Professional Documents
Culture Documents
E-Invoicing - at A Glance
E-Invoicing - at A Glance
Uploaded by
Everstudy Online ClassesCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- FS CD Functional Overview v1Document55 pagesFS CD Functional Overview v1Raven_Johnson_FqfrpE83% (6)
- Section 1. What's New: This Readme File Contains These SectionsDocument6 pagesSection 1. What's New: This Readme File Contains These SectionsNishant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bianca Hansen Masters Thesis CBP 2017 Case Study On NetflixDocument115 pagesBianca Hansen Masters Thesis CBP 2017 Case Study On NetflixOsman KüçükNo ratings yet
- SAP GST E-InvoicingDocument16 pagesSAP GST E-InvoicingLovish Rawat100% (3)
- Iris Onyx E-Invoicing Solution: How To Get Ready For The Mandate?Document28 pagesIris Onyx E-Invoicing Solution: How To Get Ready For The Mandate?private completelyNo ratings yet
- Creative Technology Limited CaseDocument19 pagesCreative Technology Limited CasefelzioNo ratings yet
- E-Invoicing - at A GlanceDocument10 pagesE-Invoicing - at A Glancew2vijayNo ratings yet
- GST eInvoiceSystemDetailedOverviewDocument12 pagesGST eInvoiceSystemDetailedOverviewYours YoursNo ratings yet
- E-Invoice Under GSTDocument2 pagesE-Invoice Under GSTKumariNo ratings yet
- Internal E-Invoice Training DeckDocument68 pagesInternal E-Invoice Training DeckVijaya Sarathy DharniNo ratings yet
- E Invoice Under GST - NovDocument2 pagesE Invoice Under GST - NovVishwanath HollaNo ratings yet
- 'GST+e Invoice+system Overview Version+Dt.+29 5 2020Document12 pages'GST+e Invoice+system Overview Version+Dt.+29 5 2020ManjunathNo ratings yet
- E-Invoice System: User Manual - Bulk Generation & Cancellation ToolDocument23 pagesE-Invoice System: User Manual - Bulk Generation & Cancellation Toolsuman.neel59386100% (1)
- Digital Compliance: Platform From SAPDocument9 pagesDigital Compliance: Platform From SAPsiddharthadeepakNo ratings yet
- E InvoicingDocument4 pagesE Invoicingvaddepallyanil goudNo ratings yet
- E-Invoice (Electronic Invoice) : List of AbbreviationsDocument5 pagesE-Invoice (Electronic Invoice) : List of AbbreviationsChirag SolankiNo ratings yet
- GST E InvoiceDocument23 pagesGST E Invoicenallarahul86No ratings yet
- UserManual BulkE InvoicegenerationtoolDocument13 pagesUserManual BulkE InvoicegenerationtoolDr. Yashodhan JoshiNo ratings yet
- E Document Framework - GST IndiaDocument16 pagesE Document Framework - GST IndiakannanNo ratings yet
- Updated e Invoice FAQs v6Document24 pagesUpdated e Invoice FAQs v6SurajNo ratings yet
- E-Invoicing ConceptDocument12 pagesE-Invoicing ConceptMohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- E INVOICE - PresentationDocument66 pagesE INVOICE - PresentationenterpriserenewalNo ratings yet
- Einvoce - Gepp User ManualDocument29 pagesEinvoce - Gepp User ManualDadang TirthaNo ratings yet
- EInvoice Webinar Jan2020Document21 pagesEInvoice Webinar Jan2020Pankaj KhatoniarNo ratings yet
- Filepay Ver2Document1 pageFilepay Ver2Aries ParazoNo ratings yet
- E InvoiceDocument23 pagesE Invoicenallarahul86No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To GST: Applicability of Utgst ActDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To GST: Applicability of Utgst ActSoul of honeyNo ratings yet
- E Invoicing GuidelinesDocument10 pagesE Invoicing GuidelinesChirag SolankiNo ratings yet
- Vat Alert July 2018 Requirments ReminderDocument2 pagesVat Alert July 2018 Requirments ReminderSudi Mohamed AbdallahNo ratings yet
- 2622 TcsfaqsDocument12 pages2622 TcsfaqsYCMOUNo ratings yet
- Final E-InvoicingDocument4 pagesFinal E-InvoicingCA Ishu BansalNo ratings yet
- Manual - PPT On EInvoice SystemDocument52 pagesManual - PPT On EInvoice SystemDadang Tirtha100% (1)
- Electronic Fiscal Receipting and Invoicing Solution: KakasaDocument6 pagesElectronic Fiscal Receipting and Invoicing Solution: KakasaMichael Kazinda100% (1)
- French Electronic Invoice From July 2024 - Vision StatementDocument3 pagesFrench Electronic Invoice From July 2024 - Vision StatementRODCAR0No ratings yet
- GST E-Invoice System - FAQsDocument20 pagesGST E-Invoice System - FAQsJigar MakwanaNo ratings yet
- E InvoicingDocument24 pagesE InvoicingBrijNo ratings yet
- Inpu T Tax CRE Dit!: Week 6Document39 pagesInpu T Tax CRE Dit!: Week 6himeesha dhiliwalNo ratings yet
- E-Invoice Tachincal - DocumentDocument12 pagesE-Invoice Tachincal - DocumentMohammed IshaqNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide To E-Invoicing in India: BooksDocument19 pagesA Complete Guide To E-Invoicing in India: BooksTrinetra AgarwalNo ratings yet
- EBIRForms-Job AidsDocument103 pagesEBIRForms-Job AidsAdyNo ratings yet
- APFFB Cohort 7 Group 1 Capstone Project - Integrated Blockchain For E-Invoice TReDS and GST For B2B TransactionsDocument18 pagesAPFFB Cohort 7 Group 1 Capstone Project - Integrated Blockchain For E-Invoice TReDS and GST For B2B TransactionsakshayibsNo ratings yet
