Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 viewsHuman Resource Management Chapter 7 Reviewer
Human Resource Management Chapter 7 Reviewer
Uploaded by
Nikkson CayananThis document discusses recruiting, selecting, training, and developing employees. It covers the meaning and process of recruiting, including organizational goals of attracting qualified candidates and providing realistic job previews. The recruiting process involves workforce planning, building a candidate pool through various methods like job postings, recommendations, advertisements, agencies, and digital recruiting. Internal recruiting has advantages like increasing motivation and sustaining company culture, while external recruiting draws from outside applicant pools.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- CHRA Reviewer 2Document9 pagesCHRA Reviewer 2Zaila Mitch100% (3)
- Business Canadian 8th Edition Griffin Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesBusiness Canadian 8th Edition Griffin Solutions Manual 1jasmineforddjbxeapiqf100% (26)
- HRM ReviewerDocument3 pagesHRM ReviewerPinks D'CarlosNo ratings yet
- Io PsychDocument30 pagesIo PsychJasmin ValloNo ratings yet
- HRM Amity AssignmentDocument9 pagesHRM Amity Assignmentsiddharth1906No ratings yet
- Business Management and EntrepreneurshipDocument5 pagesBusiness Management and EntrepreneurshipToni CruzNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 StaffingDocument8 pagesLec 7 StaffingThe Daily QuotesNo ratings yet
- StaffingDocument2 pagesStaffingchristianNo ratings yet
- LAS For Organization and Management (Grade 11)Document9 pagesLAS For Organization and Management (Grade 11)rosellerNo ratings yet
- Cbmec 2 ModuleDocument4 pagesCbmec 2 ModuleJacqueline Acera BalingitNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in OrgmaDocument6 pagesReviewer in OrgmaHannah JenneNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Handouts Chapter 5 8Document7 pages2nd Quarter Handouts Chapter 5 8kathlen mae marollanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 RecruitmentDocument44 pagesChapter 4 RecruitmentFaiz ZakariaNo ratings yet
- EM CH5 6 NotesDocument7 pagesEM CH5 6 NotesJerome LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 HR Planning and RecruitingDocument9 pagesChapter 3 HR Planning and RecruitingDaphne DublinNo ratings yet
- Staffing Quarter 2 Week 9 ExpectationsDocument5 pagesStaffing Quarter 2 Week 9 ExpectationsRemar Jhon PaineNo ratings yet
- HRM ReviewerDocument5 pagesHRM ReviewerNeekah JoyNo ratings yet
- Rubrics: Cooperation - 40%Document3 pagesRubrics: Cooperation - 40%Brenda SebandalNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management PrelimsDocument2 pagesHuman Resource Management PrelimsLei PalumponNo ratings yet
- HRM Midterm ReviewerDocument6 pagesHRM Midterm ReviewerKim Alfonzo MenozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Engineering ManagementDocument5 pagesChapter 5 - Engineering ManagementJohn Philip Molina NuñezNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapter 5Document6 pagesSummary Chapter 5Vu Tuan HungNo ratings yet
- HRM MidtermDocument5 pagesHRM MidtermDaniela BallezaNo ratings yet
- Chapter FiveDocument6 pagesChapter FiveamanuelNo ratings yet
- Notes (2nd Sem)Document19 pagesNotes (2nd Sem)GABRIELLE MARI AQUINONo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 RecruitmentDocument8 pagesChapter 4 RecruitmentPhil Andrie LocreNo ratings yet
- System (CCPS) Is One That StoresDocument7 pagesSystem (CCPS) Is One That StoresJoanne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument6 pagesHuman Resource Managementmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- Ad & Mgt. MIDTERMDocument4 pagesAd & Mgt. MIDTERMchuck kieNo ratings yet
- Selection Is As A Series of Hurdles: Development Record FormDocument4 pagesSelection Is As A Series of Hurdles: Development Record Formhesham hassanNo ratings yet
- 2 Fundamentals of HRM2Document18 pages2 Fundamentals of HRM2Wael ALyNo ratings yet
- HRM Test Bank For FinalsDocument26 pagesHRM Test Bank For FinalsdeltonNo ratings yet
