Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amir Hammond Mccoy
Amir Hammond Mccoy
Uploaded by
lilprettythang14Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amir Hammond Mccoy
Amir Hammond Mccoy
Uploaded by
lilprettythang14Copyright:
Available Formats
Amir Hammond McCoy
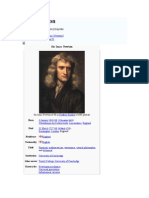
Isaac Newton
Early Life
Isaac Newton was born in Woolsthorpe, England on January 4, 1643. His father, a
farmer who was also named Isaac Newton, had died three months before his birth. His
mother remarried when Isaac was three years old and left young Isaac in the care of his
grandparents. Isaac attended a school where he was an adequate student. At one point
his mother tried to take him out of school so he could help on the farm, but Isaac had no
interest in becoming a farmer and was soon back at school. Isaac grew up mostly
alone. For the rest of his life, he would prefer to work and live alone focused on his
writing and his studies.
College and Career
In 1661, Isaac began to attend college at Cambridge. He would spend much of his life
at Cambridge, becoming a professor of mathematics and a fellow of the Royal Society
(a group of scientists in England). He eventually was elected to represent Cambridge
University as a member of parliament. Isaac had to leave Cambridge from 1665 to 1667
because of the Great Plague. He spent these two years in study and isolation at his
home in Woolsthorpe developing his theories on calculus, gravity, and the laws of
motion. In 1696 Newton became the warden of the Royal Mint in London. He took his
duties seriously and tried to get rid of corruption as well as to reform the currency of
England. He was elected President of the Royal Society in 1703 and was knighted by
Queen Anne in 1705.
Scientific Discoveries
Isaac Newton made many scientific discoveries and inventions throughout his career.
Here is a list of some of the most important and famous ones. Gravity - Newton is most
famous for discovering gravity. Outlined in Principia, his theory about gravity helped to
explain the movements of the planets and the Sun. This theory is known today as
Newton's law of universal gravitation. Laws of Motion - Newton's laws of motion were
three fundamental laws of physics that laid the foundation for classical mechanics.
Calculus - Newton invented a whole new type of mathematics which he called
"fluxions." Today we call this math calculus, and it is an important type of math used in
advanced engineering and science. Reflecting Telescope - In 1668 Newton invented the
reflecting telescope. This type of telescope uses mirrors to reflect light and form an
image. All the major telescopes used in astronomy today are reflecting telescopes.
Legacy
Newton died on March 31, 1727, in London, England. Today, he is considered one of
the most influential scientists of all time alongside greats such as Albert Einstein,
Aristotle, and Galileo.
You might also like
- C++ MCQDocument23 pagesC++ MCQVishal ManeNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument1 pageIsaac NewtonlenaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument9 pagesPhysics Project78bynzhbpvNo ratings yet
- Isaack NewtonDocument10 pagesIsaack NewtonPrashant ShindeNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton FinalDocument2 pagesIsaac Newton FinalDannyNo ratings yet
- Biography FOR MOEZDocument2 pagesBiography FOR MOEZReinXNo ratings yet
- Sir Issac NewtonDocument3 pagesSir Issac NewtonDan CristianNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton - Quotes Collection: Biography, Achievements And Life LessonsFrom EverandIsaac Newton - Quotes Collection: Biography, Achievements And Life LessonsNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument3 pagesIsaac NewtonCourtney LeipertzNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac NewtonDocument2 pagesSir Isaac NewtonMary Grace Herbania-Dahan LundayNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument15 pagesIsaac Newtonapi-3855358No ratings yet
- Recount Text - Sir Isaac NewtonDocument1 pageRecount Text - Sir Isaac NewtonLuthfan100% (1)