- E-Invoicing Under GST PPT TheTaxTellersDocument8 pagesE-Invoicing Under GST PPT TheTaxTellersThe Tax TellersNo ratings yet
- Standardised PPT On GST: Indirect Taxes Committee The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaDocument36 pagesStandardised PPT On GST: Indirect Taxes Committee The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaManjunathreddy SeshadriNo ratings yet
- Understanding Electronic Invoicing System in The PhilippinesDocument27 pagesUnderstanding Electronic Invoicing System in The PhilippinesSUMIT KUMAR AGARWALANo ratings yet
- E-Invoice FAQ-updatedDocument4 pagesE-Invoice FAQ-updatedTrue Consulting servicesNo ratings yet
- EA 2000 Desk Review & ReconciliationDocument43 pagesEA 2000 Desk Review & ReconciliationSushant SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Input Tax Credit: Cma Bibhudatta SarangiDocument3 pagesInput Tax Credit: Cma Bibhudatta SarangihanumanthaiahgowdaNo ratings yet
- E InvoicingDocument20 pagesE Invoicingpawan dhokaNo ratings yet
- Itc FinalDocument47 pagesItc FinalarshiaNo ratings yet
- TN33 Pilot Launch Revamp of eBRCDocument3 pagesTN33 Pilot Launch Revamp of eBRCIlesh GhevariyaNo ratings yet
- Cargo Agent Presentation For GST March 2018Document13 pagesCargo Agent Presentation For GST March 2018rishi pandeyNo ratings yet
- RR 18-12 Regulations - in - The - Processing - of - Authority - To - PrintDocument5 pagesRR 18-12 Regulations - in - The - Processing - of - Authority - To - PrintAlvin AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Payment Industry Go To Market-DeloitteDocument7 pagesPayment Industry Go To Market-DeloitteMegha PantNo ratings yet
- Services Exports From India Scheme ("SEIS") : Comprehensive Solutions For Complex MattersDocument13 pagesServices Exports From India Scheme ("SEIS") : Comprehensive Solutions For Complex MattersRajdeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- FAQs - On - TCSDocument10 pagesFAQs - On - TCSGiri SukumarNo ratings yet
- IDT Saar CA Final CH 8 Input Tax Credit by CA Mahesh Gour Handwritten NotesDocument27 pagesIDT Saar CA Final CH 8 Input Tax Credit by CA Mahesh Gour Handwritten NotesRonita DuttaNo ratings yet
- E-Invoice System: User Manual For Tax PayersDocument42 pagesE-Invoice System: User Manual For Tax Payerssarvagya satbhaiyaNo ratings yet
- OFI GST E-Invoicing Functionality1Document24 pagesOFI GST E-Invoicing Functionality1Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Section 165Document10 pagesSection 165aindri.sahaNo ratings yet
- Digital Service Guide EnglishDocument68 pagesDigital Service Guide EnglishSamer SayedNo ratings yet
- Jhulaghat FinalDocument108 pagesJhulaghat FinalAltafNo ratings yet
- CPA Financial Accounting and Reporting: Second EditionFrom EverandCPA Financial Accounting and Reporting: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- U.P. Higher Education Services Commission, Prayagraj Advt, No,-50 FINAL K E Y - (Subject-Commerce Code No. 68) Written Exam. Dt. 30.10.2021Document2 pagesU.P. Higher Education Services Commission, Prayagraj Advt, No,-50 FINAL K E Y - (Subject-Commerce Code No. 68) Written Exam. Dt. 30.10.2021Everstudy Online ClassesNo ratings yet
- KEA AP MCQsDocument29 pagesKEA AP MCQsEverstudy Online ClassesNo ratings yet
- Bars PDFDocument7 pagesBars PDFEverstudy Online ClassesNo ratings yet
- 360 Degree Performance AppraisalDocument15 pages360 Degree Performance AppraisalEverstudy Online ClassesNo ratings yet
- Extreme Teams Shaw en 28680Document7 pagesExtreme Teams Shaw en 28680BubbleNo ratings yet
- I.1 Marketing Management Block 1 - PRDocument88 pagesI.1 Marketing Management Block 1 - PRJerico RanadaNo ratings yet
- Negotiation StyleDocument2 pagesNegotiation StyleMaría José Valdez RussellNo ratings yet
- Mr. C. Thirumal AzhaganDocument7 pagesMr. C. Thirumal AzhaganSukeshkumarNo ratings yet
- Note01-Basic DynamicsDocument29 pagesNote01-Basic DynamicswingkitcwkNo ratings yet
- Sfiligoi-Company Introduction 2022 - ENDocument7 pagesSfiligoi-Company Introduction 2022 - ENahmadmubarokharbarindoNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Shopping ComprehensionDocument14 pagesA Brief History of Shopping ComprehensionGabriella BirdNo ratings yet
- Slides - CH 1 Microsoft Operations Framework OverviewDocument3 pagesSlides - CH 1 Microsoft Operations Framework OverviewJohann NeethlingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ReceivablesDocument23 pagesChapter 8 ReceivablesNutchanan PrateepusanonNo ratings yet
- DATE: MARCH 2014: ( ("Company") ) ( ("Agent ") )Document4 pagesDATE: MARCH 2014: ( ("Company") ) ( ("Agent ") )bobbiebogusNo ratings yet
- Branding Elements Logos Vol2Document162 pagesBranding Elements Logos Vol2Carolina Ruiz100% (1)
- Individual Assignment CB Feb 2020Document6 pagesIndividual Assignment CB Feb 2020Jalna IsaacNo ratings yet
- Sociology Project AdvertisementDocument6 pagesSociology Project AdvertisementHiriko 0709No ratings yet
- College of Business Administration Major in Marketing ManagementDocument4 pagesCollege of Business Administration Major in Marketing Managementmark louie santosNo ratings yet