- ABM11 - Organization and Management - Q2 - W1-2Document4 pagesABM11 - Organization and Management - Q2 - W1-2Emmanuel Villeja LaysonNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 13Th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesHuman Resource Management 13Th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFtanya.griggs377100% (15)
- Human Resource Management 13th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesHuman Resource Management 13th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manual 1victoriahutchinsontzbpmigrcs100% (28)
- SHRM Group-2Document44 pagesSHRM Group-2xyrieltolentinoNo ratings yet
- Attachment Summary Sheet - General Management Part 3 Lyst9140Document16 pagesAttachment Summary Sheet - General Management Part 3 Lyst9140vipulpandey005No ratings yet
- (Iom) Chap 8-11Document24 pages(Iom) Chap 8-11Tini GarciaNo ratings yet
- Attachment Summary Sheet Part 3Document16 pagesAttachment Summary Sheet Part 3Jyoti RanjanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managementchapter 5Document9 pagesIntroduction To Managementchapter 5Abdulhafiz AbdiNo ratings yet
- Indira School of Business Studies, Pune.: Human Resources ManagementDocument8 pagesIndira School of Business Studies, Pune.: Human Resources ManagementAnkita ShettyNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis and Human Resource PlanningDocument3 pagesJob Analysis and Human Resource PlanningLawrenze Abby LuceroNo ratings yet
- RAndS 048-054Document78 pagesRAndS 048-054zeewaqar aliNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and Selection: STUDENT NAME: - DATEDocument7 pagesRecruitment and Selection: STUDENT NAME: - DATEsyeda maryemNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Recruitment PDFDocument2 pagesSession 5 Recruitment PDFLeonard LiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Strategic HRMDocument12 pagesModule 2 - Strategic HRMAnna Martella FabianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document25 pagesChapter 3Aryan Bin RezaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document15 pagesChapter 03Qasim Jahangir WaraichNo ratings yet
- Recruitment (Human Resource Management)Document44 pagesRecruitment (Human Resource Management)Louise EulogioNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument15 pagesHuman Resource Managementsomasekhar reddy1908No ratings yet
- 4 - Planning JobsDocument28 pages4 - Planning JobsMehwish ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Em Kinn NGG GinsDocument6 pagesEm Kinn NGG Ginsarvin paruliNo ratings yet
- Ijramt V3 I7 11Document4 pagesIjramt V3 I7 11PREETI GUPTANo ratings yet
- HR Exam NoteDocument6 pagesHR Exam NoteMuhammad IrsyadNo ratings yet
- French: Introduction To Human Resource Management Human Resource ManagementDocument16 pagesFrench: Introduction To Human Resource Management Human Resource ManagementZ VerNo ratings yet
- PPT3 HumanResourceManagement 20230615022350Document20 pagesPPT3 HumanResourceManagement 20230615022350Grace AngelinNo ratings yet
- The Story So Far (Week 5)Document20 pagesThe Story So Far (Week 5)Mina KangNo ratings yet
- Recruitment of Employees Write UpDocument7 pagesRecruitment of Employees Write UpArlene TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Supervised By: MR - Ait CherkiDocument40 pagesHuman Resource Management: Supervised By: MR - Ait CherkiHiba jerraNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 1 Reviewer - The Nature of Human Resource ManagementDocument5 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 1 Reviewer - The Nature of Human Resource ManagementNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 9 ReviewerDocument5 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 9 ReviewerNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 6 ReviewerDocument4 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 6 ReviewerNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 5 Reviewer - Information For Making Human Resource DecisionsDocument4 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 5 Reviewer - Information For Making Human Resource DecisionsNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf - Merged (3) - 111-120Document10 pagesIlovepdf - Merged (3) - 111-120kanishka saxenaNo ratings yet
