Professional Documents
Culture Documents
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
Uploaded by
Fatima Nur Faiza HandaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Video Recap of Mutations by Amoeba SistersDocument2 pagesVideo Recap of Mutations by Amoeba Sistersapi-233187566No ratings yet
- Bio-Worksheet-MutationsDocument3 pagesBio-Worksheet-MutationsEbrahimNo ratings yet
- MutationActivity 1Document4 pagesMutationActivity 1Leo GordonNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The FollowingDocument5 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Followingapi-39708077950% (2)
- 3 TransctranslpracticeDocument2 pages3 Transctranslpracticeapi-502781581No ratings yet
- Group Act MutationDocument1 pageGroup Act MutationMonica Grace ManaloNo ratings yet
- Types of Mutations Worksheet PDFDocument3 pagesTypes of Mutations Worksheet PDFsmith joeNo ratings yet
- Video Recap of Mutations v2 by Amoeba Sisters PDFDocument2 pagesVideo Recap of Mutations v2 by Amoeba Sisters PDFsyifaNo ratings yet
- Mutations WSDocument3 pagesMutations WSShraddha BNo ratings yet
- X Men GeneticsDocument2 pagesX Men GeneticsPoohbearrr :No ratings yet
- GENE TO PROTEIN Notes 2023Document5 pagesGENE TO PROTEIN Notes 2023Kristen LindstromNo ratings yet
- Mutations WorksheetDocument5 pagesMutations Worksheetapi-32772460No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Simulation ActivityDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis Simulation ActivitySHARIFAH BINTI HASSAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Part 6 Mutation Winter 2023Document2 pagesPart 6 Mutation Winter 2023tanusehdev17No ratings yet
- RNAProteinSynthesisSE 1 2022-04-29 15 - 38 - 21Document6 pagesRNAProteinSynthesisSE 1 2022-04-29 15 - 38 - 21E ZenaNo ratings yet
- Mutations Activity - GenesyGenomas - LabDocument4 pagesMutations Activity - GenesyGenomas - LabSamuel Morales NavarroNo ratings yet
- Rna Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesRna Protein SynthesisDaniel Hanna86% (7)
- Mutations WorksheetDocument2 pagesMutations Worksheetapi-233187566No ratings yet
- A Level Homework 3Document5 pagesA Level Homework 3szyzypNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3 w5 6Document12 pagesScience 10 Q3 w5 6SaviannaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetCamryn BrickerNo ratings yet
- DNA Mutations WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Mutations Worksheetjanani pulivarthiNo ratings yet
- DNA Mutations WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Mutations WorksheetFumira MisataNo ratings yet
- 13 DNA Mutation SimulationDocument2 pages13 DNA Mutation Simulationlightning TigerNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesStudent Exploration: RNA and Protein SynthesisMasonNo ratings yet
- Rna and Protein Synthesis Guided NotesDocument6 pagesRna and Protein Synthesis Guided NotesqzweqwNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument5 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetVanessa JuatcoNo ratings yet
- N - HS-LS1-1 Protein Synthesis PracticeDocument5 pagesN - HS-LS1-1 Protein Synthesis PracticeMa Anna Cris LumongsudNo ratings yet
- Changes in Dna WorksheetDocument3 pagesChanges in Dna Worksheetapi-257187977No ratings yet
- 6.3 Activity - 3 RNAProteinSynthesisSEDocument6 pages6.3 Activity - 3 RNAProteinSynthesisSEsmol ukeleleNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Activity in Science March 7Document2 pagesAsynchronous Activity in Science March 7xenarealeNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis PPQ'sDocument25 pagesProtein Synthesis PPQ'sAnthony MoloneyNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 Self-Learning Module 3 Central Dogma of The Transfer of Genetic InformationDocument16 pagesScience: Quarter 3 Self-Learning Module 3 Central Dogma of The Transfer of Genetic InformationKaye ViolaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WSDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis WSkatherine corvera100% (1)
- Protein Synthesis Model LabDocument7 pagesProtein Synthesis Model Labmarisa corderoNo ratings yet
- RNAProteinSynthesisSEDocument6 pagesRNAProteinSynthesisSETania Melendez-LainezNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - 1667348288-DNA Mutation Simulation WorksheetDocument3 pagesKami Export - 1667348288-DNA Mutation Simulation WorksheetDava RamadhanNo ratings yet
