C-O-C bond angle in the functional group is Explanation: Because ether molecules cannot engage in hydrog
~110°. However, the C-O dipoles do not cancel out. Ethers bonding with each other, they have much lower boiling points th
possess a net dipole, even if the 2 C-O bonds are symmetrical. similar alcohols with approximately the same molecular weights
Fact: Ethers can have hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Fact: Ethers are good solvents for a wide variety of organic and
inorganic compounds.
Explanation: There are two lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen
atoms, which means that they can form hydrogen bonds with other Explanation: Without the strongly polarized O−H bond, ether
molecules (alcohols, amines, etc.) that have O−H or N−H bonds. molecules cannot engage in hydrogen bonding with each other. T
are therefore useful for forming H-bonds with other compounds.
Fact: Ethers are essentially inert to chemical reactions. Fact: The solubility of ethers in H2O is alike with that of alcoho
Explanation: An ether cannot form hydrogen bonds with other Explanation: Ethers form hydrogen bonds with water in the sam
ether molecules since there is no H to be donated. In addition, way as alcohols do with water. Also, the solubility in water decr
because of the lack of an –OH group, they don't react with most with bigger sizes of alkyl groups – due to general rules of solubi
oxidizing or reducing agents. Not to mention, ethers are stable to
most acids and bases, except at high temperatures. General: Most ethers are colorless, pleasant-smelling, volatile li
It serves as Lewis bases and Bronsted bases. Ethers are highly
flammable, so they constitute as a significant fire hazard.
Pictures: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ether
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- SchleunigerDocument74 pagesSchleunigerSakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- ETHERSDocument2 pagesETHERSApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Ethers, Epoxide, ThiolsDocument12 pagesEthers, Epoxide, Thiolsmanlangit.francislyn09No ratings yet
- Siml Geometric Presentation by SlidesgoDocument62 pagesSiml Geometric Presentation by SlidesgobltrnNo ratings yet
- Are A Class of Organic Compounds That Have An OxygenDocument6 pagesAre A Class of Organic Compounds That Have An OxygenArianne MontañoNo ratings yet
- 18章 PDFDocument41 pages18章 PDF台師大蔡銘揚No ratings yet
- Naming EthersDocument11 pagesNaming EthersPedro SuyuNo ratings yet
- Ethers PDFDocument2 pagesEthers PDFDanielNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesPage 1 of 5Cheriza BeteNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledsam cuadraNo ratings yet
- Running Head: ISOMERS 1Document4 pagesRunning Head: ISOMERS 1AssignmentLab.comNo ratings yet
- PONTERAS (Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers)Document3 pagesPONTERAS (Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers)KARYLLE JUNE PONTERASNo ratings yet
- Ethers 22Document22 pagesEthers 22waleed734445No ratings yet
- Alkohol...Document47 pagesAlkohol...R.Afr26 0403No ratings yet
- Chem 102. EthersDocument24 pagesChem 102. Etherskeanna.samaniegoNo ratings yet
- Alcoholes 2Document9 pagesAlcoholes 2Дана ЧилибаеваNo ratings yet
- Ethers and Epoxides PDFDocument2 pagesEthers and Epoxides PDFMelissaNo ratings yet
- Ethers: Dr. Naureen ShehzadiDocument28 pagesEthers: Dr. Naureen ShehzadiBismah SaeedNo ratings yet
- Loaded1-Prof - DO.Moronkola-CHE-176-2023-Course Content1Document58 pagesLoaded1-Prof - DO.Moronkola-CHE-176-2023-Course Content1taiwodamola789No ratings yet
- EthersDocument9 pagesEthersSameep KalraNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Alcohol, Ether and AldehydeDocument62 pagesModule 4 - Alcohol, Ether and AldehydePrincess NavarroNo ratings yet
- 4-Chem 109 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers 0 0Document17 pages4-Chem 109 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers 0 0Black CatNo ratings yet
- Ether IntroDocument3 pagesEther IntroCheriza BeteNo ratings yet