- Keller SBM3 01-RevisedDocument19 pagesKeller SBM3 01-RevisedamnaNo ratings yet
- Iocl Trichy 1st Po-27076875Document14 pagesIocl Trichy 1st Po-27076875SachinNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - TruefalseDocument412 pagesStrategic Management - Truefalseapi-373507750% (2)
- Chapter 2 Operational Management and Distribution in ETourismDocument24 pagesChapter 2 Operational Management and Distribution in ETourismNUR QAMARIAHNo ratings yet
- Innovation and The Market Share of Private LabelsDocument22 pagesInnovation and The Market Share of Private LabelskocasNo ratings yet
- Partnership Operations Part 2Document14 pagesPartnership Operations Part 2Nerish PlazaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2Document4 pagesAssignment - 2VNo ratings yet
- Michelin Case StudyDocument9 pagesMichelin Case StudyDivesh Mehta100% (1)
- 50 Procurement Formulas!Document9 pages50 Procurement Formulas!ebnugroho123No ratings yet
- Unit - 3 GlobalizationDocument13 pagesUnit - 3 GlobalizationYathish Us ThodaskarNo ratings yet
- Fiverr Help and Education CenterDocument1 pageFiverr Help and Education CenterTrap houseNo ratings yet
- EngleskiDocument113 pagesEngleskiBojan DimitrijevicNo ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind Maplegiatuananh.hcmNo ratings yet
E-Invoicing - at A Glance
E-Invoicing - at A Glance
Uploaded by
Everstudy Online ClassesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
E-Invoicing - at A Glance
E-Invoicing - at A Glance
Uploaded by
Everstudy Online ClassesCopyright:
Available Formats
EE-
e-invoicing – At a Glance
What is e-invoicing?
As per Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, notified class of registered persons (whose aggregate turnover
in any preceding financial year from 2017-18 onwards, is more than prescribed limit) have to
prepare invoice by uploading specified particulars of invoice (in FORM GST INV-01) on Invoice
Registration Portal (IRP) and obtain an Invoice Reference Number (IRN).
After following above ‘e-invoicing’ process, the invoice copy containing inter alia, the IRN
(with QR Code) issued by the notified supplier to buyer is commonly referred to as ‘e-invoice’.
As per Rule 48(5), any invoice issued by a notified person in any manner other than the manner
specified in Rule 48(4), the same shall not be treated as an invoice.
A standard format for e-invoice was notified as ‘INV-01’. This format (called ‘schema’)
facilitates seamless exchange of invoices between accounting systems of suppliers and buyers in
an integrated electronic format.
e-invoicing - Procedure:
Now-a-days, most businesses are using one or other Accounting/Billing/ERP Systems to create
and manage their invoices. These invoices (in JSON format) will now be reported to ‘Invoice
Registration Portal (IRP)’. IRP returns the digitally-signed invoice (in JSON) with a unique
‘Invoice Reference Number (IRN)’ and a QR Code.
That means the Accounting/ERP system of business and e-invoice system of government will be
‘talking to each other’ for exchange of invoice data. All this ‘machine-to-machine’ interaction
through APIs and generation of IRN happens in a split second indeed.
Modes of API integration are as below:
Taxpayers with Aggregate Turnover of < Rs. 500 Crores
• Through E-Way Bill APIs – If the taxpayer already has direct access to E-Way Bill APIs, then
they can use the same Client Id, Client Secret, username and password to get access to e-Invoice system.
• Through GSPs – the taxpayer can connect through GSPs. In this case, the GSTIN generates their
own username and password, ties up with GSPs to get access to e-invoice APIs using the Client ID and
Client Secret of GSPs.
• Through ERPs or Billing/Accounting Software Service Providers – the taxpayer can connect
through select ERPs and Billing/Accounting Software Service Providers. In this case, the GSTIN generates
their own username and password and ties up with ERPs or Billing/Accounting Software Service Providers,
to get access to e-invoice APIs, using the Client ID and Client Secret of said providers.
E-INVOICE 1.2 DT. 30-3-2021 1 of 10
EE-
• Through Entities having direct Access to APIs – If the taxpayer (e.g. certain automobile
companies) has tie up or using the ERP of the entity which has direct access to API, then they can access
e-invoice APIs through that entity. In this case, the GSTIN generates their own username and password
and gets access to e-invoice APIs, using Client ID and Client Secret of the entity which has such access.
Taxpayers with Aggregate Turnover of > Rs. 500 Crores
In addition to above modes, they will have direct access, as follows:
• Direct Access to API – They can get direct access to API to integrate with their ERP system. They
need to whitelist their public IPs. In addition to username and password to each GSTIN of the entity, the
entity gets the Client ID and Client Secret to get access to e-invoice APIs.