- AA3 - Worksheet On MutationsDocument2 pagesAA3 - Worksheet On MutationsBernadette NolascoNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis-Worksheet 2018Document5 pagesProtein-Synthesis-Worksheet 2018api-242868690100% (1)
- Mutations Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesMutations Worksheet PDFNouradin Ibrahim OmerNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis-WorksheetDocument3 pagesProtein-Synthesis-WorksheetJohn SchwuchowNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetrebugiocosmeNo ratings yet
- Karas Ghattas - RNA and Protein Synthesis - Pdf.kamiDocument3 pagesKaras Ghattas - RNA and Protein Synthesis - Pdf.kamiKaras GhattasNo ratings yet
- Bio Worksheet MutationsDocument2 pagesBio Worksheet MutationsFelix Robert ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Mutations Worksheet 2Document3 pagesMutations Worksheet 2Dazza DattoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis GizmoDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis GizmoCaleb HutchinsonNo ratings yet
- Molecular Lab 12 Using Neb Cutter 2013Document6 pagesMolecular Lab 12 Using Neb Cutter 2013Soledad SanzNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetG Combalicer Bernice Darielle D.No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following Passage and Answer The Questions BelowDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following Passage and Answer The Questions BelowIris LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma Module For Grade 10 ScienceDocument3 pagesCentral Dogma Module For Grade 10 ScienceJan Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument5 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyMINt Kookie100% (1)
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesROCHELLE MAGBUONo ratings yet
- DNA Mutations Worksheet 12.3Document2 pagesDNA Mutations Worksheet 12.3HS TUCKER0% (1)
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesROCHELLE MAGBUONo ratings yet
- Codon Chart - Visual TaskDocument2 pagesCodon Chart - Visual Taskmustafaabdullhadi0No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab Activity 206Document8 pagesBiochemistry Lab Activity 206Naomi NicoleNo ratings yet
- Gizmo - Rna - Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesGizmo - Rna - Protein SynthesisMarques AlsoppNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma WorksheetDocument8 pagesCentral Dogma WorksheetZyrus AntalanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology & Genetics: Essential Biology Self-Teaching GuideFrom EverandMolecular Biology & Genetics: Essential Biology Self-Teaching GuideNo ratings yet
- RNA and DNA Editing: Molecular Mechanisms and Their Integration into Biological SystemsFrom EverandRNA and DNA Editing: Molecular Mechanisms and Their Integration into Biological SystemsHarold C. SmithNo ratings yet
- BANING Activity No. 5.2 DNA Base PairingDocument3 pagesBANING Activity No. 5.2 DNA Base PairingFatima Nur Faiza HandaNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 5.2 Point and Frameshift MutationsDocument3 pagesActivity No. 5.2 Point and Frameshift MutationsFatima Nur Faiza HandaNo ratings yet
- Food Intake Is Influenced By: Geographical, Economic: Factors, Personal Taste, IdiosyncrasiesDocument1 pageFood Intake Is Influenced By: Geographical, Economic: Factors, Personal Taste, IdiosyncrasiesFatima Nur Faiza HandaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry NotesDocument2 pagesBiochemistry NotesFatima Nur Faiza HandaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Lectures - (Lesson 1-3)Document7 pagesEnvironmental Science Lectures - (Lesson 1-3)Fatima Nur Faiza HandaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Cell Division Mitosis and MeiosisDocument87 pagesLesson 4 - Cell Division Mitosis and MeiosisHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Kajtez NatCommun 2016Document11 pagesKajtez NatCommun 2016Luka JandricNo ratings yet
- Anther and Pollen CultureDocument2 pagesAnther and Pollen CulturesheetupatelNo ratings yet
- Sci8 q4 Mod2 v4Document31 pagesSci8 q4 Mod2 v4Jay-ar RiosNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Extra QuestionsDocument10 pagesReproduction Extra Questionschayyakudopa9No ratings yet
