Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Must-Know Language and Grammar For Task 1 Graphs and Charts
Must-Know Language and Grammar For Task 1 Graphs and Charts
Uploaded by
Leyla MammadovaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Must-Know Language and Grammar For Task 1 Graphs and Charts
Must-Know Language and Grammar For Task 1 Graphs and Charts
Uploaded by
Leyla MammadovaCopyright:
Available Formats
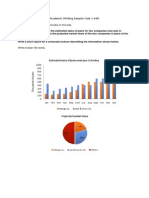
Must-know language and grammar for Task 1 graphs and charts
Pattern/trend - a track of changes over a period of time
The trend/pattern for margarine production was mostly upward until 2010.
The figures for car sales followed an upward trend/pattern until 2010.
Figure - any number with or without a symbol, regardless of what it represents (ex: 34%,
$1,000, etc.)
After 2005, the figure for hydro power had increased dramatically, reaching almost 45% of
the total in 2008.
Number – natural numbers
The number of visitors fell sharply to 4,000.
Visitor numbers fell sharply to 4,000.
Quantity - the number or amount of something (NOT people)
The quantity of book sales increased substantially.
Proportion - a number in comparative relation to a whole
The total budget was 15bln dollars. By 2011, the proportion of oil revenues in the budget had
reached more than 4 bln dollars.
Percentage
The table illustrates the percentage of school children attending four different types of
secondary school from 2000 to 2009.
Amount – volume or quantity (NOT number) of energy production, oil production, time,
precipitation, etc. You cannot use this word to refer to people.
Males and females aged between 25 and 40 spend the same amount of time online.
The amount of quality water declined dramatically between 1993 and 1994
Rate - quantity, percentage, proportion or frequency of something, such as the birth rate,
crime rate, unemployment rate, etc.)
In 2009, the rate of unemployment fell by 2%
MAKING COMPARISONS:
Contrast:
The Middle East produces high levels of oil; however, Japan produces none.
The USA produces large amounts of natural gas. In contrast/By contrast, South Korea
produces none.
European countries make great use of solar power. In comparison, most Asian countries us
this method of power generation very little.
While Iran exports the largest amount of oil, the opposite/reverse is true for Turkey
While Saudi Arabia exports the largest amount of oil, the same cannot be said for Turkey
The Middle East produces high levels of oil, whereas/while Japan produces none.
Whereas/while the Middle East produces high levels of oil, Japan produces none.
Developing countries are more reliant on alternative energy than developed countries.
Solar power generated far less energy than gas or coal.
The Middle East produces twice as much oil as Europe.
Western countries consume three times more oil than the Middle East.
Similarity
Nigeria exported more oil than it consumed. Similarly / Likewise, Libya sold more oil than it
used domestically.
Like Japan, South Korea does not produce any natural gas.
The UAE produced the same amount of oil as Saudi Arabia.
Both Iran and Kuwait saw an increase in export figures until 2002.
DESCRIBING CHANGES
There was a substantial increase in house prices in Sweden
House prices rose substantially in Sweden
Sweden had a substantial increase in house prices
Sweden experienced a substantial increase in house prices
Sweden saw a substantial increase in house prices
Sweden witnessed a substantial increase in house prices
DESCRIBING AMOUNTS OF CHANGES
There was a 20% growth in China’s population (from 1 bln to 1.2 bln)
China’s population grew by 20%.
China saw a population growth of 20%.
The figure for Canada almost doubled. (from 150 to 300)
The figured for Canada almost halved. (from 300 to 150)
The number of male students tripled. (from 40 to 120)
The fertility rate quadrupled. (from 500 to 2,000)
The number of fatal accidents decreased almost five-fold (from 150 to 30).
HP saw a six-fold increase in sales. (from 20mln to 120mln)
There was a 50% rise in the number of visits to the museum. (from 120 to 180)
The number of arrests has increased by 300%. (from 50 to 200)
(No change) From 2010 to 2017, Average house prices in Sweden plateaued/leveled
out/remained unchanged/remained constant at $95,000.
DESCRIBING HIGHEST AND LOWEST POINTS
Demand reached a peak/high of 45,000 in March
Demand hit a peak/high of 45,000 in March
Demand rose to a peak/high of 45,000 in March
Demand peaked at/hit the highest point of 45,000 in March.
Demand hit a low/trough of 5,000 in December.
Demand fell/dropped to a low/trough of 5,000 in December.
Demand bottomed out/hit the lowest point of 5,000 in December.