Some businesses may not have their own ERP/Accounting Software or have few invoices to
report. They can download the free offline utility (‘bulk generation tool’) from e-invoice portal.
Using this, invoice data can be easily uploaded on IRP for generation of IRN. While the portal
gives back ‘machine-readable’ invoice in JSON format, there is a facility to generate ‘human-
readable’ PDF copy of invoice (for save/print/e-mail etc.).
After obtaining IRN, the invoice (with QR Code) can be issued to the recipient in the same way
as is being done now. (Note: An integrated mechanism to enable system-to-system exchange of
e-invoices will be made available in due course.)
The detailed flow involved in e -invoicing is depicted below:
E-INVOICE 1.2 DT. 30-3-2021 2 of 10
EE-
Advantages:
There are many advantages e-invoice brings in for businesses, as depicted below:
Documents/Supplies Covered:
Documents covered Supplies Covered
Supplies to registered persons (B2B)
Invoices
Supplies to SEZs (with/without payment)
Credit Notes
Exports (with/without payment)
Debit Notes
Deemed Exports
Note: B2C invoices are not covered
currently.
E-INVOICE 1.2 DT. 30-3-2021 3 of 10
EE-
Applicability of e-invoice:
Where Applicable Where Not Applicable
For Registered persons whose Entities exempt from e-
aggregate turnover (based on invoicing:
PAN) in any preceding financial
year from 2017-18 onwards, is Special Economic Zone Units
more than prescribed limit (as per (including FTWZs), insurers or
relevant notification) banking companies or financial
institutions, including a non-banking
Supplies to Govt. department financial company, goods transport
agencies supplying services in
having a GSTIN (as entity
relation to transportation of goods by
supplying goods/services/
road in a goods carriage, Suppliers of
deducting TDS) passenger transportation service,
Suppliers of services by way of
Invoices between two different admission to exhibition of
GSTINs under same PAN cinematograph films in multiplex
screens. (Note: The exemption is with
Invoices issued by SEZ reference to entity as a whole and not
Developers nature of supply/transaction.)
Invoices issued by notified person Persons registered in terms of Rule
for supplies made by him but 14 of CGST Rules (OIDAR)
attracting reverse charge under
NIL-rated or wholly-exempt supplies
Section 9(3)
Financial/commercial credit notes
Invoices issued by Input Service
Distributors (ISDs)
High sea sales and bonded
warehouse sales
Supplies to Government
Departments where they don’t have
any registration under GST
Where supplies are received by
notified person from (i) an
unregistered person attracting reverse
charge under Section 9(4) or (ii)
through import of services
E-INVOICE 1.2 DT. 30-3-2021 4 of 10
EE-
Salient Features:
IRP is only a pass through validation portal. Certain key fields will be validated on IRP.
So, IRN will be generated instantaneously, in sub-200 millisecond duration. The server
capacity is robust enough to handle simultaneous uploads. Further, multiple IRPs will be
made available to distribute the load of invoice registration.
Signature (DSC) of supplier not required while reporting e-invoice to IRP.
In e-invoice schema, only 29 fields are mandatory. All others are optional.
Where e-invoicing is applicable, there is no need of issuing invoice copies in
triplicate/duplicate (Rule 48(6)).
Where e-invoicing is applicable, carrying e-invoice print during transportation of goods
is not mandatory. As per Rule 138A(2) of CGST Rules, where e-invoicing is applicable,
“the Quick Reference (QR) code having an embedded Invoice Reference Number (IRN)
in it, may be produced electronically, for verification by the proper officer, in lieu of the
physical copy of such tax invoice.”
How to verify e-invoice?
One can verify the authenticity or correctness of e-
invoice by uploading the signed JSON file or Signed
QR Code (string) on e-invoice portal:
einvoice1.gst.gov.in > Search > ‘Verify Signed
Invoice’
Alternatively, with “Verify QR Code” mobile app
which may be downloaded from einvoice1.gst.gov.in
> Help > Tools > Verify QR Code App
There is no validation to the effect that the ‘document date’ (in the payload to IRP) has
to be within a specified time window, for reporting to IRP/generation of IRN.
1000 is the maximum number of line items which can be reported in a single invoice.
This will be enhanced based on requirement in future.
Penal provisions for not issuing invoice in accordance with GST Law/rules are provided
in Section 122 of CGST/SGST Act, read with CGST/SGST Rules.
E-INVOICE 1.2 DT. 30-3-2021 5 of 10
EE-
Key particulars of e-invoice embedded in QR Code
a. GSTIN of Supplier
b. GSTIN of Recipient
c. Invoice number, as given by Supplier
d. Date of generation of invoice
e. Invoice value (taxable value and gross tax)
f. Number of line items
g. HSN Code of main item (line item having
highest taxable value)
h. Unique IRN (Invoice Reference
Number/hash)
i. IRN Generation Date
Amendment/Cancellation of e-invoice:
An invoice/IRN can’t be cancelled partially. It has to be cancelled in toto. Cancellation
of invoices is governed by Accounting Standards and other applicable rules/regulations.
An IRN/invoice reported to IRP can be cancelled within 24 hours. In case of cancellation
of IRN, GSTR-1 also will be updated with such ‘cancelled’ status. However, if the
connected e-way bill is active or verified by officer during transit, cancellation of IRN is
not permitted.
