Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2QP ECE EC8252 Model Exam-12.07.21
2QP ECE EC8252 Model Exam-12.07.21
Uploaded by
6057 MAANEESHA SOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2QP ECE EC8252 Model Exam-12.07.21
2QP ECE EC8252 Model Exam-12.07.21
Uploaded by
6057 MAANEESHA SCopyright:
Available Formats
R.M.K.
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
RSM Nagar, Puduvoyal– 601 206
Date : 12.07.2021
Model Exam – July 2021 (Online Test - through Google Classroom)
2nd Semester – B.E. / B. Tech.
Electronics and Communications Engineering
EC8252 – Electronic Devices
COs Course Outcome : The students, after the completion of the course, are expected to ….
CO1 Describe the principle and characteristics of semiconductor diode
CO2 Construct various transistor configurations
CO3 Illustrate small signal and large signal models of transistors
CO4 Express the principle and characteristics of Field effect Transistors
CO5 Explain the principle of operation and characteristics of special semiconductor diodes.
CO6 Discuss the operation of various semiconductor photo devices and power electronic devices.
Time : 3 Hours Answer ALL Questions Max. Marks : 100
Part-A (10 x 2 = 20 Marks)
1. Create a Si PN junction at T=300K with doping concentrations of Na=1010cm-3.assume that
in=1.5*1010cm-3.Calculate width of the space charge region in a PN junction when a reverse
bias Voltage Vr=5v is applied.
2. What is Einstein relationship in a PN junction?
3. Highlight the consequences of Early effect.
4. Why BJT called current controlled device?
5. Mention the operating modes of MOSFET.
6. Whether E-MOSFET is normally in OFF state condition? Justify.
7. What is Ohmic contact?
8. How miller effect reduced in Dual gate MOSFET?
9. What is the name implies VMOS?
10. State the application of photo transistor.
Part – B ( 5 x 13 = 65 Marks)
11.a. Describe the theory of PN junction and derive its diode current equation.(13)
11.a.1 Or
11.b. Explain in detail about the Zener breakdown and Avalanche breakdown. (13)
11.b.1
12.a. Express all the conductance parameters of hybrid π model of BJT? (13)
12.a.1 Or
12.b. Describe the Eber’s Moll model for a PNP transistor
12.b.1
13.a. i. Explain p-channel JFET with the Construction, operation and characteristics.(9)
ii. Identify each type of JFET (whether it is N-channel or P-channel), label the terminals, and
determine whether the JFET in each of these circuits will be turned on or off: (4)
13.a.1 Or
13.b. Examine why Depletion MOSFET is commonly known as “Normally – on” MOSFET?
13.b.1
14.a. Give the structure and working principle of Gallium Arsenide with neat diagram.
14.a.1 Or
14.b. Explain the FINFET and CNTFET circuit model with necessary diagrams.
14.b.1
15.a. Explain the construction, operation, V-I characteristics and application of DIAC ?
15.a.1 Or
15.b. Compare the characteristics and applications of UJT, SCR, DIAC and TRIAC ?
Part – C ( 1 x 15 = 15 Marks)
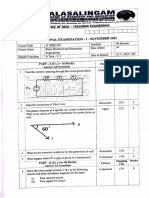
16.a. i. The circuit of Fig. uses two zener diodes, each rated at 15 V, 200 mA. If the circuit is
connected to a 45-volt unregulated supply, determine: (i) The regulated output voltage (ii) The
value of series resistance R. (8)
ii. A 10-V zener diode is used to regulate the voltage across a variable load resistor [See fig.].
