Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Business Studies: Chapter 4 Operation Management
Business Studies: Chapter 4 Operation Management
Uploaded by
Kevin YangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Business Studies: Chapter 4 Operation Management
Business Studies: Chapter 4 Operation Management
Uploaded by
Kevin YangCopyright:
Available Formats
Business Studies
Chapter 4 Operation Management
4.1 Production of Goods and Services
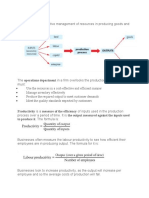
4.1.1 The Meaning of Production
Definitions:
- Production: Using resources to provide goods and services to satisfy consumers’ needs
and wants.
- Productivity: A measure of the efficiency of the use of resources in a business by
comparing the volume or value of output with the resources inputs used in production.
- Labour Productivity: Average output or revenue per employee.
- Lean Production: Improving efficiency and eliminating waste in a production process
so that products can be made better, cheaper, and faster.
- Inventories: Stocks of materials, work-in-progress and finished goods stored by a
business to ensure uninterrupted production and to meet peaks in consumer demand.
- Just-In-Time Inventory Control: Keeping inventories of materials and
work-in-progress to a minimum by taking delivery of new parts and materials only when
they are needed for production.
- Kaizen: The continuous improvement of production processes to remove waste and
increase efficiency.
Key Ideas:
Benefits of increasing productivity:
- Increase output and revenue
- Reduce the average cost of each item produced and sold
- Increase the ability of the business to compete with rivals on cost and prices
- Increase wages received by employees as their total output increases
- Increase profitability
Average Productivity of Labour = Total Output ÷ Number of Employees
Average Revenue Productivity of Labour = Total Revenue ÷ Number of Employees
Ways of increasing productivity:
- Training employees to improve their skills and to use new technologies
- Rewarding employees who increase their productivity with performance-related pay
- Improving the working environment to increase employees’ job satisfaction
- Introduce new production processes and working practices to reduce waste
- Managing inventories effectively
- Introduce lean production through new processes and ways of working to continually
reduce waste and inefficiency
- Replace old equipment and machinery with new technologies and automating
production processes
Disadvantages of overstocking:
- More cash is used up purchasing inventories leaving the business with less to pay other
commitments
- More storage space must be used or rented by the business
- Work-in-progress and finished goods held in storage for a long time will lose value if
they perish or go out of fashion
Seven types of waste recognized by lean production:
- Transportation: Moving products around unnecessarily
- Stock: Storing too many components, semi-finished and finished products
- Motion: People or equipment moving or walking more than it is required to perform a
task
- Waiting Time: Time wasted between each stage of the production process
- Overproduction: Producing more than is needed to meet customer demand
- Over Processing: Creating unnecessary activities due to poor equipment or product
design
- Defects: the effort involved in inspecting and fixing product defects
Principles of lean production
- Making continuous improvements in the production process
- Speeding up the flow of production through the various stages of the process
- Making the flow of production as continuous as possible
- Reducing waste and improving work quality at all stages
You might also like
- Question Answer Bank MBA 201Document51 pagesQuestion Answer Bank MBA 201Shanu RockNo ratings yet
- Ecs ShoesDocument24 pagesEcs ShoesBilal Yasir100% (3)
- Chapter 17Document21 pagesChapter 17marwanNo ratings yet
- Valuation Excel Shortcuts: Author: Drs. J.J.P. (Joris) Kersten RAB 16 February 2021Document15 pagesValuation Excel Shortcuts: Author: Drs. J.J.P. (Joris) Kersten RAB 16 February 2021ronnieindiaNo ratings yet
- 4.1.1 The Meaning of Production: Productivity Measures How Efficient Production IsDocument10 pages4.1.1 The Meaning of Production: Productivity Measures How Efficient Production Ishassan haniNo ratings yet