- List of 400 English Synonyms & Antonyms - Practice To Beat Competition PDFDocument18 pagesList of 400 English Synonyms & Antonyms - Practice To Beat Competition PDFSaket SaxenaNo ratings yet
- NeijiaDocument5 pagesNeijiaCarlos Estrada MarzoNo ratings yet
- 2.what Is Partnership Briefly State Special Features of A Partnership On The Basis of Which Its Existence Can Be Determined Under The Indian Partnership ActDocument162 pages2.what Is Partnership Briefly State Special Features of A Partnership On The Basis of Which Its Existence Can Be Determined Under The Indian Partnership ActJohn Wesley100% (1)
- MTICDocument5 pagesMTICSonali TanejaNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction-BIO282 LMSDocument19 pagesL1 Introduction-BIO282 LMSGaayithri RNo ratings yet
- 2011 Equipment Flyer 05272011updatedDocument24 pages2011 Equipment Flyer 05272011updatedChecho BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Art and CraftsDocument108 pagesArt and CraftsArus TündeNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons About Judicial ReviewDocument2 pagesPros and Cons About Judicial ReviewCharlotte SamuelsNo ratings yet
- Skills Framework For Design Technical Skills and Competencies (TSC) Reference DocumentDocument2 pagesSkills Framework For Design Technical Skills and Competencies (TSC) Reference DocumentdianNo ratings yet
- Xanathar's Guide To Everything Deluxe-Pages-34Document1 pageXanathar's Guide To Everything Deluxe-Pages-34Justin SteeleNo ratings yet
- Acs Hillingdon Welcomeguide2019Document55 pagesAcs Hillingdon Welcomeguide2019api-294216460No ratings yet
- UnivariateRegression 3Document81 pagesUnivariateRegression 3Alada manaNo ratings yet
- Poranek (Peer Gynt)Document21 pagesPoranek (Peer Gynt)Katarzyna ChronowskaNo ratings yet
- Mca MaterialDocument30 pagesMca MaterialsharmilaNo ratings yet
- Wwek 2Document34 pagesWwek 2repiresNo ratings yet
- Vmware Vrealize Automation: Install Configure Manage (V7.6) : View OnlineDocument5 pagesVmware Vrealize Automation: Install Configure Manage (V7.6) : View OnlineSandeep GangadharanNo ratings yet
- RETDEM - Wearing of Appropriate PPEsDocument4 pagesRETDEM - Wearing of Appropriate PPEsYo MamaNo ratings yet
- Ipo Sylabus and BooksDocument3 pagesIpo Sylabus and BooksNaseema Chan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Situational Leadership in EducationDocument22 pagesSituational Leadership in EducationRoss Thorburn100% (1)
- The Effects of New Technology On Parents Child Relationship in Dina, JhelumDocument4 pagesThe Effects of New Technology On Parents Child Relationship in Dina, JhelumThe Explorer IslamabadNo ratings yet
- The ScuttlebuttDocument10 pagesThe ScuttlebuttFlotilla 12-8No ratings yet
- Resume SeetaRamDocument2 pagesResume SeetaRamdasarinaveenNo ratings yet
- A6 Pet Geo Flyer FinalDocument2 pagesA6 Pet Geo Flyer Finalred familyNo ratings yet
- Logical Operators in CDocument5 pagesLogical Operators in CBrajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS OPERATION and IMPLEMENTATIONDocument51 pagesBUSINESS OPERATION and IMPLEMENTATIONclangdelacruz007No ratings yet
- Early AdulthoodDocument1 pageEarly AdulthoodCherry BobierNo ratings yet
- 「山場」與「岩韻」:武夷茶的風土條件與市場價値結構Document38 pages「山場」與「岩韻」:武夷茶的風土條件與市場價値結構szeon100% (1)
- SOAL-Latihan Soal UN Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesSOAL-Latihan Soal UN Bahasa InggrisMarciana Sarena TauNo ratings yet
- Teen Explorer New 7 Bank PomyslowDocument132 pagesTeen Explorer New 7 Bank PomyslowmgregorowiczNo ratings yet
Human Resource Management Chapter 7 Reviewer
Human Resource Management Chapter 7 Reviewer
Uploaded by
Nikkson Cayanan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views6 pagesThis document discusses recruiting, selecting, training, and developing employees. It covers the meaning and process of recruiting, including organizational goals of attracting qualified candidates and providing realistic job previews. The recruiting process involves workforce planning, building a candidate pool through various methods like job postings, recommendations, advertisements, agencies, and digital recruiting. Internal recruiting has advantages like increasing motivation and sustaining company culture, while external recruiting draws from outside applicant pools.