The input voltage varies between 13 V and 16 V and the load current varies between 10 mA
and 85 mA. The minimum zener current is 15 mA. Calculate the value of series resistance
R.(7)
Or
16.b. Design & explain the working of temperature controlled circuit with thermistor and TRIAC
Knowledge Level ( Blooms Taxonomy)
K1 Remembering (Knowledge) K2 Understanding (Comprehension) K3 Applying (Application of Knowledge)
K4 Analysing (Analysis) K5 Evaluating (Evaluation) K6 Creating (Synthesis)
Knowledge Level and Course Outcome – Question wise Mapping
Part Part A
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
K Level K2 K2 K2 K2 K2 K2 K2 K2 K2 K2
CO CO1 CO1 CO2 CO2 CO4 CO4 CO5 CO5 CO6 CO6
Part Part B Part C
Question 11 (a) 11(b) 12 (a) 12 (b) 13 (a) 13 (b) 14 (a) 14 (b) 15 (a) 15 (b) 16 (a) 16 (b)
K Level K2 K2 K2 K2 K2 K2 K2 K2 K2 K2 K2 K3
CO CO1 CO1 CO3 CO3 CO4 CO4 CO5 CO5 CO6 CO6 CO5 CO6
You might also like
- 7qpg1a Ece Ec8701 Amwe Qb2Document2 pages7qpg1a Ece Ec8701 Amwe Qb2Gokul V100% (1)
- 1st Sem - ESEDocument8 pages1st Sem - ESEaditya ManhasNo ratings yet
- Model QPDocument3 pagesModel QPvenkatesanpNo ratings yet
- R.M.K. College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument2 pagesR.M.K. College of Engineering and TechnologysankarsadaNo ratings yet
- Part A: (Government Aided Autonomous Institution)Document2 pagesPart A: (Government Aided Autonomous Institution)Dr.V.R.VelmuruganNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper-FinalDocument4 pagesModel Question Paper-FinalKaushik NagojuNo ratings yet
- 17ee2605a Industrial Electrical Systems MPDocument2 pages17ee2605a Industrial Electrical Systems MPkrishna chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Beee Model QP1Document3 pagesBeee Model QP1vinoth muruganNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Model Question Paper 1 (June 2021)Document3 pagesVlsi Model Question Paper 1 (June 2021)PushpalathaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument2 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsAISWARYA MNo ratings yet
- SCT College of Engineering Dept. of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument2 pagesSCT College of Engineering Dept. of Electronics and Communication EngineeringakhilarajNo ratings yet
- IAT 3 - ED QB (4) NewDocument1 pageIAT 3 - ED QB (4) Newkpkarthi80No ratings yet
- 232EE1A13TA - Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pages232EE1A13TA - Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineeringrajasree Marine Engg-Asst ProfNo ratings yet
- 18EC36 PEI Assignment3Document2 pages18EC36 PEI Assignment3Gopalakrishnamurthy C.RNo ratings yet
- EET283-Introduction To Power EngineeringDocument9 pagesEET283-Introduction To Power EngineeringbinnytmzNo ratings yet
- (Government Aided Autonomous Institution) : Part ADocument1 page(Government Aided Autonomous Institution) : Part ADr.V.R.VelmuruganNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Sathak A J College of Engineering: Assessment - II Exam EC6701Document3 pagesMohamed Sathak A J College of Engineering: Assessment - II Exam EC6701formyphdNo ratings yet
- PUE Question Paper Format - 100 MarksDocument3 pagesPUE Question Paper Format - 100 MarksnupurnehaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Dec. EE203-E - Ktu QbankDocument2 pages2018 Dec. EE203-E - Ktu QbankFarooq KhandayNo ratings yet
- EET201-Circuits and NetworksDocument10 pagesEET201-Circuits and Networksᴀꜱᴡᴀɴᴛʜ ꜱʀᴇᴇɴɪNo ratings yet
- Mid Sem 2022-2023Document17 pagesMid Sem 2022-2023Mehul GuptaNo ratings yet
- WWW Manaresults Co inDocument2 pagesWWW Manaresults Co inRehaman ShaikNo ratings yet
- BBEE103 Set 1Document2 pagesBBEE103 Set 1samanth0404No ratings yet
- CS3351 - ModelDocument2 pagesCS3351 - Modelrkkumar07No ratings yet
- Basic Eln-2021-IA-1-Set 2 - ModifiedDocument2 pagesBasic Eln-2021-IA-1-Set 2 - ModifiedProf. Nikhil KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Ec8252ed Set2 PDFDocument2 pagesEc8252ed Set2 PDFRajkumar PerumalNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)HOD ECE KNCETNo ratings yet
