Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handout - Coordinate Systems: Coordinate System X-Axis Y-Axis Origin
Handout - Coordinate Systems: Coordinate System X-Axis Y-Axis Origin
Uploaded by
AmithaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handout - Coordinate Systems: Coordinate System X-Axis Y-Axis Origin
Handout - Coordinate Systems: Coordinate System X-Axis Y-Axis Origin
Uploaded by
AmithaCopyright:
Available Formats
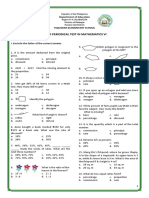
Name: __________________________
Group: __________________________
Date: __________________________
Handout – Coordinate systems
1. A coordinate system, or coordinate plane, is used to locate points in a 2-
dimensional plane.
2. The horizontal number line is the x-axis.
3. The vertical number line is the y-axis.
4. The intersection of two points is the origin.
5. The coordinate plane contains four quadrants (I, II, III, IV).
AMP_ADVETI-Shahama (adapted from various resources) Page 1
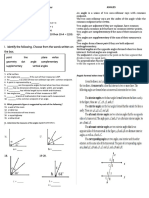
Name: __________________________
Group: __________________________
Date: __________________________
Handout – Coordinate systems
6. Any point in the coordinate plane using a specific order is an ordered pair (x, y).
7. The first number in an ordered pair is the x-coordinate.
8. The second number in an ordered pair is the y-coordinate.
9. A two-dimensional coordinate system in which each point on a plane is
determined by displacement from the origin and the angular direction.
10. These are known as the radial and angular coordinates (𝑟,𝜃).
AMP_ADVETI-Shahama (adapted from various resources) Page 2
Name: __________________________
Group: __________________________
Date: __________________________
Handout – Coordinate systems
11. There are equivalent ways of defining the same point.
Conversion to Cartesian coordinate system
12. Cartesian coordinates (𝑥,𝑦) can be written in terms of polar coordinates (𝑟,𝜃) as
𝑥=𝑟. Cos 𝜃
𝑦=𝑟. Sin 𝜃
𝝅
13. Find the Cartesian coordinates of the point (1, 𝟒 )
𝜋
𝑥=1. cos 4
𝜋
𝑦=1. sin 4
ξ𝟐 ξ𝟐
(x, y) = ( ,𝟐)
𝟐
Conversion to Polar coordinate system
14. Polar coordinates (𝑟,𝜃) can be written in terms of cartesian coordinates (x,y) as
𝑟= ඥ𝒙𝟐 + 𝒚𝟐
𝒚
𝜃=𝐭𝐚𝐧−𝟏 𝒙
15. Find the Polar coordinates of the point (2, 3)
𝑟= ξ22 + 32
3
𝜃=tan−1 2
(𝑟,𝜃) = (3.6, 56.3◦)
AMP_ADVETI-Shahama (adapted from various resources) Page 3
You might also like
- Math 6 DLP 71 - Variables in EquationDocument13 pagesMath 6 DLP 71 - Variables in EquationFerdie DG SalaoNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Please Show All Work, If Needed! Place Answers in ANSWER Box, If ProvidedDocument4 pagesExam 2 Please Show All Work, If Needed! Place Answers in ANSWER Box, If Providedngan tranNo ratings yet
- Am1 Ex3Document3 pagesAm1 Ex3CH YNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument9 pagesResearch ArticlecicwazuzuNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry in Three Dimensions: Section 11.1 The Three-Dimensional Coordinate SystemDocument2 pagesAnalytic Geometry in Three Dimensions: Section 11.1 The Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systemsarasmile2009100% (1)
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument38 pagesChapter 2 PDFNurul Dayah100% (1)
- Profundizacion MatematicasDocument10 pagesProfundizacion MatematicasNico Carreño LopezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan:: Andrew Lewis Middle School Salem City Schools, Salem, VADocument6 pagesLesson Plan:: Andrew Lewis Middle School Salem City Schools, Salem, VAeliana tm31No ratings yet
