Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Physics
What Is Physics
Uploaded by
Something ChicCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Case Problem 1 Wagner Fabricating CompanyDocument3 pagesCase Problem 1 Wagner Fabricating CompanySomething ChicNo ratings yet
- PMP Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Cheat SheetoovijaygNo ratings yet
- AST201 Assignment 3Document12 pagesAST201 Assignment 3AnnaaaNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 3 Truck Leasing StrategyDocument4 pagesCase Problem 3 Truck Leasing StrategySomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Property Purchase StrategyDocument2 pagesCase Problem 1 Property Purchase StrategySomething Chic100% (1)
- Experiment 1: Errors, Uncertainties and Measurements Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesExperiment 1: Errors, Uncertainties and Measurements Laboratory ReportEmman CervantesNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 2 Office Equipment, Inc.Document2 pagesCase Problem 2 Office Equipment, Inc.Something ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem R.C. ColemanDocument5 pagesCase Problem R.C. ColemanSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Errors, Uncertainties and Measurements Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesExperiment 1: Errors, Uncertainties and Measurements Laboratory ReportIson DyNo ratings yet
- Mensa WorkoutDocument12 pagesMensa WorkoutNeeti Gurunath100% (5)
- Case Problem 2 Phoenix ComputerDocument3 pagesCase Problem 2 Phoenix ComputerSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 3 Textile Mill SchedulingDocument4 pagesCase Problem 3 Textile Mill SchedulingSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- ESE122 Lecturer Notes - Feb2018 PDFDocument138 pagesESE122 Lecturer Notes - Feb2018 PDFMuhammad LuqmanNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Extra ActDocument28 pagesGen Chem Extra ActSEAN ELVIN DIGMANNo ratings yet
- SC +notationDocument20 pagesSC +notationVictoria FuenmayorNo ratings yet
- Performance Characteristics of Measuring Instruments of Measuring InstrumentsDocument20 pagesPerformance Characteristics of Measuring Instruments of Measuring Instrumentsyogesh.20222066No ratings yet
- L2 Accuracy, Precision and ErrorDocument25 pagesL2 Accuracy, Precision and ErrorSanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER (2) Statistical Treatment of Experimental DataDocument30 pagesCHAPTER (2) Statistical Treatment of Experimental DataAhamed Saleel C100% (1)
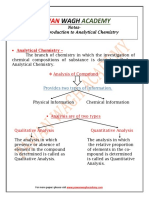
- Introduction To Analytical Chemistry Class 11th NotesDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Analytical Chemistry Class 11th NotesAkki GAMERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-1Document31 pagesChapter 2-1Malik ForbesNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Metrology NotesDocument18 pagesMeasurement and Metrology NotesAnything You Could ImagineNo ratings yet
- Uncertainties From LABBOOK2022Document4 pagesUncertainties From LABBOOK2022katethekat2.0No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MeasurementDocument28 pagesChapter 2 MeasurementJames DellavaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Measurement and ErrorDocument41 pagesUnit 1 Measurement and Erroraini norNo ratings yet
- ESE122 Lecturer Notes - Mac 2021Document115 pagesESE122 Lecturer Notes - Mac 2021Faris IzdiharNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 EstimationDocument8 pagesLecture 6 Estimationhoangminhdung2209No ratings yet
- Errors in Chemical AnalysisDocument20 pagesErrors in Chemical AnalysisZeena SalmanNo ratings yet
- S C I e N T I F I C MeasurementsDocument41 pagesS C I e N T I F I C MeasurementsAaronkim PalonNo ratings yet
- CC140 PPT Unit-1Document30 pagesCC140 PPT Unit-1hudasalhadinNo ratings yet
- Lec1-2 Accuracy & Precision (COR)Document34 pagesLec1-2 Accuracy & Precision (COR)Sadeep RautNo ratings yet
