Professional Documents
Culture Documents
151 Department of Civil Engineering
151 Department of Civil Engineering
Uploaded by
Associates zOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
151 Department of Civil Engineering
151 Department of Civil Engineering
Uploaded by
Associates zCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluid Properties
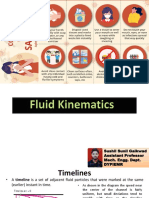
• Timelines:
• A timeline is a set of adjacent fluid particles that were marked at the same (earlier) instant in time.
• Timelines are particularly useful in situations where the uniformity of a flow (or lack thereof) is to be examined
• Timelines are formed by marking line of fluid particles, and then
that line move (and deform) through the flow field; timelines are
shown at t 5 0, t1, t2, and t3
• friction at the walls, the fluid velocity there is zero (the no-slip condition),
• and the top and bottom of the timeline are anchored at their starting locations.
• Timelines can be generated experimentally in a water channel through use of a hydrogen
• Bubble wire. When a short burst of electric current is sent through the cathode wire,
• electrolysis of the water occurs and tiny hydrogen gas bubbles form at the
• wire. Since the bubbles are so small, their buoyancy is nearly negligible,
• and the bubbles follow the water flow nicely
Timelines produced by a hydrogen bubble
wire are used to visualize the boundary layer
velocity profile shape along a flat plate. Flow
is from left to right, and the hydrogen bubble
wire is located to the left of the field of view.
Bubbles near the wall reveal a flow instability
that leads to turbulence.
Department of Civil Engineering 151
Numerical on velocities and acceleration
• In a fluid, the velocity field is given by V = (3x + 2y) i + (2z + 3x2) j + (2t – 3z) k Determine:
• (i) The velocity components u, v, w at any point in the flow field;
• (ii) The speed at point (1, 1, 1);
• (iii) The speed at time t = 2s at point (0, 0, 2).
• Also classify the velocity field as steady, or unsteady, uniform or non-uniform and one, two or three dimensional.
Department of Civil Engineering 152
Fluid Properties
• Velocity for a two dimensional flow field is given by V = (3 + 2xy + 4t2) i + (xy2 + 3t) j Find the velocity and acceleration at a point (1,2) after
2 sec.
Department of Civil Engineering 153
Fluid Properties
• Find the velocity and acceleration at a point (1, 2, 3) after 1 sec. for a threedimensional flow given by u = yz + t, v = xz – t, w = xy m/s.
Department of Civil Engineering 154
Fluid Properties
• For a three-dimensional flow the velocity distribution is given by u = – x, v = 3 – y and w = 3 – z. What is the equation of a streamline
passing through (1,2,2)?
Department of Civil Engineering 155
Fluid Properties
• Obtain the equation to the streamlines for the velocity field given as: V = 2x3i – 6x2yj
Department of Civil Engineering 156
You might also like
- Mechanics-of-Fluids by Irving Shames-4th-Ed-Ch-1-3 PDFDocument170 pagesMechanics-of-Fluids by Irving Shames-4th-Ed-Ch-1-3 PDFDJ83% (6)
- XCAP Quick GuideDocument56 pagesXCAP Quick GuideZaryab NisarNo ratings yet
- Chess King Manual 201512Document339 pagesChess King Manual 201512Song Jin100% (3)
- Xpediter Training GuideDocument280 pagesXpediter Training GuideJyolsna JyothinadhNo ratings yet
- 3 NLP Seduction Patterns To Mindwash Girls Into Attraction - Seduction ScienceDocument9 pages3 NLP Seduction Patterns To Mindwash Girls Into Attraction - Seduction ScienceMarty Mah0% (2)
