Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Draft D
Draft D
Uploaded by
Rochelle Cabingan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesOriginal Title
draft d
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesDraft D
Draft D
Uploaded by
Rochelle CabinganCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
ELS
1. What are common characteristics of animals?
Animals are multicellular. They are heterotrophic, obtaining their energy by consuming
energy-releasing food substances. Animals typically reproduce sexually and are made up of
cells that do not have cell walls. Animals are capable of motion in some stage of their lives.
2. Which characteristics of animals do you think is important?
All characteristics are important however, their ability to survive stands out the most.
Without being able to adapt to their environment and catch their prey, animals won’t have
the capability to survive long enough.
Tissues Functions Selective Location
connective tissue Attach organs and tissues Mesodermal cells in the
together embryo
Nervous tissue Monitors and regulates the Brain and spinal cord
functions of the body
Epithelial tissue Form the protective the skin, the lining of the
covering and inner lining of mouth and nose, and the
the body and organs lining of the digestive
system.
muscular tissue Helps in movement and inside of the heart, digestive
locomotion; organs, and blood vessels
Supports the bones and
other structures;
Responsible for peristalsis
and parturition.
1. What is tissue engineering?
An interdisciplinary and multidisciplinary field that aims at the development of biological
substitutes that restore, maintain, or improve tissue function. Its goal is to assemble
functional constructs that restore, maintain, or improve damaged tissues or whole
organs.
2. Do you think it would be possible to alter animal structure and organization with the
discovery of tissue culture?
Yes. According to a research done by Anju Verma, Megha Verma, and Anchal Singh, cell
culture is the process of growing human, animal, or insect cells in a favorable artificial
environment. Cells can be derived from multicellular eukaryotes, already established
cell lines, or established cell lines. Animal cell culture became a common laboratory
technique in the mid-20th century, but the concept of keeping live cell lines isolated
from their original tissue source was discovered in the 19th century. Animal cell culture
is currently one of the most important tools used in life sciences in research areas of
commercial value and potential commercialization.
BODY SYSTEM MAIN FUNCTIONS DISEASES
STRUCTURE/
ORGAN
DIGESTIVE Oral Cavity, responsible for diverticulitis; gastritis;
Esophagus, Liver, the breaking pancreatitis;
Stomach, Small down and cholecystitis; cirrhosis;
Intestine, Large absorption of hepatitis; liver cancer;
Intestine, nutrients and the irritable bowel or
Rectum, Anus elimination of the colon syndromes;
waste not utilized Crone’s disease; and
by the body/ or hemorrhoids.
identifying which
minerals,
vitamins, and
other essentials
from the foods
we eat can be
absorbed and
utilized or stored
by the body and
which are to be
disposed of, and
carrying out those
functions
EXCRETORY kidneys, ureters, regulate the Kidney disease,
bladder, and chemical incontinence,
urethra composition of Interstitial cystitis,
body fluids by kidney failure, bladder
removing
metabolic wastes cancer,
and retaining the
proper amounts
of water, salts,
and nutrients
ENDOCRINE Pineal Gland, secrete chemicals Type 1 & Type 2
Pituitary Gland, called hormones Diabetes,
Thyroid Gland, that regulate hypoglycemia,
Thymus, Adrenal most of the Addison’s disease;
Gland, Pancreas, processes in our Cushing’s syndrome;
Ovary, Testis bodies such as hyper/hypothyroidism,
growth, thyroid cancer; and
reproduction, other active cancers of
metabolism, and the endocrine glands
even the control
of the amount of
glucose in our
blood
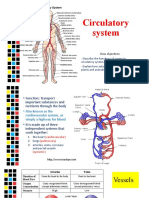
CIRCULATORY Heart, Blood pumps blood and coronary bypass
Vessels blood vessels surgery; arrhythmias;
such as arteries valve replacements;
and veins, pacemakers;
transport the transplants; heart
blood to every diseases (ischemic;
part of our body hypertensive;
providing organs arteriosclerotic);
and muscles with hypertension;
nourishment aneurysms; fistulas;
arteriosclerosis;
anaphylaxis shock;
varicose veins; cold
weather injuries; and
sarcomas of the blood
vessels
MUSCULAR Voluntary/ maintain blood muscular dystrophy;
involuntary/ flow through our fibromyalgia;
cardiac body, responsible tendinitis; multiple
for carrying out sclerosis; and muscle
the actions and strain or sprains;
movements hernias
caused by
messages sent
from our brains
through our
nervous system
SKELETAL Ribs/ skull/ supports and arthritis; cancers;
bones/ joints protects the scoliosis; osteoporosis,
body’s internal gout; bursitis;
organs fractures and breaks;
and amputations.
