Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Baliwag Polytechnic College
Baliwag Polytechnic College
Uploaded by
Paw VerdilloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Baliwag Polytechnic College
Baliwag Polytechnic College
Uploaded by
Paw VerdilloCopyright:
Available Formats
BALIWAG POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE
Baliwag, Bulacan
ACT09 – Statistical Analysis and Software Application
Second Semester | A.Y. 2021 – 2022
MODULE 3
Prepared by:
Marvic V. Ablaza, MM
Assistant Professor I
www.btech.edu.ph STATISTICAL ANALYSIS AND SOFTWARE APPLICATION Page 1 of 10
STATISTICAL
ANALYSIS AND
SOFTWARE
APPLICATION
Sample Size
Objectives:
After successful completion of this module, you should be able to:
Determine the appropriate sample size.
Differentiate various sampling techniques.
Know the sources of errors in sampling.
www.btech.edu.ph STATISTICAL ANALYSIS AND SOFTWARE APPLICATION Page 2 of 10
LESSON 3
Sample Size
“How many participants should be chosen for a survey”?
One of the most frequent problems in statistical analysis is the determination of
the appropriate sample size. One may ask why sample size is so important. The answer
to this is that an appropriate sample size is required for validity. If the samples size is
too small, it will not yield valid results. An appropriate sample size can produce accuracy
of results.
Moreover, the results from the small sample size will be questionable. A sample
size that is too large will result in wasting money and time because enough samples will
normally give an accurate result. The sample size is typically denoted by n and it is
always a positive integer. No exact sample size can be mentioned here and it can vary
in different research settings. However, all else being equal, large sized sample leads to
increased precision in estimates of various properties of the population.
Take Note!
Representativeness, not size, is the more important consideration.
Use no less than 30 subjects if possible.
If you use complex statistics, you may need a minimum of 100 or more in your
sample (varies with method).
www.btech.edu.ph STATISTICAL ANALYSIS AND SOFTWARE APPLICATION Page 3 of 10
Choosing of sample size depends on non - statistical considerations and statistical
considerations.
Non-statistical considerations – It may include availability of resources, man power,
budget, ethics and sampling frame.
Statistical considerations – It will include the desired precision of the estimate.
Three criteria need to be specified to determine the appropriate sample size:
1. Level of Precision
Also called sampling error, the level of precision, is the range in which the true value
of the population is estimated to be.
2. Confidence Interval
It is statistical measure of the number of times out of 100 that results can be
expected to be within a specified range. For example, a confidence interval of 90%
means that results of an action will probably meet expectations 90% of the time.
To find the right z – score to use, refer to the table:
3. Degree of Variability
Depending upon the target population and attributes under consideration, the degree of
variability varies considerably. The more heterogeneous a population is, the larger the
sample size is required to get an optimum level of precision.
Understanding Confidence Intervals: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tFWsuO9f74o
Methods in Determining the Sample Size
1. Estimating the Mean or Average
The sample size required to estimate the populations mean (μ) to with a level of
confidence with specified margin of error e, given by
www.btech.edu.ph STATISTICAL ANALYSIS AND SOFTWARE APPLICATION Page 4 of 10
where:
Z is the z-score corresponding to level of confidence.
e is the level of precision.
Take Note:
If When is unknown, it is common practice to conduct a preliminary survey to
determine s and use it as an estimate of or use results from previous studies to
obtain an estimate of .
When using this approach, the size of the sample should be at least 30. The formula for
the sample standard deviation s is
Example:
A soft drink machine is regulated so that the amount of drink dispensed is
approximately normally distributed with a standard deviation equal to 0.5 ounce.
Determine the sample size needed if we wish to be 95% confident that our sample
mean will be within 0.03 ounce from the true mean.
Solution: The z – score for confidence level 95% in the z – table is 1.96.
We need a 1068 sample for this study.