- Sec1 Quality (Validation)Document19 pagesSec1 Quality (Validation)ahmedmohamed01153159469No ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document36 pagesLecture 16Abood FazilNo ratings yet
- Units, Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocument38 pagesUnits, Physical Quantities and MeasurementChristian CincoNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 Wk1 Conversion of Units Scientific NotationDocument158 pagesPhysics 1 Wk1 Conversion of Units Scientific NotationCheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- CHY 123 - Chapter 1 - Fall 2019 - AnnotatedDocument48 pagesCHY 123 - Chapter 1 - Fall 2019 - AnnotatedneggoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.newDocument33 pagesChapter 2.newRochelle Anne BandaNo ratings yet
- Chap1 - Understanding Physics v4Document114 pagesChap1 - Understanding Physics v4Nicole TNo ratings yet
- Lec9 Appro. Error (P1)Document22 pagesLec9 Appro. Error (P1)nhungNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning and Linear RegressionDocument55 pagesMachine Learning and Linear RegressionKapil Chandel100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Measurement: Accuracy, Precision, and ErrorDocument20 pagesChapter 1: Measurement: Accuracy, Precision, and Errorarya starkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Additional) - Adding Up Errors, Relative AcuracyDocument3 pagesChapter 1 (Additional) - Adding Up Errors, Relative AcuracyKristine May MaturanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PresenstationDocument17 pagesChemistry PresenstationCaptian ProximaNo ratings yet
- Estimation Bertinoro09 Cristiano Porciani 1Document42 pagesEstimation Bertinoro09 Cristiano Porciani 1shikha singhNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document15 pagesChap 2triangularedgeNo ratings yet
- Measurement and UncertaintyDocument23 pagesMeasurement and UncertaintyRed islifeeNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Physical Quantities, Units and Scientific NotationDocument47 pagesMeasurement of Physical Quantities, Units and Scientific NotationKyrah ViorNo ratings yet
- Introduction ChemistryDocument42 pagesIntroduction Chemistryนุชนรี ศรีวิเชียรNo ratings yet
- Physics 1Document10 pagesPhysics 1Krizel SalidoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Estimating From A Sample Sample Mean and Confidence Intervals Upload 2Document22 pagesLecture 4 Estimating From A Sample Sample Mean and Confidence Intervals Upload 2mussy001No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Errors and Statistics and Probable ErrorsDocument46 pagesLecture 3 - Errors and Statistics and Probable Errorspeterpaul_1211No ratings yet
- Ee300 CH1Document55 pagesEe300 CH1Yousef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and Precision PDFDocument9 pagesAccuracy and Precision PDFrogok31402No ratings yet
- InstrumentationDocument47 pagesInstrumentationnitin tyagiNo ratings yet
- 1.2b Measurement and UncertaintiesDocument31 pages1.2b Measurement and UncertaintiesJiwoo SeoNo ratings yet
- 2021 Stat NotesDocument162 pages2021 Stat NotesKhushiNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology and Biostatistics Part II 2Document45 pagesResearch Methodology and Biostatistics Part II 2Sohail SheikhNo ratings yet
- Units 1.0Document8 pagesUnits 1.0AbhishekNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction To Multivariate Analysis PDFDocument55 pagesL1 Introduction To Multivariate Analysis PDFSi Hui ZhuoNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation AND Measurement Techniques: Chapter 1 (Part B) Measurement ErrorsDocument40 pagesInstrumentation AND Measurement Techniques: Chapter 1 (Part B) Measurement ErrorsCalvin KongNo ratings yet
- Topic IIIDocument27 pagesTopic IIIEmmarehBucolNo ratings yet
- Dr. KS - Errors in Chemical Analysis PDFDocument19 pagesDr. KS - Errors in Chemical Analysis PDFVijay Kumar VishvakarmaNo ratings yet
- 1 普物實驗數據的處理 (不確定度的更改)Document16 pages1 普物實驗數據的處理 (不確定度的更改)extracurricular8000No ratings yet