- Spcolumn Manual PDFDocument200 pagesSpcolumn Manual PDFAnonymous wCIlUdNo ratings yet
- 080118chapter5fluidkinematics 180325023259Document62 pages080118chapter5fluidkinematics 180325023259Ruturaj TanwadeNo ratings yet
- Dynamic #Ow Behaviour in Bubble Columns: S. Becker, H. de Bie, J. SweeneyDocument7 pagesDynamic #Ow Behaviour in Bubble Columns: S. Becker, H. de Bie, J. SweeneySalwa asyifaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Flowing Fluids and Pressure VariationDocument93 pagesCH 4 Flowing Fluids and Pressure VariationMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- ART Lou RVDocument8 pagesART Lou RVnicholas_j_vaughanNo ratings yet
- em Le HuynhDocument6 pagesem Le HuynhÚt Ú Ù UnlimitNo ratings yet
- 2013-Discussion On Relationship Between Turbulent Structure and Wave Pressure On Submerged Breakwaters - IAHR-A11334Document8 pages2013-Discussion On Relationship Between Turbulent Structure and Wave Pressure On Submerged Breakwaters - IAHR-A11334jiang.xuelianNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Local Scour Downstream of Cylindrical Bridge PiersDocument10 pagesExperimental Study of Local Scour Downstream of Cylindrical Bridge Piersomar TahaNo ratings yet
- 02 Flow FieldsDocument53 pages02 Flow Fieldstolga_enes9949No ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of Local Scour Around The Pier With and Without Airfoil Collar (AFC) Using FLOW 3DDocument19 pagesNumerical Simulation of Local Scour Around The Pier With and Without Airfoil Collar (AFC) Using FLOW 3DsoniaNo ratings yet
- CH-5 OchhDocument47 pagesCH-5 OchhSegni WandimuNo ratings yet
- Free Water PassageDocument46 pagesFree Water PassageAbiued EjigueNo ratings yet
- Ju 2007Document15 pagesJu 2007Shubham khatriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Seismic Refraction MethodsDocument55 pagesLecture 2 Seismic Refraction Methodsyayan_syncro100% (3)
- RVFDocument31 pagesRVFephNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layers & Helicopter Aerodynamics: School of Physics, Engineering & Computer ScienceDocument48 pagesBoundary Layers & Helicopter Aerodynamics: School of Physics, Engineering & Computer Sciencekewan chaudhryNo ratings yet
- Handout3 PostDocument7 pagesHandout3 PostleandropessiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Flow Fields Applied Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument75 pagesFlow Fields Applied Computational Fluid DynamicsAntonio JosephNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Chapter 3Document9 pagesHydraulics Chapter 3tekalign yerangoNo ratings yet
- 2Document32 pages2ahmad.m.mosa99No ratings yet
- Unit 3-Lecture 3Document13 pagesUnit 3-Lecture 3ukali627No ratings yet
- Hydraulics 11Document69 pagesHydraulics 11DRJULIUSJORDANNo ratings yet
- Fluid KinematicsDocument17 pagesFluid KinematicsSushil GaikwadNo ratings yet
- 8.flow in Open Channels Non Uniform FlowDocument5 pages8.flow in Open Channels Non Uniform FlowLydia CariagaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - 3rd Year Mech - Lecture #2Document17 pagesFluid Mechanics - 3rd Year Mech - Lecture #2Bahaa M NadaNo ratings yet
- Bridge Hydrology and Scour: Rajendra Raj Sharma Department of RoadsDocument40 pagesBridge Hydrology and Scour: Rajendra Raj Sharma Department of RoadsGaurabNo ratings yet
- Slug and Pulsating Flow in High Gradient ChannelDocument7 pagesSlug and Pulsating Flow in High Gradient ChannelReza JafarzadNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Electrical Type Flow MeterDocument129 pagesUnit IV Electrical Type Flow MeterJeeva JeevaNo ratings yet