- Constantinou (1998) Spectral Philia and The Imaginary Institution of NeedsDocument31 pagesConstantinou (1998) Spectral Philia and The Imaginary Institution of Needsbodil0carinaNo ratings yet
- Cleavage Partitions The Zygote Into Many Smaller CellsDocument10 pagesCleavage Partitions The Zygote Into Many Smaller CellssispulieNo ratings yet
- Neet Wizz Bio Class 12Document89 pagesNeet Wizz Bio Class 12Aarthi T. UNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Cell Division: 6.2: Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument18 pagesChapter 6: Cell Division: 6.2: Cell Cycle and MitosisMohammed Ridzuwan0% (1)
- NCERT Class 12 Biology Human ReproductionDocument15 pagesNCERT Class 12 Biology Human ReproductionSrajanNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 General Biology2 Q4 Module 1 Reproduction and Development. For PrintingDocument13 pagesGrade 12 General Biology2 Q4 Module 1 Reproduction and Development. For Printingairamaymalicdem052No ratings yet
- ACFrOgAwVytqvG4xDsbm NUyWfZ6sq1jWDZWkLfONw1PueWKn MgV8qTjPdeA-08USc5v 9KyY JeQorFlxiIXg21s0cWuiu2FnXYzJgCRb6vM62BzH8EZJJxoApxEcjCOTgLllkuzP9PhwR3phzDocument14 pagesACFrOgAwVytqvG4xDsbm NUyWfZ6sq1jWDZWkLfONw1PueWKn MgV8qTjPdeA-08USc5v 9KyY JeQorFlxiIXg21s0cWuiu2FnXYzJgCRb6vM62BzH8EZJJxoApxEcjCOTgLllkuzP9PhwR3phzjundon.ivo.deborjaNo ratings yet
- 9th Biology Chapter-WiseDocument18 pages9th Biology Chapter-WiseMalik AqibNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Genetic ControlDocument57 pagesCell Structure and Genetic ControlMOHANNAD ALNEMAHNo ratings yet
- 8 Worksheet Reproduce FloweringDocument2 pages8 Worksheet Reproduce Floweringelsa khairunnisa100% (3)
- Epigenetics and Chromatin RemodellingDocument30 pagesEpigenetics and Chromatin RemodellingMaxine RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Notes For FungiDocument10 pagesNotes For FungiФMuhammdф Atif .No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Inquiry - DPDocument5 pagesCell Cycle Inquiry - DPYuree ChoiNo ratings yet
- Botany - 2Document2 pagesBotany - 2tadepalli patanjaliNo ratings yet
- Basic PathologyDocument35 pagesBasic Pathologyshinichi kudoNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants (CAPE)Document60 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants (CAPE)shakiraNo ratings yet
- Animal ReproductionDocument93 pagesAnimal ReproductionunattractiveyouNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 ReproductionDocument46 pagesTopic 3 ReproductionHapsah MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants 7th GradeDocument14 pagesReproduction in Plants 7th Grade5545116.shreyastammeneniNo ratings yet
- Gene Regulation - Lac Operon & TRP OperonDocument25 pagesGene Regulation - Lac Operon & TRP OperonSalam Pradeep Singh75% (12)
- زراعة انسجة نباتيةDocument127 pagesزراعة انسجة نباتيةHewa HusenNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Inhibitor Dan Analisis Enzim KatalaseDocument14 pagesEnzyme Inhibitor Dan Analisis Enzim Katalaseg.islamiNo ratings yet
- Chromatin Remodeling Complexes - The Regulators of Genome FunctionDocument19 pagesChromatin Remodeling Complexes - The Regulators of Genome FunctionManisha DasNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Planner AakashDocument3 pagesPractice Test Planner AakashthekiddiedreamsNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle BBDocument103 pagesCell Cycle BBKrishna Priyam SinghNo ratings yet
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
Uploaded by
Fatima Nur Faiza HandaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
Uploaded by
Fatima Nur Faiza HandaCopyright:
Available Formats
www.LessonPlansInc.
com
Topic: Gene Mutations WS
Summary: Students will learn about frame shift mutations and base substitution
mutations.
Goals & Objectives: Students will be able to demonstrate how mutations change the
amino acid sequence. Students will be able to explain the difference between mutations.
Standards: CA Biology 4c. Students know mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene
may or may not affect the expression of the gene or the sequence of amino acids in an
encoded protein.
Time Length: 40 minutes
Prerequisite Knowledge: Students know the rules for DNA / RNA base pairing.
Students know what are protein synthesis, purines, pyrimidines, and how to use a codon
table.
