Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resources: Ronnesha Austin, Naima Edwards, Mystica Inniss
Resources: Ronnesha Austin, Naima Edwards, Mystica Inniss
Uploaded by
Mystica InnissOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Resources: Ronnesha Austin, Naima Edwards, Mystica Inniss
Resources: Ronnesha Austin, Naima Edwards, Mystica Inniss
Uploaded by
Mystica InnissCopyright:
Available Formats
Ronnesha Austin, Naima Edwards, Mystica Inniss
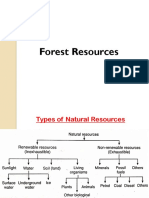
RESOURCES
More raw materials are being used up as the population of the world increases.
There are 2 main categories that raw materials fall into renewable
resources and non-renewable resources.
Plants and animals can replace renewable resources. Examples include
timber for building and making paper and fish, mollusks, and crustaceans
harvested from the sea and lakes. The term ‘renewable’ can also be applied
to forms of energy such as solar power, wind energy, hydroelectricity, and
ethanol-based fuels
Non-renewable resources are resources that once you have used them are
gone forever. These include energy sources such as fossil fuels, and minerals
such as copper, nickel, zinc, and lead.
01 Fossil fuels
Most of our energy comes from the combustion of fossil fuels and this will
eventually run out. In the Caribbean, most countries import most of their energy
like oil and natural gas. The only countries that have reserves of oil are Trinidad and
Cuba. Oil spills can occur when oil tankers run aground or there is a leak from a
drilling platform. Fossil fuels have devastating effects on the marine environment.
02 Forest Resources:
Trees have been cleared by humans for over 10,000 years and many forests have been
affected; such as forests in temperate regions, and tropical forests of SouthEast Asia and
Latin America (mainly rainforests).
Large scale deforestation has occurred to provide:
Timber for building materials
Newsprint paper, paper, and cardboard
Land for farms, ranches, and plantations (e.g. soya beans and sugarcane)
Land for roads, towns, factories, and other buildings
Fuels such as charcoal and firewood
Deforestation’s Environmental Impacts:
Land Degradation- The thin layers of soil in Tropical Rainforests are very thin and the removal
of vegetation causes the soil to be washed away. This leads to soil erosion, the formation of
gullies, and loss of plant nutrients. The loss of trees causes the land to degrade quickly.
Flooding- As floods become more frequent, more water runs off the land, since not as many
plants absorb the water and it is not transpired into the atmosphere, and not as many leaves
in the forest are there to slow the rate of evaporation from the soil and the rate at which
water reaches the soil. For example; Diego Martini in Trinidad
Habit Destruction- As habitats are destroyed the species of plants and animals that live within
them are threatened by extinction.
Excess Carbon Dioxide- After trees and plants are cut down, the decomposition of the plant
material (e.g. the roots) and the burning of vegetation releases carbon dioxide. These increased
levels of carbon dioxide are not absorbed by the plants since they have been cut down.
You might also like
- LRP - Building Eco Literacy in The 21st CenturyDocument136 pagesLRP - Building Eco Literacy in The 21st CenturyGesabel Impabido100% (2)
- Environment & Natural ResourcesDocument16 pagesEnvironment & Natural ResourcesRyuuNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument6 pagesNatural ResourcesMadhurGuptaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Natural ResourcesDocument18 pagesNotes On Natural Resourcesarjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Deforest RationDocument29 pagesDeforest RationSaif MohammadNo ratings yet
- Environmental Issues 2019Document5 pagesEnvironmental Issues 2019Tia PocoyoNo ratings yet
- FSSE 103 REVIEWER FINALS (Revised)Document13 pagesFSSE 103 REVIEWER FINALS (Revised)lopezkarenagapeNo ratings yet
- Deforestation Sub By:bryan Jasper D. Ruiz Sub To: Sir Jilbert Bong GumaruDocument8 pagesDeforestation Sub By:bryan Jasper D. Ruiz Sub To: Sir Jilbert Bong GumaruJulius MacaballugNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Renewable ResourcesDocument3 pagesAssignment: Renewable ResourcesDivisha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Esdm Notebook-1 0Document72 pagesEsdm Notebook-1 0Angerus s - 420No ratings yet
- Welcome To Study Project: DeforestationDocument34 pagesWelcome To Study Project: DeforestationJoseph ChayengiaNo ratings yet
