Professional Documents
Culture Documents
E Glaucoma
E Glaucoma
Uploaded by
Mohammed Mahmoud Abd Elhalem0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views3 pagesGlaucoma is a group of eye diseases, with damage to the optic nerve. It is one of the leading causes of blindness in the United States. Early detection and prompt treatment are keys to protecting you against permanent loss of vision.
Original Description:
Original Title
e Glaucoma
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGlaucoma is a group of eye diseases, with damage to the optic nerve. It is one of the leading causes of blindness in the United States. Early detection and prompt treatment are keys to protecting you against permanent loss of vision.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views3 pagesE Glaucoma
E Glaucoma
Uploaded by
Mohammed Mahmoud Abd ElhalemGlaucoma is a group of eye diseases, with damage to the optic nerve. It is one of the leading causes of blindness in the United States. Early detection and prompt treatment are keys to protecting you against permanent loss of vision.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
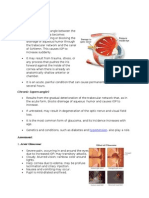
GLAUCOMA
Glaucoma affects nearly 3 million • High internal eye pressure (above 22
Americans and is one of the leading mmHg)
causes of blindness in the United States. • Diabetes, high blood pressure, or heart
Glaucoma can gradually ”steal” your vision disease
without your being aware of it. Early • Chronic eye inflammation
detection and prompt treatment are keys • Eye tumor
to protecting you against permanent loss • Severe near-sightedness/far-
of vision. sightedness
• Previous eye injury
I. What is Glaucoma? • Long-term use of corticosteroids (anti-
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases, with inflammatory drugs)
damage to the optic nerve leading to
permanent vision loss or blindness. The IV. Types of Glaucoma
optic nerve is located at the back of the The two main types of glaucoma are:
eye and is made up of over a million nerve
fibers. It sends images that you see from 1. Open-angle glaucoma (OAG)
the retina, a light sensitive layer that lines In open-angle glaucoma, the fluid drains
the interior of the eye, to the brain. too slowly leading to fluid backup and a
rise in eye pressure. The optic nerve is
II. Causes of Glaucoma slowly damaged, causing gradual loss of
In most cases, an abnormally high vision. This is the most common form of
pressure within the eye causes glaucoma. glaucoma in Caucasians and African
Inside the eye, fluid is continuously Americans. OAG is a chronic disease and
produced and circulated to nourish the usually affects both eyes at the same time.
nearby tissues, remove unwanted wastes
and maintain normal eye pressure. This 2. Closed-angle glaucoma (CAG)
fluid is not the same as tears, which are In closed-angle glaucoma, the drainage
produced on the outside of the eye. Fluid may be too narrow or blocked, causing
leaves the eye through a “drain” located at sudden buildup of pressure in the eye.
an angle where the iris and cornea meet. Asians and persons who are far-sighted
When the fluid drains too slowly out of the are more prone to develop CAG. This is a
eye, the pressure in the eye builds up, common form of glaucoma among
causing damage to the optic nerve. Chinese, Vietnamese, Filipinos, and also
Eskimos. The condition can be chronic or
III. Who is At Risk for Glaucoma? acute and usually affects one eye at a
time. Acute CAG is a medical emergency
Anyone can develop glaucoma. The
and should be treated by an eye specialist
following factors/conditions increase your
(ophthalmologist) immediately to prevent
risk of glaucoma:
severe vision loss or blindness.
• Persons over age 40
• African Americans and Asian
Americans
• Family History
Chinese Community Health Resource Center www.cchrchealth.org P. 1
V. Signs and Symptoms of Glaucoma An instrument which directly or
indirectly measures the extent of nerve
Signs and symptoms vary according to the
fiber damages in the retina around the
type of glaucoma. In the early stages of
optic discs.
glaucoma, there are often no symptoms,
pain, or change in vision. As the disease
progresses, a person begins to lose VII. Treatment of Glaucoma
peripheral (side) vision and eventually Open angle glaucoma cannot be cured,
loses vision completely if left untreated. and the damage to the optic nerve is
irreversible. The purpose of treatment is
Acute glaucoma develops suddenly as a to prevent further loss of vision. Treatment
result of sudden rise in eye pressure due options include:
to blockage of fluid drainage from the eye. 1. Medications
This requires immediate medical attention Prescription eye drops or pills to help
in order to prevent permanent vision loss, lower internal eye pressure by
which can occur within hours or days after increasing the outflow of fluid or
the onset. reducing the production of fluid in the
eye. Daily and lifetime use of these
Signs of acute glaucoma include: medications are often necessary.