Materials:
• Handouts and pencils
Procedures:
1. Review with the class about point mutations and the differences between frame shift
and base substitution.
2. Students work on the handout by themselves.
Accommodations: Students with an IEP can take the handout home if they need extra
time, and/or do questions 1 - 3 and questions 11 - 24.
Evaluation:
Each line with and underline is worth one point for a total of 25 points. Students should
have circled the mutated DNA or amino acid to help speed up grading.
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
Name: _______________________ Row: _______
Date:_____________ Period:______
Gene Mutations Worksheet
There are two types of mutations, small-scale gene mutations and large-scale
chromosomal mutations. You will do gene (point) mutations in this handout. Since
mRNA is read in threes (codons), an addition or deletion of a base changes the reading
frame of the sequence.
FRAMESHIFT MUTATIONS
The insertion shifts the reading frame to the right. The deletion frame shifts the reading
frame to the left. Insert a letter C for the two insertion questions and for the deletion
questions, delete the H or one base letter.
Write each codon per line.
DNA Sentence THE BOY CUT HIS LIP AND ATE THE HOT DOG
Insertion THE BOY ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____
٨
Deletion THE BOY CUT ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____
٧
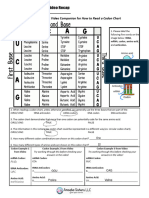
Now use real DNA code and translate it into the correct amino acids. Decide where in
the original DNA code to cause a mutation on the rest of the questions. Please use the
codon table on the last page to find the corresponding amino acids.
Write each codon per line and circle the mutated DNA base where the mutation took place.
Original DNA TAC GGA CGA TCT CAG GAG CCT ATA ATC
Insertion DNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated mRNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated Amino Acids _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Original Amino Acid Met Pro Ala Arg Val Leu Gly Tyr STOP
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
Write each codon per line and circle the mutated DNA base where the mutation took place.
Original DNA TAC GGA CGA TCT CAG GAG CCT ATA ATC
Deletion DNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated mRNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated Amino Acids _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Original Amino Acid Met Pro Ala Arg Val Leu Gly Tyr STOP
Usually a frame shift mutation results in the synthesis of a nonfunctional protein.
Why do you think your mutated proteins might not be functional?
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
BASE SUBSTITUTION MUTATIONS
For simplicity, change only one base for all the following base substitution mutations.
A different type of gene mutation is called base substitution. It is the simplest type of
mutation where a nucleotide pair is replaced with a different nucleotide pair.
Base Substitution GAC → GGC
One type of base substitution is called transversion mutation. Transversion mutation
happens when one purine (A, G) is swapped with a pryimidine (C, T).
Purine → Pyrimidine GAC → TAC
Pyrimidine → Purine GAC → GAG
Use the DNA code below to demonstrate a purine → pyrimidine transversion mutation.
All you have to do is change one DNA base.
Write each codon per line and circle the mutated amino acid.
Original DNA TAC CAT GCA GAT CTG GCC CAG TTC ATC
Transversion DNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated mRNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated Amino Acid _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Original Amino Acid Met Val Arg Leu Asp Arg Val Lys STOP
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
The opposite of transversion mutations is transition mutations. A transition mutation
happens when one purine is swapped with the other purine or pyrimidine with
pyrimidine.
Purine → Purine GAC → AAC
Pyrimidine → Pyrimidine GAC → GAT
Use the DNA code below to demonstrate a purine → purine transition mutation. All you
have to do is change one DNA base.
Write each codon per line and circle the mutated amino acid.
Original DNA TAC GTC GCT CAA CGG GAC CTG ACC ACT
Transition DNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated mRNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated Amino Acid _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Original Amino Acid Met Gln Arg Val Ala Leu Asp Trp STOP
A third type of base substitution is called silent mutation. Silent mutation happens when
one base in a codon is changed but both code for the same amino acid.
DNA CTT → CTG
Amino Acid Leu → Leu
Use the DNA code below to demonstrate a silent mutation. All you have to do is change
one DNA base but the amino acid stays the same.
Write each codon per line and circle the mutated DNA base.
Original DNA TAC CAT TCT CGG TGT AAA AGG GCG ATT
Silent DNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated mRNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated Amino Acid _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Original Amino Acid Met Val Arg Ala Thr Phe Ser Arg STOP
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
A base mutation that creates a new stop codon in place of an amino acid is called a
nonsense mutation.