- A Triple Fixed Point Theorem of Caristi Type Contraction For Multi Valued Maps in A Haussdorff Metric SpaceDocument4 pagesA Triple Fixed Point Theorem of Caristi Type Contraction For Multi Valued Maps in A Haussdorff Metric SpaceMathematical ExperiencesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument38 pagesChapter 2 PDFLi Ling TanNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Math 8Document6 pagesModule 6 Math 8Ja NeenNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Some Common Coupled Fixed Point Results For Generalized Contraction in Complex-Valued Metric SpacesDocument11 pagesResearch Article: Some Common Coupled Fixed Point Results For Generalized Contraction in Complex-Valued Metric SpacesTalha WaheedNo ratings yet
- Ed Tech Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesEd Tech Lesson PlanJanel AbaleleNo ratings yet
- Module Introduction:: This Module Aims That The Students Will Be Able To Learn The FollowingDocument12 pagesModule Introduction:: This Module Aims That The Students Will Be Able To Learn The FollowingRaven Evangelista CanaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document12 pagesModule 5Monique UnicoNo ratings yet
- LP Week 5 Day 1-2 - Math 8, Rectangular AxisDocument18 pagesLP Week 5 Day 1-2 - Math 8, Rectangular AxisFrancisco Rosellosa LoodNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 2 (3D Coordinate Systems)Document40 pagesLecture # 2 (3D Coordinate Systems)Rakhmeen GulNo ratings yet
- Activity 6.2.1 The Wrapping Function: Activity 6.2.1 Connecticut Core Algebra 2 Curriculum Version 3.0Document6 pagesActivity 6.2.1 The Wrapping Function: Activity 6.2.1 Connecticut Core Algebra 2 Curriculum Version 3.0Ric Joseph MurilloNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics For DemoDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics For DemoLA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2sameed hussainNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon City: Education, Accountancy, and Entrepreneurship DepartmentDocument13 pagesSorsogon City: Education, Accountancy, and Entrepreneurship DepartmentEmily Despabiladeras DulpinaNo ratings yet
- Am1 Ex4Document3 pagesAm1 Ex4CH YNo ratings yet
- Q1 Activity Sheet 3 W3Document1 pageQ1 Activity Sheet 3 W3Eros James JameroNo ratings yet
- SL Ch17 Definite Integration and Its Applications Lecture Notes SolutionsDocument18 pagesSL Ch17 Definite Integration and Its Applications Lecture Notes Solutionslinayan8No ratings yet
- UNIT 3-Multiple Integrals VSAQDocument3 pagesUNIT 3-Multiple Integrals VSAQdevaharshinisathaNo ratings yet
- Calculus 3 Module 2Document5 pagesCalculus 3 Module 2Maria Teresa OndoyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Delhi Public School, GandhinagarDocument7 pagesMathematics: Delhi Public School, GandhinagarSharanya ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- MA 1251 Numerical MDocument22 pagesMA 1251 Numerical MDamo_Daran_357No ratings yet
- MATH8 - Q1 - Module 4 - MELC 7,8,9Document14 pagesMATH8 - Q1 - Module 4 - MELC 7,8,9Wilma Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Studying Some Approaches To Estimate The Smoothing Parameter For The Nonparametric Regression ModelDocument11 pagesStudying Some Approaches To Estimate The Smoothing Parameter For The Nonparametric Regression ModelÚt NhỏNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NotesDocument22 pagesChapter 2 Notesrachel4uclaNo ratings yet
- cs6359_hw1_with_hints (1)Document2 pagescs6359_hw1_with_hints (1)karan katariaNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Lesson 1 HW AssignmentDocument2 pagesUnit 14 Lesson 1 HW AssignmentChad HornNo ratings yet
- POLARDocument7 pagesPOLARAnthony Rey CaneteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Relations and Functions: 1.1 Sets of Real Numbers and The Cartesian Coordinate PlaneDocument10 pagesChapter 1: Relations and Functions: 1.1 Sets of Real Numbers and The Cartesian Coordinate Planerachel4uclaNo ratings yet
- Applied math-IIDocument4 pagesApplied math-IIWezir Aliyi (Smart men)No ratings yet
- Finite Element Method Derive 2Document10 pagesFinite Element Method Derive 2heng sokundaraNo ratings yet