2. Estimating Proportion (Infinite Population)
The sample size required to obtain a confidence interval for p with specified margin of
error e is given by
www.btech.edu.ph STATISTICAL ANALYSIS AND SOFTWARE APPLICATION Page 5 of 10
Where:
Z is the z – score corresponding to level of confidence
e is the level of precision
P is the population proportion
There is a dilemma in this formula:
It depends on
which we know only after we have taken the sample.
There are two ways to solve this dilemma:
1. We could determine a preliminary value for p based on a pilot study or an earlier
study.
Example:
If last month 37% of all voters thought that state taxes are too high, then it is likely
that the proportion with that opinion this month will not be dramatically different, and
we would use the value 0.37 for p in the formula.
2. Simply to replace p in the formula by 0.5.
When p = 0.5, the maximum value of p(1- p) = 0.25. This is called the most
conservative estimate, since it gives the largest possible estimate of n.
The conservative formula using the strong law of large number.
Where:
Confidence level is 95%
www.btech.edu.ph STATISTICAL ANALYSIS AND SOFTWARE APPLICATION Page 6 of 10
The level of precision is 0.05
Example:
Suppose we are doing a study on the inhabitants of a large town, and want to find out
how many households serve breakfast in the mornings. We don’t have much
information on the subject to begin with, so we’re going to assume that half of the
families serve breakfast: this gives us maximum variability.
So p = 0.5. We want 99% confidence and at least 1% precision.
Solution: The z – score for confidence level 99% in the z – table is 2.58.
We need a 16, 641 sample for this study.
3. Slovin’s Formula
Slovin’s formula is used to calculate the sample size n given the population size and
error. It is computed as
Where:
N is the total population
e is the level of precision
Example # 1: (Total Sample Size)
A researcher plans to conduct a survey about food preference of BS Stat students. If
the population of students is 1000, find the sample size if the error is 5%.
Solution:
The researcher need to survey 286 BS Stat student.
Example #2: (Sample Size for every respondent.)
www.btech.edu.ph STATISTICAL ANALYSIS AND SOFTWARE APPLICATION Page 7 of 10
RESPONDENTS POPULATION SIZE SAMPLE SIZE
STEM 220 38
HUMSS 330 57
ABM 430 75
GAS 170 30
TVL – ICT 350 61
TVL - HE 400 69
N = 1900 n = 330
Solution:
N = 1900
Since the margin of error was not given, we will use e = 5% (0.05)
n= 1900
1 + 1900 (0.05)2
n= 1900
5.75
n = 330.4 (330)
Solving for the sample size for every respondent.
Respondent 1 = Repondent Population Size ÷ Total Population × Total Sample Size
STEM = 220 ÷ 1900 × 330 = 38.2 (38)
HUMSS = 330 ÷ 1900 × 330 = 57.3 (57)
ABM = 430 ÷ 1900 × 330 = 74.6 (75)
GAS = 170 ÷ 1900 × 330 = 29.5 (30)
ICT = 350 ÷ 1900 × 330 = 60.7 (61)
HE = 400 ÷ 1900 × 330 = 69.4 (69)
Total Sample Size = 38 + 57 + 75 + 30 + 61 + 69 = 330
Take Note:
Sometimes the total sample size is +/- 1.
www.btech.edu.ph STATISTICAL ANALYSIS AND SOFTWARE APPLICATION Page 8 of 10
Supplemental Videos for this topic:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tFWsuO9f74o
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MGTeT-ZAL_I
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IaTFpp-uzp0
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h3Sh82NcLCk
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Nbz_vkdRP-w
www.btech.edu.ph STATISTICAL ANALYSIS AND SOFTWARE APPLICATION Page 9 of 10
WHAT HAVE I LEARNED?
1. Compute the sample size of the table below using Slovin’s formula.
RESPONDENTS POPULATION SIZE SAMPLE SIZE
BSIT 250
BSCOE 350
BAHRM 180
BSAIS 385
BSA 450
BSED 125
BEED 105
2. The average test score of all students in a certain class was measured to be 84
with a standard deviation of 15. If the margin of error was calculated to be 5.367
at a 95% confidence level, how many students were in this class?
3. Sally wants to determine what proportion of high school students are planning to
enroll in college after they graduate. Given a 95% confidence level and a margin
of error of 5%, what is the maximum sample size that she should use in order to
perform statistical experiment?
ASSIGNMENT
Define the following terms:
1. Observation unit
2. Target population
3. Sample population
4. Sample
5. Sample unit
6. Sample frame
7. Sample technique
8. Sampling bias
9. Probability sample
10. Non – probability sample
www.btech.edu.ph STATISTICAL ANALYSIS AND SOFTWARE APPLICATION Page 10 of 10
You might also like
- Chat GPTDocument13 pagesChat GPTsuly maniyahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 Estimation and Confidence IntervalsDocument45 pagesCHAPTER 9 Estimation and Confidence IntervalsAyushi Jangpangi100% (1)
- Citizens CharterDocument3 pagesCitizens CharterChona Dabu100% (1)
- 4 - Hydro Jetting and Sludge RemovalDocument18 pages4 - Hydro Jetting and Sludge RemovalPerwez21100% (2)
- StatDocument70 pagesStatcj_anero67% (3)
- Power and Sample Size DeterminationDocument27 pagesPower and Sample Size DeterminationArockia SamyNo ratings yet
- Statatistical InferencesDocument22 pagesStatatistical InferencesBlen tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Summer I 2016Document6 pagesTest 2 Summer I 2016Antonio ShinneryNo ratings yet
- BRM NotesDocument17 pagesBRM NotesvipukNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledAleesha MontenegroNo ratings yet
- L6 Sample Size EstimationDocument16 pagesL6 Sample Size EstimationASHENAFI LEMESANo ratings yet
- Math11 SP Q3 M8 PDFDocument12 pagesMath11 SP Q3 M8 PDFJessa Banawan EdulanNo ratings yet
- GFK K.pusczak-Sample Size in Customer Surveys - PaperDocument27 pagesGFK K.pusczak-Sample Size in Customer Surveys - PaperVAlentino AUrishNo ratings yet
- Cui - Practical Exercise 3.1Document5 pagesCui - Practical Exercise 3.1John Ronnie Tare CuiNo ratings yet
- Data Science Interview Questions - Statistics: Mohit Kumar Dec 12, 2018 11 Min ReadDocument14 pagesData Science Interview Questions - Statistics: Mohit Kumar Dec 12, 2018 11 Min ReadHaythem Mzoughi100% (1)
- Mms Testing of HypothesisDocument69 pagesMms Testing of HypothesisKenneth MathewsNo ratings yet
- Kajal Srivastava SPM Deptt. S.N.Medical College,: Determining The Size of A SampleDocument38 pagesKajal Srivastava SPM Deptt. S.N.Medical College,: Determining The Size of A SampleAnkit TomarNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Business Statistics in Practice Canadian 3rd Edition Bowerman Test Bank Full ChapterDocument88 pages(Download PDF) Business Statistics in Practice Canadian 3rd Edition Bowerman Test Bank Full Chapteretpkoang100% (8)
- Download Business Statistics in Practice Canadian 3rd Edition Bowerman Test Bank all chaptersDocument44 pagesDownload Business Statistics in Practice Canadian 3rd Edition Bowerman Test Bank all chaptersmameyenning100% (3)
- Statistics 578 Assignemnt 3Document12 pagesStatistics 578 Assignemnt 3Mia Dee100% (1)
- Lessons in Business Statistics Prepared by P.K. ViswanathanDocument27 pagesLessons in Business Statistics Prepared by P.K. ViswanathanLloyd LamingtonNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics in Practice Canadian 3rd Edition Bowerman Test Bank instant download all chapterDocument88 pagesBusiness Statistics in Practice Canadian 3rd Edition Bowerman Test Bank instant download all chapteremurlamianda100% (3)
- 3.1 Sampling ConceptDocument10 pages3.1 Sampling Conceptshashankgulati30No ratings yet
- Forms of Test Statistic For The Population Mean: Lesson 13.2Document27 pagesForms of Test Statistic For The Population Mean: Lesson 13.2Tin CabosNo ratings yet