- 4.1 - Production of Goods and Services - IGCSE AID PDFDocument8 pages4.1 - Production of Goods and Services - IGCSE AID PDFHelenaNo ratings yet
- ngli quản trịDocument3 pagesngli quản trịphnlingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document26 pagesLecture 1davidbrubio1163No ratings yet
- MUDA - PakaimDocument30 pagesMUDA - PakaimzohaibzobiNo ratings yet
- Business Notes OPERATIONSDocument42 pagesBusiness Notes OPERATIONSCandyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document6 pagesChapter 18HiNo ratings yet
- Lean Manufacturing:: 1. DefinitionDocument5 pagesLean Manufacturing:: 1. DefinitionÓscar BaezNo ratings yet
- Business Section 4.1 NewDocument10 pagesBusiness Section 4.1 NewJuné MaraisNo ratings yet
- Stratcost Life Cycle CostingDocument5 pagesStratcost Life Cycle CostingSandraNo ratings yet
- Study On Lean Manufacturing Process in Garments ProductionDocument4 pagesStudy On Lean Manufacturing Process in Garments ProductionAnaliza IcsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Production of Goods and Services: Operations Management in A Business IsDocument12 pagesChapter 17: Production of Goods and Services: Operations Management in A Business IsWassim AlwanNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Production of Goods and ServiceDocument6 pages4.1 Production of Goods and ServiceannabellNo ratings yet
- Notes For CA5104 Operations ManagementDocument39 pagesNotes For CA5104 Operations ManagementliliNo ratings yet
- Pom Unit-1Document92 pagesPom Unit-1rashmianand712No ratings yet
- POM IntroductionDocument40 pagesPOM IntroductionShivam AgarwalNo ratings yet
- IB Business (HL) - Topic 5 - Operations ManagementDocument9 pagesIB Business (HL) - Topic 5 - Operations ManagementTanya AdvaniNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument18 pagesSupply Chain ManagementAndreaNo ratings yet
- Operations CH1 NoteDocument3 pagesOperations CH1 NoteYagiz KarsliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - The Nature of Operations - PresentationDocument96 pagesChapter 22 - The Nature of Operations - Presentationkuziva.jamesNo ratings yet
- OM ReportDocument3 pagesOM ReportTrixie Jane NeriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Review WEEK 1Document8 pagesChapter 15 Review WEEK 1malakmarzouk95No ratings yet
- What Is Production SystemDocument5 pagesWhat Is Production SystemJorge Arellano HinojosaNo ratings yet
- Lean Supply Chain Management & It Enabled Operations ManagementDocument13 pagesLean Supply Chain Management & It Enabled Operations Managementchristy bijuNo ratings yet
- Answer-Module #1Document14 pagesAnswer-Module #1yza gunidaNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS Unit 3 AOS3Document12 pagesBUSINESS Unit 3 AOS3gramcconn24No ratings yet
- Tổng Hợp Kiến Thức Tacn2Document37 pagesTổng Hợp Kiến Thức Tacn2Ngọc Trung Học 20No ratings yet
- OpmtqmDocument4 pagesOpmtqmJayson ZonsaNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Lean ShipbuildingDocument32 pagesA Presentation On Lean ShipbuildingAndre BlueNo ratings yet
- Lean Operations & JITDocument29 pagesLean Operations & JITkushalNo ratings yet
- 9 Igcse Chapter 18Document7 pages9 Igcse Chapter 18Malek MohamedNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Chapter 15Document5 pagesBusiness Studies Chapter 15sheefangcheng27No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management BriefingDocument5 pagesSupply Chain Management BriefingTomi OlinNo ratings yet
- Unit 17: Production of Goods and Services: Section 4: Operation ManagementDocument6 pagesUnit 17: Production of Goods and Services: Section 4: Operation ManagementNe PaNo ratings yet
- TransportationMethods PDFDocument11 pagesTransportationMethods PDFFullmetal GunneNo ratings yet
- Om Unit IDocument20 pagesOm Unit IMiyonNo ratings yet
- PM-Solved Paper 2006Document27 pagesPM-Solved Paper 2006anuragmamgainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Production Planning and Inventory ControlDocument80 pagesIntroduction To The Production Planning and Inventory ControlAngelina WattssNo ratings yet
- Part One Ppc-IDocument34 pagesPart One Ppc-ITMIMITWJ2030No ratings yet
- Group 1Document25 pagesGroup 1romalyn purificacionNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document9 pagesTutorial 5hathutrang742003No ratings yet