- Sir Isaac Newton-Reading SheetDocument2 pagesSir Isaac Newton-Reading Sheetp5h5y5s5i5c0sNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: Nama: Asmita Damayanti Kelas: XI Ips 1Document3 pagesIsaac Newton: Nama: Asmita Damayanti Kelas: XI Ips 1Asmita DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: Rohan BalaDocument10 pagesIsaac Newton: Rohan BalaLio MessiNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument2 pagesIsaac NewtonbhaskarmscNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument29 pagesIsaac NewtonShelly JohnNo ratings yet
- Advanced Reading 0990 Non-Fiction Final Signature Assignment123Document4 pagesAdvanced Reading 0990 Non-Fiction Final Signature Assignment123api-251231234No ratings yet
- The Principia. Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy (Concise edition)From EverandThe Principia. Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy (Concise edition)No ratings yet
- 1.isaac Newton BiographyDocument2 pages1.isaac Newton BiographyBrajamohan Thakuria100% (1)
- ScienceDocument12 pagesSciencekhadijaharoon369No ratings yet
- Sir Isaac Newton, PRS, (4 January 1643 - 31 March 1727)Document6 pagesSir Isaac Newton, PRS, (4 January 1643 - 31 March 1727)bookpalNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument13 pagesIsaac NewtonRuban BillaNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: BibliografiaDocument8 pagesIsaac Newton: BibliografiaAbraham ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: The Fluxional MethodDocument3 pagesIsaac Newton: The Fluxional MethodJajaNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac Newton Was AnDocument6 pagesSir Isaac Newton Was AnSparshNo ratings yet
- Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica: Isaac NewtonDocument6 pagesPhilosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica: Isaac NewtonPedro Soto CruzNo ratings yet
- AboutDocument1 pageAboutAli Amir SufiNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac Newton: Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia MathematicaDocument9 pagesSir Isaac Newton: Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematicaohm parmarNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac Newton: Early LifeDocument3 pagesSir Isaac Newton: Early Liferose maryNo ratings yet
- About 5 PhycistsDocument6 pagesAbout 5 PhyciststharikaNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument5 pagesIsaac Newtonapi-270467511No ratings yet
- Sir Isaac Newton PRSDocument12 pagesSir Isaac Newton PRSShamim MahamudNo ratings yet
- Biography of Isaac NewtonDocument4 pagesBiography of Isaac NewtonMary Gene Pascual FernandezNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton IV BimDocument2 pagesIsaac Newton IV BimYennifer MlNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton EssayDocument1 pageIsaac Newton EssayJocelyn DeseraiNo ratings yet
- BiographyDocument1 pageBiographysontx128901No ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument6 pagesIsaac NewtonLak DavisNo ratings yet
- DC Background Info Sir Isaac NewtonDocument1 pageDC Background Info Sir Isaac Newtonapi-272358521No ratings yet
- Glup Si Sinko Joj Jojo JojojobikcbxbidkDocument2 pagesGlup Si Sinko Joj Jojo Jojojobikcbxbidkam.krajinaNo ratings yet
- The Faith Behind The FamousDocument13 pagesThe Faith Behind The FamousrantetrgNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton BiographyDocument2 pagesIsaac Newton BiographyGeorgiaNo ratings yet
- بحث انج - نيوتنDocument8 pagesبحث انج - نيوتنOthman SharifNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac NewtonDocument29 pagesSir Isaac NewtonGladie Ann Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Reading Ac Practice9 GGBFDocument13 pagesReading Ac Practice9 GGBFQuỳnh ViNo ratings yet
- Short Stories British Tales Isaac Newton TranscriptDocument1 pageShort Stories British Tales Isaac Newton TranscriptLaura SuárezNo ratings yet
- N412-Module 8.1 Assessment - CabalseDocument2 pagesN412-Module 8.1 Assessment - CabalseKeen Gementiza CabalseNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac Newton: Group 2: MembersDocument11 pagesSir Isaac Newton: Group 2: MembersRupert John LeeNo ratings yet
- Essay About Isaac NewtonDocument1 pageEssay About Isaac NewtonMarko MedinNo ratings yet
- SDFSDFDocument8 pagesSDFSDFtatarinNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac NewtonDocument22 pagesSir Isaac NewtonUpendra Reddy100% (1)