- Accuracy Is How Close Your ObservedDocument1 pageAccuracy Is How Close Your ObservedJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- p6 - 1 RevDocument3 pagesp6 - 1 RevShirsendu MondolNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and PrecisionDocument25 pagesAccuracy and PrecisionMarArizala100% (1)
- Lecture 2Document17 pagesLecture 2technologistahamedNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument33 pagesIntroVarshini PandianNo ratings yet
- Lab#01 2Document10 pagesLab#01 2Electro OpNo ratings yet
- Objectives: General Physics 1Document8 pagesObjectives: General Physics 1Raymond De AsisNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankFrom EverandMeasurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 2 Harbor Dunes Golf CourseDocument2 pagesCase Problem 2 Harbor Dunes Golf CourseSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 2 Distribution Systems DesignDocument6 pagesCase Problem 2 Distribution Systems DesignSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 2 Forecasting Lost SalesDocument2 pagesCase Problem 2 Forecasting Lost SalesSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Workload BalancingDocument3 pagesCase Problem 1 Workload BalancingSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sol 31-39Document8 pagesChapter 2 Sol 31-39Something ChicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sol 40-43Document6 pagesChapter 2 Sol 40-43Something ChicNo ratings yet
- Types of LibrariesDocument3 pagesTypes of LibrariesSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Predetermined Overhead Rates, Flexible Budgets, and Absorption/Variable Costing QuestionsDocument4 pagesPredetermined Overhead Rates, Flexible Budgets, and Absorption/Variable Costing QuestionsSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Activity-Based Management and Activity-Based CostingDocument2 pagesActivity-Based Management and Activity-Based CostingSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Sol 11-20Document4 pagesChapter 3 Sol 11-20Something ChicNo ratings yet
- 15-61. The Following Are Independent Audit Situations For Which You Are To Recommend AnDocument4 pages15-61. The Following Are Independent Audit Situations For Which You Are To Recommend AnSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- 3-31 To 3-41 SolutionDocument5 pages3-31 To 3-41 SolutionSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Regional AirlinesDocument5 pagesCase Problem 1 Regional AirlinesSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- 3-43. The Following Computations Are For The Decision Tree That FollowsDocument3 pages3-43. The Following Computations Are For The Decision Tree That FollowsSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 2 Production StrategyDocument2 pagesCase Problem 2 Production StrategySomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 2 Investment StrategyDocument5 pagesCase Problem 2 Investment StrategySomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Planning An Advertising CampaignDocument4 pagesCase Problem 1 Planning An Advertising CampaignSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem Dealer's Absorbing State Probabilities in Black JackDocument5 pagesCase Problem Dealer's Absorbing State Probabilities in Black JackSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Forecasting SalesDocument3 pagesCase Problem 1 Forecasting SalesSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Textbook PublishingDocument2 pagesCase Problem 1 Textbook PublishingSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Questions and AnswersDocument13 pagesQuestions and AnswersKancham Harsha royalNo ratings yet
- 542 400 056 enDocument1 page542 400 056 enYi-jen ChanNo ratings yet
- Dsi 700Document30 pagesDsi 700mahh1234No ratings yet
- Web Server Log Analysis SysytemDocument3 pagesWeb Server Log Analysis SysytemNexgen TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Mainboard+FY16+2K+GN2S QW+&+QT+Segments+Easy+Repair+Guide (GN2S)Document28 pagesMainboard+FY16+2K+GN2S QW+&+QT+Segments+Easy+Repair+Guide (GN2S)oscarmdNo ratings yet
