Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project 3.2.2 and Project 3.2.3 Questions
Project 3.2.2 and Project 3.2.3 Questions
Uploaded by
brianneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Project 3.2.2 and Project 3.2.3 Questions
Project 3.2.2 and Project 3.2.3 Questions
Uploaded by
brianneCopyright:
Available Formats
Project 3.2.2 and Project 3.2.
3 Questions:
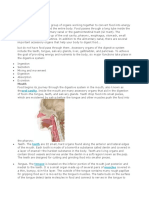
What is the oral cavity and what does it contain?
The oral cavity is the first section of the mouth, which is bordered in the front and to the sides
by the two alveolar arches containing the teeth.
What is the function of the salivary glands?
The produce saliva.
What is the function of the tongue?
It chews and swallows food and helps with speech.
What is a bolus?
It is a ball of food that has been chewed up to the point of swallowing.
Where are the soft and hard palate located and what are their functions?
They are located at the roof of the mouth. The soft palate presses down on food to swallow
while the hard palate holds the roots of the teeth.
What mechanical and chemical digestion occurs in the oral cavity?
The mechanical function is the act of chewing food, and chemical digestion is the act of breaking
food down with enzymes and catalysts, including saliva.
What mechanisms are in place to make sure food does not “go down the wrong tube” and into the
windpipe?
The epiglottis, a flag of elastic cartilage, closes temporarily to prevent food from going down the
windpipe.
Esophagus and Stomach:
What is peristaltic movement and how does it function in the esophagus?
It is a series of muscle contractions, therefore pushing the bolus down the esophagus.
Does any digestion of food occur in the esophagus?
No digestion occurs in the esophagus.
What are the primary functions of the stomach?
The stomach stores food, it releases acids and enzymes for chemical breakdown and releases
food into the small intestine.
What is chyme and how does the stomach mix this material?
Chyme is a partially digested food that is formed in the stomach and intestine. The stomach
releases enzymes and mixes with the food.
What role does the stomach play in decontaminating the incoming food matter?
Acids inside the stomach break down food matter and kill bacteria.
What cells in the stomach function to form enzymes and acids?
Parietal cells create HCI to adjust pH levels. Chief cells create pepsinogen which turns into
pepsin which breaks down proteins.
Why doesn't gastric juice digest the inside of the stomach?
The stomach is protected by an alkaline mucous membrane.
What are sphincters and how are they related to the stomach?
They are openings in and out of the stomach. They allow undigested food to enter and digested
food to exit.
What mechanical and chemical digestion occurs in the stomach?
Churning is a type of mechanical digesting and gastric acid is a type of chemical digestion.
You might also like
- Science Project - Digestive SystemDocument28 pagesScience Project - Digestive Systemapi-35222133567% (18)
- 3 2 2 Student Response SheetDocument4 pages3 2 2 Student Response Sheetapi-262497675No ratings yet
- Handout - Chapter 3 - Digestion - Google Docs - 1665372467933 3Document8 pagesHandout - Chapter 3 - Digestion - Google Docs - 1665372467933 3NC ExistentialNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Design Study GuideDocument3 pagesDigestive System Design Study Guideapi-390361165No ratings yet
- Figure 1: Cracker LabDocument4 pagesFigure 1: Cracker Labapi-296590771No ratings yet
- Q4 Science8Document60 pagesQ4 Science8AILEEN LUZON100% (1)
- Digestive System: Name: Azza Ferista Delvia Ninda Sa Ri O Kta Imelda Ikhda La Tifatun Naim Cla SS: 4BDocument7 pagesDigestive System: Name: Azza Ferista Delvia Ninda Sa Ri O Kta Imelda Ikhda La Tifatun Naim Cla SS: 4BMaulana RifkiNo ratings yet
- Bio 12.3Document2 pagesBio 12.3Adriano VizcainoNo ratings yet
- Presentation ScriptDocument7 pagesPresentation ScriptHector TejadaNo ratings yet
- Digestion in Stomach and Intestines Grade 4Document24 pagesDigestion in Stomach and Intestines Grade 4jaydalene saga macay100% (1)
- Makalah Sistem Pencernaan Bhs InggrisDocument32 pagesMakalah Sistem Pencernaan Bhs InggrisDesiNo ratings yet
- IngestionDocument35 pagesIngestionMark FuntinillaNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 1 The Human Digestive SystemDocument43 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 1 The Human Digestive SystemGenesis SarengoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System - Josue GallaneraDocument3 pagesDigestive System - Josue GallaneraRandom Anime StuffNo ratings yet