DNA TGT → TGA
Amino Acid Cys → STOP
Use the DNA code below to demonstrate a nonsense mutation. All you have to do is
change one DNA base to create a new stop codon.
Write each codon per line and circle the mutated amino acid.
Original DNA TAC GGT AAT CAA ATA GAA CCT GAG ACT
Nonsense DNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated mRNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated Amino Acid _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Original Amino Acid Met Pro Leu Val Tyr Leu Gly Leu STOP
Please explain the difference between a frame shift mutation and a base substitution
mutation.
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
Codon Table
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
Gene Mutations Worksheet Key
There are two types of mutations, small-scale gene mutations and large-scale
chromosomal mutations. You will do gene (point) mutations in this handout. Since
mRNA is read in threes (codons), an addition or deletion of a base changes the reading
frame of the sequence.
FRAMESHIFT MUTATIONS
The insertion shifts the reading frame to the right. The deletion frame shifts the reading
frame to the left. Complete the following lines for frame shift mutations.
Write each codon per line.
DNA Sentence THE BOY CUT HIS LIP AND ATE THE HOT DOG
Insertion THE BOY CCU THI SLI PAN DAT ETH EHO TDO
C
Comment [S1]: Insert base C
٨
Deletion THE BOY CUT ISL IPA NDA TET HEH OTD OG Comment [S2]: Delete base H
٧
Now use real DNA code and translate it into the correct amino acids. Decide where in
the original DNA code to cause a mutation on the rest of the questions. Please use the
codon table on the last page to find the corresponding amino acids.
Write each codon per line and circle the mutated DNA base where the mutation took place. Comment [S3]: Students can choose
where to insert a new base anywhere
Original DNA TAC GGA CGA TCT CAG GAG CCT ATA ATC which will cause different answers.
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
Insertion DNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated mRNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated Amino Acids _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Original Amino Acid Met Pro Ala Arg Val Leu Gly Try STOP
Write each codon per line and circle the mutated DNA base where the mutation took place. Comment [S4]: Students can choose
where to delete a base anywhere.
Original DNA TAC GGA CGA TCT CAG GAG CCT ATA ATC
Deletion DNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated mRNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated Amino Acids _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Original Amino Acid Met Pro Ala Arg Val Leu Gly Try STOP
Usually a frame shift mutation results in the synthesis of a nonfunctional protein.
Why do you think your mutated proteins might not be functional?
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
BASE SUBSTITUTION MUTATIONS
A different type of gene mutation is called base substitution. It is the simplest type of
mutation where a nucleotide pair is replaced with a different nucleotide pair.
Base Substitution GAC → GGC
One type of base substitution is called transversion mutation. Transversion mutation
happens when one purine (A, G) is swapped with a pryimidine (C, T).
Purine → Pyrimidine GAC → TAC
Pyrimidine → Purine GAC → GAG
Use the DNA code below to demonstrate a purine → pyrimidine transversion mutation.
All you have to do is change one DNA base.
Write each codon per line and circle the mutated amino acid.
Original DNA TAC CAT GCA GAT CTG GCC CAG TTC ATC
Transversion DNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
Mutated mRNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated Amino Acid _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Original Amino Acid Met Val Arg Leu Asp Arg Val Lys STOP
The opposite of transversion mutations is transition mutations. A transition mutation
happens when one purine is swapped with the other purine or pyrimidine with
pyrimidine.
Purine → Purine GAC → AAC
Pyrimidine → Pyrimidine GAC → GAT
Use the DNA code below to demonstrate a purine → purine transition mutation. All you
have to do is change one DNA base.
Write each codon per line and circle the mutated amino acid.
Original DNA TAC GTC GCT CAA CGG GAC CTG ACC ACT
Transition DNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated mRNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated Amino Acid _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Original Amino Acid Met Gln Arg Val Ala Leu Asp Trp STOP
A third type of base substitution is called silent mutation. Silent mutation happens when
one base in a codon is changed but both code for the same amino acid.
DNA CTT → CTG
Amino Acid Leu → Leu
Use the DNA code below to demonstrate a silent mutation. All you have to do is change
one DNA base but the amino acid stays the same.
Write each codon per line and circle the mutated DNA base.