- Turbo Codes Promises and ChallengesDocument5 pagesTurbo Codes Promises and Challengesyancgece9763No ratings yet
- Clase 13072019 Ccna2Document5 pagesClase 13072019 Ccna2Carlos LuisNo ratings yet
- 22 Bollinger Band RulesDocument4 pages22 Bollinger Band Rulesravee100% (2)
- Combined VariationsDocument16 pagesCombined VariationsFiacre Winchell0% (1)
- Experiment 4Document28 pagesExperiment 4nellyNo ratings yet
- Mustek Ups Powermust 1000 Usb P Powermust 1000 Usb ListovkaDocument1 pageMustek Ups Powermust 1000 Usb P Powermust 1000 Usb ListovkaВиктор БабкоNo ratings yet
- ES 5 06 0019 - Flange Bolting GuidelinesDocument12 pagesES 5 06 0019 - Flange Bolting Guidelinessam.trags100% (1)
- Electric Charges and Fields 2ndPUC PYQsDocument2 pagesElectric Charges and Fields 2ndPUC PYQsXyzzNo ratings yet
- Yeh 2012Document8 pagesYeh 2012Luis PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Sortino - A "Sharper" Ratio! - Red Rock CapitalDocument6 pagesSortino - A "Sharper" Ratio! - Red Rock CapitalInterconti Ltd.No ratings yet
- Chapter 09 Excercises Part IIDocument5 pagesChapter 09 Excercises Part IIFatbardha MorinaNo ratings yet
- BBZDocument6 pagesBBZbm_ntNo ratings yet
- Dynamic ProgrammingDocument5 pagesDynamic ProgrammingKrafton GamingNo ratings yet
- Correlation Between The Standard PenetrationDocument64 pagesCorrelation Between The Standard PenetrationDavid GurionNo ratings yet
- RP6 S7 RMTC2 LRP22018 June PDFDocument12 pagesRP6 S7 RMTC2 LRP22018 June PDFZaliNo ratings yet
- Theodor Wilhelm EngelmannDocument3 pagesTheodor Wilhelm EngelmannJames FranklinNo ratings yet
- 1-INRODUCTION TO MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-10-Jul-2019Material - I - 10-Jul-2019 - 1 - IntroductionDocument6 pages1-INRODUCTION TO MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-10-Jul-2019Material - I - 10-Jul-2019 - 1 - Introductionabhignan routhuNo ratings yet
- Proposal ETPDocument4 pagesProposal ETPBanerjee SuvranilNo ratings yet
- 11Document23 pages11Vishakha GaurNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Inverse Functions & LogarithmsDocument11 pages1.5 Inverse Functions & Logarithms郭大維No ratings yet
- Protective Transformers: by N.H, Shton, Revised by E.J.MellorDocument31 pagesProtective Transformers: by N.H, Shton, Revised by E.J.MellorJavier MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Locally Design Plastic Crushing Machine For Domestic and Industrial Use in NigeriaDocument6 pagesPerformance Analysis of Locally Design Plastic Crushing Machine For Domestic and Industrial Use in NigeriaRishokNo ratings yet
What Is Physics
What Is Physics
Uploaded by
Something ChicOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Physics
What Is Physics
Uploaded by
Something ChicCopyright:
Available Formats
What is Physics?
Physics is the study of the basic components of the universe and their interactions. Theories of physics
have to be verified by the experimental measurements.
Physical Quantities
• Physical quantities are a characteristic or property of an object that can be measured or calculated
from other measurements.
• Consist of numerical value and units.
Quantitative versus Qualitative
• Most observation in physics are quantitative
• Descriptive observations (or qualitative) are usually imprecise
Physical Quantities are classified into two types:
Base quantity Derived quantity
* is like the brick – the basic * is like the house that was build up from a
building block of a house collection of bricks (basic quantity)
A conversion factor is a ratio that expresses how many of one unit are equal to another unit.
Scientific Notation
• Scientific notation is used to express very large or very small numbers
• It consists of a number between 1 & 10 followed by x 10 to an exponent
• Exponent can be determined by the number of decimal places you have to move to get only 1
number in front of the decimal
Ex: Mr. Smith bought an adult male cow that weighs 1,700 lbs. What is the weight of the cow in kg?