- 4 PDFDocument6 pages4 PDFkamalNo ratings yet
- River Crossing Pipeline - PaperDocument6 pagesRiver Crossing Pipeline - PaperJoko NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow in Coiled Tubing - A Literature Review and Experimental Investigation - Shah and Zhow PDFDocument10 pagesFluid Flow in Coiled Tubing - A Literature Review and Experimental Investigation - Shah and Zhow PDFYesidCamiloTrujillo100% (1)
- Szelangiewicz Zelazny Buczkowski - Computer - 52 2017 PDFDocument8 pagesSzelangiewicz Zelazny Buczkowski - Computer - 52 2017 PDFtruva_kissNo ratings yet
- Seismic Refraction MethodsDocument48 pagesSeismic Refraction MethodsnagalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Numerical Modelling of Vortex Induced VibrationsDocument6 pagesNumerical Modelling of Vortex Induced VibrationscteranscribdNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Non-Destructive Tests in ConcreteDocument40 pagesLecture 8 Non-Destructive Tests in ConcreteGirum MenassieNo ratings yet
- Zhu 2012Document9 pagesZhu 2012Ahmad HelmiNo ratings yet
- Compiled Question Ce 3227Document9 pagesCompiled Question Ce 3227Hamisi MzariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Hydraulic Structures: BFC21103 HydraulicsDocument51 pagesChapter 5. Hydraulic Structures: BFC21103 HydraulicsSky FireNo ratings yet
- Hapter Four: Kinematics of Fluid FlowDocument15 pagesHapter Four: Kinematics of Fluid Flowabdata wakjiraNo ratings yet
- plynett@tamu.edu,+4895-20466-1-CEDocument14 pagesplynett@tamu.edu,+4895-20466-1-CEshayanasadi.787No ratings yet
- Cross Waves and Pulsating Flows inDocument7 pagesCross Waves and Pulsating Flows inDima AljubouriNo ratings yet
- MCE 244 - Lecture Notes Wk1Document5 pagesMCE 244 - Lecture Notes Wk1Karen DavisNo ratings yet
- 02 Streamflow CharacteristicsDocument16 pages02 Streamflow CharacteristicscfyonnamarieNo ratings yet
- Flood RoutingDocument13 pagesFlood RoutingMomostafaNo ratings yet
- Undular Hydraulic JumpDocument14 pagesUndular Hydraulic JumpSeemantShuklaNo ratings yet
- HY B00030 Hydraulic Characteristics and Discharge Control of Sluice GatesDocument10 pagesHY B00030 Hydraulic Characteristics and Discharge Control of Sluice GatesFelipe VillegasarangoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Fluid KinematicsDocument15 pagesChapter 3 Fluid Kinematicsaduyekirkosu1scribdNo ratings yet
- Ceg 503 Lecture 1Document23 pagesCeg 503 Lecture 1ayodejiayinde765No ratings yet
- BFC21103 Chapter5Document51 pagesBFC21103 Chapter5nurinNo ratings yet
- Topic 5. Hydraulic Structures: HydraulicsDocument51 pagesTopic 5. Hydraulic Structures: HydraulicsmaizansofiaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Signal Quality of A Vortex Flowmeter Downstream of Two ElbowsDocument11 pagesA Study On Signal Quality of A Vortex Flowmeter Downstream of Two ElbowsGrega BobovnikNo ratings yet
- 2008, A. A. Avramenko and A. V. Kuznetsov, Journal of Porous Media, Flow in A Curved Porous Channel With A Rectangular Cross SectionDocument7 pages2008, A. A. Avramenko and A. V. Kuznetsov, Journal of Porous Media, Flow in A Curved Porous Channel With A Rectangular Cross SectionPrabal AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Cylinder & PlateDocument11 pagesCylinder & PlateFykNo ratings yet
- Week2 - Density N Velocity FieldDocument20 pagesWeek2 - Density N Velocity FieldITS Team SapuanginNo ratings yet