After expiry of cancellation window, any changes in the invoice details reported to IRP
can be carried out on GST portal (while filing GSTR-1). In case GSTR-1 has already
been filed, then using the mechanism of amendment as provided under GST.
However, these changes will be flagged to proper officer for information.
IRN is a unique string based on Supplier’s GSTIN, Document Number, Type of Document
& Financial Year. So, once an IRN is cancelled, the concerned invoice number cannot
be used again to generate another e-invoice/IRN (even within the permitted cancellation
window). If it is used again, then the same will be rejected when it is uploaded on IRP.
Auto-population of GSTR-1/2A and generation of e-way bill:
On successful reporting of invoice details to IRP, the GST system will auto-populate
them into GSTR-1 of the supplier and GSTR-2A of respective receivers. With source
marked as ‘e-invoice’, IRN and IRN date will also be shown in GSTR-1 and GSTR-2A.
E-INVOICE 1.2 DT. 30-3-2021 6 of 10
EE-
Auto-population of details from e-invoices into GSTR-1 is only a facility extended to
taxpayers. In self-assessment, the statutory obligation to file GSTR-1 with accurate
details as per documents raised during the relevant tax period lies with taxpayer.
Where the details auto-populated into GSTR-1 from e-invoices are edited/deleted or re-
uploaded afresh by the supplier, the ‘Source’, ‘IRN’ and ‘IRN date’ will be reset to blank
in respective tables of GSTR-1 and also won’t get reflected in GSTR-2A also. So, non-
appearance of IRN details in GSTR-1/2A alone shouldn’t be assumed to mean that such
invoices were not reported to IRP.
In case both Part-A and Part-B of e-way bill are provided while reporting invoice details
to IRP, they will be used to generate e-way bill. In case Part-B details are not provided at
the time of reporting invoice to IRP, the same will have to be provided by the user through
‘e-way bill’ tab in IRP log in or e-Way Bill Portal, so as to generate e-way bill.
After generation of IRN, presently, there is no time limit for generation of e-way bill
using that IRN (where applicable/desired).
Key Clarifications:
Presently, e-invoicing is not voluntary, i.e. entities having prescribed aggregate turnover
only can report invoices to IRP.
If your turnover exceeds the prescribed limit in the current financial year, then starting e-
invoicing would be required w.e.f. beginning of next financial year.
For the Financial Year 2017-18, the ‘aggregate turnover’ has to be reckoned from 1-7-
2017 till the end of FY.
Some charges to be shown in invoice are leviable to GST, e.g. freight, insurance, packing
& forwarding charges etc. These may be added as one more line item in the invoice.
TCS (Tax Collected at Source) collected by suppliers under Income Tax Act, 1961 can
be shown under “Other Charges (Invoice Level)”.
In INV-01 schema, the field, “IGST Applicability despite Supplier and Recipient located
in same State/UT” is meant for reporting scenarios such as Notification No. 11/2018-
Central Tax (Rate) dated 28.05.2018 levying GST on supply/trading of Priority Sector
Lending Certificates (PSLCs) among banks.
E-INVOICE 1.2 DT. 30-3-2021 7 of 10
EE-
INV-01 schema is only to report specified invoice particulars to IRP. Once IRN is
obtained from the portal, the business may add any other elements not relevant to GST,
while issuing invoice finally to buyer.
For items outside GST levy, separate invoice may be given by such businesses, e.g. a
hotel invoicing a B2B supply where the supply includes food and beverages (leviable to
GST) and Alcoholic beverages (outside GST).
After obtaining signed JSON (along with IRN/QR Code) from e-invoice portal and
while issuing invoice copy to the recipient, the requirement of supplier’s signature /
digital signature is governed by the provisions of Rule 46 of CGST Rules, 2017.
IRP doesn’t store invoices and hence the facility to download e-invoice JSON from IRP
is available only for limited number of days. So, the taxpayers shall take care accordingly.
The facility to download signed invoice JSON from GST System (for suppliers and
recipients, over a longer period of time) will be made available in due course.
Even in the e-invoicing regime, while transporting goods, wherever the e-way bill is
needed, the requirement continues to be mandatory.
B2C Dynamic QR Code: Notification No. 14/2020-Central Tax dated 21st March, 2020
(as amended)) mandated certain entities to include a dynamic Quick Response Code (QR
Code) on their B2C invoices. This is a separate requirement and has no relevance or
applicability to ‘e-invoicing’ under Rule 48(4).
Clarifications issued by CBIC on applicability of Dynamic QR Code can be seen HERE
Popular FAQs
Q. Where can I get the list of all taxpayers who are required to issue e-invoice?
A. It is difficult to make such precise list because the fulfilment of conditions prescribed
for e-invoicing (e.g. crossing of turnover threshold, exemptions, nature of supplies made
etc.) is dynamic in nature.
However, the list of GSTINs which are eligible and/or actually generating IRNs is
published: https://einvoice1.gst.gov.in/Others/GSTINsGeneratingIRN
Further, onus is on the concerned taxpayer to check the conditions and follow the law
while the recipient shall confirm this fact with his suppliers.
E-INVOICE 1.2 DT. 30-3-2021 8 of 10
EE-
Q. I am a buyer. For some of my suppliers, the status on IRP is shown as ‘enabled
for e-invoice’. But, my supplier says e -invoicing is not applicable for them. What
about this?
A. Please note that the enablement status on e-invoice portal doesn’t automatically mean
that a taxpayer is legally obligated to do e-invoicing.