- Early Life of NewtonDocument3 pagesEarly Life of Newtonich114No ratings yet
- Biography of Isaac NewtonDocument7 pagesBiography of Isaac NewtonReyna Avila Ramírez-Arellano100% (1)
- English Reference 1 - Isaac NewtonDocument2 pagesEnglish Reference 1 - Isaac NewtonAndrewNo ratings yet
- Presentation For MathDocument9 pagesPresentation For Mathapi-273439822No ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: The Smartest Person That Ever Lived - Biography of Famous People Grade 3 | Children's Biography BooksFrom EverandIsaac Newton: The Smartest Person That Ever Lived - Biography of Famous People Grade 3 | Children's Biography BooksNo ratings yet
- Omron Cp1l El M UsersmanualDocument800 pagesOmron Cp1l El M Usersmanualarmandoa71565No ratings yet
- HTTP Rep - Clickastro.com Reports 25558484 SoibamKhag PDFDocument65 pagesHTTP Rep - Clickastro.com Reports 25558484 SoibamKhag PDFKhagembaNo ratings yet
- Defence Account CodeDocument41 pagesDefence Account Codem kNo ratings yet
- Data Structures DDPC2423: Chapter 3 - STACKSDocument40 pagesData Structures DDPC2423: Chapter 3 - STACKSIRDINA FATINI DZUL NAZRINo ratings yet
- R AssignmentDocument2 pagesR AssignmentKapardhi kkNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix Design CalculationDocument10 pagesConcrete Mix Design CalculationHari RNo ratings yet
- Constructionism Learning by Design and PDocument18 pagesConstructionism Learning by Design and PKostas BezaitisNo ratings yet
- MM 4 4th Edition Dawn Iacobucci Test Bank 1Document22 pagesMM 4 4th Edition Dawn Iacobucci Test Bank 1jessica100% (53)
- 7-3 IP Board Part (SMPS Part) : 7 Block DiagramsDocument8 pages7-3 IP Board Part (SMPS Part) : 7 Block DiagramsSonu KumarNo ratings yet
- Analytica 03 00027 v2Document12 pagesAnalytica 03 00027 v2Jesús SilvaNo ratings yet
- Python Classes: ClassDocument24 pagesPython Classes: Classns0447496No ratings yet
- MUCLecture 2022 51954485Document21 pagesMUCLecture 2022 51954485Mr AliNo ratings yet
- Customer Service Email:: Voice Type Multifunctional Gas Detector User's ManualDocument20 pagesCustomer Service Email:: Voice Type Multifunctional Gas Detector User's ManualIGNACIO ANDAURNo ratings yet
- Why Rent A HelicopterDocument2 pagesWhy Rent A HelicopterLeena SalamNo ratings yet
- Daniel P PinkDocument12 pagesDaniel P PinkNautNo ratings yet
- Leica FS C: More User Manuals OnDocument154 pagesLeica FS C: More User Manuals Onjuk expertNo ratings yet
- FinGAT Financial Graph Attention Networks For Recommending Top-KK Profitable StocksDocument13 pagesFinGAT Financial Graph Attention Networks For Recommending Top-KK Profitable StocksSivaramakrishnan KanagarajNo ratings yet
- Micro Medical MicroLab ML3500 - Service ManualDocument16 pagesMicro Medical MicroLab ML3500 - Service ManualAsep MustopaNo ratings yet
- Assembly Technologies For Piezoelectric Sensors Up To 1000 °CDocument20 pagesAssembly Technologies For Piezoelectric Sensors Up To 1000 °CkashmiraNo ratings yet
- Cdi 1 Slide 30 To 55Document27 pagesCdi 1 Slide 30 To 55Cristine AvancenaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Marketing Communication Tools and SalesDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Marketing Communication Tools and SalesAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- The Vital Role of Social CapitalDocument8 pagesThe Vital Role of Social Capitalfirefairy5761No ratings yet
- S03 Rotary Drill RHR50 - ADocument18 pagesS03 Rotary Drill RHR50 - ArolandNo ratings yet
- 2007 Sajc GP Prelim p1 AnsDocument12 pages2007 Sajc GP Prelim p1 AnspopthudlerNo ratings yet
- Theory Critique NursingDocument4 pagesTheory Critique NursingLowellaJulioNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument46 pagesPDFLidijaSpaseskaNo ratings yet
- Eds 07 3102 50 Plinth Design For Freestanding 6 8 Way LV Pillars 1Document2 pagesEds 07 3102 50 Plinth Design For Freestanding 6 8 Way LV Pillars 1Umerfarooq TawriNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle Systems Engineering Training Brochure Revised V1.1Document3 pagesElectric Vehicle Systems Engineering Training Brochure Revised V1.1Ranjith RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Openmind 1 End-Of-Course Test Answer KeyDocument6 pagesOpenmind 1 End-Of-Course Test Answer KeyrmilseNo ratings yet