- Strategic Issues in SCDocument35 pagesStrategic Issues in SCSahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Production of Goods andDocument17 pagesProduction of Goods andHelenaNo ratings yet
- What Is Operations Management?Document11 pagesWhat Is Operations Management?Anjali AngelNo ratings yet
- 4.1: Production Is The Effective Management of Resources in Producing Goods andDocument16 pages4.1: Production Is The Effective Management of Resources in Producing Goods andSAINo ratings yet
- Lean AccountingDocument31 pagesLean Accountingjitendrasutar1975100% (2)
- 4.1 - Production of Goods and Services - 2Document9 pages4.1 - Production of Goods and Services - 2Haris ParkerNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Lean AccountingDocument5 pagesModule 8 Lean AccountingCaliNo ratings yet
- Lean Manufacturing OverviewDocument57 pagesLean Manufacturing OverviewpaudubaiNo ratings yet
- Nestle Case StudyDocument4 pagesNestle Case StudyOmair ShaikhNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument64 pagesSummaryssanik1No ratings yet
- Operations Management ReviewerDocument3 pagesOperations Management Reviewerchrae0913No ratings yet
- Work Content 2Document10 pagesWork Content 2Vishal MeenaNo ratings yet
- Bus 103 (Final Revision)Document11 pagesBus 103 (Final Revision)amr khaledNo ratings yet
- Production & Productivity (Sheet-4)Document31 pagesProduction & Productivity (Sheet-4)2223401015No ratings yet
- BM Review Notes 4.6 - 5.6Document22 pagesBM Review Notes 4.6 - 5.6howard.chen0604No ratings yet
- CH 1-5 OMDocument71 pagesCH 1-5 OMAbu DadiNo ratings yet
- CH 1-5 OMDocument71 pagesCH 1-5 OMAbu DadiNo ratings yet
- Mba Thesis Proposal PDFDocument10 pagesMba Thesis Proposal PDFBellaNo ratings yet
- BOQ & Bill VerificationDocument20 pagesBOQ & Bill VerificationAftabAliNo ratings yet
- Case - Network SolutionsDocument3 pagesCase - Network SolutionsSameera AroraNo ratings yet
- ZONE 15 - Super Markets & GroceryDocument2 pagesZONE 15 - Super Markets & GroceryDeepak SaravananNo ratings yet
- Document Control Information Manager in Houston TX Resume Oksana SaboDocument4 pagesDocument Control Information Manager in Houston TX Resume Oksana SaboOksanaSaboNo ratings yet
- Parcel InformationDocument1 pageParcel InformationArnau Bataller RuizNo ratings yet
- Final Gitman - pmf13 - PPT 07 GE Stock Valuation To 50Document51 pagesFinal Gitman - pmf13 - PPT 07 GE Stock Valuation To 50asimNo ratings yet
- Satya PDFDocument6 pagesSatya PDFmoonmoonNo ratings yet
- Engro Foods Marketing ProjectDocument12 pagesEngro Foods Marketing ProjectHaxi KhanNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Uber and VakrangeeDocument3 pagesQualitative Analysis of Uber and VakrangeeArunabh ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- How To Create Stock Items in TallyDocument6 pagesHow To Create Stock Items in TallyMahendra Jena100% (1)
- Chapter 9Document15 pagesChapter 9Leah Rose Feldman0% (1)
- Physical FacilitiesDocument15 pagesPhysical FacilitiesMalou Ruiz DenolanNo ratings yet
- Reviewers: Project Transition ChecklistDocument6 pagesReviewers: Project Transition Checklistnsadnan100% (2)
- Business Ethics & CSRDocument49 pagesBusiness Ethics & CSR11bharat8998100% (1)
- What Are The Most Important Changes in Incoterms 2020Document5 pagesWhat Are The Most Important Changes in Incoterms 2020frNo ratings yet
- Jindal Vijayanagar Steel LTD Oracle Ebs ImplementationDocument2 pagesJindal Vijayanagar Steel LTD Oracle Ebs ImplementationenigmanishNo ratings yet
- Roxas Vs CtaDocument23 pagesRoxas Vs CtaMyra De Guzman PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Douglas Mcgregor Theory X and yDocument5 pagesDouglas Mcgregor Theory X and yAnonymous CwJeBCAXp100% (2)
- Memorandum of Understanding: BetweenDocument3 pagesMemorandum of Understanding: BetweenAnonymous 58LGc3No ratings yet
- 03 Sap MMDocument11 pages03 Sap MMraj rajanNo ratings yet
- The Changing Theatre LandscapeDocument37 pagesThe Changing Theatre LandscapeKaren RobinetNo ratings yet
- Locator SlipDocument1 pageLocator SlipQueenzel Belbis MoralesNo ratings yet
- Market Trend and Forecast 22 - 30 - IBED ReportDocument33 pagesMarket Trend and Forecast 22 - 30 - IBED Report7 cloudNo ratings yet
- Riding SawariDocument26 pagesRiding SawariUmar Farooq100% (1)
- Nathan Ives, StrategyDriven Principal, BiographyDocument2 pagesNathan Ives, StrategyDriven Principal, BiographyNathan IvesNo ratings yet