- Gradually Varied FlowDocument37 pagesGradually Varied Flowprashanthreddyh100% (1)
- Reservoir RoutingDocument15 pagesReservoir RoutingMomostafaNo ratings yet
- II - Techniques in Structural Geology-SeismicDocument27 pagesII - Techniques in Structural Geology-SeismicAlionk GaaraNo ratings yet
- Windows Audit Part 3 - Tracing File Deletions - Michael FirsovDocument6 pagesWindows Audit Part 3 - Tracing File Deletions - Michael FirsovsivextienNo ratings yet
- Math Problem Solving Year 4Document31 pagesMath Problem Solving Year 4zulkifli ismailNo ratings yet
- Software Project ManagementDocument15 pagesSoftware Project ManagementMemes JunctionNo ratings yet
- B.SC - Sem II Honours Admit Male 1Document50 pagesB.SC - Sem II Honours Admit Male 1Neelarka RoyNo ratings yet
- IRC Urban Roads Manual - Parking Managment - DraftDocument26 pagesIRC Urban Roads Manual - Parking Managment - DraftRahul MassNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Bar Element AE5030 Advanced Finite Element MethodDocument20 pagesAssignment 2 Bar Element AE5030 Advanced Finite Element MethodBudiAjiNo ratings yet
- 120140084-10 InglesDocument2 pages120140084-10 InglesMelany Lopez50% (4)
- D300s Advanced - Shooting Custom Menu Banks 12-09-8pDocument8 pagesD300s Advanced - Shooting Custom Menu Banks 12-09-8ptelmopNo ratings yet
- CIBA Annual Report 2015 16Document228 pagesCIBA Annual Report 2015 16Eric S Y KwokNo ratings yet
- CMJ Revised Fee Structure Other CoursesDocument10 pagesCMJ Revised Fee Structure Other CoursesSaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- SM 4500 Cloro ResidualDocument14 pagesSM 4500 Cloro ResidualDiego AngeloNo ratings yet
- Nebosh How To Pass Your Open Book Exam On The First AttemptDocument4 pagesNebosh How To Pass Your Open Book Exam On The First Attemptdp.cavozziNo ratings yet
- Boundary Value ProblemsDocument15 pagesBoundary Value ProblemsShadman Saqlain Rahman, 170021057No ratings yet
- Claude Shannon Masters Thesis MitDocument7 pagesClaude Shannon Masters Thesis Mitdwf6nx2z100% (2)
- ScalaDocument16 pagesScalaSamara SequeiraNo ratings yet
- Social, Academic, and Business Communication in The Junctures of LifeDocument2 pagesSocial, Academic, and Business Communication in The Junctures of LifeCristina RocheNo ratings yet
- Mbti Step II For PMC 04 2Document49 pagesMbti Step II For PMC 04 2TPNo ratings yet
- Koenigsegg AgeraRS Specification PDFDocument1 pageKoenigsegg AgeraRS Specification PDFVian ToroNo ratings yet
- Upaya Hukum Terhadap Pelanggaran Implementasi (Iot) Di Bidang Pelayanan Kesehatan Menurut Ketentuan Perlindungan Data PribadiDocument17 pagesUpaya Hukum Terhadap Pelanggaran Implementasi (Iot) Di Bidang Pelayanan Kesehatan Menurut Ketentuan Perlindungan Data PribadiValentina AdindaNo ratings yet
- Sample ManuscriptDocument5 pagesSample Manuscriptadi kadarsihNo ratings yet
- Detail Drawing of Pump and Blower Room ITBPDocument1 pageDetail Drawing of Pump and Blower Room ITBPAminur RahmanNo ratings yet
- downloadMathsA levelPapersEdexcel IALFurther PureF1QPJanuary20201520QP PDFDocument14 pagesdownloadMathsA levelPapersEdexcel IALFurther PureF1QPJanuary20201520QP PDFMaria RobellonNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Format of Ph.D. Thesis Submission (W.e.f. 28-12-2018) - 448920Document32 pagesGuidelines For Format of Ph.D. Thesis Submission (W.e.f. 28-12-2018) - 448920Bhumika PatelNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document14 pagesProblem Set 2Daniel ChangNo ratings yet
- NJYB3Document3 pagesNJYB3Prime ProNo ratings yet