- Dll-Cartesian Coordinates SystemDocument4 pagesDll-Cartesian Coordinates SystemJo-Amver Valera Manzano100% (2)
- NotesDocument2 pagesNoteslandonNo ratings yet
- ϖ-Interpolative Ciric-Reich-Rus-Type Contactions in m-metric spaceDocument6 pagesϖ-Interpolative Ciric-Reich-Rus-Type Contactions in m-metric spaceIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- HW #S 7 - 10Document11 pagesHW #S 7 - 10dmcavoyNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Convergence Theorem For A Family of New Modified Halley's Method in Banach SpaceDocument9 pagesResearch Article: Convergence Theorem For A Family of New Modified Halley's Method in Banach SpaceJose Miguel GomezNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 12Document2 pagesPractice Paper 12uma varshanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 3rd Quarter 3Document40 pagesModule 1 3rd Quarter 3averylchulsi563No ratings yet
- Unit 5 3D Object Representation: A) Boundary Representations (B-Reps) : The Boundary Representations Describe A ThreeDocument17 pagesUnit 5 3D Object Representation: A) Boundary Representations (B-Reps) : The Boundary Representations Describe A ThreeBinoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field Theory: A Problem Solving ApproachDocument40 pagesElectromagnetic Field Theory: A Problem Solving ApproachdavidNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Complex NumbersDocument12 pagesAssignment 3 Complex NumbersFonNo ratings yet
- Summary (WS3-5)Document5 pagesSummary (WS3-5)Mohammed KhalilNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 PDFDocument49 pagesChapter1 PDFchinmay pattnayakNo ratings yet
- 2nd QTR Week 1 Module 3 Linear Equations in Two Variables (Part 1)Document12 pages2nd QTR Week 1 Module 3 Linear Equations in Two Variables (Part 1)Erwin dela PuntaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Review of Coordinate SystemDocument3 pagesChapter - 2 Review of Coordinate SystemAnandNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods (ME610) : Mid-Semester ExaminationDocument1 pageMathematical Methods (ME610) : Mid-Semester ExaminationTushar SinghNo ratings yet
- GM Week2 Day4Document5 pagesGM Week2 Day4Good vouNo ratings yet
- Lecture162617 TripleIntegralsDocument29 pagesLecture162617 TripleIntegralsdogd2301No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Functions: Module in General MathematicsDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Functions: Module in General MathematicsL AlcosabaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 3 SW ExercisesDocument4 pagesLesson 1 3 SW ExercisesL AlcosabaNo ratings yet
- WS4.3 Factoring and Dividing PolynomialsDocument1 pageWS4.3 Factoring and Dividing PolynomialsIshaan SinghNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 8: Proof. Let Be A Differentiable Function Whose Value Is Never Zero, and ConsiderDocument3 pagesProblem Set 8: Proof. Let Be A Differentiable Function Whose Value Is Never Zero, and ConsiderSarah TseungNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Let's Play Ball! - Vocabulary & Skills - 01 June 22 - C3 - AMPDocument17 pagesPresentation - Let's Play Ball! - Vocabulary & Skills - 01 June 22 - C3 - AMPAmithaNo ratings yet
- ALCPT Practice - Warmup - 10 Qns - 01 June 22 - C3Document1 pageALCPT Practice - Warmup - 10 Qns - 01 June 22 - C3AmithaNo ratings yet
- LP 01 June 22 c3 AmpDocument1 pageLP 01 June 22 c3 AmpAmithaNo ratings yet
- ALCPT Practice Warmup 01 June 22 C3 AMPDocument1 pageALCPT Practice Warmup 01 June 22 C3 AMPAmithaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-Coordinate Systems - Classwork: A B C D Based On The Given Figure, Answer The Questions Below: A B C DDocument4 pagesWorksheet-Coordinate Systems - Classwork: A B C D Based On The Given Figure, Answer The Questions Below: A B C DAmithaNo ratings yet