- Guia para Human Body CareDocument48 pagesGuia para Human Body CareVyelkaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument15 pagesDigestive SystemAlicia ValverdeNo ratings yet
- PembahasanDocument32 pagesPembahasanwening gbNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiolog AMOEBIASISDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiolog AMOEBIASISSamer SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Digestive System AnatomyDocument11 pagesDigestive System AnatomyYeni Jesika SilitongaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Research PaperDocument6 pagesDigestive System Research Paperrdssibwgf100% (1)
- Digestion and Absorption of Food in ManDocument3 pagesDigestion and Absorption of Food in Mancd78x8xbsxNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive SystemMiguel LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument12 pagesBiologyvidottma kolheNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesModule 6 Digestive SystemShane GempasaoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive System: Tongue MusclesDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Digestive System: Tongue Musclesbarbiegirl9497No ratings yet
- SCIENCE Module-1Document22 pagesSCIENCE Module-1Mark Alexis P. RimorinNo ratings yet
- Presentazione SCIENZEDocument19 pagesPresentazione SCIENZEMattia ScartonNo ratings yet
- Digestive System #3Document10 pagesDigestive System #3Roosebel De Tauro SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System AnatomyDocument15 pagesDigestive System AnatomyRisxx pNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesDigestive SystemJerald CodillaNo ratings yet
- Process of Food DigestionDocument14 pagesProcess of Food DigestionDananjaya RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Q4 - Week 1 - Lesson 1Document19 pagesScience 8 - Q4 - Week 1 - Lesson 1Cris Tolentino100% (1)
- Digestive System Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesDigestive System Lesson PlanAnna Dixon100% (1)
- Full Download Nutrition For Life 4th Edition Thompson Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Nutrition For Life 4th Edition Thompson Solutions Manualkeathleyjessiavipfx100% (32)
- 19 Week Assignment Topic Digestive System of HumanDocument19 pages19 Week Assignment Topic Digestive System of HumanHuZáiFá MaQBoOlNo ratings yet
- Digestive System DraftDocument39 pagesDigestive System DraftDiosa BakingNo ratings yet
- Study of The Human Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesStudy of The Human Digestive Systemchess accNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Lab Report: Part I Structures of The MouthDocument7 pagesDigestive System Lab Report: Part I Structures of The Mouthapi-296603950No ratings yet
- DIGESTIVEDocument17 pagesDIGESTIVEFahmi IlyasNo ratings yet
- Mouth: Oral CavityDocument6 pagesMouth: Oral CavityMaria Teresa Casili - PerezNo ratings yet
- 09 DigestionDocument85 pages09 DigestionSumihar PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Science Class 7Document217 pagesScience Class 7hafiza arishaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Nutrition For Life 4th Edition Thompson Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Nutrition For Life 4th Edition Thompson Solutions Manual PDFsanjaktouchbox1wfw100% (14)
- A&P Study Guide - Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesA&P Study Guide - Digestive SystemMuhammad FirdausNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Processes and Regulation - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesDigestive System Processes and Regulation - Anatomy and PhysiologyFlonie DensingNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument3 pagesDigestivePrishaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology DigestiveDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology DigestiveFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention Material: Dig Esti Ve Syst emDocument16 pagesStrategic Intervention Material: Dig Esti Ve Syst emKarla Javier PadinNo ratings yet
- B InggrisDocument35 pagesB InggrisMeiaroh PitrianiNo ratings yet
- Visible Body DigestiveDocument8 pagesVisible Body Digestivejellypish269No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Week 13-14Document22 pagesEarth and Life Science Week 13-14Aleli Joy Profugo DalisayNo ratings yet
- Body of HumanDocument14 pagesBody of HumanArlene Joy BuqueNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Digestive System and Their FunctionsDocument2 pagesOrgans of The Digestive System and Their FunctionsChari Mae Tamayo Panganiban100% (1)
- Minute Friut CoolerDocument6 pagesMinute Friut CoolerCamaya RumbleNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesDigestive Systemjellyngan1022No ratings yet