- Forests: Deforestation and DesertificationDocument15 pagesForests: Deforestation and DesertificationFaiza NoorNo ratings yet
- ES Unit 2Document13 pagesES Unit 2InstagramNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentRogue KnightNo ratings yet
- Forest ResourcesDocument23 pagesForest ResourcesLevi LeviNo ratings yet
- NR Biotech1Document25 pagesNR Biotech1Frasha EduNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document25 pagesUnit 2BalaKrishna Batta100% (1)
- Evs Unit-IiiDocument208 pagesEvs Unit-IiishivagamingoffNo ratings yet
- What Does Deforestation MeanDocument6 pagesWhat Does Deforestation MeanPankaj hedaooNo ratings yet
- Theory EnviornmentDocument132 pagesTheory EnviornmentAnu Sandeep AggrawalNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 9Document5 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 9Viola Voon Li WeiNo ratings yet
- Evs Unit-3Document61 pagesEvs Unit-3Pandiya RajanNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument17 pagesEnergy ResourcesBandi PrasadNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument8 pagesNatural Resourcessandhyarani beheraNo ratings yet
- Natural Resource1Document38 pagesNatural Resource1Yogesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Deforestation Causes, Effects, and Solutions: TOPIC: For The Month MAY 2019Document5 pagesDeforestation Causes, Effects, and Solutions: TOPIC: For The Month MAY 2019Marlon BongatoNo ratings yet
- Deforestation DefinitionDocument3 pagesDeforestation DefinitionthierrysoulauchinoooooNo ratings yet
- EVS - Unit 1 - Natural ResourceDocument41 pagesEVS - Unit 1 - Natural Resourcer1u2No ratings yet
- Resource 20231107150326 5 Natural ResourcesDocument30 pagesResource 20231107150326 5 Natural ResourcesHarshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-3-ENvironmental-ConservationDocument12 pagesCHAPTER-3-ENvironmental-ConservationHannah PaceteNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 EVSDocument11 pagesUnit 1 EVSSravan Sai YadavNo ratings yet
- Es CH 09Document5 pagesEs CH 09MaliCk TaimoorNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources PDFDocument25 pagesNatural Resources PDFNIPER BNGNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument39 pagesNatural ResourcesChennaiSuperkings100% (2)
- Unit 1-Natural ResourcesDocument52 pagesUnit 1-Natural ResourcesRidhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Concepts & ConcernsDocument10 pagesEnvironmental Concepts & Concernsestheronkabetse2No ratings yet
- Social Studies HandoutDocument103 pagesSocial Studies Handoutestheronkabetse2No ratings yet
- Habitat DestructionDocument12 pagesHabitat DestructionGaurjan0% (1)
- Evs 1Document13 pagesEvs 1roiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science and Engineering UNIT-1 Introduction To Environmental Studies and Natural ResourcesDocument24 pagesEnvironmental Science and Engineering UNIT-1 Introduction To Environmental Studies and Natural ResourcesSuruthiPriyanNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument18 pagesNatural ResourcesTEJAS .M.S.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental Studies and Natural ResourcesDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Environmental Studies and Natural ResourcesRahul89% (19)
- Mity Niversity Harkhand: Subject: Environmental ScienceDocument36 pagesMity Niversity Harkhand: Subject: Environmental ScienceRakeshagentNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument5 pagesAir PollutionRosa Adriana Egas DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument5 pagesAir PollutionRosa Adriana Egas DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Ques - Bank With SolutionDocument101 pagesQues - Bank With Solutionkomal0% (1)
- Types of Natural ResourcesDocument10 pagesTypes of Natural Resourcesaizaz646No ratings yet
- DeforestationDocument5 pagesDeforestationonofreiilincaNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Conservation Protecting Our Plant ResourcesDocument33 pagesTopic 10 Conservation Protecting Our Plant ResourcesChuan Ung SiiNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument14 pagesNatural ResourcesCLASH OF DARKNo ratings yet
- DeforestationDocument2 pagesDeforestationSoumya SNo ratings yet
- Deforestation and Its Impact On Environment: Gursharn Singh, Beant SinghDocument7 pagesDeforestation and Its Impact On Environment: Gursharn Singh, Beant SinghChaitanya KadambalaNo ratings yet