The ‘enablement’ was to primarily ensure only the taxpayers having notified turnover
limits (and not any taxpayer at their option) are able to register and test/report invoices
on trial portal / IRP.
The listing of enabled GSTINs was solely based on the turnover criteria of GSTR-3B, as
reported to GST System. So, it may contain those entities, depending on facts of a case,
to whom e-invoicing might not be applicable for some reason. Thus, it is for the
concerned taxpayer (both Buyers and Suppliers) to confirm fulfilment or otherwise of
conditions as per notification/rules.
Q. As per notification/rules, we are supposed to do e -invoicing, but our GSTIN is
shown as ‘not enabled’ on the Portal. What to do?
A. In case any registered person, is required to prepare invoice in terms of Rule 48(4)
but not enabled on the portal, he/she may request for enablement on portal: ‘Registration
-> e-Invoice Enablement’.
Q. I have generated IRN for an invoice. There is a discrepancy in the invoice and
supply also didn’t materialise, so, I had to cancel it in my system. However, I could
not cancel the IRN on IRP as the cancellation window (24 hours) has expired. What
to do?
A. Obtaining IRN by notified taxpayers is a legal requirement before issue of specified
documents to recipients. Upon generation of IRN, amendments are not possible on IRP
and cancellation of IRN only is permitted within a time window. So, the details of
invoices actually issued during the tax period have to be reported in GSTR-1.
GSTR-1 is the final and self-assessed statutory statement of outward supplies by
taxpayer, at the end of tax period. In the e-invoices auto-populated in GSTR-1 tables,
taxpayers shall delete the details, wherever required, as per the documents actually
cancelled during the tax period.
E-INVOICE 1.2 DT. 30-3-2021 9 of 10
EE-
Q. What is to be printed while issuing e -invoice?
To be printed Need not be printed
Particulars as per Rule 46/53, including Acknowledgement No.
QR Code containing IRN
Acknowledgement Date
Note: While the printed QR code shall be
clear enough to be readable by a QR Code IRN
reader, the size and its placing on invoice is
upto the preference of the businesses. Digital Signature given by IRP
Q. In case of breakdown of internet connectivity in certain areas, will there be any
relaxation in the requirement to obtain IRN?
A. A localised mechanism to provide relaxation in such contingent situations is put in
place.
As per proviso to Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, “…Commissioner may, on the
recommendations of the Council, by notification, exempt a person or a class of registered
persons from issuance of invoice under this sub-rule for a specified period, subject to
such conditions and restrictions as may be specified in the said notification.”
Resources:
More FAQs on e-invoice can be found here: https://www.gstn.org.in/einvoice-faqs
API Specs & FAQs from developer’s angle are available at https://einv-
apisandbox.nic.in/
Many awareness videos on e-invoice are available at ‘e-invoice’ play list on GSTN’s
YouTube Channel
Help Options:
For any technical issue with APIs / Sandbox / e-invoice portal (trial/production) / Offline
Utility / auto-population into GSTR-1 etc., please raise a ticket with GST Self-Service
Portal
Any other feedback & suggestions on e-invoice are welcome at e-invoice@gstn.org.in
*****
E-INVOICE 1.2 DT. 30-3-2021 10 of 10
You might also like
- FS CD Functional Overview v1Document55 pagesFS CD Functional Overview v1Raven_Johnson_FqfrpE83% (6)
- Section 1. What's New: This Readme File Contains These SectionsDocument6 pagesSection 1. What's New: This Readme File Contains These SectionsNishant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bianca Hansen Masters Thesis CBP 2017 Case Study On NetflixDocument115 pagesBianca Hansen Masters Thesis CBP 2017 Case Study On NetflixOsman KüçükNo ratings yet
- SAP GST E-InvoicingDocument16 pagesSAP GST E-InvoicingLovish Rawat100% (3)
- Iris Onyx E-Invoicing Solution: How To Get Ready For The Mandate?Document28 pagesIris Onyx E-Invoicing Solution: How To Get Ready For The Mandate?private completelyNo ratings yet
- Creative Technology Limited CaseDocument19 pagesCreative Technology Limited CasefelzioNo ratings yet
- E-Invoicing - at A GlanceDocument10 pagesE-Invoicing - at A Glancew2vijayNo ratings yet
- GST eInvoiceSystemDetailedOverviewDocument12 pagesGST eInvoiceSystemDetailedOverviewYours YoursNo ratings yet
- E-Invoice Under GSTDocument2 pagesE-Invoice Under GSTKumariNo ratings yet
- Internal E-Invoice Training DeckDocument68 pagesInternal E-Invoice Training DeckVijaya Sarathy DharniNo ratings yet
- E Invoice Under GST - NovDocument2 pagesE Invoice Under GST - NovVishwanath HollaNo ratings yet
- 'GST+e Invoice+system Overview Version+Dt.+29 5 2020Document12 pages'GST+e Invoice+system Overview Version+Dt.+29 5 2020ManjunathNo ratings yet
- E-Invoice System: User Manual - Bulk Generation & Cancellation ToolDocument23 pagesE-Invoice System: User Manual - Bulk Generation & Cancellation Toolsuman.neel59386100% (1)
- Digital Compliance: Platform From SAPDocument9 pagesDigital Compliance: Platform From SAPsiddharthadeepakNo ratings yet
- E InvoicingDocument4 pagesE Invoicingvaddepallyanil goudNo ratings yet
- E-Invoice (Electronic Invoice) : List of AbbreviationsDocument5 pagesE-Invoice (Electronic Invoice) : List of AbbreviationsChirag SolankiNo ratings yet
- GST E InvoiceDocument23 pagesGST E Invoicenallarahul86No ratings yet
- UserManual BulkE InvoicegenerationtoolDocument13 pagesUserManual BulkE InvoicegenerationtoolDr. Yashodhan JoshiNo ratings yet
- E Document Framework - GST IndiaDocument16 pagesE Document Framework - GST IndiakannanNo ratings yet
- Updated e Invoice FAQs v6Document24 pagesUpdated e Invoice FAQs v6SurajNo ratings yet
- E-Invoicing ConceptDocument12 pagesE-Invoicing ConceptMohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- E INVOICE - PresentationDocument66 pagesE INVOICE - PresentationenterpriserenewalNo ratings yet
- Einvoce - Gepp User ManualDocument29 pagesEinvoce - Gepp User ManualDadang TirthaNo ratings yet
- EInvoice Webinar Jan2020Document21 pagesEInvoice Webinar Jan2020Pankaj KhatoniarNo ratings yet
- Filepay Ver2Document1 pageFilepay Ver2Aries ParazoNo ratings yet
- E InvoiceDocument23 pagesE Invoicenallarahul86No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To GST: Applicability of Utgst ActDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To GST: Applicability of Utgst ActSoul of honeyNo ratings yet
- E Invoicing GuidelinesDocument10 pagesE Invoicing GuidelinesChirag SolankiNo ratings yet
- Vat Alert July 2018 Requirments ReminderDocument2 pagesVat Alert July 2018 Requirments ReminderSudi Mohamed AbdallahNo ratings yet
- 2622 TcsfaqsDocument12 pages2622 TcsfaqsYCMOUNo ratings yet
- Final E-InvoicingDocument4 pagesFinal E-InvoicingCA Ishu BansalNo ratings yet
- Manual - PPT On EInvoice SystemDocument52 pagesManual - PPT On EInvoice SystemDadang Tirtha100% (1)
- Electronic Fiscal Receipting and Invoicing Solution: KakasaDocument6 pagesElectronic Fiscal Receipting and Invoicing Solution: KakasaMichael Kazinda100% (1)
- French Electronic Invoice From July 2024 - Vision StatementDocument3 pagesFrench Electronic Invoice From July 2024 - Vision StatementRODCAR0No ratings yet
- GST E-Invoice System - FAQsDocument20 pagesGST E-Invoice System - FAQsJigar MakwanaNo ratings yet
- E InvoicingDocument24 pagesE InvoicingBrijNo ratings yet
- Inpu T Tax CRE Dit!: Week 6Document39 pagesInpu T Tax CRE Dit!: Week 6himeesha dhiliwalNo ratings yet
- E-Invoice Tachincal - DocumentDocument12 pagesE-Invoice Tachincal - DocumentMohammed IshaqNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide To E-Invoicing in India: BooksDocument19 pagesA Complete Guide To E-Invoicing in India: BooksTrinetra AgarwalNo ratings yet
- EBIRForms-Job AidsDocument103 pagesEBIRForms-Job AidsAdyNo ratings yet
- APFFB Cohort 7 Group 1 Capstone Project - Integrated Blockchain For E-Invoice TReDS and GST For B2B TransactionsDocument18 pagesAPFFB Cohort 7 Group 1 Capstone Project - Integrated Blockchain For E-Invoice TReDS and GST For B2B TransactionsakshayibsNo ratings yet
- E-Invoicing Under GST PPT TheTaxTellersDocument8 pagesE-Invoicing Under GST PPT TheTaxTellersThe Tax TellersNo ratings yet
- Standardised PPT On GST: Indirect Taxes Committee The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaDocument36 pagesStandardised PPT On GST: Indirect Taxes Committee The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaManjunathreddy SeshadriNo ratings yet
- Understanding Electronic Invoicing System in The PhilippinesDocument27 pagesUnderstanding Electronic Invoicing System in The PhilippinesSUMIT KUMAR AGARWALANo ratings yet
- E-Invoice FAQ-updatedDocument4 pagesE-Invoice FAQ-updatedTrue Consulting servicesNo ratings yet
- EA 2000 Desk Review & ReconciliationDocument43 pagesEA 2000 Desk Review & ReconciliationSushant SaxenaNo ratings yet
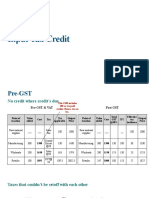
- Input Tax Credit: Cma Bibhudatta SarangiDocument3 pagesInput Tax Credit: Cma Bibhudatta SarangihanumanthaiahgowdaNo ratings yet
- E InvoicingDocument20 pagesE Invoicingpawan dhokaNo ratings yet
- Itc FinalDocument47 pagesItc FinalarshiaNo ratings yet
- TN33 Pilot Launch Revamp of eBRCDocument3 pagesTN33 Pilot Launch Revamp of eBRCIlesh GhevariyaNo ratings yet
- Cargo Agent Presentation For GST March 2018Document13 pagesCargo Agent Presentation For GST March 2018rishi pandeyNo ratings yet
- RR 18-12 Regulations - in - The - Processing - of - Authority - To - PrintDocument5 pagesRR 18-12 Regulations - in - The - Processing - of - Authority - To - PrintAlvin AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Payment Industry Go To Market-DeloitteDocument7 pagesPayment Industry Go To Market-DeloitteMegha PantNo ratings yet