- Handout - Introduction To Vectors - Physics - AMPDocument2 pagesHandout - Introduction To Vectors - Physics - AMPAmithaNo ratings yet
- Ratios and ProportionsDocument23 pagesRatios and Proportionsapi-239769876No ratings yet
- MMC 2019 Grade 7 Division Finals - Team Oral Competition Questions With SolutionsDocument33 pagesMMC 2019 Grade 7 Division Finals - Team Oral Competition Questions With SolutionsNoreenNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions: Lesson 1Document22 pagesAlgebraic Expressions: Lesson 1ALongNo ratings yet
- Trig Graphs MME QuestionsDocument8 pagesTrig Graphs MME QuestionsPrarthana VinothNo ratings yet
- 3rd PT in Math VIDocument4 pages3rd PT in Math VIRodnick BodinoNo ratings yet
- Indian Olympiad Qualifier in Mathematics Sample Paper - 1: Duration: 1 Hour Max. Marks: 34Document11 pagesIndian Olympiad Qualifier in Mathematics Sample Paper - 1: Duration: 1 Hour Max. Marks: 34Siddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 7 Reviewer 3rd QuarterDocument1 pageMathematics 7 Reviewer 3rd QuarterJo Ann Chrysol IringanNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification: Science and Math DepartmentDocument2 pagesTable of Specification: Science and Math DepartmentKen AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Equations in Real LifeDocument19 pagesEquations in Real LifeMAHJABEEN NASEEMNo ratings yet
- Alg 2 Resource Ws CH 8Document101 pagesAlg 2 Resource Ws CH 8Anoop Sreedhar100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document72 pagesChapter 3parn8972No ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus: Quarter 2 - Module 8Document26 pagesPre-Calculus: Quarter 2 - Module 8Eilinre Olin100% (1)
- 2022 Mathematical Methods Year 12 Application TaskDocument14 pages2022 Mathematical Methods Year 12 Application TaskRobin MowlaNo ratings yet
- China National - Olympiad 2011 65Document2 pagesChina National - Olympiad 2011 65Ngạo Cuồng TàNo ratings yet
- TOS GenMath PrelimDocument1 pageTOS GenMath PrelimJesamie Bactol SeriñoNo ratings yet
- Number of Digits (Questions) : DK Iz KSX Djds 4 Vadksa DH Fdruh La ( K, A Cuk H TK LDRH GsaDocument6 pagesNumber of Digits (Questions) : DK Iz KSX Djds 4 Vadksa DH Fdruh La ( K, A Cuk H TK LDRH GsaA.K. BNo ratings yet
- Regular Evaluation Test IV Maths VI ADocument3 pagesRegular Evaluation Test IV Maths VI AB.L. Indo Anglian Public School, Aurngabad, BiharNo ratings yet
- Stanford Math Circle: Sunday, April 4, 2010 Farey Sequences and Ford CirclesDocument3 pagesStanford Math Circle: Sunday, April 4, 2010 Farey Sequences and Ford CirclesBal Bahadur TamangNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties of LogarithmsDocument35 pagesBasic Properties of LogarithmsDajhri TuqueroNo ratings yet
- Algebraic ExpressionDocument15 pagesAlgebraic ExpressionAbdul Rashid GuroNo ratings yet
- 4th Periodical Test (Math)Document6 pages4th Periodical Test (Math)Lourence CapaNo ratings yet
- 74225CglMainsMock 1 (WithoutAnserkey) CRDocument20 pages74225CglMainsMock 1 (WithoutAnserkey) CRAman KeshriNo ratings yet
- 0580 Trigonometry P4Document52 pages0580 Trigonometry P4AditiNo ratings yet
- Precalculus A Right Triangle Approach 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesPrecalculus A Right Triangle Approach 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions ManualChelseaSmithprqa100% (43)
- Class 9 IMO PDFDocument5 pagesClass 9 IMO PDFSkc pmcNo ratings yet
- 14 Theorems On Area (CLASS SHEET)Document22 pages14 Theorems On Area (CLASS SHEET)Prince Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Integral MCQDocument11 pagesMathematics Integral MCQRaju ShresthaNo ratings yet
- CSEC June 2006 Mathematics P1Document11 pagesCSEC June 2006 Mathematics P1Tamera GreenNo ratings yet
- w5 - Stu Differentiation 1Document46 pagesw5 - Stu Differentiation 1Mohd FadhliNo ratings yet