Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reported Speech Erklärung Wichtig
Reported Speech Erklärung Wichtig
Uploaded by
heidi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesThis document discusses how to report speech in indirect form by making changes to verb tenses and references to time/place. When reporting a statement, verb tenses in indirect speech change according to rules like present simple becoming past simple. Questions in indirect speech become subordinate clauses with interrogative words like "when" or "if". Imperatives become infinitive constructions. Time/place references that are no longer applicable for the reporter change to alternatives like "the next day" instead of "tomorrow".
Original Description:
general roules
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses how to report speech in indirect form by making changes to verb tenses and references to time/place. When reporting a statement, verb tenses in indirect speech change according to rules like present simple becoming past simple. Questions in indirect speech become subordinate clauses with interrogative words like "when" or "if". Imperatives become infinitive constructions. Time/place references that are no longer applicable for the reporter change to alternatives like "the next day" instead of "tomorrow".
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesReported Speech Erklärung Wichtig
Reported Speech Erklärung Wichtig
Uploaded by
heidiThis document discusses how to report speech in indirect form by making changes to verb tenses and references to time/place. When reporting a statement, verb tenses in indirect speech change according to rules like present simple becoming past simple. Questions in indirect speech become subordinate clauses with interrogative words like "when" or "if". Imperatives become infinitive constructions. Time/place references that are no longer applicable for the reporter change to alternatives like "the next day" instead of "tomorrow".
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
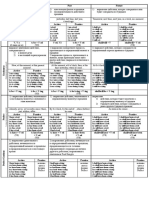
Reported speech
A) Steht der Einfuehrungssatz in einer Zeitform der
Gegenwart (z.B. Present Tense, Present Perfect), so werden in der
indirekten Rede die Zeitformen der direkten Rede beibehalten.
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
“I hate fish.” Judy says (that) she hates fish.
“I am still writing the essay.” He has just told me (that) he is
still writing the essay.
Steht der Einfuehrungssatz in einer Zeitform der Vergangenheit (z.B.
Past Tense, Past Perfect), so aendern sich die Zeitformen in der
indirekten Rede nach folgendem Muster:
1) Present Simple Past Simple
2) Present Continuous Past Continuous
3) Present Perfect Simple Past Perfect Simple
4) Present Perfect Continuous Past Perfect Continuous
5) Past Simple Past Perfect Simple
6) Past Continuous Past Perfect Continuous
7) Will-Future Conditional (would + Infinitive)
1) “I like walking in the Lake District.” Moritz said (that) he liked
walking in the Lake District.
2) “John is playing football.” I thought (that) John was
playing football.
3) “Have you seen him recently?” I wondered if you had seen
him recently.
4) “I have been working all afternoon.” Pat’s parents believed (that)
she had been working all
afternoon.
5) “My brother visited the USA in 1986.” I told them (that) my brother
had visited the U.S.A. in
1986.
6) “We were playing cards the whole They replied (that) they had
evening.” been playing cards the
whole evening.
7) “I’ll (I will) ring you next week.” I promised (that) I would
ring her the following week.
Bei der Umwandlung der direkten in die indirekte Rede veraendern sich
Orts- und Zeitangaben, wenn der urspruengliche Orts –und Zeitbezug
fuer den Berichterstatter nicht mehr zutrifft.
Z.B.
tomorrow the next day / following day
last year the year before
here there
yesterday the day before
this week that week
now then
today that day
2 days ago 2 days earlier
Jenny (Frankfurt) Brian (London)
“The exams are being held here.” Jenny told me that the exams were
being held there (in Frankfurt).
Judy (on Sunday) Philip (on Wednesday)
“I’m going to the judo club Judy told me (on Sunday) that she
tomorrow.” was going to the judo club the
following day.
B) Question in indirect speech
Fragen werden in der indirekten Rede zu Nebensaetzen mit Fragewort
(when, where, etc.oder if = ob).
Die Wortstellungbei diesen Nebensaetzen ist Subjekt-Praedikat (keine
Umstellung von Hilfsverb und Subjekt, keine do-Umschreibung!). Wenn
der Einfuehrungssatz in einer Zeitform der Vergangenheit steht, so
aendern sich die Zeitformen wie oben.
“When did you start playing the His fans often ask him when he
guitar?” started playing the guitar.
“Are you giving a concert?” Rick asked if we were giving a
concert.
III) The imperative in indirect speech
Aufforderungssaetze werden in der indirekten Rede in
infinitivkonstruktionen umgewandelt.
“Don’t come late.” Harry told us not to come late.
“Give it to me.” She asked me to give it to her.