- DC Machines and TransformersDocument8 pagesDC Machines and TransformersAlakaaa PromodNo ratings yet
- BEEEDocument6 pagesBEEEIts my VlogsNo ratings yet
- RF & MW Iat 1 QP 2019 Set1Document2 pagesRF & MW Iat 1 QP 2019 Set1formyphdNo ratings yet
- Bpe QB FinalDocument12 pagesBpe QB FinalHarshada ShindeNo ratings yet
- EET402 ElectricalSystemDesignandEstimationDocument10 pagesEET402 ElectricalSystemDesignandEstimationgowrisindhu03No ratings yet
- EET202 - Ktu QbankDocument8 pagesEET202 - Ktu QbankJisha KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- S8 SyllabusDocument208 pagesS8 Syllabusshyam krishnan sNo ratings yet
- 18EC36 PEI Assignment2Document48 pages18EC36 PEI Assignment2Gopalakrishnamurthy C.RNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem QPDocument16 pages3rd Sem QPRITHVIKHA VNo ratings yet
- EXAM Phys Elec II 2016 SolutionsDocument10 pagesEXAM Phys Elec II 2016 SolutionsThulasizwe PhethaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument129 pagesElectrical and Electronics EngineeringKTU ASSISTNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering - 2019 Scheme s3 Syllabus - Ktustudents - inDocument63 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engineering - 2019 Scheme s3 Syllabus - Ktustudents - inAswin RNo ratings yet
- BBEE103 Set 1Document2 pagesBBEE103 Set 1Sachin K PNo ratings yet
- Lic Model Set 2Document1 pageLic Model Set 2santhosh sekarNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING - 2019-Scheme-S4-Syllabus - Ktustudents - in PDFDocument66 pagesELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING - 2019-Scheme-S4-Syllabus - Ktustudents - in PDFgeethuNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Model Question Paper 3 (June 2021)Document4 pagesVlsi Model Question Paper 3 (June 2021)PushpalathaNo ratings yet
- EET285-Dynamic Circuits and SystemsDocument9 pagesEET285-Dynamic Circuits and SystemsDeepa M SNo ratings yet
- Kings: Question BankDocument6 pagesKings: Question BankRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- University Question Bank - EdcDocument16 pagesUniversity Question Bank - EdcSenthil IlangovanNo ratings yet
- Course Outcomes, Question Number, Marks: Cos Co1 Co2 Co3 Co4 Co5 Ques. No. Max. Marks Cos & K-LevelDocument14 pagesCourse Outcomes, Question Number, Marks: Cos Co1 Co2 Co3 Co4 Co5 Ques. No. Max. Marks Cos & K-LevelMATHAN RAJ MNo ratings yet
- University QsDocument41 pagesUniversity Qskaruppasamy17No ratings yet
- Set B: OfflineDocument2 pagesSet B: OfflineSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- 232EE1A13TA - Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - End SemDocument3 pages232EE1A13TA - Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - End Semrajasree Marine Engg-Asst ProfNo ratings yet
- S5 S6 Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument209 pagesS5 S6 Electrical & Electronics EngineeringThomas NigilNo ratings yet
- (B19EC1101) I B. Tech I Semester (R19) Regular Examinations Basic ElectronicsDocument2 pages(B19EC1101) I B. Tech I Semester (R19) Regular Examinations Basic Electronicsmadhu.jayamangalaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering - NewDocument28 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engineering - NewanushafiNo ratings yet
- Microwave and Radar QPDocument16 pagesMicrowave and Radar QPAdarsh RaiNo ratings yet
- 3QPG1 Cse It CS8351 DPSD QB1Document2 pages3QPG1 Cse It CS8351 DPSD QB1Pragna SidhireddyNo ratings yet
- 1QPG1 Ug 21CH101Document2 pages1QPG1 Ug 21CH101URK21CS7046 KARTHIK MNo ratings yet
- 15A04301 Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument1 page15A04301 Electronic Devices and CircuitsSivaprasad ReddyNo ratings yet
- Test 1 CMOS VLSI Design QP 11.1.22Document2 pagesTest 1 CMOS VLSI Design QP 11.1.22Chandru RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysFrom EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet