Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Resource Management Chapter 9 Reviewer
Human Resource Management Chapter 9 Reviewer
Uploaded by
Nikkson Cayanan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views5 pagesThis document discusses compensation and benefits in organizations. It defines compensation as rewards provided to employees for their work, including wages and salaries. Benefits are additional items of value beyond wages like healthcare. The purposes of compensation are to provide fair pay according to the law and employee performance, help employees focus on important tasks, and serve as motivation. Compensation strategies consider the organization's strategy, ability to pay, ability to attract workers, and ability to bargain with unions. Job evaluation methods like classification systems and point systems determine the relative value of jobs to set appropriate compensation.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses compensation and benefits in organizations. It defines compensation as rewards provided to employees for their work, including wages and salaries. Benefits are additional items of value beyond wages like healthcare. The purposes of compensation are to provide fair pay according to the law and employee performance, help employees focus on important tasks, and serve as motivation. Compensation strategies consider the organization's strategy, ability to pay, ability to attract workers, and ability to bargain with unions. Job evaluation methods like classification systems and point systems determine the relative value of jobs to set appropriate compensation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views5 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 9 Reviewer
Human Resource Management Chapter 9 Reviewer
Uploaded by
Nikkson CayananThis document discusses compensation and benefits in organizations. It defines compensation as rewards provided to employees for their work, including wages and salaries. Benefits are additional items of value beyond wages like healthcare. The purposes of compensation are to provide fair pay according to the law and employee performance, help employees focus on important tasks, and serve as motivation. Compensation strategies consider the organization's strategy, ability to pay, ability to attract workers, and ability to bargain with unions. Job evaluation methods like classification systems and point systems determine the relative value of jobs to set appropriate compensation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
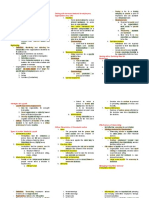
Chapter 9: Compensation and Benefits - Proper amount of wage or salary given - How do they compare?
to employee based on the law; what is a. Pay surveys: surveys of
The Meaning of Compensation and Benefits prescribed compensation paid to
Compensation - Equitable means fair or impartial; employees by other employers
- Set of rewards that organizations provide to employee wants to feel valued in a particular geographic area,
individuals for their willingness to perform - Salary should be reflective of the industry, or occupational group
tasks employee’s performance b. Wage surveys: surveys for
Benefits 2. Help employees focus on activities that the organizations so they have a
- Various items of value beyond wages that organization considers important basis for wage; business
employees receive from the organization - If they can finish a task earlier than publications; Businessweek,
a. Rewards expected, companies often give Fortune; National Business
b. Incentives benefits. Wage versus Salary
Total Compensation - Employees may work extra if they Wages
- Refers to the overall value of financial receive extra benefits - Hourly compensation paid to operating
compensation plus the value of additional 3. Can serve as a motivational purpose. employees
benefits that the organization provides. Increase employee efforts along desired - Time acts as the basis for determining wages
● In any organization, the amount of value create lines ➢ Lower level of operational jobs (40
for an organization and what the organization - Can be both a motivator and hours)
gives them as compensation are important demotivator; ➢ For specific blocks of their hours; one
determinants of organizational competitiveness - If what they receive is fair, then they or two weeks; employees rendering
Compensation and Benefits are likely to be inspired to work harder. service per hour or day
- Various types of incentives employees receive Vice versa. ➢ Laborers, sales lady, milktea,
for their time at work snackbars, fast food chains
- It could never be the result of just random Two Types of Equity Salary
decisions 1. Internal Equity - Income paid to an individual on the basis of
- It is a result of careful and systematic strategy - Comparisons made by employees to performance, not on the basis of time
and understanding of the basic purposes other employees within the same - Usually every 15th or end of month
- Pay service organization - These are for professionals or managerial