- QUARTER: 2/ SEMESTER: First (Week 1-3) :: Concept Notes With Formative ActivitiesDocument15 pagesQUARTER: 2/ SEMESTER: First (Week 1-3) :: Concept Notes With Formative ActivitiesMonica SolomonNo ratings yet
- Jsmith Microbe 09Document0 pagesJsmith Microbe 09Lionel PinuerNo ratings yet
- Interval EstimationDocument33 pagesInterval EstimationArvind ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Cochran's FormulaDocument10 pagesCochran's FormulaAmythize ChemadianNo ratings yet
- Sampling Fundamentals CompleteDocument7 pagesSampling Fundamentals CompleteGerry WoNo ratings yet
- Learning Competency 4Document53 pagesLearning Competency 4John ClausNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document21 pagesModule 5Ivy Ann P. VillarinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Sample Size DeterminationDocument16 pagesLesson 4 Sample Size Determinationana mejicoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EstimationDocument9 pagesIntroduction To EstimationRegina Raymundo AlbayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Notes PDFDocument15 pagesLecture 7 Notes PDFsound05No ratings yet
- Six Sigma Mission: Statistical Sample Population ParameterDocument4 pagesSix Sigma Mission: Statistical Sample Population ParameterFaheem HussainNo ratings yet
- Sample Size Determination: BY DR Zubair K.ODocument43 pagesSample Size Determination: BY DR Zubair K.OOK ViewNo ratings yet
- Sample Size Determination: BY DR Zubair K.ODocument43 pagesSample Size Determination: BY DR Zubair K.OMakmur SejatiNo ratings yet
- Summer 578 Assignment 3 SolutionsDocument13 pagesSummer 578 Assignment 3 SolutionsGradu8tedOne100% (1)
- Statistical Inference NewDocument25 pagesStatistical Inference NewAbhinav SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Audit Sampling For Substantive TestingDocument14 pagesChapter 19 Audit Sampling For Substantive TestingRose Ann Russel0% (1)
- Mba Semester 1 Mb0040 - Statistics For Management-4 Credits (Book ID: B1129) Assignment Set - 1 (60 Marks)Document10 pagesMba Semester 1 Mb0040 - Statistics For Management-4 Credits (Book ID: B1129) Assignment Set - 1 (60 Marks)Rajesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Sample SizeDocument28 pagesChapter 4 Sample Sizetemesgen yohannesNo ratings yet
- Sample Size CalculationDocument10 pagesSample Size Calculationrizul SAININo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument13 pagesFinal ExamILIG, Pauline Joy E.No ratings yet
- Lecture 24 PDFDocument12 pagesLecture 24 PDFAnonymous 7HfJimvNo ratings yet
- Estimation Through BootsrtappingDocument6 pagesEstimation Through Bootsrtappingmayankmittal27No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Business Statistics in Practice 6th Edition Bowerman Full DownloadDocument77 pagesTest Bank For Business Statistics in Practice 6th Edition Bowerman Full Downloaderichughesbdnxfgqyra100% (53)
- Practice FinalDocument17 pagesPractice Finalterrygoh6972No ratings yet
- APPROACHESDocument5 pagesAPPROACHESRENIER ACE ABORDONo ratings yet
- Statistics Lecture Part 2 PDFDocument60 pagesStatistics Lecture Part 2 PDFBarbara MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Stats LAS Q4 2Document3 pagesStats LAS Q4 2nimenzochristian0No ratings yet
- Sample Size in Statistics (How To Find It) Excel Cochran's Formula General TipsDocument5 pagesSample Size in Statistics (How To Find It) Excel Cochran's Formula General Tipsrigan100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Sampling - 2019Document34 pagesChapter 3 - Sampling - 2019Ti SINo ratings yet
- 2estimation of The Mean PDFDocument11 pages2estimation of The Mean PDFJim Paul ManaoNo ratings yet