Original Description:
A reviewer for students taking up Human Resource Management on chapter 7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses recruiting, selecting, training, and developing employees. It covers the meaning and process of recruiting, including organizational goals of attracting qualified candidates and providing realistic job previews. The recruiting process involves workforce planning, building a candidate pool through various methods like job postings, recommendations, advertisements, agencies, and digital recruiting. Internal recruiting has advantages like increasing motivation and sustaining company culture, while external recruiting draws from outside applicant pools.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views6 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 7 Reviewer
Human Resource Management Chapter 7 Reviewer
Uploaded by
Nikkson CayananThis document discusses recruiting, selecting, training, and developing employees. It covers the meaning and process of recruiting, including organizational goals of attracting qualified candidates and providing realistic job previews. The recruiting process involves workforce planning, building a candidate pool through various methods like job postings, recommendations, advertisements, agencies, and digital recruiting. Internal recruiting has advantages like increasing motivation and sustaining company culture, while external recruiting draws from outside applicant pools.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Chapter 7: Recruiting, Selecting, 1.
Various potential employment - examining past data to predict
opportunities future demands
Training, and Developing Employees
➢ Financial income 2. Ratio analysis
➢ Job security - ratio between a particular
The Meaning of Recruiting
➢ Promotion opportunities business variable and the
Recruitment and Selection
➢ Benefits number of employees a
- The process of recruitment and selection are
➢ Challenging work assignments company needs
the means whereby organizations acquire new
The Recruiting and Selection Process 3. The scatter plot
human resources (Due to demand in labor
1. Workforce planning and forecasting - graphical method used to help
workforce)
2. Build a pool of candidates for these jobs by identify the relationship
- They work together and if carried out
recruiting internal or external candidates between two variables.
effectively, organizations will not only have the
3. Have candidates complete application forms
numbers but also the type of human resources
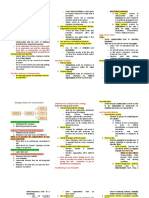
and undergo initial screening interviews Figure 7.1 Organizational and Individual Goals in
it needs for strategy implementation.
4. Use selection tools like tests, background Recruiting
investigations, physical examinations to - Shows the psychological contract
Recruiting
screen candidates 1. Organizational Goals
- Process of developing a pool of qualified
5. Decide who to make an offer to by supervisors a. Attract a pool of qualified candidates
applicants who are interested in working for
b. Keep pool at manageable size
the organization
Workforce Planning c. Provide realistic job previews
- Select the best individuals (those who possess
- Process of deciding what positions the firms 2. Individual Goals
the appropriate KSA)
will have to fill, and how to fill them. a. Meet work-related goals
- The process of locating, identifying, and
- Identify and address the gaps between the b. Meet personal goals
attracting capables to an organization
employer’s workforce today and its projected c. Address personal needs
- Organizational Goals:
workforce needs (Through forecasting and
1. Optimization of qualified applicant pool
looking into employees trends within Internal and External Recruiting
2. Generation of a pool of applicants who organization, retirees or employees leaving) Internal Recruiting
are both qualified and interested - Embrace all future positions from maintenance - Process of looking inside the organization for
3. Providing an honest and candid clerk to CEO existing qualified employees who are eligible
assessment of available jobs and ➢ Succession planning-executive jobs for promotion
opportunities - Employment plans are build on forecast - Given large number of lay-offs and workforce
- Prospective Employee (Applicant’s) Goal - Basic assumptions about the future reductions in recent years, potential applicants
1. Trend analysis
are somewhere between the classification of 4. Word of mouth
there is really an posting openings and
internal and external candidates opportunity for getting inside - Same with referrals
- First to consider: advancement (source of applicants 5. Advertisements
a. Laid-off individuals without motivation - Use of different techniques such as tv
termination (under union ads, newspaper
contracts) Internal candidates May be more committed 6. Employment Agencies
to the company
b. Officially terminated are - Public employment agencies
external candidates, but can be Morale and engagement - Private employment agencies
considered may rise - Agencies associated with non-profit
Methods of Internal Recruiting orgs.