• Sudden blurred vision with pain and 2. Surgery
redness in the eye When medications fail to control eye
• Appearance of colored rings (halos) pressure, laser treatment or surgical
around lights operations may be needed to open
• Headache blocked drainage, stretch drainage
• Nausea and vomiting holes or create a new opening to allow
fluids to flow out of the eye. In more
VI. Diagnosis of Glaucoma severe cases, procedures to destroy
the part of the eye that produces fluid
The following tests are frequently used to may be done.
diagnose glaucoma:
• Dilated eye exam Closed angle glaucoma can be cured by
An instrument called an laser treatment of the iris.
ophthalmoscope is used to look
through the pupil and check for VIII. Prevention of Glaucoma
changes in the optic nerve.
• Eye pressure measurement Open angle glaucoma is not preventable.
An instrument called a tonometer is However, with early detection and
used to measure eye pressure. treatment, OAG can be controlled.
• Visual field test Comprehensive eye exams are
A computerized eye test is used to recommended every 2 years for persons
measure your field of vision. between the ages of 40-65, and every
year for those over 65. More frequent
• Nerve fiber analyzer
checkups may be needed for those at high
risk.
Chinese Community Health Resource Center www.cchrchealth.org P. 2
Closed angle glaucoma is preventable by laser treatment of the iris. If you are currently
under treatment for glaucoma, be sure to use or take your medications exactly as prescribed
and see your eye doctor regularly. To learn more about eye health, contact:
National Eye Institute
(301) 496-5248
www.nei.nih.gov
Prevent Blindness California
(415) 387-0934
www.eyeinfo.org
©2003 Chinese Community Health Resource Center
Revised 3/2007
Chinese Community Health Resource Center www.cchrchealth.org P. 3
You might also like
- PDF Extracorporeal Life Support The Elso Red Book Thomas V Brogan Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Extracorporeal Life Support The Elso Red Book Thomas V Brogan Ebook Full Chapterpauline.martin372100% (2)
- Pedia Platinum (1st Edition)Document546 pagesPedia Platinum (1st Edition)Mao Dela Cruz100% (4)
- Glaukoma CSDocument13 pagesGlaukoma CSKevinVun100% (4)
- GlaucomaDocument6 pagesGlaucomaBasit AliNo ratings yet
- GLAUCOMa Edited2Document8 pagesGLAUCOMa Edited2Maki CabuenaNo ratings yet
- GLAUCOMADocument5 pagesGLAUCOMArocioisabelacamposNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma What Is Glaucoma?Document4 pagesGlaucoma What Is Glaucoma?Marini Christin PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma Case StudyDocument5 pagesGlaucoma Case StudyEdgel QuidolesNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma: DR - Nugraha Wahyu Cahyana, SPMDocument16 pagesGlaucoma: DR - Nugraha Wahyu Cahyana, SPMArdy SantosoNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument27 pagesGlaucomaSteph VistalNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma Case StudyDocument5 pagesGlaucoma Case StudyEdgel QuidolesNo ratings yet
- American Optometric Association. Glaucoma HTTP - WWW - Aoa.org - Glaucoma - Xml.Document8 pagesAmerican Optometric Association. Glaucoma HTTP - WWW - Aoa.org - Glaucoma - Xml.Adriana Falla100% (1)
- Retinal DiseaseDocument16 pagesRetinal DiseaseNikoleta TuleaNo ratings yet
- Advance Trends in Eye Care: DR Divya Kesarwani Consultant Cataract and Glaucoma ServicesDocument42 pagesAdvance Trends in Eye Care: DR Divya Kesarwani Consultant Cataract and Glaucoma ServicesdrdivyakesarwaniNo ratings yet
- Classification of GlaucomaDocument6 pagesClassification of GlaucomaAli Al.JuffairiNo ratings yet
- Endpd PDFDocument29 pagesEndpd PDFNaveen AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Two Major FormsDocument5 pagesTwo Major FormsKath CuevasNo ratings yet
- A Project ReportDocument80 pagesA Project ReportShakun VidyottamaNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma Booklet: Presented by The Eye Digest: Authored by University of Illinois Eye & Ear Infirmary PhysiciansDocument25 pagesGlaucoma Booklet: Presented by The Eye Digest: Authored by University of Illinois Eye & Ear Infirmary PhysiciansThe Eye Digest100% (2)