REPRODUCTIVE prostate gland, mainly functions breast cancer, removal
penis, testis, to create human of breast or
scrotum, ductus life lumpectomy;
deferens hysterectomy;
mammary glands, pregnancy
ovary, uterus, complications;
vagina, fallopian endometriosis; ovarian
tube or cervical cancers;
and diseases or
injuries of the vulva,
vagina, cervix, uterus,
fallopian tubes, or
ovaries/ prostate
cancer, prostatitis,
erectile dysfunction
NERVOUS Brain, Spinal controls all of the paralysis; Parkinson’s
Cord, Nerves other systems of Disease; palsy,
the body embolisms;
thrombosis;
arteriosclerosis; polio;
myelitis; ALS;
meningitis; Multiple
Sclerosis; muscular
tics; Huntington’s
Disease; cancers of the
brain, spinal cord or
nerves; epilepsy,
seizure disorders;
narcolepsy; migraine
headaches; peripheral
neuropathy; and
traumatic brain injury
RESPIRATORY Nasal cavity/ supplies the body allergies; rhinitis and
pharynx/ larynx/ with oxygen for sinusitis; laryngitis;
trachea/ cellular COPD; pleurisy;
bronchus/ lungs/ respiration by bronchitis;
collecting oxygen emphysema; asthma;
in the lungs and sarcoidosis; fibrosis;
disposes of asbestosis; pulmonary
carbon dioxide by vascular diseases;
breathing out the fungal or bacterial
waste product infections of the lungs;
sleep apnea;
tuberculosis
IMMUNE white blood cells, made up of allergic diseases,
antibodies, special organs, immunodeficiencies
complement cells and and autoimmune
system, chemicals that disorders
lymphatic fight infection
system, (microbes)
spleen,
bone marrow,
thymus
INTEGUMENTARY Skin/ nails/ hair/ barrier to acne, and chloracne;
physical, dermatitis/eczema;
chemical, and hives; lupus
biological agents
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lesson 1.1 Maternal Anatomy Dr. Jane PublicoDocument11 pagesLesson 1.1 Maternal Anatomy Dr. Jane PublicoKristel Saturn SalvadNo ratings yet
- Draft 1Document2 pagesDraft 1Rochelle CabinganNo ratings yet
- Maryjoy RisksDocument2 pagesMaryjoy RisksRochelle CabinganNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Fluid Replenishment AdvertisementDocument2 pagesAnalyzing Fluid Replenishment AdvertisementRochelle CabinganNo ratings yet
- Aeziah A and D AnalysisDocument14 pagesAeziah A and D AnalysisRochelle CabinganNo ratings yet
- MM, EnglishDocument2 pagesMM, EnglishRochelle CabinganNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper ResearchDocument2 pagesReaction Paper ResearchRochelle CabinganNo ratings yet
- St. Thomas More College - Clark: A Professional Business SchoolDocument8 pagesSt. Thomas More College - Clark: A Professional Business SchoolRochelle CabinganNo ratings yet
- Frog Dissection WorksheetDocument8 pagesFrog Dissection WorksheetEn ZeNo ratings yet
- Adeel Assignment No 2Document7 pagesAdeel Assignment No 2Adeel AfzalNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy SessionsDocument161 pagesHuman Anatomy SessionsFabian MahonaNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy & Physiology: NotesDocument5 pagesRenal Anatomy & Physiology: NotesTawhid ZihadNo ratings yet
- Pharynx-I: Presented By:-Dr. Sushma Tomar Associate Professor Department of AnatomyDocument17 pagesPharynx-I: Presented By:-Dr. Sushma Tomar Associate Professor Department of AnatomyAbishek JNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Lungs and HistologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Lungs and HistologyOmar Ali AyoubkhanNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument121 pagesAnatomyBlack InsomniaNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Tissues/ Dr. Yousif Al-JuboriDocument14 pagesThe Human Body Tissues/ Dr. Yousif Al-Juboriعلي جاسم الكعبيNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Human AnatomyDavid HamalalaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesCirculatory SystemSebastian VillegasNo ratings yet
- Liver and GallbladderDocument2 pagesLiver and GallbladderDanielle CapangpanganNo ratings yet
- Cronica Agatha RuizDocument5 pagesCronica Agatha Ruizkarol franco naranjoNo ratings yet
- Distosia Kelompok 1Document10 pagesDistosia Kelompok 1Kamu SiapaNo ratings yet
- Raine. Worksheet 11.1 Respiratory System.Document2 pagesRaine. Worksheet 11.1 Respiratory System.Kristine Lorainne DelamideNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary Lymphoid Organs - Aditi SinghDocument50 pagesPrimary and Secondary Lymphoid Organs - Aditi SinghEunice PalloganNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - The Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesLesson 4 - The Circulatory SystemAimee GraceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. The Circulatory System: Short QuestionsDocument31 pagesChapter 6. The Circulatory System: Short QuestionsParardha DharNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - EctopicDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - EctopicReyzelinNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics Outline (MCHN) Chapter 1Document8 pagesObstetrics Outline (MCHN) Chapter 1Marinill Soliman100% (1)
- Rekapitulasi ERT PONEKDocument48 pagesRekapitulasi ERT PONEKKaleb Rudy HartawanNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Tissues Post-Lab WorksheetDocument5 pagesMammalian Tissues Post-Lab WorksheetPiperNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Sistem Pencernaan Pada ManusiaDocument5 pagesJurnal Sistem Pencernaan Pada ManusiaJeannete Claudia WulandariNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Perineum and The Anal SphincterDocument12 pagesAnatomy of The Perineum and The Anal SphincterReyhan AdityaaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 TissuesDocument55 pagesCh. 4 TissuesBora YaNo ratings yet
- Equine Lymph Nodes Anatomy VCA 400 AssignmentDocument4 pagesEquine Lymph Nodes Anatomy VCA 400 AssignmentcharlieNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7 - Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesChapter-7 - Cardiovascular SystemAaQib Ali RaZaNo ratings yet
- Liver:: Anatomy The Abdomen Liver and Gall BladderDocument5 pagesLiver:: Anatomy The Abdomen Liver and Gall BladderWaeel AbdullatifNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ScriptDocument7 pagesDigestive System ScriptGeraldine Co TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 1 The Human Body SystemsDocument33 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 1 The Human Body Systemsmaricar paracadNo ratings yet