Matrix_the_future@web.de
You might also like
- Full Download Solution Manual For Discrete Mathematics With Applications 5th Edition Susanna S Epp PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Discrete Mathematics With Applications 5th Edition Susanna S Epp PDF Full Chapterrabate.toiler.vv5s091% (23)
- Turning Direct Speech Into Reported SpeechDocument1 pageTurning Direct Speech Into Reported SpeechcrissNo ratings yet
- Rules For Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesRules For Reported SpeechPannaNo ratings yet
- Rules For Reported Speech 1Document10 pagesRules For Reported Speech 1Panna100% (1)
- Rule For Changing Direct Speech Into Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesRule For Changing Direct Speech Into Indirect SpeechVanita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Theory of The Use of English TensesDocument1 pageTheory of The Use of English Tensesmd asad akhtarNo ratings yet
- Future FormsDocument3 pagesFuture FormsAnda AdaNo ratings yet
- Название Past Simple Present Simple Present Continuous Future Simple Present Perfect Past ContinuousDocument1 pageНазвание Past Simple Present Simple Present Continuous Future Simple Present Perfect Past ContinuousСветлана ТепловаNo ratings yet
- Uses of Future Tenses 18Document19 pagesUses of Future Tenses 18jamalNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect NarrationDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect Narrationrizwan afzalNo ratings yet
- Diateza Pasiva Si Vorbirea Directa-Indirecta PT ScoalaDocument14 pagesDiateza Pasiva Si Vorbirea Directa-Indirecta PT ScoalaAndreea Emanuela MateiNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument12 pagesDirect and Indirect Speechkanbouch100% (1)
- English ТаблицыDocument2 pagesEnglish ТаблицыWill HalloNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech 2 059301231688472156Document10 pagesReported Speech 2 059301231688472156AMAL JOHNSONNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechKarola CosmeNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech RulesDocument5 pagesDirect Speech Rulesusman ghaniNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechDanielleOkNo ratings yet
- Or What They Say. There Are Two Main Types of Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesOr What They Say. There Are Two Main Types of Reported SpeechMariana GimenezNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument8 pagesReported SpeechDockerNo ratings yet
- When The Reporting Verb Is in The Past TenseDocument3 pagesWhen The Reporting Verb Is in The Past TenseGlobal Learners' ProgrammesNo ratings yet
- Loi Noi Gian TiepDocument5 pagesLoi Noi Gian TiepNguyễn Bảo Gia HânNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Direct & Indirect Speech) : (S + Is/am/are + V Ing) (S+was/were+ Ving)Document4 pagesReported Speech (Direct & Indirect Speech) : (S + Is/am/are + V Ing) (S+was/were+ Ving)Viona FransiskaNo ratings yet
- Expressions With Say, Tell and AskDocument4 pagesExpressions With Say, Tell and AskJuliaWąsikNo ratings yet
- Anglų Kalbos Laikų SudarymasDocument10 pagesAnglų Kalbos Laikų SudarymasStasys VincevičiusNo ratings yet
- Sequence of Tenses: Teacher:Petcu PaulaDocument13 pagesSequence of Tenses: Teacher:Petcu Paulakasandra_style3751No ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech: 1. Change of PronounsDocument17 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech: 1. Change of PronounsAndidwiyuniartiNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument3 pagesEnglish TensesAnimus PhotographerNo ratings yet
- Is She Reading A Good Novel Now?Document4 pagesIs She Reading A Good Novel Now?GABRIELA MIHAELA MĂRĂCINENo ratings yet
- Direct Dan Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect Dan Indirect SpeechFerdianugrahaNo ratings yet
- DirectIndirect Speech PPT 1Document17 pagesDirectIndirect Speech PPT 1Puja RatanNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechNoa PahlićNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument17 pagesReported SpeechalwiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Grammar Revision CBSEDocument9 pagesClass 10 Grammar Revision CBSEcyrilgilbertsonNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To English Tenses (Lorena and José)Document1 pageThe Complete Guide To English Tenses (Lorena and José)Marcelo Vega Rojas100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechAnh VuNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument21 pagesActive and Passive VoiceZakir Ullah100% (1)
- Future FormsDocument5 pagesFuture FormsLilian SelvaggioNo ratings yet
- Curs Limba Engleza2Document10 pagesCurs Limba Engleza2Eugen NituNo ratings yet
- EstiloindirectoDocument19 pagesEstiloindirectoTatiana García SolanoNo ratings yet
- Mfa2 Time and Tense - 3 2019Document5 pagesMfa2 Time and Tense - 3 2019María Fernanda Sánchez AraizaNo ratings yet