Original DNA TAC CAT TCT CGG TGT AAA AGG GCG ATT
Silent DNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated mRNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
Mutated Amino Acid _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Original Amino Acid Met Val Arg Ala Thr Phe Ser Arg STOP
A base mutation that creates a new stop codon in place of an amino acid is called a
nonsense mutation.
DNA TGT → TGA
Amino Acid Cys → STOP
Use the DNA code below to demonstrate a nonsense mutation. All you have to do is
change one DNA base to create a new stop codon.
Write each codon per line and circle the mutated amino acid.
Original DNA TAC GGT AAT CAA ATA GAA CCT GAG ACT
Nonsense DNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated mRNA _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Mutated Amino Acid _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Original Amino Acid Met Pro Leu Val Tyr Leu Gly Leu STOP
Please explain the difference between a frame shift mutation and a base substitution
mutation.
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
© Lesson Plans Inc. 2007
You might also like
- Video Recap of Mutations by Amoeba SistersDocument2 pagesVideo Recap of Mutations by Amoeba Sistersapi-233187566No ratings yet
- Bio-Worksheet-MutationsDocument3 pagesBio-Worksheet-MutationsEbrahimNo ratings yet
- MutationActivity 1Document4 pagesMutationActivity 1Leo GordonNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The FollowingDocument5 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Followingapi-39708077950% (2)
- 3 TransctranslpracticeDocument2 pages3 Transctranslpracticeapi-502781581No ratings yet
- Group Act MutationDocument1 pageGroup Act MutationMonica Grace ManaloNo ratings yet
- Types of Mutations Worksheet PDFDocument3 pagesTypes of Mutations Worksheet PDFsmith joeNo ratings yet
- Video Recap of Mutations v2 by Amoeba Sisters PDFDocument2 pagesVideo Recap of Mutations v2 by Amoeba Sisters PDFsyifaNo ratings yet
- Mutations WSDocument3 pagesMutations WSShraddha BNo ratings yet
- X Men GeneticsDocument2 pagesX Men GeneticsPoohbearrr :No ratings yet
- GENE TO PROTEIN Notes 2023Document5 pagesGENE TO PROTEIN Notes 2023Kristen LindstromNo ratings yet
- Mutations WorksheetDocument5 pagesMutations Worksheetapi-32772460No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Simulation ActivityDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis Simulation ActivitySHARIFAH BINTI HASSAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Part 6 Mutation Winter 2023Document2 pagesPart 6 Mutation Winter 2023tanusehdev17No ratings yet
- RNAProteinSynthesisSE 1 2022-04-29 15 - 38 - 21Document6 pagesRNAProteinSynthesisSE 1 2022-04-29 15 - 38 - 21E ZenaNo ratings yet
- Mutations Activity - GenesyGenomas - LabDocument4 pagesMutations Activity - GenesyGenomas - LabSamuel Morales NavarroNo ratings yet
- Rna Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesRna Protein SynthesisDaniel Hanna86% (7)
- Mutations WorksheetDocument2 pagesMutations Worksheetapi-233187566No ratings yet
- A Level Homework 3Document5 pagesA Level Homework 3szyzypNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3 w5 6Document12 pagesScience 10 Q3 w5 6SaviannaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetCamryn BrickerNo ratings yet
- DNA Mutations WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Mutations Worksheetjanani pulivarthiNo ratings yet
- DNA Mutations WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Mutations WorksheetFumira MisataNo ratings yet
- 13 DNA Mutation SimulationDocument2 pages13 DNA Mutation Simulationlightning TigerNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesStudent Exploration: RNA and Protein SynthesisMasonNo ratings yet
- Rna and Protein Synthesis Guided NotesDocument6 pagesRna and Protein Synthesis Guided NotesqzweqwNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument5 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetVanessa JuatcoNo ratings yet
- N - HS-LS1-1 Protein Synthesis PracticeDocument5 pagesN - HS-LS1-1 Protein Synthesis PracticeMa Anna Cris LumongsudNo ratings yet
- Changes in Dna WorksheetDocument3 pagesChanges in Dna Worksheetapi-257187977No ratings yet