2. External Equity employees
The Basic Purposes of Compensation - Comparisons made by employees to - Product managers in areas of finance or
1. Provide appropriate and equitable rewards others employed by different accounting
to employees organizations performing similar jobs - Annual long basis for their salaries
Job Evaluation
Determinants of Compensation Strategy - Determining the relative value or worth of a job
Aside from looking at the market to the organization to compensate an
1. Overall organizational strategy individual adequately and appropriately
- How can the organization accomplish
its goal through its strategy Job-Evaluation Methods
- Vision, mission, weaknesses, 1. Classification system
strengths, opportunities, and threats - Attempts to group sets of jobs together
- What is going on in the global market into clusters
- On what it will give to employees as a. Grades
Benefits of paying above-market rate
salary based on its existing funds or b. Ranked at level of importance
1. Attracting better employee
financial resources in terms of difficult,
2. Minimizing voluntary turnover
2. Ability to pay sophistication, or required skills
- Knowing the strategies, will result in and abilities
Disadvantage of paying above-market rate
profit that will also determine the c. Determine how many
1. Additional cost to employer
reserves and resources of its ability to classifications or categories to
2. Employees may have sense of entitlement
pay use
When is it possible for organizations to pay
3. Ability to bargain with the unions 2. Point system
below-market rate
- Some companies have their unions, it - Requires managers to quantify value of
- When there is an existing high unemployment
is important that the union’s demands various elements of specific jobs in
rate
are met. objective terms
- What would you choose? Employed but low
4. Ability to attract and retain employees a. Point manual: Carefully and
salary or no job at all
- Whether located in attractive specifically defines the degrees
Benefits of paying below-market rate
employees of points from first to fifth
1. Lower labor cost
- Whether organization offers different - What is the Basis:
Disadvantage Of paying below-market rate
perks Responsibilities, skills,
1. Employes will not be satisfied
● Once you know which strategy to use, you physical effort, mental
2. Less motivated
have to consider also what is the basis of effort, and working
3. Low-morale because they are not being paid
giving this rate - evaluation of job or conditions.
properly
performance of employees b. Factor-comparison method:
4. Employees feel that they are paid and there
Assesses jobs on a
might be resentment
The Meaning of Job Evaluation factor-by-factor basis using a
factor-comparison scale as a - Some organizations have an avail of maternity, sickness, disability,
benchmark open-system retirement, funeral and death benefits.
- Jobs are evaluated 2. Pay compression 2. Government Service Insurance System
against standard - Equal pay granted to employees with (GSIS)
key-points different levels of experience, or - serves as the counterpart social
- Detailed and meticulous performance abilities, or both insurance program for those who work
method for evaluation ➢ Pay inversion: New in government.
jobs employees are paid more than 3. Worker’s/ Employees' Compensation (EC)
- Extremely complex, experienced employees - program aims to assist workers who
time-consuming, and Nature of Benefits Programs suffer work-connected sickness or
expensive Most organizations provide their employees with an injury resulting in disability or death.
array of benefits. Some companies actually spend The benefits under the EC program
Pay for Knowledge and Skill-Based Pay more with benefits than the actual salary to attract may be enjoyed simultaneously with
Pay for knowledge employees benefits under the Social Security
- Involves compensating employees for learning - Cost of benefits programs program effective June 1984. 1.
specific information ➢ Organizations spend huge amounts on 4. Retirement Benefit (% under Labor Laws)
- Example: Programmers, specialists benefits - For retired employees
Skill-based pay ➢ Employees are asked to bear costs of
- Rewards employees for acquiring new skills benefits 5. Philippine Health Insurance Corporation
- Example Laborers, mananahi, construction (PhilHealth)
workers - Purposes of benefits programs - is a government corporation attached
➢ Attracts better-qualified people to the Department of Health. It
Wage and Salary Administration ➢ Affects job satisfaction and subsequent administers the National Health
- Ongoing process of managing a wage and turnover Insurance Program, which was
salary structure; can never be permanent Mandated Benefits established to provide health insurance
because of laws or revisions in labor code 1. Social Security System coverage and ensure affordable and
- Designed to provide limited income to accessible health care services for all
Issues Related to Compensation retired individuals Filipinos.