1. Job posting Brings the advantage of 7. Executive search firms
familiarity with the
- Promotion or lateral transfer (same - Headhunter
company (heritage,
effect in salary, just movement in 8. College placements offices
culture, policies,
position) procedures, strategies, - Inexpensive method
2. Supervisory recommendations ways - Can specify qualifications
- Not really recommended as some ➢ Major
supervisors may have certain biases Require less orientation ➢ Grade point average
towards to their inner circle and training
➢ Work experience
Internal Recruiting 9. Digital recruiting
External Recruiting - More diverse group of applicants
Advantages Disadvantages - Process of looking to sources outside the - Time saving
organization for prospective employees 10. Internships
Increases Motivation May foster stagnation
- On-the-job trainings
and stifle creativity
Methods of External Recruiting 11. Recruitment Process Outsourcers
Sustains knowledge and May cause a ripple 1. Drawing from the general pool - Temporary workers and alternative
culture effect (if you promote - If you already have a list of possible staffing
someone to a higher candidates ➢ Temporary agencies
position, his position 2. Using referrals from existing employees 12. Offshoring and Outsourcing
will be vacant so you - Use of employees; telling friends or ● Note: The organization is liable if an
need to hire someone
recommendations organization engages in the services of
again)
3. Using direct applicants or walk-ins discriminating agency. So that it is important
Employees can see that Waste of time in - Those who have submitted resumes
that employment agencies offer equal of qualified applicants developed during the d. Predict which candidates will
opportunity to all recruiting process succeed on the job
- Once you have gathered applicants, it's time - Problematical items:
External Recruiting to identify who to select a. Education
Steps in the Selection Process b. Arrest record
Advantages Disadvantages 1. The recruiting process c. Criminal record
2. Gather information about pool of qualified d. Marital status
Bringing new ideas, new Motivational problems
applicants regarding the levels of requisite e. Membership in organization
perspectives, and new in the organization
ways of doing things knowledge, skills, and abilities possessed by f. Housing
each applicant g. Notification in case of emergency
Avoids ripple effects More expensive than - What they should look into:
internal a. Education, experience, and Basic Selection Criteria
attitude towards work 1. Education and experience
Current Trends in Recruitment b. Impression of current managers - Educational attainment
1. Recruiting a more diverse workforce about their likelihood of success 2. Personal characteristics
➢ Recruiting women 3. Evaluate applications of each applicant - Big Five Personality Traits
➢ Recruiting single parents - Application of explicit and implicit a. Neuroticism
➢ Older workers standards assessing how closely the b. Extraversion
➢ Recruiting minorities individual fits the desired profiles c. Openness to experience
➢ The disabled 4. Make decisions about employment offers d. Agreeableness
2. External Recruiting and Realistic Job e. Conscientiousness
Previews 3. Skills and abilities
- Realistic Job Previews Developing and Using Application Forms - Characteristics that an employee must
➢ Technique for ensuring that job - First step in the process possess
seekers understand the actual - Types of information provided by 4. Hiring for fit
nature of jobs available to them ➢ Make judgements on substantive - The firm might consider hiring a person
matters such as not because of skills alone, but whose
The Meaning of Selection a. Education and experience personal values or personalities align
Selection b. Applicant’s previous progress with the organization
- Concerned with identifying the best candidate and growth
or candidates for the job from among the pool c. Applicant’s stability based on Popular Selection Techniques