- Services Exports From India Scheme ("SEIS") : Comprehensive Solutions For Complex MattersDocument13 pagesServices Exports From India Scheme ("SEIS") : Comprehensive Solutions For Complex MattersRajdeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- FAQs - On - TCSDocument10 pagesFAQs - On - TCSGiri SukumarNo ratings yet
- IDT Saar CA Final CH 8 Input Tax Credit by CA Mahesh Gour Handwritten NotesDocument27 pagesIDT Saar CA Final CH 8 Input Tax Credit by CA Mahesh Gour Handwritten NotesRonita DuttaNo ratings yet
- E-Invoice System: User Manual For Tax PayersDocument42 pagesE-Invoice System: User Manual For Tax Payerssarvagya satbhaiyaNo ratings yet
- OFI GST E-Invoicing Functionality1Document24 pagesOFI GST E-Invoicing Functionality1Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Section 165Document10 pagesSection 165aindri.sahaNo ratings yet
- Digital Service Guide EnglishDocument68 pagesDigital Service Guide EnglishSamer SayedNo ratings yet
- Jhulaghat FinalDocument108 pagesJhulaghat FinalAltafNo ratings yet
- CPA Financial Accounting and Reporting: Second EditionFrom EverandCPA Financial Accounting and Reporting: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- U.P. Higher Education Services Commission, Prayagraj Advt, No,-50 FINAL K E Y - (Subject-Commerce Code No. 68) Written Exam. Dt. 30.10.2021Document2 pagesU.P. Higher Education Services Commission, Prayagraj Advt, No,-50 FINAL K E Y - (Subject-Commerce Code No. 68) Written Exam. Dt. 30.10.2021Everstudy Online ClassesNo ratings yet
- KEA AP MCQsDocument29 pagesKEA AP MCQsEverstudy Online ClassesNo ratings yet
- Bars PDFDocument7 pagesBars PDFEverstudy Online ClassesNo ratings yet
- 360 Degree Performance AppraisalDocument15 pages360 Degree Performance AppraisalEverstudy Online ClassesNo ratings yet
- Extreme Teams Shaw en 28680Document7 pagesExtreme Teams Shaw en 28680BubbleNo ratings yet
- I.1 Marketing Management Block 1 - PRDocument88 pagesI.1 Marketing Management Block 1 - PRJerico RanadaNo ratings yet
- Negotiation StyleDocument2 pagesNegotiation StyleMaría José Valdez RussellNo ratings yet
- Mr. C. Thirumal AzhaganDocument7 pagesMr. C. Thirumal AzhaganSukeshkumarNo ratings yet
- Note01-Basic DynamicsDocument29 pagesNote01-Basic DynamicswingkitcwkNo ratings yet
- Sfiligoi-Company Introduction 2022 - ENDocument7 pagesSfiligoi-Company Introduction 2022 - ENahmadmubarokharbarindoNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Shopping ComprehensionDocument14 pagesA Brief History of Shopping ComprehensionGabriella BirdNo ratings yet
- Slides - CH 1 Microsoft Operations Framework OverviewDocument3 pagesSlides - CH 1 Microsoft Operations Framework OverviewJohann NeethlingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ReceivablesDocument23 pagesChapter 8 ReceivablesNutchanan PrateepusanonNo ratings yet
- DATE: MARCH 2014: ( ("Company") ) ( ("Agent ") )Document4 pagesDATE: MARCH 2014: ( ("Company") ) ( ("Agent ") )bobbiebogusNo ratings yet
- Branding Elements Logos Vol2Document162 pagesBranding Elements Logos Vol2Carolina Ruiz100% (1)
- Individual Assignment CB Feb 2020Document6 pagesIndividual Assignment CB Feb 2020Jalna IsaacNo ratings yet
- Sociology Project AdvertisementDocument6 pagesSociology Project AdvertisementHiriko 0709No ratings yet
- College of Business Administration Major in Marketing ManagementDocument4 pagesCollege of Business Administration Major in Marketing Managementmark louie santosNo ratings yet
- Keller SBM3 01-RevisedDocument19 pagesKeller SBM3 01-RevisedamnaNo ratings yet
- Iocl Trichy 1st Po-27076875Document14 pagesIocl Trichy 1st Po-27076875SachinNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - TruefalseDocument412 pagesStrategic Management - Truefalseapi-373507750% (2)
- Chapter 2 Operational Management and Distribution in ETourismDocument24 pagesChapter 2 Operational Management and Distribution in ETourismNUR QAMARIAHNo ratings yet
- Innovation and The Market Share of Private LabelsDocument22 pagesInnovation and The Market Share of Private LabelskocasNo ratings yet
- Partnership Operations Part 2Document14 pagesPartnership Operations Part 2Nerish PlazaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2Document4 pagesAssignment - 2VNo ratings yet
- Michelin Case StudyDocument9 pagesMichelin Case StudyDivesh Mehta100% (1)
- 50 Procurement Formulas!Document9 pages50 Procurement Formulas!ebnugroho123No ratings yet
- Unit - 3 GlobalizationDocument13 pagesUnit - 3 GlobalizationYathish Us ThodaskarNo ratings yet
- Fiverr Help and Education CenterDocument1 pageFiverr Help and Education CenterTrap houseNo ratings yet
- EngleskiDocument113 pagesEngleskiBojan DimitrijevicNo ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind Maplegiatuananh.hcmNo ratings yet