- TYPES:1.solar Energy 2.wind e 3hydropower e 5.biomass:: Economic Value Oil Natural GasDocument6 pagesTYPES:1.solar Energy 2.wind e 3hydropower e 5.biomass:: Economic Value Oil Natural GasswatiNo ratings yet
- Deforrest at I OnDocument1 pageDeforrest at I OnMarga BrisueñoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Natural ResourcesDocument7 pagesModule 4 Natural ResourcesKarl angelo LorzanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Evs Unit - 2Document14 pagesLecture Notes - Evs Unit - 2Nambi RajanNo ratings yet
- EVS Natural Resourses Session 1Document17 pagesEVS Natural Resourses Session 1Ritesh KelkarNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document26 pagesUnit 3rajeev.sbilife78No ratings yet
- Scholarship Flyer 2023-24Document1 pageScholarship Flyer 2023-24Mystica InnissNo ratings yet
- Your Big IdeaDocument20 pagesYour Big IdeaMystica InnissNo ratings yet
- Moments&LeversDocument16 pagesMoments&LeversMystica InnissNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic TheoryDocument4 pagesThe Kinetic TheoryMystica InnissNo ratings yet
- The Top 10 Ocean IssuesDocument6 pagesThe Top 10 Ocean IssuesNickKyNo ratings yet
- Li Et Al 2006Document8 pagesLi Et Al 2006Ishu NuwaNo ratings yet
- Dissolved Organic Matter 2018Document58 pagesDissolved Organic Matter 2018Nicolas CancioNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Conservation: Module - 5Document22 pagesBiodiversity Conservation: Module - 5Pratyush Goel100% (1)
- Bidiversity and The Healthy SocietyDocument2 pagesBidiversity and The Healthy SocietyMariella MallariNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem PDFDocument13 pagesEcosystem PDFSakshiNo ratings yet
- Crist 2009Document11 pagesCrist 2009Guilherme MartinsNo ratings yet
- Food Chains and Food WebsDocument16 pagesFood Chains and Food WebsLee Lhouine Kaidz II LirazanNo ratings yet
- Our Environment: Activity 15.1 Activity 15.1 Activity 15.1 Activity 15.1 Activity 15.1Document10 pagesOur Environment: Activity 15.1 Activity 15.1 Activity 15.1 Activity 15.1 Activity 15.1Arvinder WaliaNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Forest Biodiversity in India: K. VenkataramanDocument8 pagesConservation of Forest Biodiversity in India: K. VenkataramanAshutosh ManiNo ratings yet
- Sarita TripathiDocument8 pagesSarita TripathiAhmad BurhanudinNo ratings yet
- Riparian Landscape Design Based On Urban Forest at Cisadane River, South Tangerang City, IndonesiaDocument10 pagesRiparian Landscape Design Based On Urban Forest at Cisadane River, South Tangerang City, IndonesiaDwi SetyantiNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Guide TeacherDocument12 pagesUnit 6 Guide Teacherapi-198603477No ratings yet
- 5 Forest and Veld ProductsDocument3 pages5 Forest and Veld ProductsTumisang PitiroseNo ratings yet
- Acr DanggitDocument6 pagesAcr DanggitLeziel Gordiones MulatoNo ratings yet
- FORESTS ReDocument10 pagesFORESTS RenorrrrNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Ix Ecology Nsejs-1 230420 213823Document9 pagesWorksheet Ix Ecology Nsejs-1 230420 213823Rishabh RNo ratings yet
- Sparkill Creek Water Quality - SCWADocument40 pagesSparkill Creek Water Quality - SCWAHRNERRNo ratings yet
- Ocean 2009I UNMSM Ion ChromatographyDocument15 pagesOcean 2009I UNMSM Ion ChromatographyMoisesNo ratings yet
- EVS - CO3 - Study MaterialDocument20 pagesEVS - CO3 - Study MaterialBalraj DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Article (PDF Version)Document6 pagesArticle (PDF Version)Aunur RahmanNo ratings yet
- ProceedingsDocument163 pagesProceedingsCornelius Olsa OlberntNo ratings yet
- WS E6 U1 Eng AnsDocument5 pagesWS E6 U1 Eng AnsMatthew LongNo ratings yet
- Avila - STS Activity 2Document5 pagesAvila - STS Activity 2Jannine AvilaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Geography: Baulkham Hills High SchoolDocument13 pagesYear 10 Geography: Baulkham Hills High SchoolchenNo ratings yet
- Plitvice Lakes National Park Is One of The Oldest National Parks in Southeast Europe and The Largest National Park in CroatiaDocument2 pagesPlitvice Lakes National Park Is One of The Oldest National Parks in Southeast Europe and The Largest National Park in CroatiaRicardo MenendezNo ratings yet
- Portage Escarpment Final ReportDocument18 pagesPortage Escarpment Final ReportJim ChambersNo ratings yet
- Freshwater Aquaculture Systems DesignDocument11 pagesFreshwater Aquaculture Systems DesignAre NiedaNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles Worksheet TCDocument8 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles Worksheet TCAwny Naim100% (1)