previous work record 1. Applications and background checks
- Ask applicants to fill an employment - Project a professional image because
application you are selling yourself so you need to
➢ Weighted application blank make a good impression; first
(predicting person’s ability to impressions last; sometimes
perform a job effectively) impressions are not what you really get
➢ Biodata application blank later on
(more complex and detailed 2. Contrasts error
assessments about the - Evaluation of a target person in a
background) group is affected by the level of
2. Employment tests performance of others in the group.
- Measure characteristics of an 3. Similarity error
individual - Familiarity; if the interviewer and you
➢ Cognitive ability tests came from the same school; bias
➢ Psychomotor ability tests 4. Non-relevancy
➢ Personality tests - External factors that may not be
➢ integrity tests included in interview questions such as
3. Work simulations or work samples appearance, dress, etc.
4. Physical examinations 5. Interviewer’s knowledge of the job
- Not familiar with the job
5. Personal interviews
a. Structured employment interview
b. Semi-structured employment interview
c. Unstructured employment interview The Selection Decision - Multiple Indicators
d. Situational interview By using multiple approaches, firms can
6. Other selection techniques counterbalance the measurement error in one
- References selection technique against another
- Recommendations 1. Banding
- Assessment centers - Permits firms to select applicants from
some underrepresented group in the
Personal Interviews Error organization while still ensuring high
1. First Impression Error performance standards
Selection Errors
Firms make at least one occasional selection error - Apprenticeships: Combination of
and hire the wrong person Legal and Effectiveness Issues in Recruiting and on-the-job training and classroom
1. False Positives Selection instruction
- Applicants who are predicted to be Legal Issues - Vestibule training: Job is performed
successful and are hired but who 1. Organization faced with a prima facie case of under a condition that closely simulates
ultimately fail discrimination must prove that the basis for the real work environment
2. False Negatives selection decision was job related 2. Instructional-based programs
- Applicants who are predicted to fail and - Solution: Demonstrated by - Lectures or discussions
are not hired but who would have been establishing the validity of a selection - Computer-assisted instruction
successful if hired instrument - Programmed instruction
How to address these errors? 2. Evaluating recruiting and selection
a. Using more rigorous tests - Utility analysis:
b. Challenging interviews to selection decisions ➢ Determines the extent to which 3. Management development
a selection system provides - Involves more generalized training for
Two Types of Looking into the instruments in the real benefit to the organization future managerial roles and positions
selection process ➢ Calculating the costs involved 4. Organizational development (OD)
Reliability in the selection errors - System-wide effort to increase the
- Meaning: Consistency of a particular selection Training Techniques organization’s overall performance via
device - A planned attempt by an organization to planned interventions
- Test–retest reliability, alternate-forms reliability, facilitate employee learning of job-related - Techniques used include
and internal consistency reliability (SAT knowledge a. survey
GMAT) ➢ Teaching operational or technical b. feedback,
- All items on the test are measuring the same employees how to do their jobs more c. third-party peacemaking,
thing effectively and efficiently d. process consultation
Validity - Teaching managers and professionals the
- Meaning: Scores on a test are related to skills needed for both present and future jobs
performance on a job ➢ Better understanding of how to work
- Criterion-related validity more effectively
➢ extent to which a selection technique ➢ How to better motivate employees
accurately predicts elements of ➢ How to make better decisions
performance Training and Development Techniques
➢ Simulation or on the job performance 1. Work-based programs
You might also like
- CHRA Reviewer 2Document9 pagesCHRA Reviewer 2Zaila Mitch100% (3)
- Business Canadian 8th Edition Griffin Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesBusiness Canadian 8th Edition Griffin Solutions Manual 1jasmineforddjbxeapiqf100% (26)
- HRM ReviewerDocument3 pagesHRM ReviewerPinks D'CarlosNo ratings yet
- Io PsychDocument30 pagesIo PsychJasmin ValloNo ratings yet
- HRM Amity AssignmentDocument9 pagesHRM Amity Assignmentsiddharth1906No ratings yet
- Business Management and EntrepreneurshipDocument5 pagesBusiness Management and EntrepreneurshipToni CruzNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 StaffingDocument8 pagesLec 7 StaffingThe Daily QuotesNo ratings yet
- StaffingDocument2 pagesStaffingchristianNo ratings yet
- LAS For Organization and Management (Grade 11)Document9 pagesLAS For Organization and Management (Grade 11)rosellerNo ratings yet