- Theory of EstimationDocument30 pagesTheory of EstimationTech_MX100% (1)
- CH 09Document10 pagesCH 09aqillahNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 3Rd Edition Nolan Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesEssentials of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 3Rd Edition Nolan Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFkelly.adams280100% (11)
- Essentials of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 3rd Edition Nolan Solutions Manual 1Document9 pagesEssentials of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 3rd Edition Nolan Solutions Manual 1marsha100% (43)
- Bayesian Non- and Semi-parametric Methods and ApplicationsFrom EverandBayesian Non- and Semi-parametric Methods and ApplicationsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Applied Statistics Manual: A Guide to Improving and Sustaining Quality with MinitabFrom EverandApplied Statistics Manual: A Guide to Improving and Sustaining Quality with MinitabNo ratings yet
- How to Find Inter-Groups Differences Using Spss/Excel/Web Tools in Common Experimental Designs: Book 1From EverandHow to Find Inter-Groups Differences Using Spss/Excel/Web Tools in Common Experimental Designs: Book 1No ratings yet
- Republic Act 9184Document94 pagesRepublic Act 9184Paw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document7 pagesLesson 1Paw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- 4.2 (FINAL) Ease of Doing Business ActDocument59 pages4.2 (FINAL) Ease of Doing Business ActPaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Procurement ProcedureDocument1 pageProcurement ProcedurePaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem 7.0Document4 pagesPractice Problem 7.0Paw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document1 pageLesson 3Paw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- The Accounting Equation: Sir Chua's Accounting Lessons PHDocument2 pagesThe Accounting Equation: Sir Chua's Accounting Lessons PHPaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- 4.1 (FINAL) FRIA - Part 1Document12 pages4.1 (FINAL) FRIA - Part 1Paw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- The Law On Sales, Agency, and Credit Transactions de Leon & de Leon 2010Document5 pagesThe Law On Sales, Agency, and Credit Transactions de Leon & de Leon 2010Paw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Background On Mortgages: Mortgage MarketsDocument7 pagesBackground On Mortgages: Mortgage MarketsPaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document13 pagesLesson 1Paw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Module in Contemporary WorldDocument50 pagesModule in Contemporary WorldPaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document9 pagesCH 10Paw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- ACT15 Prelim ExamDocument8 pagesACT15 Prelim ExamPaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- L1 The World of ComputerDocument23 pagesL1 The World of ComputerPaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Social Sciences: Nature, Disciplines, Theories and IdeasDocument42 pagesSocial Sciences: Nature, Disciplines, Theories and IdeasPaw Verdillo100% (1)
- Social Sciences: Nature, Disciplines, Theories and IdeasDocument23 pagesSocial Sciences: Nature, Disciplines, Theories and IdeasPaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Ch03 Money MarketDocument8 pagesCh03 Money MarketPaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
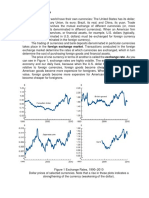