- Glaucoma and Your EyesDocument4 pagesGlaucoma and Your EyesclubsanatateNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument52 pagesGlaucomaEden NamwabaNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma: Information and TreatmentDocument22 pagesGlaucoma: Information and TreatmentsanjivdasNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma and Cataract - ContentannDocument20 pagesGlaucoma and Cataract - ContentannDR. KUMARASWAMI HEALTH CENTRE COLLEGE OF NURSING KANYAKUMARINo ratings yet
- Glaucoma 2 PDFDocument16 pagesGlaucoma 2 PDFAgus HrtNo ratings yet
- GLAUCOMA FinalDocument3 pagesGLAUCOMA FinalplethoraldorkNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniDocument42 pagesGlaucoma: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniSaha DirllahNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma: Seminar OnDocument43 pagesGlaucoma: Seminar OnSanjay GarasiyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Part 1 Kmu IhsanDocument38 pagesUnit 7 Part 1 Kmu IhsanHasnain Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Glaukoma Dan KonjungtivitisDocument24 pagesGlaukoma Dan KonjungtivitisAnnisa DeasyNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma: Referat Presentation By: Ilma Amalia, S.KedDocument22 pagesGlaucoma: Referat Presentation By: Ilma Amalia, S.KedIlma AmaliaNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument4 pagesGlaucomaMohammed Shamiul ShahidNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms of Macular DegenerationDocument19 pagesSigns and Symptoms of Macular DegenerationJayveersinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma: by Tekia BuntynDocument18 pagesGlaucoma: by Tekia BuntynTekia BuntynNo ratings yet
- Understanding Glaucoma ENDocument44 pagesUnderstanding Glaucoma ENTheophilus Oduro-NyarkoNo ratings yet
- GloukomaDocument7 pagesGloukomaGraitaaNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma 191024141130Document25 pagesGlaucoma 191024141130Broz100% (1)
- Glaucoma: Information From WWW - Nhs.ukDocument9 pagesGlaucoma: Information From WWW - Nhs.ukJenmar HemmingsNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument6 pagesCataractSairileenDoradoNo ratings yet
- Glacoma What You Should KnowDocument26 pagesGlacoma What You Should KnowTaranisaNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma OverviewDocument4 pagesGlaucoma OverviewSurya Cahyadi JunusNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma and CataractDocument30 pagesGlaucoma and CataractJayselle ArvieNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument3 pagesGlaucomaPuviyarasiNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma & Retinal Detachment-1Document29 pagesGlaucoma & Retinal Detachment-1Priya bhattiNo ratings yet
- Angle-Closure Glaucoma - UpToDateDocument9 pagesAngle-Closure Glaucoma - UpToDateElaine June FielNo ratings yet
- VI (Visual ImpairmentDocument24 pagesVI (Visual ImpairmentSanishka NiroshanNo ratings yet
- Search Uptodate: Grade 1CDocument1 pageSearch Uptodate: Grade 1CGabriella TjondroNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument30 pagesGlaucomaamsabavanNo ratings yet
- GlaukomaDocument30 pagesGlaukomaSyahrani HajriNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument2 pagesGlaucomagaurang03No ratings yet
- Guideline of Glaucoma PDFDocument30 pagesGuideline of Glaucoma PDFYunita Eka Putri DunggaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Eye & Vision DisordersDocument72 pagesChapter 11 Eye & Vision DisordersMYLENE GRACE ELARCOSANo ratings yet
- Urgencias OftalmológicasDocument20 pagesUrgencias OftalmológicasDaniela León CastilloNo ratings yet
- GlaucomeaDocument21 pagesGlaucomeamalathiNo ratings yet
- What Is Glaucoma?Document9 pagesWhat Is Glaucoma?Subhash Digambar VisalNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Mohamed - SeadDocument12 pagesChapter One Mohamed - SeadAbdirahman Hassan MohamedNo ratings yet