- Cbmec 2 ModuleDocument4 pagesCbmec 2 ModuleJacqueline Acera BalingitNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in OrgmaDocument6 pagesReviewer in OrgmaHannah JenneNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Handouts Chapter 5 8Document7 pages2nd Quarter Handouts Chapter 5 8kathlen mae marollanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 RecruitmentDocument44 pagesChapter 4 RecruitmentFaiz ZakariaNo ratings yet
- EM CH5 6 NotesDocument7 pagesEM CH5 6 NotesJerome LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 HR Planning and RecruitingDocument9 pagesChapter 3 HR Planning and RecruitingDaphne DublinNo ratings yet
- Staffing Quarter 2 Week 9 ExpectationsDocument5 pagesStaffing Quarter 2 Week 9 ExpectationsRemar Jhon PaineNo ratings yet
- HRM ReviewerDocument5 pagesHRM ReviewerNeekah JoyNo ratings yet
- Rubrics: Cooperation - 40%Document3 pagesRubrics: Cooperation - 40%Brenda SebandalNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management PrelimsDocument2 pagesHuman Resource Management PrelimsLei PalumponNo ratings yet
- HRM Midterm ReviewerDocument6 pagesHRM Midterm ReviewerKim Alfonzo MenozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Engineering ManagementDocument5 pagesChapter 5 - Engineering ManagementJohn Philip Molina NuñezNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapter 5Document6 pagesSummary Chapter 5Vu Tuan HungNo ratings yet
- HRM MidtermDocument5 pagesHRM MidtermDaniela BallezaNo ratings yet
- Chapter FiveDocument6 pagesChapter FiveamanuelNo ratings yet
- Notes (2nd Sem)Document19 pagesNotes (2nd Sem)GABRIELLE MARI AQUINONo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 RecruitmentDocument8 pagesChapter 4 RecruitmentPhil Andrie LocreNo ratings yet
- System (CCPS) Is One That StoresDocument7 pagesSystem (CCPS) Is One That StoresJoanne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument6 pagesHuman Resource Managementmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- Ad & Mgt. MIDTERMDocument4 pagesAd & Mgt. MIDTERMchuck kieNo ratings yet
- Selection Is As A Series of Hurdles: Development Record FormDocument4 pagesSelection Is As A Series of Hurdles: Development Record Formhesham hassanNo ratings yet
- 2 Fundamentals of HRM2Document18 pages2 Fundamentals of HRM2Wael ALyNo ratings yet
- HRM Test Bank For FinalsDocument26 pagesHRM Test Bank For FinalsdeltonNo ratings yet
- ABM11 - Organization and Management - Q2 - W1-2Document4 pagesABM11 - Organization and Management - Q2 - W1-2Emmanuel Villeja LaysonNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 13Th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesHuman Resource Management 13Th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFtanya.griggs377100% (15)
- Human Resource Management 13th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesHuman Resource Management 13th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manual 1victoriahutchinsontzbpmigrcs100% (28)
- SHRM Group-2Document44 pagesSHRM Group-2xyrieltolentinoNo ratings yet
- Attachment Summary Sheet - General Management Part 3 Lyst9140Document16 pagesAttachment Summary Sheet - General Management Part 3 Lyst9140vipulpandey005No ratings yet
- (Iom) Chap 8-11Document24 pages(Iom) Chap 8-11Tini GarciaNo ratings yet
- Attachment Summary Sheet Part 3Document16 pagesAttachment Summary Sheet Part 3Jyoti RanjanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managementchapter 5Document9 pagesIntroduction To Managementchapter 5Abdulhafiz AbdiNo ratings yet
- Indira School of Business Studies, Pune.: Human Resources ManagementDocument8 pagesIndira School of Business Studies, Pune.: Human Resources ManagementAnkita ShettyNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis and Human Resource PlanningDocument3 pagesJob Analysis and Human Resource PlanningLawrenze Abby LuceroNo ratings yet
- RAndS 048-054Document78 pagesRAndS 048-054zeewaqar aliNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and Selection: STUDENT NAME: - DATEDocument7 pagesRecruitment and Selection: STUDENT NAME: - DATEsyeda maryemNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Recruitment PDFDocument2 pagesSession 5 Recruitment PDFLeonard LiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Strategic HRMDocument12 pagesModule 2 - Strategic HRMAnna Martella FabianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document25 pagesChapter 3Aryan Bin RezaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document15 pagesChapter 03Qasim Jahangir WaraichNo ratings yet
- Recruitment (Human Resource Management)Document44 pagesRecruitment (Human Resource Management)Louise EulogioNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument15 pagesHuman Resource Managementsomasekhar reddy1908No ratings yet
- 4 - Planning JobsDocument28 pages4 - Planning JobsMehwish ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Em Kinn NGG GinsDocument6 pagesEm Kinn NGG Ginsarvin paruliNo ratings yet
- Ijramt V3 I7 11Document4 pagesIjramt V3 I7 11PREETI GUPTANo ratings yet
- HR Exam NoteDocument6 pagesHR Exam NoteMuhammad IrsyadNo ratings yet