- Ch02 Foreign Exchange MarketsDocument8 pagesCh02 Foreign Exchange MarketsPaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Ch02 Foreign Exchange MarketsDocument8 pagesCh02 Foreign Exchange MarketsPaw VerdilloNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes-Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Notes PDFDocument30 pagesLecture Notes-Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Notes PDFMDR PRAPHU100% (1)
- Basement and Retaining WallsDocument42 pagesBasement and Retaining WallsSamata Mahajan0% (1)
- Salen WWE Offer LetterDocument3 pagesSalen WWE Offer LetterHeel By NatureNo ratings yet
- A Profect Report On Star Claytech Pvt. LTDDocument44 pagesA Profect Report On Star Claytech Pvt. LTDraj danichaNo ratings yet
- The 60 MM Diameter Solid Shaft Is Subjected To The... PDFDocument3 pagesThe 60 MM Diameter Solid Shaft Is Subjected To The... PDFxy2h5bjs27No ratings yet
- AnswersDocument24 pagesAnswersDeul ErNo ratings yet
- AralPan9 q2 Mod10 Ang-Pamilihan-V5Document29 pagesAralPan9 q2 Mod10 Ang-Pamilihan-V5Wizly Von Ledesma TanduyanNo ratings yet
- MarxismDocument13 pagesMarxismFelicia AtmadjaNo ratings yet
- Cable Incendio 2X18 Awg S/P: UL1424FPLRDocument1 pageCable Incendio 2X18 Awg S/P: UL1424FPLR04143510504gallucciNo ratings yet
- Vol.11 Issue 46 March 23-29, 2019Document32 pagesVol.11 Issue 46 March 23-29, 2019Thesouthasian TimesNo ratings yet
- Altagamma Bain Worldwide Market Monitor - Update 2019 PDFDocument15 pagesAltagamma Bain Worldwide Market Monitor - Update 2019 PDFHaider RazaNo ratings yet
- Sop - CccuDocument3 pagesSop - CccuAiman HassanNo ratings yet
- Upshur County ReportDocument16 pagesUpshur County ReportAnna SaundersNo ratings yet
- Soliven vs. FastformsDocument2 pagesSoliven vs. FastformsClaudine Allyson DungoNo ratings yet
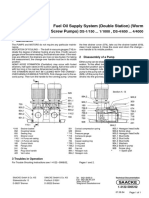
- Fuel Oil Supply System (Double Station) (Worm Screw Pumps) : DS 1/150 ... 1/1000, DS 4/650 ... 4/4000Document1 pageFuel Oil Supply System (Double Station) (Worm Screw Pumps) : DS 1/150 ... 1/1000, DS 4/650 ... 4/4000徐玉坤No ratings yet
- QUIZ 3 Financial Forecasting and BudgetingDocument9 pagesQUIZ 3 Financial Forecasting and BudgetingPRINCESS HONEYLET SIGESMUNDONo ratings yet
- DS - 20201123 - MVS3150-LV Datasheet - V1.2.2 - ENDocument2 pagesDS - 20201123 - MVS3150-LV Datasheet - V1.2.2 - ENGabooNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Using Wimax Technology: Journal of Engineering and Sustainable Development September 2010Document21 pagesWireless Communication Using Wimax Technology: Journal of Engineering and Sustainable Development September 2010ahmed alshamliNo ratings yet
- Cut List Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCut List Cheat SheetmeredithNo ratings yet
- Superbad (Film) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument87 pagesSuperbad (Film) - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaresearcher911No ratings yet
- 3admin - 7Document13 pages3admin - 7JMXNo ratings yet
- Full Name: Work Experience Career SynopsisDocument2 pagesFull Name: Work Experience Career SynopsisYelchuri Kumar PhanindraNo ratings yet
- Ace3 Unit8 TestDocument3 pagesAce3 Unit8 Testnatacha100% (3)
- Full Chapter Blockchain and Smart Contract Technologies For Innovative Applications 1St Edition Nour El Madhoun PDFDocument54 pagesFull Chapter Blockchain and Smart Contract Technologies For Innovative Applications 1St Edition Nour El Madhoun PDFjames.harrington239100% (4)
- Business Unit Performance Measurement: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument17 pagesBusiness Unit Performance Measurement: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwinimran_chaudhryNo ratings yet
- CS Lecture Notes PDFDocument138 pagesCS Lecture Notes PDFNikhil GaidhaneNo ratings yet
- Dicionário Assírio SDocument452 pagesDicionário Assírio SAlexandre Luis Dos Santos100% (1)