1. Pay secrecy - is a social insurance program that aims 6. Home Development Mutual Fund (HDMF)
- Extent to which the compensation of to provide protection to its members - more popularly known as the Pag-IBIG
any individual in an organization is and beneficiaries. SSS members can Fund, is a Philippine
secret government-owned and controlled
corporation under the Department of 2. Company Retirement Incentives - Efficiency of benefit programs depend on
Human Settlements and Urban 3. Perquisite or Perk effective communication with employees
Development (DHSUD) responsible for
4. Paid Time Off
the administration of the national Legal Issues in Compensation and Benefits
savings program and affordable shelter 5. Wellness Programs ● Fair Labor Standards Act
. - A special program that helps ● Employee Retirement Income Security Act
7. 13th Month Pay (ERISA) of 1974\\
prevent employee sickness
- a mandatory compensation that is
provided to rank-and-file employees by 6. Life cycle benefits (child/elderly care) Contemporary Issues in Compensation and
the end of the calendar year 7. Employee Assistance Plans and Benefits
8. Minimum Wage ● Executive compensation
Perquisites
- lowest remuneration that employers ● Growing legal issues
can legally pay their employees 8. Cafeteria-Style Benefits Plans (Plans that ● Finding the best ways to evaluate
employees can choose/free will) compensation and benefits programs
Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974
(ERISA) Executive Compensation Unemployment insurance
- is a federal United States tax and labor law Provided in two forms - Mandated Benefits
that establishes minimum standards for 1. Base salary - Provides a basic subsistence payment to
pension plans in private industry. It contains - Monthly salary employees who are between jobs
rules on the federal income tax effects of 2. Some form of incentive pay
transactions associated with employee benefit - Bonus
plans. - Stock-option plan
- Passed to protect employees who contributed Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938
to their pensions but were unable to collect Evaluating Compensation and Benefit - Includes provisions for the minimum wage,
those benefits later Programs overtime, and child labor
- Vesting rights become operational after 6 - Organizations that do not offer competitive pay - •Comp time: Time off that is offered to
years at the most, and employees with less and benefit packages find it difficult to attract nonexempt workers in exchange for working
service are still usually eligible to receive some employees more than 40 hours with no overtime pay
portion of their retirement benefits. ➢ Also leads to high rates of voluntary
turnover Private Pension Plans
Non-Mandated Benefits - Provide income to employees at their
1. Health Plan retirement
- Non-mandated benefit
Employee Assistance Plan
- A special program that helps employees with
drug or alcohol problems
You might also like
- Solomon Islands Truth and Reconciliation Volume 5Document205 pagesSolomon Islands Truth and Reconciliation Volume 5Rexy RosesNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Services MarketingDocument84 pagesMCQ in Services MarketingAnonymous WtjVcZCg58% (12)
- Glaxo Smith Klien Sales PresentationDocument28 pagesGlaxo Smith Klien Sales PresentationAdnan JawedNo ratings yet
- Data Integration Specification V4Document74 pagesData Integration Specification V4Siva MaNo ratings yet
- Managing Health Services Organizations and Systems Table of ContentsDocument6 pagesManaging Health Services Organizations and Systems Table of ContentsHealth Professions Press, an imprint of Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co., Inc.0% (4)
- Internship Report MBA - UpdatedDocument47 pagesInternship Report MBA - Updatedshakeel_pak71% (7)
- Compensation HRMDocument27 pagesCompensation HRMAkshat SinghNo ratings yet
- Job-Based, Skill/competency-Based, Market-Based, or A Combination ofDocument9 pagesJob-Based, Skill/competency-Based, Market-Based, or A Combination ofCristina Crong MorgiaNo ratings yet