1 kg=2.2lbs . ( Conversionfactor )
1 700lbs . ( 1 kg
2.2lbs . )
→1 700 ( )
1 kg
2.2
2
772.727 kg∨7.72727 ×10 kg
Accuracy Precision
- % Error - Significant Figures/Digits
• How close you are to the actual value • How finely tuned your measurements
• Depends on the person measuring are or how close they can be to each
• Calculated by the formula: other
% Error=¿ • Depends on the measuring tool
• Determined by the number of
Theoretical Value−Experimental Value significant digits.
¿ ×100 %
Theoretical Value
Accuracy - Calculating % Error
Accuracy is the closeness of a measured value to the true value.
Theoretical Value−Experimental Value
% Error= × 100 %
Theoretical Value
Where: Experimental value = measured value Theoretical value = accepted value
Ex: If a student measured the room width at 8.46 m and the accepted value was 9.45 m. What was their
accuracy?
Theoretical Value−Experimental Value
% Error= × 100 %
Theoretical Value
9.45 m−8.46 m
% Error= × 100 %
9.45 m
% Error=10.5 %
A. Low accuracy, B. Low accuracy, C. High accuracy, D. High accuracy,
low precision high precision low precision high precision
You might also like
- Case Problem 1 Wagner Fabricating CompanyDocument3 pagesCase Problem 1 Wagner Fabricating CompanySomething ChicNo ratings yet
- PMP Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Cheat SheetoovijaygNo ratings yet
- AST201 Assignment 3Document12 pagesAST201 Assignment 3AnnaaaNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 3 Truck Leasing StrategyDocument4 pagesCase Problem 3 Truck Leasing StrategySomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Property Purchase StrategyDocument2 pagesCase Problem 1 Property Purchase StrategySomething Chic100% (1)
- Experiment 1: Errors, Uncertainties and Measurements Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesExperiment 1: Errors, Uncertainties and Measurements Laboratory ReportEmman CervantesNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 2 Office Equipment, Inc.Document2 pagesCase Problem 2 Office Equipment, Inc.Something ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem R.C. ColemanDocument5 pagesCase Problem R.C. ColemanSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Errors, Uncertainties and Measurements Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesExperiment 1: Errors, Uncertainties and Measurements Laboratory ReportIson DyNo ratings yet
- Mensa WorkoutDocument12 pagesMensa WorkoutNeeti Gurunath100% (5)
- Case Problem 2 Phoenix ComputerDocument3 pagesCase Problem 2 Phoenix ComputerSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 3 Textile Mill SchedulingDocument4 pagesCase Problem 3 Textile Mill SchedulingSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- ESE122 Lecturer Notes - Feb2018 PDFDocument138 pagesESE122 Lecturer Notes - Feb2018 PDFMuhammad LuqmanNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Extra ActDocument28 pagesGen Chem Extra ActSEAN ELVIN DIGMANNo ratings yet
- SC +notationDocument20 pagesSC +notationVictoria FuenmayorNo ratings yet
- Performance Characteristics of Measuring Instruments of Measuring InstrumentsDocument20 pagesPerformance Characteristics of Measuring Instruments of Measuring Instrumentsyogesh.20222066No ratings yet
- L2 Accuracy, Precision and ErrorDocument25 pagesL2 Accuracy, Precision and ErrorSanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER (2) Statistical Treatment of Experimental DataDocument30 pagesCHAPTER (2) Statistical Treatment of Experimental DataAhamed Saleel C100% (1)
- Introduction To Analytical Chemistry Class 11th NotesDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Analytical Chemistry Class 11th NotesAkki GAMERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-1Document31 pagesChapter 2-1Malik ForbesNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Metrology NotesDocument18 pagesMeasurement and Metrology NotesAnything You Could ImagineNo ratings yet