ROUNDING UP AND DOWN
994 – just under a thousand / just below a thousand / slightly less than a thousand
1,007 – just over a thousand / just above a thousand / slightly more than a thousand
965 – well under a thousand / well below a thousand / considerably less than a thousand
1,040 – well over a thousand / well above a thousand / considerably more than a thousand
Below 1,000 = close to / nearly / almost a thousand
Below or above 1,000 = around 50 / approximately 50 / roughly 50
REFERENCING & AVOIDANCE OF REPETITION
The number of males reached 300, and that of females rose to 350.
The numbers of males and females reached 300 and 350 respectively.
In 2005, both solar and wind power contributed equally to the total production; however,
during the five years that followed, the former became more common, while the latter was
the least harnessed.
In 2015, the number of male students gradually rose to a peak of 4,100 in 2015, while the
figure/trend/pattern for females stayed constant at 3,800.
USEFUL STRUCTURES
The upward pattern continued until it reached a high of 200 in 2006.
The number of factories in Japan hit a peak of 26,000 in 2000, before falling back to 16,000
in 2006.
The zoo witnessed a dramatic increase, with visitor numbers reaching 20,000 in 2005.
After a brief rise to 23,000 in 2006, the number of visitors started to decline again.
HP witnessed a surge to 2mln in sales figures, leaving the other two companies far behind.
PARAPHRASING FIGURES:
It is extremely important to use the following expressions wherever possible, rather than write in
digits all the time. This will show your vocabulary range for this type of task.
Percentages and fractions:
2% - a tiny percentage; a small percentage
10% or 1/10 – less than a tenth
9% - just under a tenth
25% or 1/4 - a quarter
27% - more than a quarter
33% or 1/3 - a third; one third
32% - almost a third
50% or 1/2 - a half
46% - close to a half
66% or 2/3 – two-thirds
67% - over two-thirds
75% or 3/4 – three-fourths; three-quarters
76% - just over three-fourths
95% - an overwhelming majority; a vast majority; almost all;
Key vocabulary for graphs and charts
VERBS
ADJECTIVE + NOUN ADVERBS
You might also like
- TASK 1 Writing IeltsDocument17 pagesTASK 1 Writing IeltsIntan Hajar FauzaninNo ratings yet
- ERP Implementation at NestleDocument6 pagesERP Implementation at NestleKumar SaurabhNo ratings yet
- Film Financing and TelevisionDocument21 pagesFilm Financing and TelevisionTsn DavidNo ratings yet
- Crypto Pearls 2021Document34 pagesCrypto Pearls 2021Crypto Atlas100% (5)
- Adam Huseynli Task 1Document32 pagesAdam Huseynli Task 1farhanmammadovupsystemsNo ratings yet
- Line GraphDocument13 pagesLine GraphMikelAgberoNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1Document21 pagesWriting Task 1Radwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- De Writing Task 1Document19 pagesDe Writing Task 1api-27550358100% (1)
- Graphs Writing Task 1Document27 pagesGraphs Writing Task 1Shefali ChauhanNo ratings yet
- C1 Writing ChartsDocument16 pagesC1 Writing ChartsIldiko BiroNo ratings yet
- Graph Sample For Ielts To ReadDocument11 pagesGraph Sample For Ielts To ReadgoyeniranNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing IeltsDocument12 pagesAcademic Writing IeltsMikelAgberoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Line GraphDocument5 pagesLesson 4 - Line GraphHuynh Van NguyenNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document14 pagesTask 1Lê Thu NguyetNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 1Document24 pagesIELTS Writing Task 1gimm_more1010No ratings yet
- Academic Writing Sample Task 1Document44 pagesAcademic Writing Sample Task 1Punnatee PromminNo ratings yet
- IELTS Task 1Document12 pagesIELTS Task 1saidur183No ratings yet
- Chart StructuresDocument3 pagesChart StructuresNgô Minh TriếtNo ratings yet
- Note Tacs 9.11Document5 pagesNote Tacs 9.11Nghiêm Thị Phương ThảoNo ratings yet
- BC-Unit 9 - Business Report 2 - Finding Section - Findings With ChartsDocument50 pagesBC-Unit 9 - Business Report 2 - Finding Section - Findings With ChartsPhước LêNo ratings yet
- 中级班写作课笔记+作业7 19Document10 pages中级班写作课笔记+作业7 1920080508zyrNo ratings yet
- Linking DevicesDocument3 pagesLinking DevicesGa RunNo ratings yet
- Academic Task 1 - J15Document12 pagesAcademic Task 1 - J15Khuteja NawazNo ratings yet
- TASK 1 WritingDocument15 pagesTASK 1 WritingIla RofatillahNo ratings yet
- Useful Language For Analyzing NumbersDocument5 pagesUseful Language For Analyzing NumbersNam NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Writing Describing Changes and ConsequencesDocument27 pagesWriting Describing Changes and ConsequencesTạThanhHiềnNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1 - Sample Bar ChartDocument22 pagesWriting Task 1 - Sample Bar ChartOanh OanhNo ratings yet
- Sample Report WritingDocument6 pagesSample Report WritingdeathmoonkillerNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1Document36 pagesWriting Task 1calemolech0% (1)
- Screenshot 2021-03-12 at 9.16.14 PMDocument57 pagesScreenshot 2021-03-12 at 9.16.14 PMQuỳnh Anh TrươngNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing Sample AnswerDocument75 pagesIelts Writing Sample Answerfirstgabriel52No ratings yet
- The Bar Chart Shows The Number of Times Per Week (In 1000s), Over Five Weeks, That Three Computer Packages Were Downloaded From The InternetDocument21 pagesThe Bar Chart Shows The Number of Times Per Week (In 1000s), Over Five Weeks, That Three Computer Packages Were Downloaded From The InternetAnonymous 2HWqnKqI4WNo ratings yet
- Full ModelDocument9 pagesFull ModelMansiPatelNo ratings yet
- (Writing Task 1) Useful LanguageDocument17 pages(Writing Task 1) Useful LanguageThuNo ratings yet
- Academic Ielts Writing SamplesDocument10 pagesAcademic Ielts Writing SamplesMikelAgberoNo ratings yet
- B段雅思写作lesson 4Document9 pagesB段雅思写作lesson 4monazhou316No ratings yet
- WT1 Model AnswerDocument21 pagesWT1 Model AnswerRafiqa HayaatiNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Vol 2Document13 pagesIELTS Writing Vol 2Linh Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Graph WordDocument12 pagesGraph Wordarunbnsal3507No ratings yet
- Sub - Technical VocabularyDocument20 pagesSub - Technical VocabularyFendi AchmadNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1 - Transition and Grammar - Meeting 3Document22 pagesWriting Task 1 - Transition and Grammar - Meeting 3delima nasutionNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 1 (Vocab)Document13 pagesIELTS Writing Task 1 (Vocab)Mohamad GhazaliNo ratings yet
- (Bản Chính Thức) Bộ Đề Dự Đoán IELTS Writing Forecast Q2-2024Document73 pages(Bản Chính Thức) Bộ Đề Dự Đoán IELTS Writing Forecast Q2-2024Min MinNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document5 pagesPart 1Behrooz ShahabNo ratings yet
- Writing-1 (209 Words) : VisitingDocument11 pagesWriting-1 (209 Words) : VisitingAnkur TripathiNo ratings yet
- Useful Vocabulary To Use in IELTS Task 1 EssaysDocument7 pagesUseful Vocabulary To Use in IELTS Task 1 Essayskalapala sai kalyaNo ratings yet
- Useful Language For Task 1 IeltsDocument9 pagesUseful Language For Task 1 IeltsDIYORBEK UZNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1 Model AnswerDocument10 pagesWriting Task 1 Model AnswerLinh Nhật HàNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task - 1 Samples 8Document8 pagesIELTS Writing Task - 1 Samples 8Nishant VincentNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing Ila - SiapDocument25 pagesIelts Writing Ila - SiapKANi dudezNo ratings yet
- BA - ACADEMIC Task 1 Sheet - 7 Sample Questions & Answers Out of 14Document13 pagesBA - ACADEMIC Task 1 Sheet - 7 Sample Questions & Answers Out of 14tompa dasNo ratings yet
- LINeDocument4 pagesLINephuonganh1556No ratings yet
- ON TASK 1Document4 pagesON TASK 1Chiến Vũ VănNo ratings yet
- IELTS WRITING TASK 1 - Line Graph, Bar Chart, TableDocument3 pagesIELTS WRITING TASK 1 - Line Graph, Bar Chart, TableNhư NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IELTS Graph1-7-2Document28 pagesIELTS Graph1-7-2Fransisca AngelNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document8 pagesTask 1kapil pushadapuNo ratings yet
- IELTS Graph1-7Document28 pagesIELTS Graph1-7Fransisca AngelNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing Task 1Document23 pagesIelts Writing Task 1Thanh An Nguyễn LêNo ratings yet
- Mixed ChartsDocument4 pagesMixed Chartsninangoc.nov17No ratings yet
- Bộ Đề Dự Đoán Sớm IELTS Writing Forecast Q2-2024Document37 pagesBộ Đề Dự Đoán Sớm IELTS Writing Forecast Q2-2024Trang VoNo ratings yet