- SCIENCE. 8 Q4 Week-1 7Document39 pagesSCIENCE. 8 Q4 Week-1 7Javier AugustNo ratings yet
- Science PreDocument11 pagesScience PreCARL JUSTIN TUMALANo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology:gastrointestinal Tract Powerpoint PresentationDocument28 pagesAnatomy and Physiology:gastrointestinal Tract Powerpoint PresentationKatherine 'Chingboo' Leonico Laud100% (16)
- Your Super Gut Feeling Restored – How to Restore Your Life Energy and Overall Health from The Inside OutFrom EverandYour Super Gut Feeling Restored – How to Restore Your Life Energy and Overall Health from The Inside OutNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System and Female Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesMale Reproductive System and Female Reproductive SystemChristian Ezekiel LagmayNo ratings yet
- Kin 2222B - HS 2300B PDFDocument5 pagesKin 2222B - HS 2300B PDFbuy sellNo ratings yet
- ACT Personal Trainer Certification Textbook v1 2Document315 pagesACT Personal Trainer Certification Textbook v1 2AwyrMerddyn100% (7)
- Circulation and Gas Exchange: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocument116 pagesCirculation and Gas Exchange: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionMahnoor AnjumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With The Other Organ SystemsDocument60 pagesChapter 1 - Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With The Other Organ SystemsPatricia Sofia DizonNo ratings yet
- Sistrunk Operation ArticleDocument4 pagesSistrunk Operation Articleআবু আব্দুল্লাহ শাদীদNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The Gastrointestinal TractDocument2 pagesBlood Supply of The Gastrointestinal TractAli AkeelNo ratings yet
- VNSG 1409 - Exam 3Document24 pagesVNSG 1409 - Exam 3luna nguyenNo ratings yet
- IB BIOLOGY TOPIC 1 QuestionsDocument3 pagesIB BIOLOGY TOPIC 1 QuestionsSarah Mason100% (1)
- C. Vijayalakshmi and M.Jothilakshmi: Mechanism of Acupressure Exercises and Its FunctioningDocument7 pagesC. Vijayalakshmi and M.Jothilakshmi: Mechanism of Acupressure Exercises and Its Functioningavrrao1No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal UltrasonographyDocument17 pagesMusculoskeletal UltrasonographyAde CahyaningtyasNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Abdominal Wall Hernia (Jerome Villacorta's Conflicted Copy 2014-03-22)Document7 pages4.2 Abdominal Wall Hernia (Jerome Villacorta's Conflicted Copy 2014-03-22)Miguel C. DolotNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Protocols in NeonatesDocument12 pagesBlood Transfusion Protocols in NeonatesSupriya M A SuppiNo ratings yet
- Blood and Tissue FlagellatesDocument27 pagesBlood and Tissue FlagellatesAtef HusseinNo ratings yet
- Antibody Detection, Identification, and Compatibility TestingDocument19 pagesAntibody Detection, Identification, and Compatibility TestingJOPHUONGNo ratings yet
- Zoology Laboratory - Activity No. 12 - Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesZoology Laboratory - Activity No. 12 - Nervous SystemShinobu OshinoNo ratings yet
- Ex Cert IonDocument11 pagesEx Cert IonVicky BhardwajNo ratings yet
- இஸ்லாமும் அறிவியலும்Document18 pagesஇஸ்லாமும் அறிவியலும்rosgazNo ratings yet
- Hes006 CNS Lab 15 18Document50 pagesHes006 CNS Lab 15 18Joana Elizabeth A. CastroNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue FinalDocument18 pagesPlant Tissue FinalEunice AcunaNo ratings yet
- PA Tool Revised 2019 111Document30 pagesPA Tool Revised 2019 111Risha Ethel G. BerondoNo ratings yet
- Waec Biology ExampulseDocument82 pagesWaec Biology ExampulsealbertayomideakiodeNo ratings yet
- Hematology NotesDocument2 pagesHematology NotesPrativa RajbhandariNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Module Complete (Highlighted Endocrine and Nervous)Document19 pagesBody Systems Module Complete (Highlighted Endocrine and Nervous)Ramon GasgasNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System Grade 5Document21 pagesCentral Nervous System Grade 5shamshadNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Morphology of The Reproductive System and Anatomy of Hen's EggDocument11 pagesAn Introduction To Morphology of The Reproductive System and Anatomy of Hen's EggGusti Anggih WibowoNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: (Chapter 15)Document59 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: (Chapter 15)Hasanuddin NuruNo ratings yet
- 2-10 Medical Terminology and Anatomy PDFDocument16 pages2-10 Medical Terminology and Anatomy PDFBALA PRANAY100% (1)
- Blood Group Incompatibility PDFDocument7 pagesBlood Group Incompatibility PDFSekar MarzukiNo ratings yet
- Limfoid HiperplasiaDocument4 pagesLimfoid HiperplasiaIvan-ty FamNo ratings yet