- Warna-Warni Ilustratif Lucu Presentasi SainsDocument11 pagesWarna-Warni Ilustratif Lucu Presentasi Sains18. MUHAMMAD ATSIIL DHAIFULLAHNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ethers James Richard FrommDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Ethers James Richard FrommFrician Bernadette MuycoNo ratings yet
- EtherDocument23 pagesEtherOng Kok Leong100% (1)
- Chemistry Module 9Document4 pagesChemistry Module 9angelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- Final ScriptDocument6 pagesFinal ScriptKresley GamayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Functional GroupsDocument81 pagesChapter 23 Functional GroupsYudi PermanaNo ratings yet
- Ether: Navigation Search AetherDocument7 pagesEther: Navigation Search AetherMuhammad Wahyu Nugraha0% (1)
- Diethyl EtherDocument13 pagesDiethyl EtherPreyansh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & EthersDocument27 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & Ethershgp9ms5gjcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Alcohols, Phenols, and EthersDocument37 pagesChapter 3 Alcohols, Phenols, and EthersGreedy FoodieNo ratings yet
- EthersDocument16 pagesEthersPriskoNo ratings yet
- Ether and AldehydesDocument11 pagesEther and Aldehydes18. MUHAMMAD ATSIIL DHAIFULLAHNo ratings yet
- EtherDocument23 pagesEtherTitin Evania ManaluNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Derivatives Notes 2013 Chemistry 2202Document43 pagesHydrocarbon Derivatives Notes 2013 Chemistry 2202ShainaNo ratings yet
- 8.4 Solvents in Organic Chemistry: A. Classification of SolventsDocument8 pages8.4 Solvents in Organic Chemistry: A. Classification of SolventsjacNo ratings yet
- EthersDocument27 pagesEtherssafiabarkat5No ratings yet
- G6 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument64 pagesG6 Alcohols Phenols and EthersHarijaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and EtherDocument29 pagesAlcohol and Etherapi-276904981No ratings yet
- Publication - Aston - Personal Care Mag Esters Article Nov 17Document4 pagesPublication - Aston - Personal Care Mag Esters Article Nov 17Mayra PeñaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 1668930466231767088Document33 pagesInbound 1668930466231767088urprettygirl14No ratings yet
- Applied Chem Week 4Document8 pagesApplied Chem Week 4Loraine May R. AcopNo ratings yet
- Yow BroDocument20 pagesYow BroPatricia Mae RegalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Ethers and Epoxides: Ether Functional GroupDocument12 pagesChapter 8: Ethers and Epoxides: Ether Functional Grouphussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Ethers Ethers: Inhalation Apparatus Inhalation ApparatusDocument21 pagesEthers Ethers: Inhalation Apparatus Inhalation ApparatusMalar Mathi MannanNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Alcohols, Ethers, ThiolsDocument17 pages1.4 Alcohols, Ethers, ThiolsMia PereiraNo ratings yet
- Ethers Ethers: Dr. Mohamed El-NewehyDocument9 pagesEthers Ethers: Dr. Mohamed El-NewehysarahNo ratings yet
- P11-13 Isomerisms Functional Groups and ReactionDocument62 pagesP11-13 Isomerisms Functional Groups and ReactionNing CahNo ratings yet
- Ethers: By: DR Saima NajmDocument10 pagesEthers: By: DR Saima NajmSaima NajmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 2SPPDocument37 pagesChapter 03 2SPPnuhaanwar26No ratings yet
- Name: Andi Ria Indahsari Asik ID: 1913442004: AldehydeDocument6 pagesName: Andi Ria Indahsari Asik ID: 1913442004: AldehydeAndi RiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form-Four (Chapters Summery of Questions With Answers)Document13 pagesChemistry Form-Four (Chapters Summery of Questions With Answers)Mohamed Abuukar AbdukadirNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones KODocument2 pagesAldehydes and Ketones KOabhishektheoneNo ratings yet
- Bautista, John Mhar M. (Experiment 7)Document4 pagesBautista, John Mhar M. (Experiment 7)2g8vdspqm5No ratings yet
- Biochem Prelim NotesDocument14 pagesBiochem Prelim NotesPretty Grace101No ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument35 pagesChapter FourAsad MohNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Macsteel VRN VRN 200 DatasheetDocument1 pageMacsteel VRN VRN 200 DatasheetIgor NhamanoNo ratings yet