- Uncertainties From LABBOOK2022Document4 pagesUncertainties From LABBOOK2022katethekat2.0No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MeasurementDocument28 pagesChapter 2 MeasurementJames DellavaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Measurement and ErrorDocument41 pagesUnit 1 Measurement and Erroraini norNo ratings yet
- ESE122 Lecturer Notes - Mac 2021Document115 pagesESE122 Lecturer Notes - Mac 2021Faris IzdiharNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 EstimationDocument8 pagesLecture 6 Estimationhoangminhdung2209No ratings yet
- Errors in Chemical AnalysisDocument20 pagesErrors in Chemical AnalysisZeena SalmanNo ratings yet
- S C I e N T I F I C MeasurementsDocument41 pagesS C I e N T I F I C MeasurementsAaronkim PalonNo ratings yet
- CC140 PPT Unit-1Document30 pagesCC140 PPT Unit-1hudasalhadinNo ratings yet
- Lec1-2 Accuracy & Precision (COR)Document34 pagesLec1-2 Accuracy & Precision (COR)Sadeep RautNo ratings yet
- Sec1 Quality (Validation)Document19 pagesSec1 Quality (Validation)ahmedmohamed01153159469No ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document36 pagesLecture 16Abood FazilNo ratings yet
- Units, Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocument38 pagesUnits, Physical Quantities and MeasurementChristian CincoNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 Wk1 Conversion of Units Scientific NotationDocument158 pagesPhysics 1 Wk1 Conversion of Units Scientific NotationCheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- CHY 123 - Chapter 1 - Fall 2019 - AnnotatedDocument48 pagesCHY 123 - Chapter 1 - Fall 2019 - AnnotatedneggoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.newDocument33 pagesChapter 2.newRochelle Anne BandaNo ratings yet
- Chap1 - Understanding Physics v4Document114 pagesChap1 - Understanding Physics v4Nicole TNo ratings yet
- Lec9 Appro. Error (P1)Document22 pagesLec9 Appro. Error (P1)nhungNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning and Linear RegressionDocument55 pagesMachine Learning and Linear RegressionKapil Chandel100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Measurement: Accuracy, Precision, and ErrorDocument20 pagesChapter 1: Measurement: Accuracy, Precision, and Errorarya starkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Additional) - Adding Up Errors, Relative AcuracyDocument3 pagesChapter 1 (Additional) - Adding Up Errors, Relative AcuracyKristine May MaturanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PresenstationDocument17 pagesChemistry PresenstationCaptian ProximaNo ratings yet
- Estimation Bertinoro09 Cristiano Porciani 1Document42 pagesEstimation Bertinoro09 Cristiano Porciani 1shikha singhNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document15 pagesChap 2triangularedgeNo ratings yet
- Measurement and UncertaintyDocument23 pagesMeasurement and UncertaintyRed islifeeNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Physical Quantities, Units and Scientific NotationDocument47 pagesMeasurement of Physical Quantities, Units and Scientific NotationKyrah ViorNo ratings yet
- Introduction ChemistryDocument42 pagesIntroduction Chemistryนุชนรี ศรีวิเชียรNo ratings yet
- Physics 1Document10 pagesPhysics 1Krizel SalidoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Estimating From A Sample Sample Mean and Confidence Intervals Upload 2Document22 pagesLecture 4 Estimating From A Sample Sample Mean and Confidence Intervals Upload 2mussy001No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Errors and Statistics and Probable ErrorsDocument46 pagesLecture 3 - Errors and Statistics and Probable Errorspeterpaul_1211No ratings yet
- Ee300 CH1Document55 pagesEe300 CH1Yousef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and Precision PDFDocument9 pagesAccuracy and Precision PDFrogok31402No ratings yet
- InstrumentationDocument47 pagesInstrumentationnitin tyagiNo ratings yet