- Compensation Administration ReviewerDocument26 pagesCompensation Administration ReviewerprivsobelNo ratings yet
- Compensation Administration (Chap. 1)Document7 pagesCompensation Administration (Chap. 1)Mekko EllaineNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument8 pagesHuman Resource ManagementBielan Fabian GrayNo ratings yet
- Compensation ReviewerDocument17 pagesCompensation Reviewerdenise marieNo ratings yet
- G11 Org. MNGT Q2WK11 ABCDwithAnswerKeyDocument9 pagesG11 Org. MNGT Q2WK11 ABCDwithAnswerKeyMelanie Anaud Magro-AmosNo ratings yet
- Lesson #1Document2 pagesLesson #1Michaella Dela torreNo ratings yet
- 3 HRM Basics - Compensation ManagementDocument2 pages3 HRM Basics - Compensation ManagementWilvert WongNo ratings yet
- COMPENSATIONDocument19 pagesCOMPENSATIONkerynsantos026No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 HBO 1Document10 pagesChapter 6 HBO 1Mars MandigmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-8Document6 pagesLecture 6-8kerynsantos026No ratings yet
- Compensation Management - Session 1Document17 pagesCompensation Management - Session 1IrfaN TamimNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Employee Compensation GuideDocument4 pagesHuman Resource Management: Employee Compensation Guideaqsa goharNo ratings yet
- Assignment Cover Sheet: School of BusinessDocument6 pagesAssignment Cover Sheet: School of BusinessThao Nguyen Thi ThuNo ratings yet
- Compensation/wages and Performance Evaluation/appraisal: Group 3Document18 pagesCompensation/wages and Performance Evaluation/appraisal: Group 3Ellen BuddyNo ratings yet
- ABM11 - Organization and Management - Q2 - W3-4Document5 pagesABM11 - Organization and Management - Q2 - W3-4Emmanuel Villeja LaysonNo ratings yet
- Compensation & Benefits SessionDocument65 pagesCompensation & Benefits Sessionahmed HammoudNo ratings yet
- Compensation and AdminitrationDocument3 pagesCompensation and Adminitrationkhrizia abadNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Wage, Salary and Reward AdministrationDocument34 pagesHuman Resource Management: Wage, Salary and Reward AdministrationMOHAMMED ALI CHOWDHURY100% (1)
- F COMPENSATION SYSTEMstudDocument6 pagesF COMPENSATION SYSTEMstudDivjaNo ratings yet
- HRM8 Compensating HRDocument12 pagesHRM8 Compensating HRarantonizhaNo ratings yet
- CHPTR9 CompensationDocument26 pagesCHPTR9 CompensationElyn PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Motivation: From Concepts To ApplicationsDocument21 pagesMotivation: From Concepts To ApplicationsranjanNo ratings yet
- HRM - C10 - Developing Compensation Plans (Students)Document27 pagesHRM - C10 - Developing Compensation Plans (Students)kiettran20122004No ratings yet
- CH 5 - Compensation MGTDocument28 pagesCH 5 - Compensation MGTGetnat BahiruNo ratings yet
- It Is All About PeopleDocument21 pagesIt Is All About Peopletharani1771_32442248No ratings yet
- Comp Ben ReviewerDocument5 pagesComp Ben ReviewerJean AlbaciteNo ratings yet
- Reward Management SystemDocument17 pagesReward Management SystemSiya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: TERM-3 Instructor-Kirti MishraDocument22 pagesHuman Resource Management: TERM-3 Instructor-Kirti MishraAnya JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Compensating Human ResourcesDocument27 pagesChapter 8 Compensating Human ResourcesFaye YburanNo ratings yet
- 20n71e0026-Evaluation of Wages and Salary AdministrationDocument16 pages20n71e0026-Evaluation of Wages and Salary Administrationsmartway projectsNo ratings yet
- Compensation Is Any Form of Payment Given To TheDocument24 pagesCompensation Is Any Form of Payment Given To TheRaghu Kishore SasanalaNo ratings yet
- Pay Structures: Dr. Poonam Kaushal Assistant Professor Icfai Business SchoolDocument39 pagesPay Structures: Dr. Poonam Kaushal Assistant Professor Icfai Business SchoolPoonam KaushalNo ratings yet