- 6.3 Activity - 3 RNAProteinSynthesisSEDocument6 pages6.3 Activity - 3 RNAProteinSynthesisSEsmol ukeleleNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Activity in Science March 7Document2 pagesAsynchronous Activity in Science March 7xenarealeNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis PPQ'sDocument25 pagesProtein Synthesis PPQ'sAnthony MoloneyNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 Self-Learning Module 3 Central Dogma of The Transfer of Genetic InformationDocument16 pagesScience: Quarter 3 Self-Learning Module 3 Central Dogma of The Transfer of Genetic InformationKaye ViolaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WSDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis WSkatherine corvera100% (1)
- Protein Synthesis Model LabDocument7 pagesProtein Synthesis Model Labmarisa corderoNo ratings yet
- RNAProteinSynthesisSEDocument6 pagesRNAProteinSynthesisSETania Melendez-LainezNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - 1667348288-DNA Mutation Simulation WorksheetDocument3 pagesKami Export - 1667348288-DNA Mutation Simulation WorksheetDava RamadhanNo ratings yet
- AA3 - Worksheet On MutationsDocument2 pagesAA3 - Worksheet On MutationsBernadette NolascoNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis-Worksheet 2018Document5 pagesProtein-Synthesis-Worksheet 2018api-242868690100% (1)
- Mutations Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesMutations Worksheet PDFNouradin Ibrahim OmerNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis-WorksheetDocument3 pagesProtein-Synthesis-WorksheetJohn SchwuchowNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetrebugiocosmeNo ratings yet
- Karas Ghattas - RNA and Protein Synthesis - Pdf.kamiDocument3 pagesKaras Ghattas - RNA and Protein Synthesis - Pdf.kamiKaras GhattasNo ratings yet
- Bio Worksheet MutationsDocument2 pagesBio Worksheet MutationsFelix Robert ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Mutations Worksheet 2Document3 pagesMutations Worksheet 2Dazza DattoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis GizmoDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis GizmoCaleb HutchinsonNo ratings yet
- Molecular Lab 12 Using Neb Cutter 2013Document6 pagesMolecular Lab 12 Using Neb Cutter 2013Soledad SanzNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetG Combalicer Bernice Darielle D.No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following Passage and Answer The Questions BelowDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following Passage and Answer The Questions BelowIris LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma Module For Grade 10 ScienceDocument3 pagesCentral Dogma Module For Grade 10 ScienceJan Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument5 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyMINt Kookie100% (1)
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesROCHELLE MAGBUONo ratings yet
- DNA Mutations Worksheet 12.3Document2 pagesDNA Mutations Worksheet 12.3HS TUCKER0% (1)
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesROCHELLE MAGBUONo ratings yet
- Codon Chart - Visual TaskDocument2 pagesCodon Chart - Visual Taskmustafaabdullhadi0No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab Activity 206Document8 pagesBiochemistry Lab Activity 206Naomi NicoleNo ratings yet
- Gizmo - Rna - Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesGizmo - Rna - Protein SynthesisMarques AlsoppNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma WorksheetDocument8 pagesCentral Dogma WorksheetZyrus AntalanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology & Genetics: Essential Biology Self-Teaching GuideFrom EverandMolecular Biology & Genetics: Essential Biology Self-Teaching GuideNo ratings yet
- RNA and DNA Editing: Molecular Mechanisms and Their Integration into Biological SystemsFrom EverandRNA and DNA Editing: Molecular Mechanisms and Their Integration into Biological SystemsHarold C. SmithNo ratings yet
- BANING Activity No. 5.2 DNA Base PairingDocument3 pagesBANING Activity No. 5.2 DNA Base PairingFatima Nur Faiza HandaNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 5.2 Point and Frameshift MutationsDocument3 pagesActivity No. 5.2 Point and Frameshift MutationsFatima Nur Faiza HandaNo ratings yet