- Age-Related Cataract & GlaucomaDocument26 pagesAge-Related Cataract & Glaucomasweetyeyal2002No ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument34 pagesGlaucomabobamaryNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument9 pagesGlaucomat2ybrkm5hwNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma Note (DR - Abeba)Document17 pagesGlaucoma Note (DR - Abeba)creativejoburgNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma New Zealand - A Charitable TrustDocument49 pagesGlaucoma New Zealand - A Charitable TrustMiazan SheikhNo ratings yet
- About 70% of All Sensory Information Reaches The Brain Through The EyesDocument127 pagesAbout 70% of All Sensory Information Reaches The Brain Through The Eyesjoan olanteNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Heart Disease: A Proposed Clinical ClassificationDocument2 pagesHypertensive Heart Disease: A Proposed Clinical ClassificationireneaureliaNo ratings yet
- Deacon Scott J. Conway Rhonda Rose Theresa LittleDocument2 pagesDeacon Scott J. Conway Rhonda Rose Theresa LittleActionNewsJaxNo ratings yet
- The Onset of Acute Type A Aortic Dissection Following Recovery of Type B Intramural Haematoma-A Case ReportDocument4 pagesThe Onset of Acute Type A Aortic Dissection Following Recovery of Type B Intramural Haematoma-A Case ReportNguyễn Thời Hải NguyênNo ratings yet
- European League Against Rheumatism (Eular) : Horizon 2020 Framework ProgrammeDocument21 pagesEuropean League Against Rheumatism (Eular) : Horizon 2020 Framework ProgrammeAkhmad IsnaNo ratings yet
- Medico Legal Report - ThamaeDocument13 pagesMedico Legal Report - ThamaencetaniNo ratings yet
- Choledocholithiasis: Prevalence IncidenceDocument9 pagesCholedocholithiasis: Prevalence IncidenceMike GNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument30 pagesHead InjuryAngel MakinNo ratings yet
- Clemente v. GSIS and ECC, G.R. No. L-47521, July 31, 1987Document6 pagesClemente v. GSIS and ECC, G.R. No. L-47521, July 31, 1987Martin SNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Quarter 2 in MAPEH 4Document6 pagesReviewer For Quarter 2 in MAPEH 4Maricar AtienzaNo ratings yet
- UWORLDgood NeuroDocument7 pagesUWORLDgood NeurombarreirNo ratings yet
- Occupational English Test: Writing Sub-Test: Nursing Time Allowed: Reading Time: 5 Minutes Writing Time: 40 MinutesDocument2 pagesOccupational English Test: Writing Sub-Test: Nursing Time Allowed: Reading Time: 5 Minutes Writing Time: 40 MinutesAnit XingNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Physical TreatmentDocument5 pagesEffectiveness of Physical TreatmentomboNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Period and ComplicationsDocument63 pagesPostpartum Period and ComplicationsSharmaineAnnePoliciosNo ratings yet
- Michael Fraser BookletDocument5 pagesMichael Fraser BookletRushika PurohitNo ratings yet
- Stamaril Pasteur Serbuk Injeksi Liofilisasi 1000 U - Vaksin Yellow Fever - DKI1059702744A1 - 2018Document1 pageStamaril Pasteur Serbuk Injeksi Liofilisasi 1000 U - Vaksin Yellow Fever - DKI1059702744A1 - 2018raraNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument7 pagesHead InjuryRoshan Ghimire100% (1)
- Ortholecture 1Document102 pagesOrtholecture 1Sam Raven AndresNo ratings yet
- 2022 Book TheCoagulationLabyrinthOfCovidDocument215 pages2022 Book TheCoagulationLabyrinthOfCovidgustavo orsoliniNo ratings yet
- Course Specification Template EmergencyDocument6 pagesCourse Specification Template EmergencyWael LotfyNo ratings yet
- Apiterapia em PortugalDocument88 pagesApiterapia em PortugalMarcelo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological StudiesDocument21 pagesEpidemiological Studiespriyaa100% (1)
- Abdul Malik Hassim Lecturer DMA Management & Science UniversityDocument21 pagesAbdul Malik Hassim Lecturer DMA Management & Science UniversitykimmgizelleNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rishank Kishore Resident: ENT & Head-Neck SurgeryDocument19 pagesDr. Rishank Kishore Resident: ENT & Head-Neck SurgeryMayur IngaleNo ratings yet
- Leuk OrrheaDocument6 pagesLeuk Orrheababon3No ratings yet
- Fig psychiatricAssessmentFormDocument3 pagesFig psychiatricAssessmentFormPatricia Eunise HerañaNo ratings yet
- Lin 2019Document3 pagesLin 2019Mahmoud AbouelsoudNo ratings yet
- Arni PPT 2 PDFDocument19 pagesArni PPT 2 PDFKumarsai Durusoju100% (1)
- Micardis PlusDocument2 pagesMicardis PlusKristine YoungNo ratings yet