- 5 Compensation and Reward ManagementDocument3 pages5 Compensation and Reward ManagementHeirron LugueNo ratings yet
- Pay For Performance - Motivating or DemotivatedDocument11 pagesPay For Performance - Motivating or DemotivatedShiv JumaniNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Compensation and Benefit ManagementDocument37 pagesHuman Resource Management: Compensation and Benefit Managementankesh_devNo ratings yet
- HBO Chapter VI - Appraising and Rewarding PerformanceDocument53 pagesHBO Chapter VI - Appraising and Rewarding PerformanceDorisday Caballes EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Compensating Human ResourcesDocument4 pagesCompensating Human ResourcesCherry NavalNo ratings yet
- L11 StrategicPayPlanandIncentivePlansDocument57 pagesL11 StrategicPayPlanandIncentivePlansChíi KiệttNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8: Compensating Human ResourcesDocument41 pagesCHAPTER 8: Compensating Human Resourcesshane50% (2)
- Compensation and RewardDocument7 pagesCompensation and RewardMARC URRUTIA MIRÓNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Written Report Appraising and Rewarding PerformanceDocument5 pagesGroup 4 Written Report Appraising and Rewarding PerformanceEtorne CharlinNo ratings yet
- CLC HRM W9 CompensationDocument27 pagesCLC HRM W9 CompensationThư NguyễnNo ratings yet
- It Is All About PeopleDocument23 pagesIt Is All About PeopleshyamsundarNo ratings yet
- Employee Compensation and Reward ManagementDocument4 pagesEmployee Compensation and Reward ManagementPrabhat AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Module III BM LLL CMDocument24 pagesModule III BM LLL CMNaman AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Math 12 ABM Organization MGT Q2 Week 4Document18 pagesMath 12 ABM Organization MGT Q2 Week 4Lea Faborada100% (1)
- HRM CompensationDocument21 pagesHRM CompensationUnicorn SpiderNo ratings yet
- Io Psych Chap7 Report - 20240320 - 154527 - 0000Document19 pagesIo Psych Chap7 Report - 20240320 - 154527 - 0000claire001024No ratings yet
- CompensationDocument20 pagesCompensationKashif AnwerNo ratings yet
- Krystel Ann Tanawon BSCADocument1 pageKrystel Ann Tanawon BSCAChristelle Kaye BisnarNo ratings yet
- Compensating Human Resource GROUP 3Document41 pagesCompensating Human Resource GROUP 3Mabel RosalesNo ratings yet
- Strategic CompensationDocument24 pagesStrategic Compensationjoahn.rocreo1234No ratings yet
- Unit 2.4 - Motivation - Business HLDocument18 pagesUnit 2.4 - Motivation - Business HLAmbar DunskiNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 14 Edition Chapter 9 & 10 CompensationDocument43 pagesHuman Resource Management 14 Edition Chapter 9 & 10 CompensationTanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- PMRS - Salary & Wages Intro - DhavalDocument49 pagesPMRS - Salary & Wages Intro - Dhavalricha24No ratings yet
- Oam Module 4 - Q2Document22 pagesOam Module 4 - Q2Sherilyn InsonNo ratings yet
- Establishing Strategic Pay PlanDocument29 pagesEstablishing Strategic Pay Planshindidtamim2000No ratings yet
- Model Answer: Literature review on Employee motivation, rewards and performanceFrom EverandModel Answer: Literature review on Employee motivation, rewards and performanceNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 1 Reviewer - The Nature of Human Resource ManagementDocument5 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 1 Reviewer - The Nature of Human Resource ManagementNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 6 ReviewerDocument4 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 6 ReviewerNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 5 Reviewer - Information For Making Human Resource DecisionsDocument4 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 5 Reviewer - Information For Making Human Resource DecisionsNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Chapter 7 ReviewerDocument6 pagesHuman Resource Management Chapter 7 ReviewerNikkson CayananNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument5 pagesPDFsagrikakhandkaNo ratings yet