- Заняття 5. The Past IndefiniteDocument3 pagesЗаняття 5. The Past IndefiniteІрина МиськівNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech-1Document34 pagesReported Speech-1sanchisanchita9No ratings yet
- 8. REPORTED SPEECH (Lời nói gián tiếp)Document6 pages8. REPORTED SPEECH (Lời nói gián tiếp)HangNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Past Continuous Past Perfect Past Perfect ContinuousDocument1 pagePast Simple Past Continuous Past Perfect Past Perfect ContinuousМария ЕвсееваNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Speech CLASS 8Document22 pagesDirect Indirect Speech CLASS 8yashikapNo ratings yet
- Table TensesDocument2 pagesTable TensesSweetheart KsyushaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Tense, Aspect and Voice HandoutDocument4 pagesWeek 6 Tense, Aspect and Voice HandouttomNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument22 pagesActive and Passive VoiceRohit Chaudhary95% (20)
- Module 13 Future-in-the-PastDocument4 pagesModule 13 Future-in-the-PastВиктор ОблоговNo ratings yet
- Direct and IndirectDocument11 pagesDirect and IndirectAssel SmagulovaNo ratings yet
- Graella VbosDocument2 pagesGraella VboslauralucasrosaNo ratings yet
- Clickworker AnswersDocument12 pagesClickworker AnswersAndreea Diana100% (1)
- Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect Speech Reported SpeechCarlos MartinezNo ratings yet
- Simple Past: Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesSimple Past: Reported SpeechtaiutiNo ratings yet
- Modern Chinese (BOOK 2) – Learn Chinese in a Simple and Successful Way – Series BOOK 1, 2, 3, 4From EverandModern Chinese (BOOK 2) – Learn Chinese in a Simple and Successful Way – Series BOOK 1, 2, 3, 4Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Randomized Controlled Trial On The Performance of Direct and in - 2021 - DentalDocument10 pagesRandomized Controlled Trial On The Performance of Direct and in - 2021 - Dentalnintendo anjayNo ratings yet
- Digipay GuruDocument13 pagesDigipay GuruPeterhill100% (1)
- Principles of Electricity PDFDocument371 pagesPrinciples of Electricity PDFJohn C. Stephens100% (5)
- TIME PumpsDocument13 pagesTIME PumpsAndres RedondoNo ratings yet
- WPP2019 Pop F01 2 Total Population MaleDocument547 pagesWPP2019 Pop F01 2 Total Population MaleMaria BozhkoNo ratings yet
- Load Cell ActuatorsDocument2 pagesLoad Cell Actuatorssandeep100% (1)
- Operating Range Recommended Applications: Mechanical Seals - Mechanical Seals For Pumps - Pusher SealsDocument3 pagesOperating Range Recommended Applications: Mechanical Seals - Mechanical Seals For Pumps - Pusher Sealsneurolepsia3790No ratings yet
- John Hagstrom: Philip BiggsDocument4 pagesJohn Hagstrom: Philip BiggsDarci HallNo ratings yet
- CNS-Classifications by Dr-Islahkhan (Humble Pharmacist)Document24 pagesCNS-Classifications by Dr-Islahkhan (Humble Pharmacist)M Ils Meteor Pharmacist0% (1)
- Agrirobot PDFDocument103 pagesAgrirobot PDFMuhamad Azlan ShahNo ratings yet
- Section 2 Digital OutputDocument1 pageSection 2 Digital Outputsamim_khNo ratings yet
- Opsrey - Acre 1291Document97 pagesOpsrey - Acre 1291Hieronymus Sousa PintoNo ratings yet
- Egger Nursery's in KeralaDocument6 pagesEgger Nursery's in KeralanidhinpillaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CVPDocument26 pagesChapter 3 CVPshuhadaNo ratings yet
- Veritas NetBackup 6.5 Vault Administrator's GuideDocument268 pagesVeritas NetBackup 6.5 Vault Administrator's GuideS LS ChanNo ratings yet
- Stabilitation of BetalainsDocument6 pagesStabilitation of BetalainsKevin MendezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans WK 26Document7 pagesLesson Plans WK 26api-280840865No ratings yet
- Assignment2 Santos CarlosJoaquin MECp1Document8 pagesAssignment2 Santos CarlosJoaquin MECp1Jake SantosNo ratings yet
- 2021 DBaaS Security Architect and SolutionsDocument26 pages2021 DBaaS Security Architect and Solutionsluke luNo ratings yet
- Teacher Should Be Very Strict in ClassDocument1 pageTeacher Should Be Very Strict in ClassAbdul ArifNo ratings yet
- 2021 YISS - INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS - Hyunjung KimDocument3 pages2021 YISS - INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS - Hyunjung KimFung AlexNo ratings yet
- Test 9Document16 pagesTest 9buivankhangNo ratings yet
- JLTR, 02Document8 pagesJLTR, 02Junalyn Villegas FerbesNo ratings yet
- Math Chapter 3 Study GuideDocument3 pagesMath Chapter 3 Study Guideapi-311999132No ratings yet
- The Metaphysics of The Upanishads VicharDocument461 pagesThe Metaphysics of The Upanishads VicharAyush GaikwadNo ratings yet
- A Bluetooth ModulesDocument19 pagesA Bluetooth ModulesBruno PalašekNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument8 pagesHardness TestlvasuthavanNo ratings yet
- Website ErrorDocument5 pagesWebsite ErrorJosé DavidNo ratings yet
- Wizard - School of DiabolismDocument1 pageWizard - School of DiabolismHope LaneNo ratings yet