- 1.2b Measurement and UncertaintiesDocument31 pages1.2b Measurement and UncertaintiesJiwoo SeoNo ratings yet
- 2021 Stat NotesDocument162 pages2021 Stat NotesKhushiNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology and Biostatistics Part II 2Document45 pagesResearch Methodology and Biostatistics Part II 2Sohail SheikhNo ratings yet
- Units 1.0Document8 pagesUnits 1.0AbhishekNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction To Multivariate Analysis PDFDocument55 pagesL1 Introduction To Multivariate Analysis PDFSi Hui ZhuoNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation AND Measurement Techniques: Chapter 1 (Part B) Measurement ErrorsDocument40 pagesInstrumentation AND Measurement Techniques: Chapter 1 (Part B) Measurement ErrorsCalvin KongNo ratings yet
- Topic IIIDocument27 pagesTopic IIIEmmarehBucolNo ratings yet
- Dr. KS - Errors in Chemical Analysis PDFDocument19 pagesDr. KS - Errors in Chemical Analysis PDFVijay Kumar VishvakarmaNo ratings yet
- 1 普物實驗數據的處理 (不確定度的更改)Document16 pages1 普物實驗數據的處理 (不確定度的更改)extracurricular8000No ratings yet
- Accuracy Is How Close Your ObservedDocument1 pageAccuracy Is How Close Your ObservedJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- p6 - 1 RevDocument3 pagesp6 - 1 RevShirsendu MondolNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and PrecisionDocument25 pagesAccuracy and PrecisionMarArizala100% (1)
- Lecture 2Document17 pagesLecture 2technologistahamedNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument33 pagesIntroVarshini PandianNo ratings yet
- Lab#01 2Document10 pagesLab#01 2Electro OpNo ratings yet
- Objectives: General Physics 1Document8 pagesObjectives: General Physics 1Raymond De AsisNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankFrom EverandMeasurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 2 Harbor Dunes Golf CourseDocument2 pagesCase Problem 2 Harbor Dunes Golf CourseSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 2 Distribution Systems DesignDocument6 pagesCase Problem 2 Distribution Systems DesignSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 2 Forecasting Lost SalesDocument2 pagesCase Problem 2 Forecasting Lost SalesSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Workload BalancingDocument3 pagesCase Problem 1 Workload BalancingSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sol 31-39Document8 pagesChapter 2 Sol 31-39Something ChicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sol 40-43Document6 pagesChapter 2 Sol 40-43Something ChicNo ratings yet
- Types of LibrariesDocument3 pagesTypes of LibrariesSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Predetermined Overhead Rates, Flexible Budgets, and Absorption/Variable Costing QuestionsDocument4 pagesPredetermined Overhead Rates, Flexible Budgets, and Absorption/Variable Costing QuestionsSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Activity-Based Management and Activity-Based CostingDocument2 pagesActivity-Based Management and Activity-Based CostingSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Sol 11-20Document4 pagesChapter 3 Sol 11-20Something ChicNo ratings yet
- 15-61. The Following Are Independent Audit Situations For Which You Are To Recommend AnDocument4 pages15-61. The Following Are Independent Audit Situations For Which You Are To Recommend AnSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- 3-31 To 3-41 SolutionDocument5 pages3-31 To 3-41 SolutionSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Regional AirlinesDocument5 pagesCase Problem 1 Regional AirlinesSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- 3-43. The Following Computations Are For The Decision Tree That FollowsDocument3 pages3-43. The Following Computations Are For The Decision Tree That FollowsSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 2 Production StrategyDocument2 