- Food Intake Is Influenced By: Geographical, Economic: Factors, Personal Taste, IdiosyncrasiesDocument1 pageFood Intake Is Influenced By: Geographical, Economic: Factors, Personal Taste, IdiosyncrasiesFatima Nur Faiza HandaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry NotesDocument2 pagesBiochemistry NotesFatima Nur Faiza HandaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Lectures - (Lesson 1-3)Document7 pagesEnvironmental Science Lectures - (Lesson 1-3)Fatima Nur Faiza HandaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Cell Division Mitosis and MeiosisDocument87 pagesLesson 4 - Cell Division Mitosis and MeiosisHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Kajtez NatCommun 2016Document11 pagesKajtez NatCommun 2016Luka JandricNo ratings yet
- Anther and Pollen CultureDocument2 pagesAnther and Pollen CulturesheetupatelNo ratings yet
- Sci8 q4 Mod2 v4Document31 pagesSci8 q4 Mod2 v4Jay-ar RiosNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Extra QuestionsDocument10 pagesReproduction Extra Questionschayyakudopa9No ratings yet
- Constantinou (1998) Spectral Philia and The Imaginary Institution of NeedsDocument31 pagesConstantinou (1998) Spectral Philia and The Imaginary Institution of Needsbodil0carinaNo ratings yet
- Cleavage Partitions The Zygote Into Many Smaller CellsDocument10 pagesCleavage Partitions The Zygote Into Many Smaller CellssispulieNo ratings yet
- Neet Wizz Bio Class 12Document89 pagesNeet Wizz Bio Class 12Aarthi T. UNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Cell Division: 6.2: Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument18 pagesChapter 6: Cell Division: 6.2: Cell Cycle and MitosisMohammed Ridzuwan0% (1)
- NCERT Class 12 Biology Human ReproductionDocument15 pagesNCERT Class 12 Biology Human ReproductionSrajanNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 General Biology2 Q4 Module 1 Reproduction and Development. For PrintingDocument13 pagesGrade 12 General Biology2 Q4 Module 1 Reproduction and Development. For Printingairamaymalicdem052No ratings yet
- ACFrOgAwVytqvG4xDsbm NUyWfZ6sq1jWDZWkLfONw1PueWKn MgV8qTjPdeA-08USc5v 9KyY JeQorFlxiIXg21s0cWuiu2FnXYzJgCRb6vM62BzH8EZJJxoApxEcjCOTgLllkuzP9PhwR3phzDocument14 pagesACFrOgAwVytqvG4xDsbm NUyWfZ6sq1jWDZWkLfONw1PueWKn MgV8qTjPdeA-08USc5v 9KyY JeQorFlxiIXg21s0cWuiu2FnXYzJgCRb6vM62BzH8EZJJxoApxEcjCOTgLllkuzP9PhwR3phzjundon.ivo.deborjaNo ratings yet
- 9th Biology Chapter-WiseDocument18 pages9th Biology Chapter-WiseMalik AqibNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Genetic ControlDocument57 pagesCell Structure and Genetic ControlMOHANNAD ALNEMAHNo ratings yet
- 8 Worksheet Reproduce FloweringDocument2 pages8 Worksheet Reproduce Floweringelsa khairunnisa100% (3)
- Epigenetics and Chromatin RemodellingDocument30 pagesEpigenetics and Chromatin RemodellingMaxine RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Notes For FungiDocument10 pagesNotes For FungiФMuhammdф Atif .No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Inquiry - DPDocument5 pagesCell Cycle Inquiry - DPYuree ChoiNo ratings yet
- Botany - 2Document2 pagesBotany - 2tadepalli patanjaliNo ratings yet
- Basic PathologyDocument35 pagesBasic Pathologyshinichi kudoNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants (CAPE)Document60 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants (CAPE)shakiraNo ratings yet
- Animal ReproductionDocument93 pagesAnimal ReproductionunattractiveyouNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 ReproductionDocument46 pagesTopic 3 ReproductionHapsah MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants 7th GradeDocument14 pagesReproduction in Plants 7th Grade5545116.shreyastammeneniNo ratings yet
- Gene Regulation - Lac Operon & TRP OperonDocument25 pagesGene Regulation - Lac Operon & TRP OperonSalam Pradeep Singh75% (12)
- زراعة انسجة نباتيةDocument127 pagesزراعة انسجة نباتيةHewa HusenNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Inhibitor Dan Analisis Enzim KatalaseDocument14 pagesEnzyme Inhibitor Dan Analisis Enzim Katalaseg.islamiNo ratings yet
- Chromatin Remodeling Complexes - The Regulators of Genome FunctionDocument19 pagesChromatin Remodeling Complexes - The Regulators of Genome FunctionManisha DasNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Planner AakashDocument3 pagesPractice Test Planner AakashthekiddiedreamsNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle BBDocument103 pagesCell Cycle BBKrishna Priyam SinghNo ratings yet