- LSU Digital Commons LSU Digital Commons: Louisiana State University Louisiana State UniversityDocument284 pagesLSU Digital Commons LSU Digital Commons: Louisiana State University Louisiana State UniversityPhil DinningNo ratings yet
- Secondary 1 & 2 Science-Chemical Composition of MatterDocument15 pagesSecondary 1 & 2 Science-Chemical Composition of MatterKoh Kai XuanNo ratings yet
- Formulasi Krim Ekstrak Etanol Herba Krokot (Portulacca Oleracea L.) Sebagai Tabir SuryaDocument5 pagesFormulasi Krim Ekstrak Etanol Herba Krokot (Portulacca Oleracea L.) Sebagai Tabir SuryaTeguh Hidayat PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Nitofi LL UR63: Solvent Free, Two Part Polyurethane Resin For Sealing CracksDocument3 pagesNitofi LL UR63: Solvent Free, Two Part Polyurethane Resin For Sealing CracksFaisal FaizNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Chamois Leather Tanning ProcessDocument11 pagesAccelerated Chamois Leather Tanning ProcessAlejandro MirandaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Rice Husk Ash (Rha) Brick As Partial Replacement of ClayDocument9 pagesMechanical Properties of Rice Husk Ash (Rha) Brick As Partial Replacement of ClayMauricio David Ruiz OdarNo ratings yet
- LAB QO 1 - P-MethoxyacetanilideDocument17 pagesLAB QO 1 - P-MethoxyacetanilidemarioNo ratings yet
- Amity International School Class: XIDocument10 pagesAmity International School Class: XIksjinnieNo ratings yet
- Naming and Formula Practice QuizDocument2 pagesNaming and Formula Practice QuizSharesse Joy GumalalNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan: "Nayi Disha"Document2 pagesLearning Plan: "Nayi Disha"Vikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- High Temperature MaterialsDocument120 pagesHigh Temperature MaterialsMithun Ravichandran80% (5)
- Chemical Analysis of Graphite: Standard Test Methods ForDocument8 pagesChemical Analysis of Graphite: Standard Test Methods For916bushraNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Crosslinked Sodium Alginate/Gelatin Hydrogels For Wound DressingDocument6 pagesA Comparative Study of Crosslinked Sodium Alginate/Gelatin Hydrogels For Wound DressingJake EjaNo ratings yet
- 2.is Matter Around Us PureDocument23 pages2.is Matter Around Us PureGin vhjkk hjkkNo ratings yet
- Zeal Foundation (A Unit of Eduniverse Edusolutions) : Class X - Science Subjective Test - 4 Max - Marks: 80Document5 pagesZeal Foundation (A Unit of Eduniverse Edusolutions) : Class X - Science Subjective Test - 4 Max - Marks: 80Himanshu SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Sans10177 4Document12 pagesSans10177 4engqualsolutionsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry InvestigatoryDocument16 pagesChemistry InvestigatorySai NandhaNo ratings yet
- Week 7-9 Module (Hema 1 Laboratory)Document25 pagesWeek 7-9 Module (Hema 1 Laboratory)Jam RamosNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Green University of BangladeshDocument10 pagesAssignment: Green University of BangladeshNafis HossainNo ratings yet
- Gases: Behavior & PropertiesDocument35 pagesGases: Behavior & PropertiesAdelia SetianingsihNo ratings yet
- Penguard Universal: Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesPenguard Universal: Technical Data Sheetkanogkand kasrirakuptNo ratings yet
- Strengthening Mechanism-30102017Document18 pagesStrengthening Mechanism-30102017Amina MubasharNo ratings yet
- Adjustment of Physical Properties of Viscoelastic Foam (Paper)Document15 pagesAdjustment of Physical Properties of Viscoelastic Foam (Paper)Сергей ДружининNo ratings yet
- Annex Vi List of Preservatives Which Cosmetic Products May ContainDocument11 pagesAnnex Vi List of Preservatives Which Cosmetic Products May ContainNor SurayaNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin DetectionDocument21 pagesHemoglobin Detectionmohannad banatNo ratings yet
- Soil Science Post Test IiiDocument52 pagesSoil Science Post Test IiiTeam Agri CulturaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Summative Test Third Quarter Name: - Year and SectionDocument2 pagesScience 8 Summative Test Third Quarter Name: - Year and SectionJobel Nuestro100% (1)
- BIOL BCHM 111 BiomoleculesDocument49 pagesBIOL BCHM 111 BiomoleculeshavenNo ratings yet