pagesCase Problem 2 Production StrategySomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 2 Investment StrategyDocument5 pagesCase Problem 2 Investment StrategySomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Planning An Advertising CampaignDocument4 pagesCase Problem 1 Planning An Advertising CampaignSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem Dealer's Absorbing State Probabilities in Black JackDocument5 pagesCase Problem Dealer's Absorbing State Probabilities in Black JackSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Forecasting SalesDocument3 pagesCase Problem 1 Forecasting SalesSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Textbook PublishingDocument2 pagesCase Problem 1 Textbook PublishingSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Questions and AnswersDocument13 pagesQuestions and AnswersKancham Harsha royalNo ratings yet
- 542 400 056 enDocument1 page542 400 056 enYi-jen ChanNo ratings yet
- Dsi 700Document30 pagesDsi 700mahh1234No ratings yet
- Web Server Log Analysis SysytemDocument3 pagesWeb Server Log Analysis SysytemNexgen TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Mainboard+FY16+2K+GN2S QW+&+QT+Segments+Easy+Repair+Guide (GN2S)Document28 pagesMainboard+FY16+2K+GN2S QW+&+QT+Segments+Easy+Repair+Guide (GN2S)oscarmdNo ratings yet
- Turbo Codes Promises and ChallengesDocument5 pagesTurbo Codes Promises and Challengesyancgece9763No ratings yet
- Clase 13072019 Ccna2Document5 pagesClase 13072019 Ccna2Carlos LuisNo ratings yet
- 22 Bollinger Band RulesDocument4 pages22 Bollinger Band Rulesravee100% (2)
- Combined VariationsDocument16 pagesCombined VariationsFiacre Winchell0% (1)
- Experiment 4Document28 pagesExperiment 4nellyNo ratings yet
- Mustek Ups Powermust 1000 Usb P Powermust 1000 Usb ListovkaDocument1 pageMustek Ups Powermust 1000 Usb P Powermust 1000 Usb ListovkaВиктор БабкоNo ratings yet
- ES 5 06 0019 - Flange Bolting GuidelinesDocument12 pagesES 5 06 0019 - Flange Bolting Guidelinessam.trags100% (1)
- Electric Charges and Fields 2ndPUC PYQsDocument2 pagesElectric Charges and Fields 2ndPUC PYQsXyzzNo ratings yet
- Yeh 2012Document8 pagesYeh 2012Luis PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Sortino - A "Sharper" Ratio! - Red Rock CapitalDocument6 pagesSortino - A "Sharper" Ratio! - Red Rock CapitalInterconti Ltd.No ratings yet
- Chapter 09 Excercises Part IIDocument5 pagesChapter 09 Excercises Part IIFatbardha MorinaNo ratings yet
- BBZDocument6 pagesBBZbm_ntNo ratings yet
- Dynamic ProgrammingDocument5 pagesDynamic ProgrammingKrafton GamingNo ratings yet
- Correlation Between The Standard PenetrationDocument64 pagesCorrelation Between The Standard PenetrationDavid GurionNo ratings yet
- RP6 S7 RMTC2 LRP22018 June PDFDocument12 pagesRP6 S7 RMTC2 LRP22018 June PDFZaliNo ratings yet
- Theodor Wilhelm EngelmannDocument3 pagesTheodor Wilhelm EngelmannJames FranklinNo ratings yet
- 1-INRODUCTION TO MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-10-Jul-2019Material - I - 10-Jul-2019 - 1 - IntroductionDocument6 pages1-INRODUCTION TO MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-10-Jul-2019Material - I - 10-Jul-2019 - 1 - Introductionabhignan routhuNo ratings yet
- Proposal ETPDocument4 pagesProposal ETPBanerjee SuvranilNo ratings yet
- 11Document23 pages11Vishakha GaurNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Inverse Functions & LogarithmsDocument11 pages1.5 Inverse Functions & Logarithms郭大維No ratings yet
- Protective Transformers: by N.H, Shton, Revised by E.J.MellorDocument31 pagesProtective Transformers: by N.H, Shton, Revised by E.J.MellorJavier MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Locally Design Plastic Crushing Machine For Domestic and Industrial Use in NigeriaDocument6 pagesPerformance Analysis of Locally Design Plastic Crushing Machine For Domestic and Industrial Use in NigeriaRishokNo ratings yet