- French: Introduction To Human Resource Management Human Resource ManagementDocument16 pagesFrench: Introduction To Human Resource Management Human Resource ManagementZ VerNo ratings yet
- PPT3 HumanResourceManagement 20230615022350Document20 pagesPPT3 HumanResourceManagement 20230615022350Grace AngelinNo ratings yet
- The Story So Far (Week 5)Document20 pagesThe Story So Far (Week 5)Mina KangNo ratings yet
- Recruitment of Employees Write UpDocument7 pagesRecruitment of Employees Write UpArlene TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Supervised By: MR - Ait CherkiDocument40 pagesHuman Resource Management: Supervised By: MR - Ait CherkiHiba jerraNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 1 Reviewer - The Nature of Human Resource ManagementDocument5 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 1 Reviewer - The Nature of Human Resource ManagementNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 9 ReviewerDocument5 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 9 ReviewerNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 6 ReviewerDocument4 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 6 ReviewerNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 5 Reviewer - Information For Making Human Resource DecisionsDocument4 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 5 Reviewer - Information For Making Human Resource DecisionsNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf - Merged (3) - 111-120Document10 pagesIlovepdf - Merged (3) - 111-120kanishka saxenaNo ratings yet
- List of 400 English Synonyms & Antonyms - Practice To Beat Competition PDFDocument18 pagesList of 400 English Synonyms & Antonyms - Practice To Beat Competition PDFSaket SaxenaNo ratings yet
- NeijiaDocument5 pagesNeijiaCarlos Estrada MarzoNo ratings yet
- 2.what Is Partnership Briefly State Special Features of A Partnership On The Basis of Which Its Existence Can Be Determined Under The Indian Partnership ActDocument162 pages2.what Is Partnership Briefly State Special Features of A Partnership On The Basis of Which Its Existence Can Be Determined Under The Indian Partnership ActJohn Wesley100% (1)
- MTICDocument5 pagesMTICSonali TanejaNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction-BIO282 LMSDocument19 pagesL1 Introduction-BIO282 LMSGaayithri RNo ratings yet
- 2011 Equipment Flyer 05272011updatedDocument24 pages2011 Equipment Flyer 05272011updatedChecho BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Art and CraftsDocument108 pagesArt and CraftsArus TündeNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons About Judicial ReviewDocument2 pagesPros and Cons About Judicial ReviewCharlotte SamuelsNo ratings yet
- Skills Framework For Design Technical Skills and Competencies (TSC) Reference DocumentDocument2 pagesSkills Framework For Design Technical Skills and Competencies (TSC) Reference DocumentdianNo ratings yet
- Xanathar's Guide To Everything Deluxe-Pages-34Document1 pageXanathar's Guide To Everything Deluxe-Pages-34Justin SteeleNo ratings yet
- Acs Hillingdon Welcomeguide2019Document55 pagesAcs Hillingdon Welcomeguide2019api-294216460No ratings yet
- UnivariateRegression 3Document81 pagesUnivariateRegression 3Alada manaNo ratings yet
- Poranek (Peer Gynt)Document21 pagesPoranek (Peer Gynt)Katarzyna ChronowskaNo ratings yet
- Mca MaterialDocument30 pagesMca MaterialsharmilaNo ratings yet
- Wwek 2Document34 pagesWwek 2repiresNo ratings yet
- Vmware Vrealize Automation: Install Configure Manage (V7.6) : View OnlineDocument5 pagesVmware Vrealize Automation: Install Configure Manage (V7.6) : View OnlineSandeep GangadharanNo ratings yet
- RETDEM - Wearing of Appropriate PPEsDocument4 pagesRETDEM - Wearing of Appropriate PPEsYo MamaNo ratings yet
- Ipo Sylabus and BooksDocument3 pagesIpo Sylabus and BooksNaseema Chan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Situational Leadership in EducationDocument22 pagesSituational Leadership in EducationRoss Thorburn100% (1)
- The Effects of New Technology On Parents Child Relationship in Dina, JhelumDocument4 pagesThe Effects of New Technology On Parents Child Relationship in Dina, JhelumThe Explorer IslamabadNo ratings yet
- The ScuttlebuttDocument10 pagesThe ScuttlebuttFlotilla 12-8No ratings yet
- Resume SeetaRamDocument2 pagesResume SeetaRamdasarinaveenNo ratings yet
- A6 Pet Geo Flyer FinalDocument2 pagesA6 Pet Geo Flyer Finalred familyNo ratings yet
- Logical Operators in CDocument5 pagesLogical Operators in CBrajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS OPERATION and IMPLEMENTATIONDocument51 pagesBUSINESS OPERATION and IMPLEMENTATIONclangdelacruz007No ratings yet
- Early AdulthoodDocument1 pageEarly AdulthoodCherry BobierNo ratings yet
- 「山場」與「岩韻」:武夷茶的風土條件與市場價値結構Document38 pages「山場」與「岩韻」:武夷茶的風土條件與市場價値結構szeon100% (1)
- SOAL-Latihan Soal UN Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesSOAL-Latihan Soal UN Bahasa InggrisMarciana Sarena TauNo ratings yet
- Teen Explorer New 7 Bank PomyslowDocument132 pagesTeen Explorer New 7 Bank PomyslowmgregorowiczNo ratings yet