- Consti2 Cases (C)Document73 pagesConsti2 Cases (C)Ralph HonoricoNo ratings yet
- Ijtk 9 (4) 651-655Document5 pagesIjtk 9 (4) 651-655manash85No ratings yet
- Matrix OrganizationsDocument9 pagesMatrix OrganizationsFairuz Nawfal HamidNo ratings yet
- Ent Case StudyDocument14 pagesEnt Case StudyAmir Aiman33% (3)
- Summative Assessment - Resource & Talent Management - 2Document11 pagesSummative Assessment - Resource & Talent Management - 2riannemarie12No ratings yet
- Berman Enterprises Inc., Standard Tank Cleaning Corp., and General Marine Transport Corp. v. Local 333, United Marine Division, International Longshoremen's Association, Marine Towing and Transportation Employers' Association, McAllister Brothers, Inc., Diesel Vessel Operators, Inc., Spentonbush Transport Service, Inc., Morania Oil Tanker Corporation, Bouchard Transportation Company, Inc., Moran Towing & Transportation Company, Inc., Poling Transportation Corporation, Eklof Marine Corporation, Red Star Marine Services, Inc., Reinauer Transportation Companies, Inc., and Turecamo Coastal & Harbor Towing Corporation, 644 F.2d 930, 2d Cir. (1981)Document13 pagesBerman Enterprises Inc., Standard Tank Cleaning Corp., and General Marine Transport Corp. v. Local 333, United Marine Division, International Longshoremen's Association, Marine Towing and Transportation Employers' Association, McAllister Brothers, Inc., Diesel Vessel Operators, Inc., Spentonbush Transport Service, Inc., Morania Oil Tanker Corporation, Bouchard Transportation Company, Inc., Moran Towing & Transportation Company, Inc., Poling Transportation Corporation, Eklof Marine Corporation, Red Star Marine Services, Inc., Reinauer Transportation Companies, Inc., and Turecamo Coastal & Harbor Towing Corporation, 644 F.2d 930, 2d Cir. (1981)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Bata HRMDocument12 pagesBata HRMNAYAN83% (6)
- Telia ARDocument232 pagesTelia ARmilinthakkar7629No ratings yet
- 12 Chapter3goodDocument44 pages12 Chapter3goodAkbar JanNo ratings yet
- Igcse Econ 2013Document19 pagesIgcse Econ 2013Desmund YewNo ratings yet
- Trade Union Class NotesDocument36 pagesTrade Union Class NotesJitendra DasNo ratings yet
- Motivational Methods and ProgramDocument2 pagesMotivational Methods and ProgramCamae Snyder GangcuangcoNo ratings yet
- Managing Organizational Change For SchoolDocument43 pagesManaging Organizational Change For SchoolAlif IqbalNo ratings yet
- By Yongyuth Chalamwong, Raphaella Prugsamatz, and Khanittha HongprayoonDocument16 pagesBy Yongyuth Chalamwong, Raphaella Prugsamatz, and Khanittha Hongprayoonอภิรักษ์ มานะกิจศิริสุทธิNo ratings yet
- PM Assistance Package (Death Case of Government Service) - Rules of Pakistani GovernmentDocument20 pagesPM Assistance Package (Death Case of Government Service) - Rules of Pakistani GovernmentMuhammad HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- EP RefineriesDocument16 pagesEP Refinerieskselvan_1No ratings yet
- Bus 5910 Written Assignment Unit 2Document6 pagesBus 5910 Written Assignment Unit 2Sheu BasharuNo ratings yet
- Coursework MeaningDocument6 pagesCoursework Meaningvyp0bog1w1m3100% (2)
- CMC vs. LaguesmaDocument4 pagesCMC vs. LaguesmaEnan IntonNo ratings yet
- In The United States District Court For The Northern District of Illinois Eastern DivisionDocument14 pagesIn The United States District Court For The Northern District of Illinois Eastern DivisionThe Daily LineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Day To Day Concern 1Document25 pagesChapter 8 Day To Day Concern 1Umair HashmiNo ratings yet
- INTER 1 Comparatives - Superlatives With Best Countries in The WorldDocument6 pagesINTER 1 Comparatives - Superlatives With Best Countries in The WorldSam PokqtNo ratings yet
- Seminar Slides HRM Application Blanks Group 1Document13 pagesSeminar Slides HRM Application Blanks Group 1navin9849No ratings yet