- 1-Precison and ConcisionDocument40 pages1-Precison and ConcisionLeyla MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Independent Task, 05.02.2021Document2 pagesIndependent Task, 05.02.2021Leyla MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Independent Task, 04.02.2021Document2 pagesIndependent Task, 04.02.2021Leyla MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Independent Task, 15.02.2021Document2 pagesIndependent Task, 15.02.2021Leyla MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Task 1: Process Diagram: Present SimpleDocument4 pagesTask 1: Process Diagram: Present SimpleLeyla MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages EssayDocument3 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages EssayLeyla MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Essay Type: Opinion To What Extent Do You Agree or Disagree? Do You Think... ?Document4 pagesEssay Type: Opinion To What Extent Do You Agree or Disagree? Do You Think... ?Leyla MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect EssayDocument6 pagesCause and Effect EssayLeyla MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Double Question EssayDocument4 pagesDouble Question EssayLeyla MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Essay Type: Discussion With A Personal Opinion Discuss Both Views and Give Your Own OpinionDocument3 pagesEssay Type: Discussion With A Personal Opinion Discuss Both Views and Give Your Own OpinionLeyla MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Unep - 24 Cleaner Production - ReferenciaDocument96 pagesUnep - 24 Cleaner Production - ReferenciaAxelVanBrsNo ratings yet
- On December 1 2014 Boline Distributing Company Had The FollowingDocument1 pageOn December 1 2014 Boline Distributing Company Had The Followingtrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Project Flexibility MatrixDocument2 pagesProject Flexibility MatrixhariomsairamNo ratings yet
- Talent Management AnalyticsDocument8 pagesTalent Management AnalyticsAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Merchandising AgreementDocument19 pagesMerchandising AgreementNaqiuddin NazrinNo ratings yet
- Ali Traders - Kotli: Pepsi Cola Agency Kolti Ajk PH# 0343-5750770Document26 pagesAli Traders - Kotli: Pepsi Cola Agency Kolti Ajk PH# 0343-5750770Imtiaz ButtNo ratings yet
- LK Spto 2018 - Q4Document104 pagesLK Spto 2018 - Q4siput_lembekNo ratings yet
- Nationalized IndustriesDocument3 pagesNationalized IndustriesAmeera ChaitramNo ratings yet
- The Islamic Finance Trading Framework: Legitimizing Profit MakingDocument91 pagesThe Islamic Finance Trading Framework: Legitimizing Profit MakingYellow CarterNo ratings yet
- Slide 6-1 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing As Prentice HallDocument27 pagesSlide 6-1 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing As Prentice HallAbid HossainNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5-Session-GuideDocument6 pagesLesson 5-Session-GuideElaine UnoNo ratings yet
- IBFT - Member Bank Account Number FormatDocument1 pageIBFT - Member Bank Account Number FormatSyed Shah Jehan GillaniNo ratings yet
- EBAYDocument27 pagesEBAYChristine He100% (2)
- Six Sigma: High Quality Can Lower Costs and Raise Customer SatisfactionDocument5 pagesSix Sigma: High Quality Can Lower Costs and Raise Customer SatisfactionsukhpreetbachhalNo ratings yet
- Tailoring UnitDocument8 pagesTailoring UnitSuresh sureshNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship 1Document40 pagesEntrepreneurship 1Nishtha SharmaNo ratings yet
- IJM Plantations Berhad: Buys More Land in Indonesia - 04/08/2010Document2 pagesIJM Plantations Berhad: Buys More Land in Indonesia - 04/08/2010Rhb InvestNo ratings yet
- Louis Vuitton in IndiaDocument5 pagesLouis Vuitton in IndiaHandoko AjjaNo ratings yet
- Ab) Government Intervention To Protect Consumers, Suppliers and EmployeesDocument6 pagesAb) Government Intervention To Protect Consumers, Suppliers and EmployeesCharlie DeltaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of SmeDocument5 pagesIntroduction of SmeHafiz Muhammad Zulqarnain JamilNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Motor India ParkDocument30 pagesHyundai Motor India ParkMir HassanNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting IIDocument189 pagesFinancial Accounting IIbest OneNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document9 pagesModule 1ᜊ᜔ᜎᜀᜈ᜔ᜃ᜔ ᜃᜈ᜔ᜊᜐ᜔No ratings yet
- Vertical Analysis For Att and VerizonDocument4 pagesVertical Analysis For Att and Verizonapi-299644289No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 IntroductionDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 1 IntroductionCarissa May Maloloy-on100% (1)
- NCERT Solution For Class 11 Economics Chapter 2 - Indian Economy (1950 - 1990)Document7 pagesNCERT Solution For Class 11 Economics Chapter 2 - Indian Economy (1950 - 1990)Kuldeep PanwarNo ratings yet
- Memorandum of Agreement 22Document3 pagesMemorandum of Agreement 22Rodnel MonceraNo ratings yet